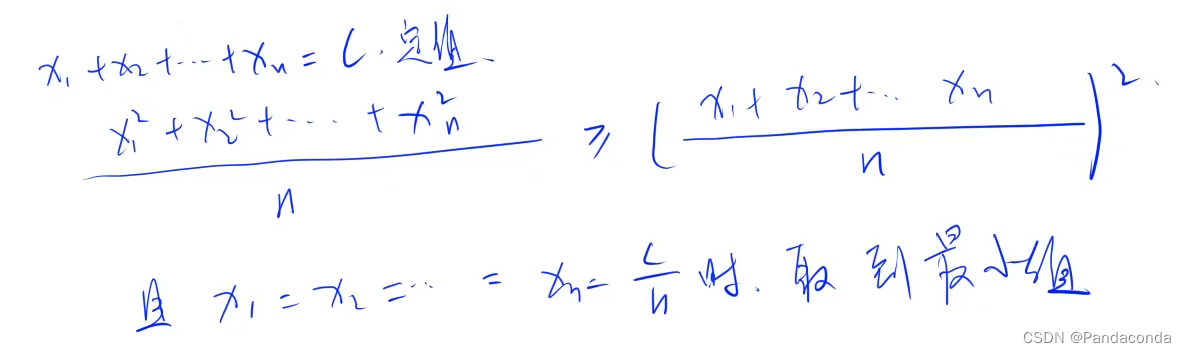给你一个单链表,随机选择链表的一个节点,并返回相应的节点值。每个节点 被选中的概率一样 。
实现 Solution 类:
Solution(ListNode head) 使用整数数组初始化对象。
int getRandom() 从链表中随机选择一个节点并返回该节点的值。链表中所有节点被选中的概率相等。
示例:

输入
[“Solution”, “getRandom”, “getRandom”, “getRandom”, “getRandom”, “getRandom”]
[[[1, 2, 3]], [], [], [], [], []]
输出
[null, 1, 3, 2, 2, 3]
解释
Solution solution = new Solution([1, 2, 3]);
solution.getRandom(); // 返回 1
solution.getRandom(); // 返回 3
solution.getRandom(); // 返回 2
solution.getRandom(); // 返回 2
solution.getRandom(); // 返回 3
// getRandom() 方法应随机返回 1、2、3中的一个,每个元素被返回的概率相等。
提示:
链表中的节点数在范围 [1, 104] 内
-104 <= Node.val <= 104
至多调用 getRandom 方法 104次
进阶:
如果链表非常大且长度未知,该怎么处理?
你能否在不使用额外空间的情况下解决此问题?
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-random-node
方法一:记录链表元素
C++提交内容:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
vector<int> arr;
public:
Solution(ListNode *head) {
while (head) {
arr.emplace_back(head->val);
head = head->next;
}
}
int getRandom() {
return arr[rand() % arr.size()];
}
};
/**
* Your Solution object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Solution* obj = new Solution(head);
* int param_1 = obj->getRandom();
*/



![[NSSRound#6 Team]Web学习](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c90709111dcb4e0f9c1f6c1ef2e1287e.png)