前言
select语句查询得到的结果集是一张二维表,水平方向上看是一个个字段,垂直方向上看是一条条记录。而Java是面向对象的程序设计语言,对象是根据类定义创建的,类之间的引用关
系可以认为是嵌套的结构。在JDBC编程中,为了将结果集中的数据映射成对象,我们需要自己写代码从结果集中获取数据,然后封装成对应的对象并设置对象之间的关系,而这些都是大量的重复性代码。为了减少这些重复的代码,MyBatis使用<resultMap>节点定义了结果集与结果对象(JavaBean 对象)之间的映射规则,<resultMap>节点可以满足绝大部分的映射需求,从而减少开发人员的重复性劳动,提高开发效率。
ResultMap标签结构
- constructor - 用于在实例化类时,注入结果到构造方法中
- idArg - ID 参数;标记出作为 ID 的结果可以帮助提高整体性能
- arg - 将被注入到构造方法的一个普通结果
- id – 一个 ID 结果;标记出作为 ID 的结果可以帮助提高整体性能
- result – 注入到字段或 JavaBean 属性的普通结果
- association – 一个复杂类型的关联;许多结果将包装成这种类型
- 嵌套结果映射 – 关联可以是 resultMap 元素,或是对其它结果映射的引用
- collection – 一个复杂类型的集合
- 嵌套结果映射 – 集合可以是 resultMap 元素,或是对其它结果映射的引用
- discriminator – 使用结果值来决定使用哪个 resultMap
- case – 基于某些值的结果映射
- 嵌套结果映射 – case 也是一个结果映射,因此具有相同的结构和元素;或者引用其它的结果映射
- case – 基于某些值的结果映射
图示查询结果转为Java对象的过程
假设有这样一个场景:一个博客有一个作者和多条评论。根据博客设置的权限,动态展示阅读数和点赞数。
- 公开:博客信息 + 阅读数 + 点赞数(PublicBlog)
- 仅展示阅读数 : 博客信息 + 阅读数(ReadBlog)

如何用ResultMap来描述这种关系
创建mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<properties>
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</properties>
<settings>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
<environments default="default">
<environment id="default">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper/ResultMapMapper.xml" />
</mappers>
</configuration>创建ResultMapMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.ys.mybatis.mapper.ResultMapMapper">
<resultMap id="blogMap" type="com.ys.mybatis.resultmap.Blog">
<constructor>
<idArg name="id" column="id"/>
<arg name="title" column="title"/>
</constructor>
<result property="authority" column="authority"/>
<association property="author">
<id property="id" column="author_id"/>
<result property="nickName" column="nick_name"/>
</association>
<collection property="comments" ofType="com.ys.mybatis.resultmap.Comment">
<result property="blogId" column="blog_id"/>
<result property="content" column="content"/>
</collection>
<discriminator javaType="string" column="authority">
<case value="公开" resultType="com.ys.mybatis.resultmap.PublicBlog">
<result property="readNum" column="read_num"/>
<result property="likeNum" column="like_num"/>
</case>
<case value="仅显示阅读数" resultType="com.ys.mybatis.resultmap.ReadBlog">
<result property="readNum" column="read_num"/>
</case>
</discriminator>
</resultMap>
<select id="listBlog" resultMap="blogMap">
select
b.id,
b.title,
a.id as author_id,
a.nick_name,
c.blog_id,
c.content,
b.read_num,
b.like_num,
b.authority
from blog b
left join author a on a.id = b.author_id
left join `comment` c on c.blog_id = b.id
</select>
</mapper>创建ResultMapMapper
public interface ResultMapMapper {
List<Blog> listBlog();
}创建实体类
@Data
public class Blog {
private Integer id;
private String title;
private Author author;
private List<Comment> comments;
private String authority;
public Blog() {
System.out.println("调用了空构造方法");
}
public Blog(@Param("id") Integer id, @Param("title") String title) {
System.out.println("调用了两个参数构造方法");
this.id = id;
this.title = title;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Blog{" +
"id=" + id +
", title='" + title + '\'' +
", author=" + author +
", comments=" + comments +
", authority='" + authority + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
@Data
public class Author {
private Integer id;
private String nickName;
}
@Data
public class Comment {
private Integer id;
private Integer blogId;
private String content;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Comment{" +
"content='" + content + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
@Data
public class PublicBlog extends Blog {
private Integer readNum;
private Integer likeNum;
public PublicBlog() {
}
public PublicBlog(@Param("id") Integer id, @Param("title") String title) {
super(id, title);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Blog{" +
"id=" + this.getId() +
", title='" + this.getTitle() + '\'' +
", author=" + this.getAuthor().toString() +
", comments=" + this.getComments() +
", authority='" + this.getAuthority() + '\'' +
", readNum='" + this.getReadNum() + '\'' +
", likeNum='" + this.getLikeNum() + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
@Data
public class ReadBlog extends Blog {
private Integer readNum;
public ReadBlog() {
}
public ReadBlog(@Param("id") Integer id, @Param("title") String title) {
super(id, title);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Blog{" +
"id=" + this.getId() +
", title='" + this.getTitle() + '\'' +
", author=" + this.getAuthor().toString() +
", comments=" + this.getComments() +
", authority='" + this.getAuthority() + '\'' +
", readNum='" + this.getReadNum() + '\'' +
'}';
}
}创建测试类ResultMapTest
public class ResultMapTest {
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
@BeforeEach
public void parse() {
InputStream inputStream = ConfigurationTest.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(inputStream);
}
@Test
public void listBlog() {
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
ResultMapMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(ResultMapMapper.class);
List<Blog> blogs = mapper.listBlog();
blogs.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
ResultMapMapper.xml 中的 blogMap,通过association标签表示博客和作者一对一的关系,通过collection标签表示博客和评论一对多的关系,通过discriminator标签和authority属性值来动态显示一些数据。
SQL在数据库中的查询结果
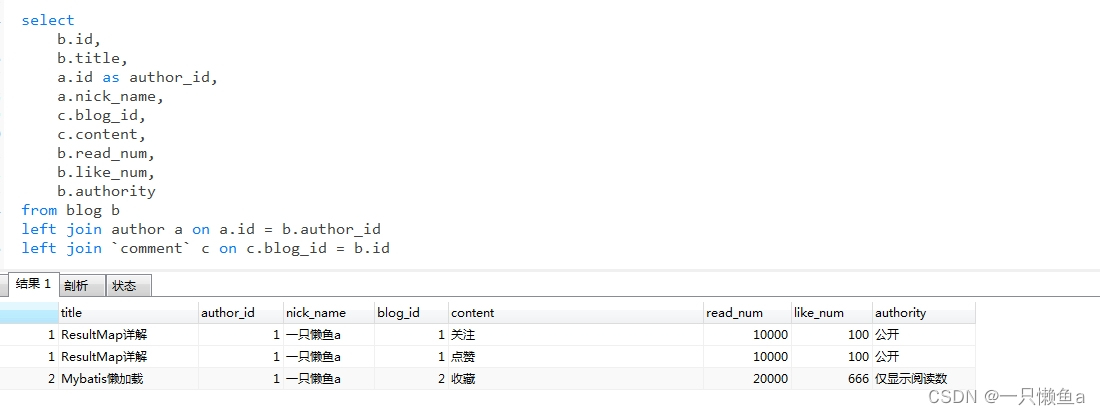
执行测试方法

通过测试结果,我们得出以下结论:
- PublicBlog 、ReadBlog 选择了constructor配置的构造方法实例化对象
- 一共查出来三条数据,根据博客ID分组(分成两组),最后解析成两个Blog对象
源码解析
XMLMapperBuilder#resultMapElement


从上述源码,我们可以得出以下结论:
- discriminator标签最终会被解析成Discriminator对象
- 除了discriminator标签以外的其他标签都会被解析成ResultMapping,然后放入一个list中
PS : discriminator标签下有多少个case子标签,就会解析成多少个ResultMap对象
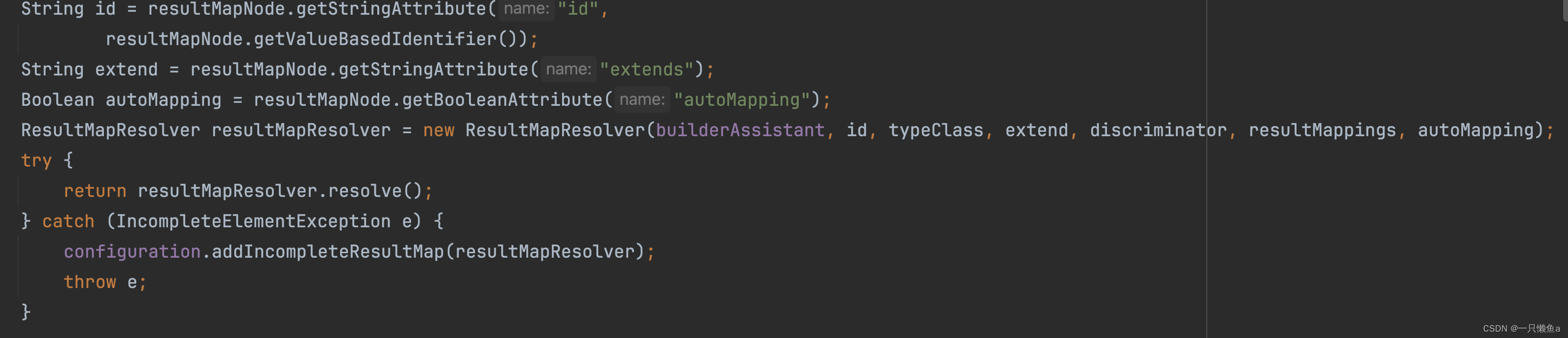
在得到Discriminator对象和ResultMapping集合过后,又结合ResultMap标签的id,type,extends,autoMapping属性构建出一个ResultMapResolver对象,通过其resolve方法,解析出一个ResultMap对象
ResultMap类结构
public class ResultMap {
private Configuration configuration;
private String id;
private Class<?> type;
private List<ResultMapping> resultMappings;
private List<ResultMapping> idResultMappings;
private List<ResultMapping> constructorResultMappings;
private List<ResultMapping> propertyResultMappings;
private Set<String> mappedColumns;
private Set<String> mappedProperties;
private Discriminator discriminator;
private boolean hasNestedResultMaps;
private boolean hasNestedQueries;
private Boolean autoMapping;
}其中id,type,resultMappings,discriminator,autoMapping属性都是在构建ResultMapResolver对象的时候,通过构造方法传递过去的,我们不做过多分析
- idResultMappings :id,idArg标签解析出来的ResultMapping,也会放一份在这个list中,该list用来对查询结果进行分组
- constructorResultMappings :idArg,arg标签解析出来的ResultMapping,也会放一份在这个list中,该list用来指定构造器实例化对象
- propertyResultMappings : 非idArg,arg标签解析出来的ResultMapping,也会放一份在这个list中。
- mappedColumns :ResultMap标签子节点column属性集合
- mappedProperties :ResultMap标签子节点property属性集合
hasNestedResultMaps,hasNestedQueries我们单独分析
嵌套映射
当hasNestedResultMaps属性为true,我们就称这是一个存在嵌套映射的查询,我们通过源码,分析一下
XMLMapperBuilder#buildResultMappingFromContext
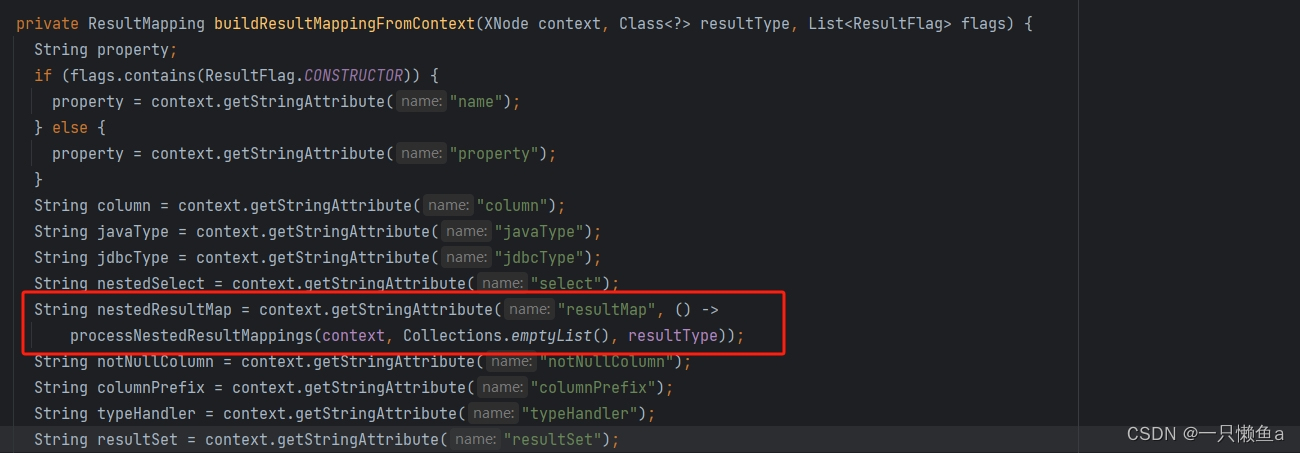

显示指定 : 存在子标签显示指定resultMap。比如ResultMapMapper.xml 中的blogMap,我们可以改成显示指定的形式,明细如下:
<resultMap id="blogMap" type="com.ys.mybatis.resultmap.Blog">
<constructor>
<idArg name="id" column="id"/>
<arg name="title" column="title"/>
</constructor>
<result property="authority" column="authority"/>
<association property="author" resultMap="authorMap"/>
<collection property="comments" ofType="com.ys.mybatis.parse.Comment" resultMap="commentMap"/>
<discriminator javaType="string" column="authority">
<case value="公开" resultMap="publicBlog" resultType="com.ys.mybatis.resultmap.PublicBlog" />
<case value="仅显示阅读数" resultMap="readBlog" resultType="com.ys.mybatis.resultmap.ReadBlog"/>
</discriminator>
</resultMap>
<resultMap id="publicBlog" type="com.ys.mybatis.resultmap.PublicBlog" extends="blogMap">
<result property="readNum" column="read_num"/>
<result property="likeNum" column="like_num"/>
</resultMap>
<resultMap id="readBlog" type="com.ys.mybatis.resultmap.ReadBlog" extends="blogMap">
<result property="readNum" column="read_num"/>
</resultMap>
<resultMap id="authorMap" type="com.ys.mybatis.resultmap.Author">
<id property="id" column="author_id"/>
<result property="nickName" column="nick_name"/>
</resultMap>
<resultMap id="commentMap" type="com.ys.mybatis.resultmap.Comment">
<result property="blogId" column="blog_id"/>
<result property="content" column="content"/>
</resultMap>PS : 如果ResultMap标签中同时存在constructor和discriminator标签,discriminator标签的子标签case必须要指定resultType
隐式构建 : 存在association,collection,case标签,且未配置select属性,Mybatis会隐式构建一个ResultMap对象。测试文件中的blogMap就属于隐式构建
嵌套查询
存在子标签中配置了select属性。比如测试文件中的author属性,我们改成下列形式:
<association property="author" column="author_id" select="getAuthorById"/>
<select id="getAuthorById" resultType="com.ys.mybatis.resultmap.Author">
select id,nick_name from author where id = #{authorId}
</select>延迟加载
在嵌套查询的基础上,开启延迟加载的两种方式
1. 在mybatis-config.xml中添加配置
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>2.在association、collection等标签中配置fetchType属性,举例如下:
<association property="author" column="author_id" select="getAuthorById" fetchType="lazy"/>PS : fetchType优先级高于全局配置lazyLoadingEnabled
延迟加载在mybatis中的应用
DefaultResultSetHandler#createResultObject

如果存在嵌套查询,且属性是懒加载的,则进行动态代理。详情请移步相关博客:Mybatis懒加载
extends
MapperBuilderAssistant#addMap
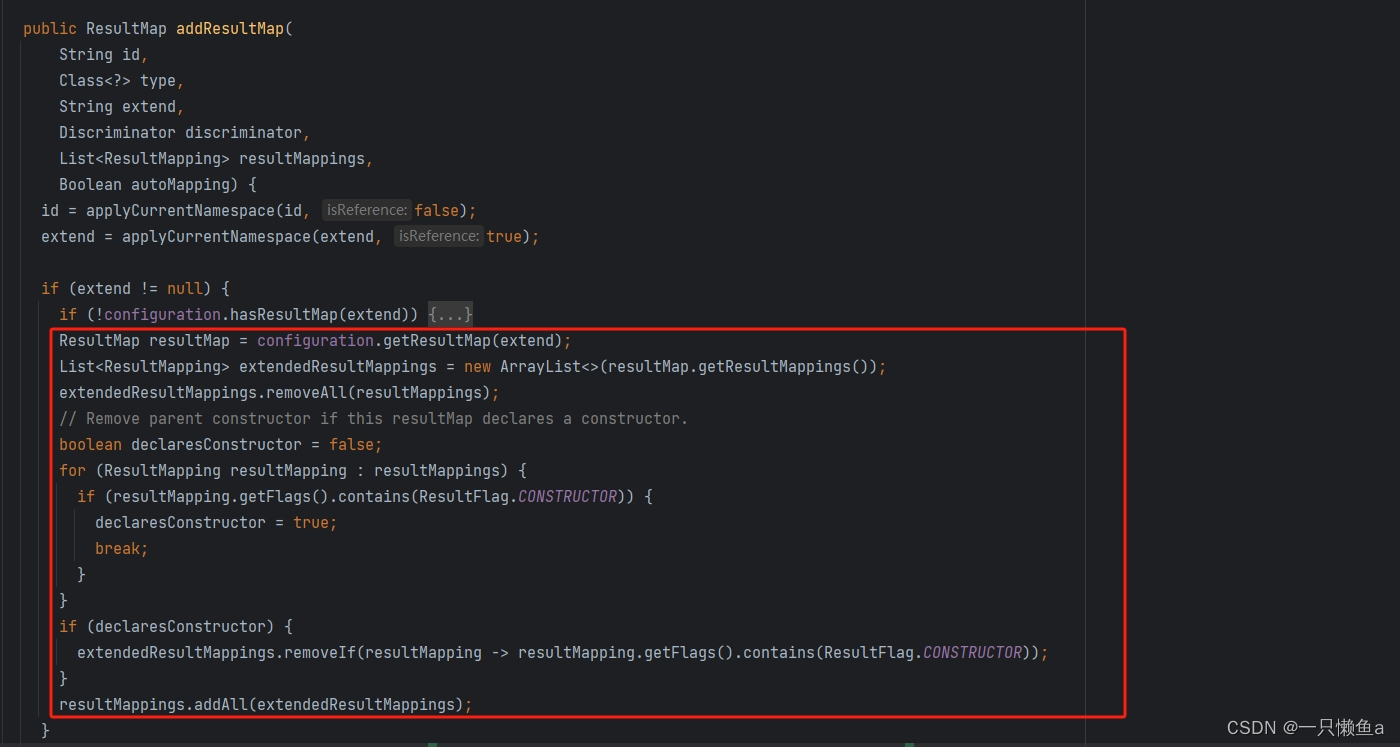
- 子map中配置的对象关系映射会覆盖父map中配置的对象关系映射
- 子map中配置的对象实例化方式会覆盖父map中配置的对象实例化方式
autoMapping
- 属性值为 true : 嵌套和非嵌套的情况下,都会自动映射
- 属性值为 false : autoMappingBehavior属性值控制其自动映射行为
- NONE:表示关闭自动映射
- PARTIAL:只会自动映射没有定义嵌套结果映射的字段 (默认值)
- FULL:会自动映射任何复杂的结果集(无论是否嵌套)
修改autoMappingBehavior属性默认值
<setting name="autoMappingBehavior" value="NONE"/>