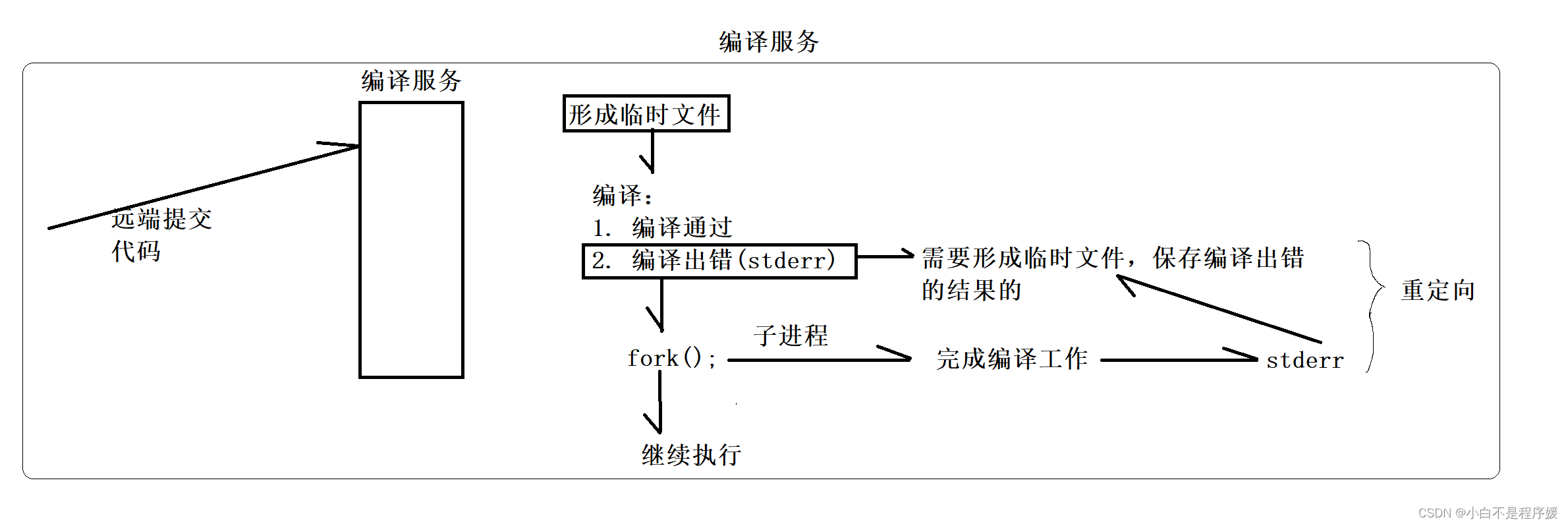
方法引用就是把已经有的方法拿过来用,当作函数式接口中抽象方法的方法体。
条件:
1.引用处需要是函数式接口
2.被引用的方法需要已经存在
3.被引用的方法的形参和返回值需要跟抽象方法的形参和返回值保持一致
4.被引用方法的功能需要满足当前的要求
简单代码演示:
注意:方法引用也算引用,初始数组应使用引用数据类型Integer
public class FunctionDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建数组
Integer[] arr = {5,2,6,3,4,1};
//按倒序排序
Arrays.sort(arr, FunctionDemo1::subtraction);
//输出数组
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public static int subtraction(int num1, int num2) {
return num2 - num1;
}
}运行结果:

详细方法引用:
1.引用静态方法
代码演示
public class FunctionDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
集合中有以下字符串
"1","2","3","4","5"
引用静态方法,把他们都变成int类型
*/
//创建集合并添加元素
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"1","2","3","4","5");
//引用静态方法
list.stream().map(Integer::parseInt).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s + 1));
}
}运行结果:

2.引用成员方法
1)引用其他类成员方法
格式:其他类对象::方法名
代码演示:
成员方法类:
public class StringOperation {
public boolean StringOperation(String str) {
return str.startsWith("张") && str.length() == 3;
}
}测试类:
public class FunctionDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//要求:将集合中姓张并且名字为3个字的人名提取出来
//创建集合
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
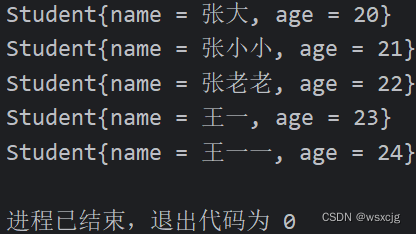
Collections.addAll(list, "张大","张小小","张老老","王一","王一一");
//引用其他类成员方法过滤
list.stream()
.filter(new StringOperation()::StringOperation)
.forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
}
}运行结果:

2)引用本类成员方法
格式:this::方法名
3)引用父类成员方法
格式:super::方法名
其他两种方法和第一种同理,在次不做演示,但是需要注意:不能在静态方法中引用本类成员方法或者父类成员方法,因为static修饰的方法中,没有this和super。
3.引用构造方法
格式:类名::new
代码演示:
public class FunctionDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//将集合中的元素转换成Student类型
//创建集合
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list, "张大,20","张小小,21","张老老,22","王一,23","王一一,24");
list.stream().map(Student::new).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
}
}运行结果:
4.其他调用方式
1)使用类名引用成员方法
格式:
类名::成员方法
规则:
1.需要有函数式接口
2.被引用的方法必须已经存在
3.被引用方法的形参,需要跟抽象方法的第二个形参到最后一个形参保持一致,返回值需要保持一致
4.被引用方法的功能需要满足当前的需求
抽象方法形参的详解:
第一个参数:表示被引用方法的调用者,决定了可以引用哪些类中的方法,在Stream流中,第一个参数一般都表示流里面的每一个数据。
第二个参数到最后一个参数:跟被引用方法的形参保持一致,如果没有第二个参数,说明被引用的方法需要是无参的成员方法。
局限性:
不能引用所有类中的成员方法,是跟抽象方法的第一个参数有关,这个参数是什么类型的,那么就只能引用这个类中的方法
代码演示:
public class FunctionDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//集合里面添加一些字符串,要求变成大写后输出
//创建集合
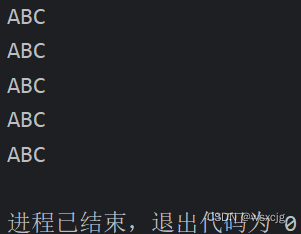
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list, "abC","ABC","abc","ABc","Abc");
list.stream().map(String::toUpperCase).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
}
}运行结果:
2)引用数组的构造方法
格式:
数据类型[ ]::new
规则:
数组类型需要跟流中数据的类型保持一致
代码演示:
public class FunctionDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//要求:集合中存储一些整数,收集到数组当中
//创建集合
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list, 1,2,3,4,5);
//收集到数组中
Integer[] arr = list.stream().toArray(Integer[]::new);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}运行结果:

综合练习
练习一:
集合中存储一些字符串数据,比如:"张三,23" 收集到Student类型的数组当中(使用方法引用完成)
代码演示:
public class FunctionTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
集合中存储一些字符串数据,比如:"张三,23"
收集到Student类型的数组当中(使用方法引用完成)
*/
//创建集合并添加元素
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"han,21","ma,22","zhao,23");
Student[] arr = list.stream().map(Student::new).toArray(Student[]::new);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}运行结果:

练习二:
创建集合添加学生对象,学生对象属性:name,age 只获取姓名放到数组当中(使用方法引用完成)
代码演示:
public class FunctionTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
创建集合添加学生对象,学生对象属性:name,age
只获取姓名放到数组当中(使用方法引用完成)
*/
//创建集合并添加元素
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Student("han",21));
list.add(new Student("ma",22));
list.add(new Student("zhao",23));
//只获取姓名放到数组当中
String[] arr = list.stream().map(Student::getName).toArray(String[]::new);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}运行结果:

![[leetcode] 67. 二进制求和](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/a36c1b59f2eb48eebd27dc7ba26116ca.png)