变量
变量要素
1、类型;每一个变量都需要定义类型(强类型)其它语言有弱类型(js)
2、变量名;
3、存储的值;
声明方式:
数据类型 变量名 = 变量值;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 方式一
char gender;//变量的声明;
gender = '女'; //变量的赋值;初始化;
// gender = "男"; //不能是用双引号,会报错:String无法转换为char;
// 方式二
int age = 19;
byte bt = 0;
long ll = 123123L;
System.out.println(gender);
System.out.println("age = " + age);
System.out.println(ll); //123123
}
数据类型
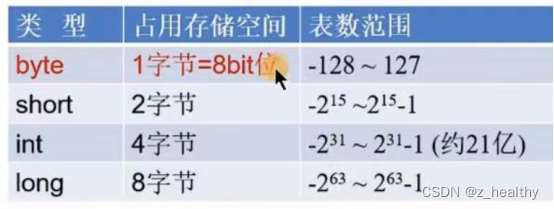
一、基本数据类型:(8种)
1、整型;
(1)byte
(2)short
(3)int
(4)long
2、浮点型
(1)float
- 4字节 尾数可以精确到7位;
(2)double
- 8字节 通常采用此类型;
float 占用空间比long要小,表述范围比long还要大~~~~~;但是精度太差; 声明float类型的话,需要添加后缀:f或者F;否则就是double了; //从double转换到float可能会有损失
如果没有特殊情况就使用double; 浮点型变量的精度都不高; 开发中使用通过BidDecimal类去替换;
double = 1; 整型可以赋值给浮点型;之后就自动转为浮点型1.0;
class Float{
public static void main(String[] args) {
float f1 = 1.1f;
double d1 = 1.1;
double d2 = 666;
System.out.println(f1 + d1);
double pi = 3.14;
double radius = 1.22;
double radius2 = 3.444;
double radius3 = 4.5555;
double area1 = pi * radius * radius;
double area2 = pi * radius2 * radius2;
double area3 = pi * radius3 * radius3;
System.out.println("area1Ãæ»ýΪ:" + area1);
System.out.println("area2Ãæ»ýΪ:" + area2);
System.out.println("area3Ãæ»ýΪ:" + area3);
// c = (f-32)/1.8;
double h = 80;
double s = (h - 32) / 1.8;
System.out.println("f_" + h + "=s_" + s);
}
}
3、字符型:char
1、占用两个字节;和short占用空间一样;
三种表现形式:
1、使用单引号表示,内部只有一个字符;有且只有一个;
所有的字符都使用unicode编码来表示;
所以全世界所有的值都可以付给字符;
2、形式2:
char c = ‘\uxxxx’; xxxx为unicode编号值(十六进制、四位);
3、形式3;
使用转义字符:‘\n’, ‘\t’;
4、形式4;
直接表示一个数值;(对应的是asc2码);
char c = 97; // =>结果是:a;
class Char{
public static void main(String[] args) {
char c1 = 's';
// char c2 = ''; // 必须要有值;
// char c3 = 'ss'; //而且只能有一位
char c3 = '\u0001';
System.out.println(c3);
char line = '\n';
System.out.println("sdfsdf" + line + "sdfsdf");
char a = 97;
System.out.println(a);
}
}
4、布尔型:
只有两个取值: true/false;
常使用在流程控制中;
Boolean占用几个字节?
就两个值;==》在内存中放的话就两个值:1、0;占用空间默认为int,四个字节; (不谈布尔占几个字节)
class Boolean {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double d1 = 111L;
System.out.println(d1);
byte b = 1;
int i = 111 + b;
System.out.println(i);
byte bb = 12;
short s1 = 10;
// short s2 = b + s1; //×Ô¶¯×ªÎªintÀàÐÍ£»±¨´í£»
byte b2 = 10;
byte b3 = 11;
// byte b4 = b2 + b3; //×Ô¶¯×ªÎªintÀàÐÍ£»±¨´í£»
short s2 = 11;
short s3 = 123;
// short s4 = s2 + s3; //
// long l1 = 1234564563333; //
// 1234564563333
long l2 =1234564563333L; //
System.out.println(l2);
}
}
类型转换
布尔类型
Boolean:略;
javac.exe是编译器、jvm是java虚拟机、公认最强的虚拟机
可以做运算的数据类型有七中;,布尔类型不行:**所以true+1会转换为1+1;
运算规则:
1、自动类型提升;
(1)、容量小的变量与容量大的变量做运算时,结果自动转换为容量大的数据类型;
这个容量大指的是:表示数据范围的大小;8个字节、4个字节;等等
byte 、 short、char => int => long => float => double;所以 double f1 = 111L;是成立的;没有问题的;
特殊的情况;
1、Byte和byte 、short和 short、byte 和 short 之间任意相加之后自动转为int类型;(整型常量,规定是int类型)
Long ll = 123; 将int 类型123转为long类型;自动类型提升;123的值不能超过int的范围;
2、char 和 char、char 和 byte/short 相加之后自动转为int;
其他:
3、浮点类型常量,规定是double类型;
Float ff = 12.2; 将double转为float类型,会报错;应该float ff = 12.2F;
2、强制类型转换;
(1)、使用强转符:”小括号” 来进行转换;
Long ll = 123L;
Int ii = (int)ll;
**
short s2 = 123;
short s3 = (short)s2;//这样也可以,虽然没有必要;
(2)、使用强制转换可能会经度丢失;(长转短)
不仅仅是截断,
Int i = 128;
(3)Byte b =(byte)i;//-127; 高位删除,符号位变化;
public class Translate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double d1 = 111.11;
// int i1 = d1; //´óתСʧ°Ü£»
/* Ç¿ÖÆÀàÐÍת»» */
int i2 = (int)d1;
System.out.println(i2);
long l1 = 123L;
short s1 = (short)l1;
short s2 = 123;
short s3 = (short)s2;//ÕâÑùÒ²¿ÉÒÔ£¬ËäȻûÓбØÒª£»
}
}
二、引用数据类型:
1、类(class)
2、数组(array)
3、接口(interface)
4、枚举(enum)
5、注解(annotation)————新特性
6、记录(record)–新特性
- **定义变量时,记得遵循规范;
**变量都有其作用域;只在作用域内有效;
Byte 一个字节最大是127;-128~127;
一个k = 1024byte
一个字节8位(bit),256种可能;正负各一半;
Short 两个字节:
声明long类型时需要后缀l(大写或者小写)
Long l = 123L;无特殊情况都是用int;
常量默认是int类型;
人机交互方式
1、GUI 图形化界面;
2、CLI 命令行交互方式:DOS命令;
JIT 即时编译器;所以效率提升和C#齐平;
即时编译器(JIT compiler,just-in-time compiler)是一个把Java的字节码(包括需要被解释的指令的程序)转换成可以直接发送给处理器的指令的程序。
十大排序;
之快速排序;得写几十遍才能成事- -。;
变量与运算符
1、 关键字;(都是小写字母)
2、标识符;identifier(自己起的名字就是标识符)
命名规则:
1、 26个英文字母大小写,0-9, _,$ 四种类型组成;
2、数字不可以开头;
3、 避开关键字和保留字;(不可以使用,但可以包含myClasse)
4、不能包含空格;
5、 区分小写,长度无限制;
命名规范:(道德范围)
1、包名: 都小写;
2、类名、接口名:大驼峰;
3、变量、方法名: 小驼峰;
4、常量名: 全大写,使用下划线连接: XXX_BBB_JJJ
5、见名知意;