文章目录
- 数据库介绍
- MySQL的入门应用
- SQL的基础与DDL
- SQL的分类:
- SQL的基础语法特性:
- DDL库管理:
- DDL表管理:
- SQL-DML
- SQL-DQL
- DQL基础查询
- DQL分组聚合
- 排序分页
- Python&MySQL
- commit
数据库介绍
- 数据库的层级:按照库->表->数据进行储存(简单字面理解即可)。
- 数据库就是指数据存储的库,作用是组织数据或者存储数据。
- 常见的数据库软件有:Oracle 、MySQL 、SQL Server 、PostgreSQL 、SQLite,这里介绍以MySQL为主。
- 数据库和SQL的关系:数据库(软件)提供数据组织存储的能力,SQL就是在这个过程中帮助我们处理的工具。
具体的安装过程就不细说了:
大家可以通过mysql -uroot -p进行访问,看看自己有没有安装错误。
MySQL的入门应用
常见的基础操作:
| 操作 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| mysql -uroot -p | 登陆操作 |
| show databases | 查看有哪些数据库 |
| use 数据库名称 | 使用某个数据库 |
| show tables | 查看数据库内有哪些表 |
| exit | 退出MySQL命令行环境 |
命令框上具体的操作:
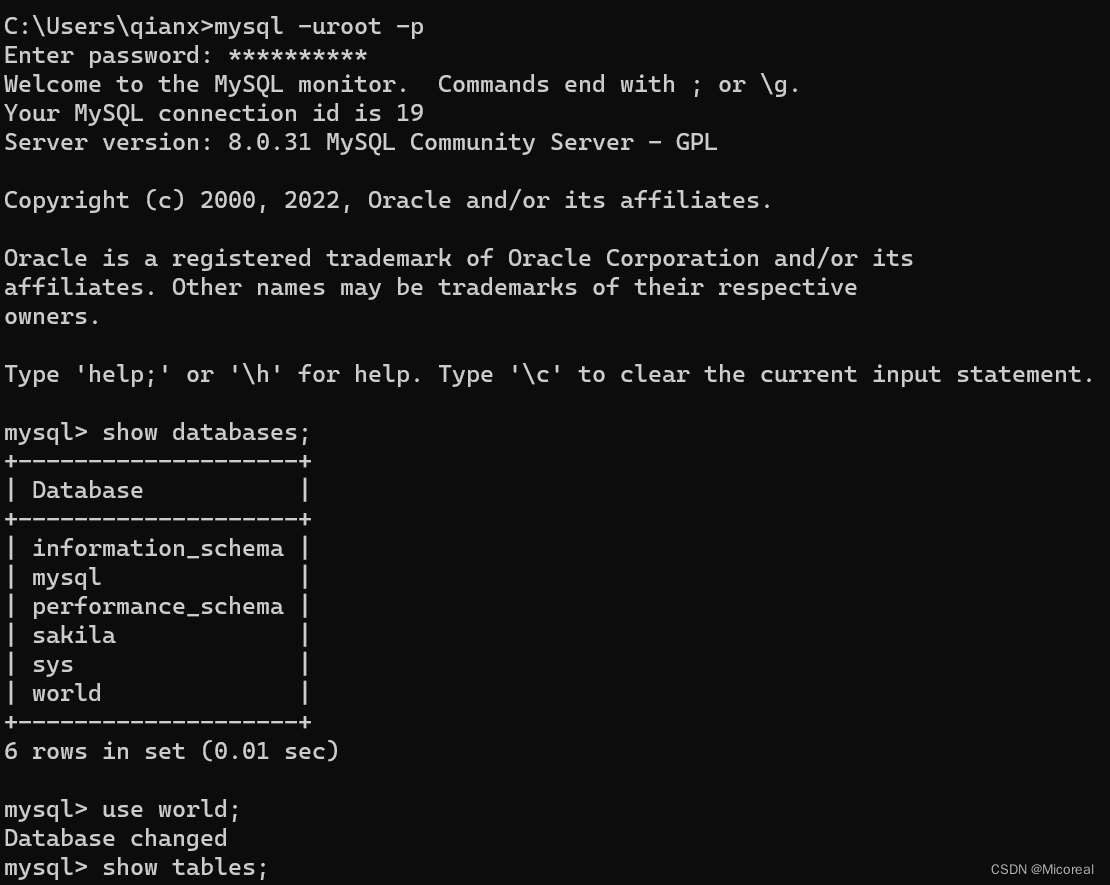
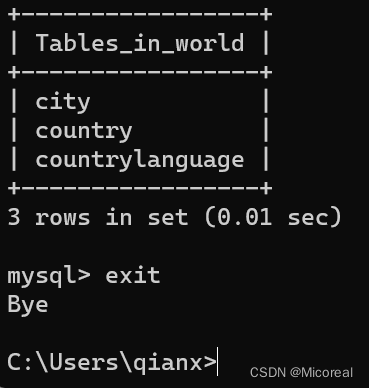
而不可能所有的操作都在命令框当中进行使用,所有后续的介绍以软件DBeaver进行介绍:
SQL的基础与DDL
SQL的分类:
数据定义:DDL(库的创建删除,表的创建删除等)
数据操纵:DML(新增数据,删除数据,修改数据等)
数据控制:DCL(新增用户,删除用户,密码修改,权限管理)
数据查询:DQL(基于需求查询和计算数据)
SQL的基础语法特性:
1. SQL语言,大小写不敏感。
2. SQL可以单行或者多行书写,最后以;结束
3. SQL支持注释:
(1)单行注释:-- 注释内容(--之后需要有一个空格)
(2)单行注释:# 注释内容(#之后可加可不加空格,推荐加上)
(3)多行注释:/*注释内容*/
小样例:
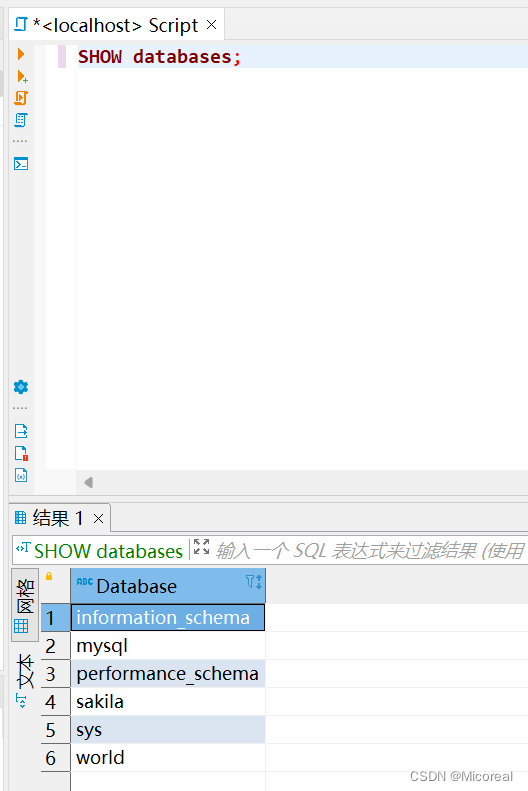
DDL库管理:
| 管理函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| show databases; | 查看数据库 |
| use 数据库名称 | 使用数据库 |
| create database 数据库名称[charset UTF8] | 创建数据库 |
| drop database 数据库名称 | 删除数据库 |
| select database() | 查看当前使用的数据库 |
DDL表管理:
| 管理函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| show tables; | 查看有那些表,前提是先选择哪一个数据库 |
| drop table 表名称; | 删除表 |
| drop table if exists 表名称; | 删除表 |
| create 表名称(列名称 列类型,列名称 列类型······); | 创建一个新表 |
| 列的类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| int | 整数 |
| float | 浮点数 |
| varchar(长度) | 文本,长度为数字(最大255),做最大长度限制 |
| data | 日期类型 |
| timestamp | 时间戳类型 |
SQL-DML
# 数据插入
insert into 表名称[(列1,列2······)] values(值1,值2······)[,(值1,值2······),······];
# 数据删除
# 条件判断操纵符:= 、!=、<、<=、>、>=
# 值得关注的是是 = 不是 ==。
# 如果不存在条件判断,则是将表当中的数据全部删除。
delete from 表名称[where 条件判断];
# 数据更新
# 如果不存在条件判断,则将整张表的所有列的值改变成相对应的修改值
updata 表名 set 列=值[where 条件判断];
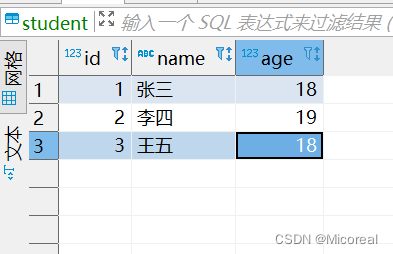
关于插入样例:
create table student(id int,name varchar(10),age int);
insert into student (id,name,age) values(1,'张三',18),(2,'李四',19),(3,'王五',18);
输出结果:
关于删除样例:
create table student(id int,name varchar(10),age int);
insert into student (id,name,age) values(1,'张三',18),(2,'李四',19),(3,'王五',18);
delete from student where id=1;
输出样例:
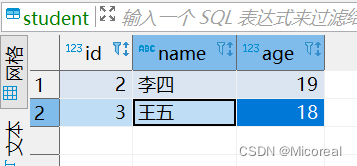
关于数据更新:
create table student(id int,name varchar(10),age int);
insert into student (id,name,age) values(1,'张三',18),(2,'李四',19),(3,'王五',18);
delete from student where id=1;
update student set name = '张三' where id = 2;
输出结果:
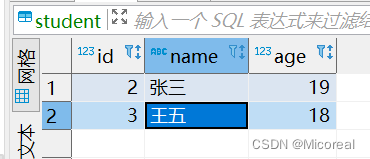
值得关注的是DML当中字符串的值,如果是字符串,应该用’'(单引号)包裹起来。
SQL-DQL
DQL基础查询
# 基础查询
# *代表查询所有的内容
select 字段列表|* from 表 [where 条件判断]
查询样例1:
select name,age from student ;
输出结果:
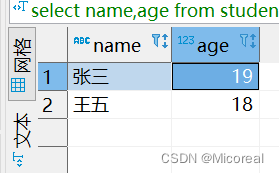
查询案例2:
select * from student where age=19;
输出结果:
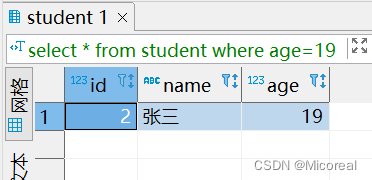
DQL分组聚合
# 分组聚合
# 聚合函数:
# sum(列) 求和
# avg(列) 求平均值
# min(列) 求最小值
# max(列) 求最大值
# count(列|*) 求数量
# 一个小的条件限制:字段仅能出现列出现的。
select 字段|聚合函数 from 表名称[where 判断条件] group by 列;
样例:
create table student(id int,name varchar(10),age int,gender varchar(5));
insert into student (id,name,age,gender) values(1,'张三',18,'男'),(2,'李四',19,'女'),(3,'王五',18,'男');
select gender,avg(age) from student group by gender;
输出结果:
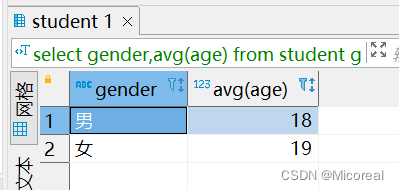
实际上的理解:select gender,avg(age) from student group by gender;
- 按照gender分组,计算每一组的age的平均值。
- gender,avg(age) 代表输出的结果显示为。
- 可以改成id,avg(age)吗?肯定是不行的,在select之后的列只能填组名列。
- count的理解 count(age)实际上是判断age是否为0,如果不为0,则加一,实际上我们count()当中写一个万能的*即可,即count(*)。
排序分页
# 排序
select 字段|聚合函数 from 表名称[where 判断条件] group by 列 加上下面的 ;
# 前面和正常的写法一样,爱怎么写,怎么写,最后面写上order by 标准[ASC|DESC]
# asc升序 ,DESC降序
# 分页
# 再在后面加上limit n[,m]
# 如果是limit n代表仅从头取5条数据。
# 如果是limit n,m代表从n+1条开始取m条数据。
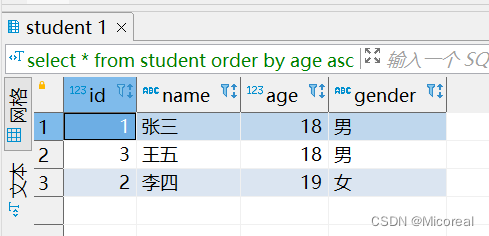
排序例子:
select * from student order by age asc;
输出结果:
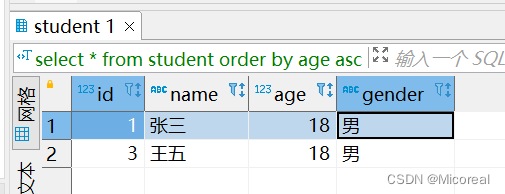
分页例子1:
select * from student order by age asc limit 2;
输出结果:
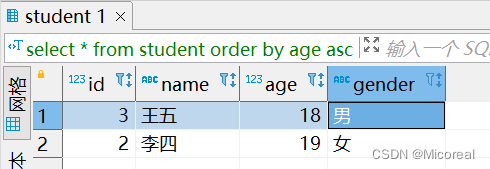
分页例子2:
select * from student order by age asc limit 1,2;
输出结果:
总结:
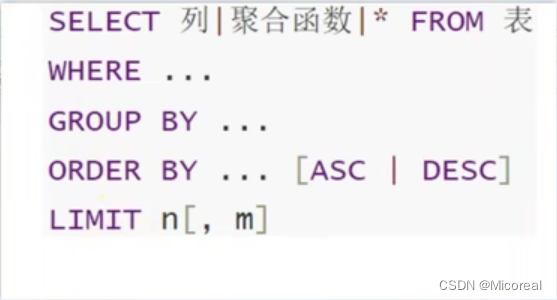
Python&MySQL
使用Python当中的第三方数据库:pymysql
from pymysql import Connection
conn = Connection(
host='localhost', # 主机名,或者ip地址
port=3306, # 端口默认3306
user='root', # 账户名
password='123456' # 密码
)
# 选择游标对象
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 选择数据库相当于use操作
conn.select_db('test')
# 使用游标对象
# 执行非查询性质的SQL
cursor.execute('create table test_pymysql2(id int,name varchar(5))')
# 使用查询性质的SQL
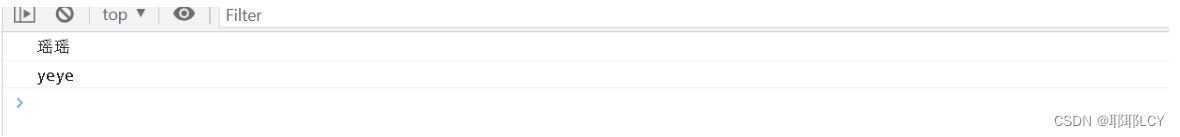
cursor.execute('select * from test_pymysql2')
result = cursor.fetchall()
for r in result :
print(r)
# 关闭链接
conn.close()
commit
以及插入数据的:
手动commit版本:
from pymysql import Connection
conn = Connection(
host='localhost', # 主机名,或者ip地址
port=3306, # 端口默认3306
user='root', # 账户名
password='123456' # 密码
)
# 选择游标对象
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 选择数据库相当于use操作
conn.select_db('test')
# 使用游标对象
# 执行非查询性质的SQL
cursor.execute('create table student(id int,name varchar(10),age int);')
cursor.execute('insert into student (id,name,age) values(1,"张三",18),(2,"李四",19),(3,"王五",18);')
# 插入语句之后,需要添加一个commit函数进行确认
conn.commit()
# 使用查询性质的SQL
cursor.execute('select * from student')
result = cursor.fetchall()
for r in result :
print(r)
# 关闭链接
conn.close()
当然也有自动版本:
conn = Connection(
host='localhost', # 主机名,或者ip地址
port=3306, # 端口默认3306
user='root', # 账户名
password='123456' # 密码
autocommit = True # 设置自动提交
)