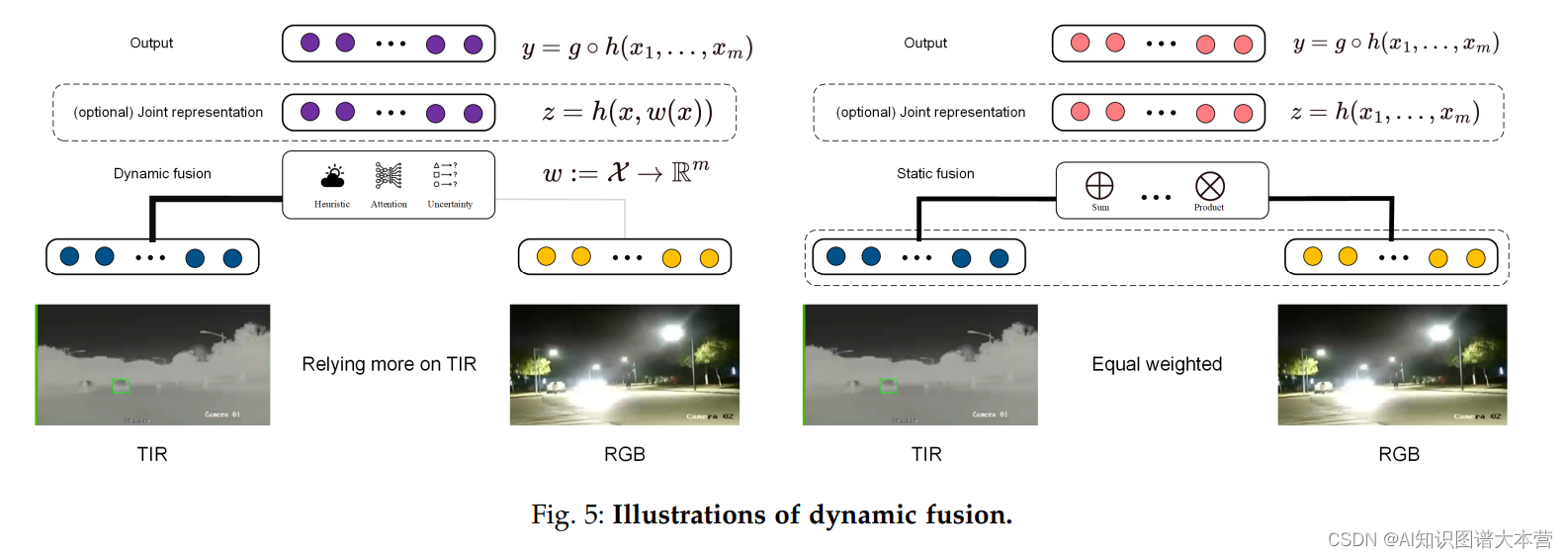
又学习了一种方法,类别引导diffusion模型,使用mnist数据集,记录一下它的用法吧。
Diffusion实战篇:
【Diffusion实战】训练一个diffusion模型生成S曲线(Pytorch代码详解)
【Diffusion实战】训练一个diffusion模型生成蝴蝶图像(Pytorch代码详解)
【Diffusion实战】引导一个diffusion模型根据文字生成图像(Pytorch代码详解)
Diffusion综述篇:
【Diffusion综述】医学图像分析中的扩散模型(一)
【Diffusion综述】医学图像分析中的扩散模型(二)
1、数据集装载
使用mnist数据集来训练类别引导diffusion模型,因为其比较简单清晰:
import torch
import torchvision
from torchvision import transforms
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from diffusers import DDPMScheduler, UNet2DModel
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(f'Using device: {device}')
dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root="mnist/", train=True, download=False,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor())
train_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=8, shuffle=True)
# 查看MNIST数据集样本
x, y = next(iter(train_dataloader))
print('Input shape:', x.shape)
print('Labels:', y)
plt.imshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(x)[0], cmap='Greys')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
看一看我们朴素的样本:
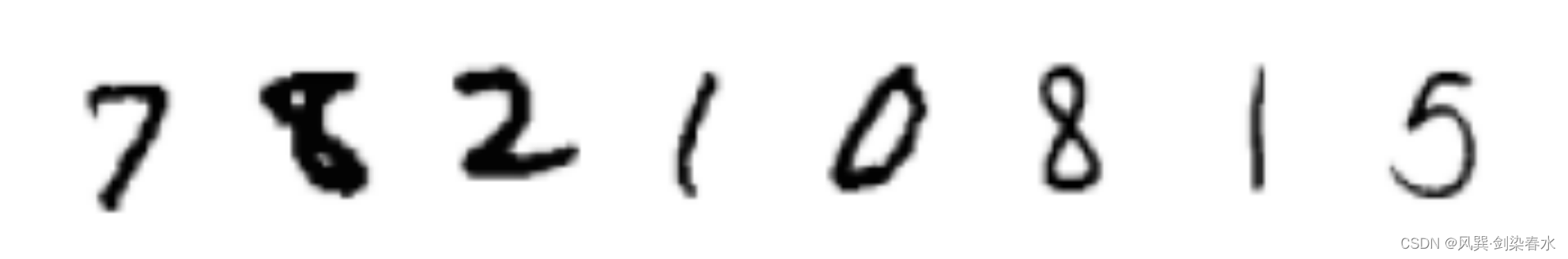
2、创建条件扩散模型
创建了一个名为ClassConditionedUnet的条件扩散模型,定义了一个可学习的嵌入层,用以将数字类别映射到特征向量上,将类别嵌入与原始输入拼接之后,送入常规的UNet网络即可。
知识传送:【python函数】torch.nn.Embedding函数用法图解
class ClassConditionedUnet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=10, class_emb_size=4):
super().__init__()
# 嵌入层将数字类别映射到特征向量上
self.class_emb = nn.Embedding(num_classes, class_emb_size)
# 一个常规的UNet网络
self.model = UNet2DModel(
sample_size=28, # 图像尺寸
in_channels=1 + class_emb_size, # 增加一个通道, 用于条件生成
out_channels=1, # 输出通道
layers_per_block=2, # 残差连接层数目
block_out_channels=(32, 64, 64),
down_block_types=(
"DownBlock2D", # a regular ResNet downsampling block
"AttnDownBlock2D", # a ResNet downsampling block with spatial self-attention
"AttnDownBlock2D",
),
up_block_types=(
"AttnUpBlock2D",
"AttnUpBlock2D", # a ResNet upsampling block with spatial self-attention
"UpBlock2D", # a regular ResNet upsampling block
),
)
def forward(self, x, t, class_labels):
bs, ch, w, h = x.shape # [8, 1, 28, 28]
# 类别条件以额外通道的形式输入
class_cond = self.class_emb(class_labels) # [8, 4]
class_cond = class_cond.view(bs, class_cond.shape[1], 1, 1).expand(bs, class_cond.shape[1], w, h) # [8, 4, 28, 28]
# 拼接原始输入与类别条件映射
net_input = torch.cat((x, class_cond), 1) # (8, 5, 28, 28)
# 模型预测
return self.model(net_input, t).sample # (8, 1, 28, 28)
noisy_xb = torch.randn(8, 1, 28, 28).to(device)
timesteps = torch.linspace(0, 999, 8).long().to(device)
y = torch.tensor([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]).to(device)
model = ClassConditionedUnet().to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
model_prediction = model(noisy_xb, timesteps, y)
model_prediction.shape # 验证输出与输出尺寸相同
3、模型训练
训练过程就跟之前的一样啦~
# 创建调度器
noise_scheduler = DDPMScheduler(num_train_timesteps=1000, beta_schedule='squaredcos_cap_v2')
train_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=128, shuffle=True)
n_epochs = 10
net = ClassConditionedUnet().to(device)
loss_fn = nn.MSELoss()
opt = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
losses = []
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
for x, y in tqdm(train_dataloader):
# 获取数据并添加噪声
x = x.to(device) * 2 - 1 # 归一化到[-1, 1]
y = y.to(device)
noise = torch.randn_like(x)
timesteps = torch.randint(0, 999, (x.shape[0],)).long().to(device)
# 前向加噪
noisy_x = noise_scheduler.add_noise(x, noise, timesteps)
# 获得模型预测结果
pred = net(noisy_x, timesteps, y) # 此处传入了类别标签
# 损失计算
loss = loss_fn(pred, noise)
# 损失回传, 参数更新
opt.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
opt.step()
# 损失保存
losses.append(loss.item())
# 输出损失
avg_loss = sum(losses[-100:])/100
print(f'Finished epoch {epoch}. Average of the last 100 loss values: {avg_loss:05f}')
# 查看损失曲线
plt.figure(dpi=300)
plt.plot(losses)
plt.show()
输出损失曲线为:
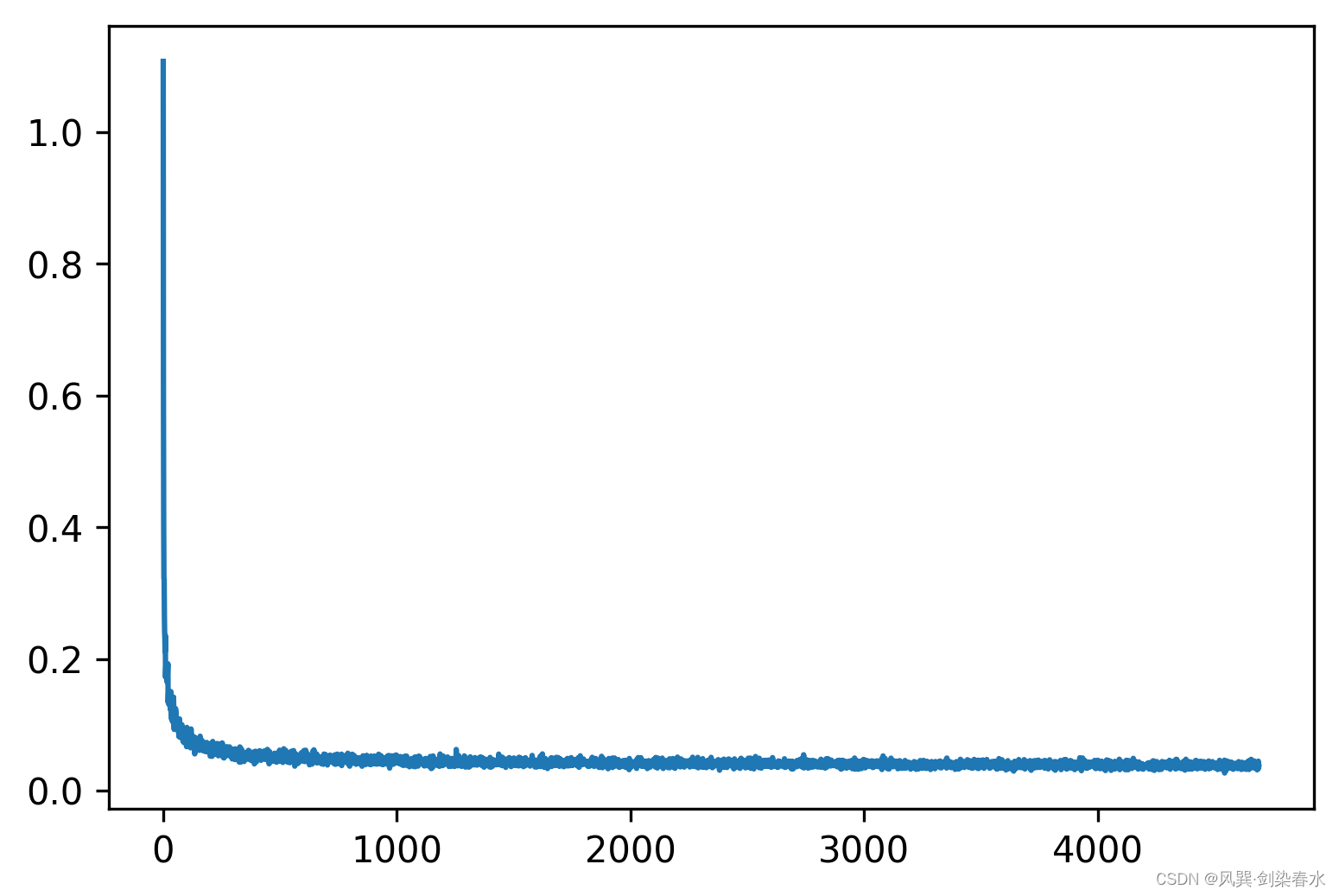
4、模型推理
进行采样循环,用类别标签引导图像生成:
x = torch.randn(80, 1, 28, 28).to(device) # 随机噪声
y = torch.tensor([[i]*8 for i in range(10)]).flatten().to(device) # 类别标签
# 采样循环
for i, t in tqdm(enumerate(noise_scheduler.timesteps)):
# 模型预测结果
with torch.no_grad():
residual = net(x, t, y)
# 根据预测噪声和时间步更新图像
x = noise_scheduler.step(residual, t, x).prev_sample
# 结果可视化
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(12, 12))
ax.imshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(x.detach().cpu().clip(-1, 1), nrow=8)[0], 'Greys')
ax.axis('off')
类别引导效果如下,效果还是挺好的哩:
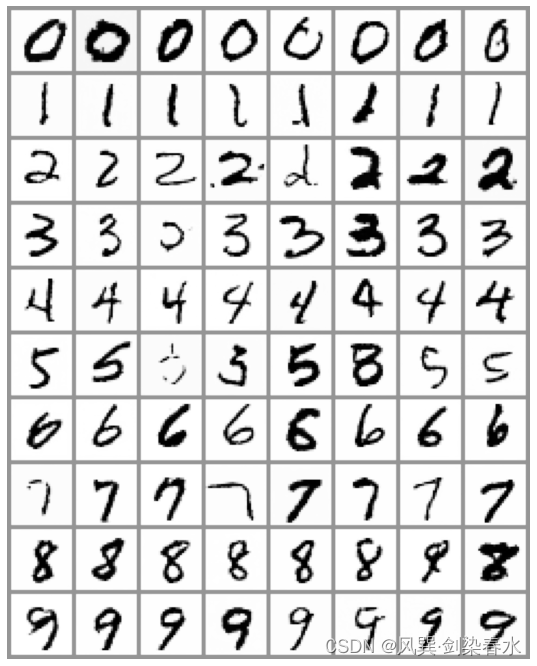
5、代码汇总
import torch
import torchvision
from torchvision import transforms
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from diffusers import DDPMScheduler, UNet2DModel
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(f'Using device: {device}')
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 1、数据集装载
dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root="mnist/", train=True, download=False,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor())
train_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=8, shuffle=True)
# 查看MNIST数据集样本
x, y = next(iter(train_dataloader))
print('Input shape:', x.shape)
print('Labels:', y)
plt.imshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(x)[0], cmap='Greys')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 2、创建条件扩散模型
class ClassConditionedUnet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=10, class_emb_size=4):
super().__init__()
# 嵌入层将数字类别映射到特征向量上
self.class_emb = nn.Embedding(num_classes, class_emb_size)
# 一个常规的UNet网络
self.model = UNet2DModel(
sample_size=28, # 图像尺寸
in_channels=1 + class_emb_size, # 增加一个通道, 用于条件生成
out_channels=1, # 输出通道
layers_per_block=2, # 残差连接层数目
block_out_channels=(32, 64, 64),
down_block_types=(
"DownBlock2D", # a regular ResNet downsampling block
"AttnDownBlock2D", # a ResNet downsampling block with spatial self-attention
"AttnDownBlock2D",
),
up_block_types=(
"AttnUpBlock2D",
"AttnUpBlock2D", # a ResNet upsampling block with spatial self-attention
"UpBlock2D", # a regular ResNet upsampling block
),
)
def forward(self, x, t, class_labels):
bs, ch, w, h = x.shape # [8, 1, 28, 28]
# 类别条件以额外通道的形式输入
class_cond = self.class_emb(class_labels) # [8, 4]
class_cond = class_cond.view(bs, class_cond.shape[1], 1, 1).expand(bs, class_cond.shape[1], w, h) # [8, 4, 28, 28]
# 拼接原始输入与类别条件映射
net_input = torch.cat((x, class_cond), 1) # (8, 5, 28, 28)
# 模型预测
return self.model(net_input, t).sample # (8, 1, 28, 28)
noisy_xb = torch.randn(8, 1, 28, 28).to(device)
timesteps = torch.linspace(0, 999, 8).long().to(device)
y = torch.tensor([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]).to(device)
model = ClassConditionedUnet().to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
model_prediction = model(noisy_xb, timesteps, y)
model_prediction.shape # 验证输出与输出尺寸相同
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 3、模型训练
# 创建调度器
noise_scheduler = DDPMScheduler(num_train_timesteps=1000, beta_schedule='squaredcos_cap_v2')
train_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=128, shuffle=True)
n_epochs = 10
net = ClassConditionedUnet().to(device)
loss_fn = nn.MSELoss()
opt = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
losses = []
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
for x, y in tqdm(train_dataloader):
# 获取数据并添加噪声
x = x.to(device) * 2 - 1 # 归一化到[-1, 1]
y = y.to(device)
noise = torch.randn_like(x)
timesteps = torch.randint(0, 999, (x.shape[0],)).long().to(device)
# 前向加噪
noisy_x = noise_scheduler.add_noise(x, noise, timesteps)
# 获得模型预测结果
pred = net(noisy_x, timesteps, y) # 此处传入了类别标签
# 损失计算
loss = loss_fn(pred, noise)
# 损失回传, 参数更新
opt.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
opt.step()
# 损失保存
losses.append(loss.item())
# 输出损失
avg_loss = sum(losses[-100:])/100
print(f'Finished epoch {epoch}. Average of the last 100 loss values: {avg_loss:05f}')
# 查看损失曲线
plt.figure(dpi=300)
plt.plot(losses)
plt.show()
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 4、模型推理
x = torch.randn(80, 1, 28, 28).to(device) # 随机噪声
y = torch.tensor([[i]*8 for i in range(10)]).flatten().to(device) # 类别标签
# 采样循环
for i, t in tqdm(enumerate(noise_scheduler.timesteps)):
# 模型预测结果
with torch.no_grad():
residual = net(x, t, y)
# 根据预测噪声和时间步更新图像
x = noise_scheduler.step(residual, t, x).prev_sample
# 结果可视化
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(12, 12))
ax.imshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(x.detach().cpu().clip(-1, 1), nrow=8)[0], 'Greys')
ax.axis('off')
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
diffusion的修炼境界又提升了一级~