返回:OpenCV系列文章目录(持续更新中......)
上一篇:OpenCV如何通过梯度结构张量进行各向异性图像分割(69)
下一篇 :OpenCV如何为我们的应用程序添加跟踪栏(71)

目录
目标
理论
如何消除傅里叶域中的周期性噪声?
源代码
解释
结果
目标
在本教程中,您将学习:
- 如何消除傅里叶域中的周期性噪声
理论
注意
解释基于该书[108]。此页面上的图像是真实世界的图像。
周期性噪声在傅里叶域中产生尖峰,通常可以通过视觉分析检测到。
如何消除傅里叶域中的周期性噪声?
通过频域滤波可以显著降低周期性噪声。在此页面上,我们使用具有适当半径的陷波抑制滤波器来完全封闭傅里叶域中的噪声尖峰。陷波滤波器抑制中心频率附近预定义邻域中的频率。陷波滤波器的数量是任意的。缺口区域的形状也可以是任意的(例如矩形或圆形)。在此页面上,我们使用三个圆形陷波抑制滤光片。图像的功率谱致密化用于噪声尖峰的视觉检测。
源代码
您可以在 OpenCV 源代码库中找到源代码。samples/cpp/tutorial_code/ImgProc/periodic_noise_removing_filter/periodic_noise_removing_filter.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include <opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
void fftshift(const Mat& inputImg, Mat& outputImg);
void filter2DFreq(const Mat& inputImg, Mat& outputImg, const Mat& H);
void synthesizeFilterH(Mat& inputOutput_H, Point center, int radius);
void calcPSD(const Mat& inputImg, Mat& outputImg, int flag = 0);
const String keys =
"{help h usage ? | | print this message }"
"{@image |period_input.jpg | input image name }"
;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CommandLineParser parser(argc, argv, keys);
string strInFileName = parser.get<String>("@image");
samples::addSamplesDataSearchSubDirectory("doc/tutorials/imgproc/periodic_noise_removing_filter/images");
Mat imgIn = imread(samples::findFile(strInFileName), IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
if (imgIn.empty()) //check whether the image is loaded or not
{
cout << "ERROR : Image cannot be loaded..!!" << endl;
return -1;
}
imshow("Image corrupted", imgIn);
imgIn.convertTo(imgIn, CV_32F);
// it needs to process even image only
Rect roi = Rect(0, 0, imgIn.cols & -2, imgIn.rows & -2);
imgIn = imgIn(roi);
// PSD calculation (start)
Mat imgPSD;
calcPSD(imgIn, imgPSD);
fftshift(imgPSD, imgPSD);
normalize(imgPSD, imgPSD, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX);
// PSD calculation (stop)
//H calculation (start)
Mat H = Mat(roi.size(), CV_32F, Scalar(1));
const int r = 21;
synthesizeFilterH(H, Point(705, 458), r);
synthesizeFilterH(H, Point(850, 391), r);
synthesizeFilterH(H, Point(993, 325), r);
//H calculation (stop)
// filtering (start)
Mat imgOut;
fftshift(H, H);
filter2DFreq(imgIn, imgOut, H);
// filtering (stop)
imgOut.convertTo(imgOut, CV_8U);
normalize(imgOut, imgOut, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX);
imwrite("result.jpg", imgOut);
imwrite("PSD.jpg", imgPSD);
fftshift(H, H);
normalize(H, H, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX);
imshow("Debluring", imgOut);
imwrite("filter.jpg", H);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
void fftshift(const Mat& inputImg, Mat& outputImg)
{
outputImg = inputImg.clone();
int cx = outputImg.cols / 2;
int cy = outputImg.rows / 2;
Mat q0(outputImg, Rect(0, 0, cx, cy));
Mat q1(outputImg, Rect(cx, 0, cx, cy));
Mat q2(outputImg, Rect(0, cy, cx, cy));
Mat q3(outputImg, Rect(cx, cy, cx, cy));
Mat tmp;
q0.copyTo(tmp);
q3.copyTo(q0);
tmp.copyTo(q3);
q1.copyTo(tmp);
q2.copyTo(q1);
tmp.copyTo(q2);
}
void filter2DFreq(const Mat& inputImg, Mat& outputImg, const Mat& H)
{
Mat planes[2] = { Mat_<float>(inputImg.clone()), Mat::zeros(inputImg.size(), CV_32F) };
Mat complexI;
merge(planes, 2, complexI);
dft(complexI, complexI, DFT_SCALE);
Mat planesH[2] = { Mat_<float>(H.clone()), Mat::zeros(H.size(), CV_32F) };
Mat complexH;
merge(planesH, 2, complexH);
Mat complexIH;
mulSpectrums(complexI, complexH, complexIH, 0);
idft(complexIH, complexIH);
split(complexIH, planes);
outputImg = planes[0];
}
void synthesizeFilterH(Mat& inputOutput_H, Point center, int radius)
{
Point c2 = center, c3 = center, c4 = center;
c2.y = inputOutput_H.rows - center.y;
c3.x = inputOutput_H.cols - center.x;
c4 = Point(c3.x,c2.y);
circle(inputOutput_H, center, radius, 0, -1, 8);
circle(inputOutput_H, c2, radius, 0, -1, 8);
circle(inputOutput_H, c3, radius, 0, -1, 8);
circle(inputOutput_H, c4, radius, 0, -1, 8);
}
// Function calculates PSD(Power spectrum density) by fft with two flags
// flag = 0 means to return PSD
// flag = 1 means to return log(PSD)
void calcPSD(const Mat& inputImg, Mat& outputImg, int flag)
{
Mat planes[2] = { Mat_<float>(inputImg.clone()), Mat::zeros(inputImg.size(), CV_32F) };
Mat complexI;
merge(planes, 2, complexI);
dft(complexI, complexI);
split(complexI, planes); // planes[0] = Re(DFT(I)), planes[1] = Im(DFT(I))
planes[0].at<float>(0) = 0;
planes[1].at<float>(0) = 0;
// compute the PSD = sqrt(Re(DFT(I))^2 + Im(DFT(I))^2)^2
Mat imgPSD;
magnitude(planes[0], planes[1], imgPSD); //imgPSD = sqrt(Power spectrum density)
pow(imgPSD, 2, imgPSD); //it needs ^2 in order to get PSD
outputImg = imgPSD;
// logPSD = log(1 + PSD)
if (flag)
{
Mat imglogPSD;
imglogPSD = imgPSD + Scalar::all(1);
log(imglogPSD, imglogPSD);
outputImg = imglogPSD;
}
}解释
通过频域滤波进行周期性降噪,包括功率谱密度计算(用于噪声尖峰视觉检测)、陷波抑制滤波器合成和频率滤波:
// it needs to process even image only
Rect roi = Rect(0, 0, imgIn.cols & -2, imgIn.rows & -2);
imgIn = imgIn(roi);
// PSD calculation (start)
Mat imgPSD;
calcPSD(imgIn, imgPSD);
fftshift(imgPSD, imgPSD);
normalize(imgPSD, imgPSD, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX);
// PSD calculation (stop)
//H calculation (start)
Mat H = Mat(roi.size(), CV_32F, Scalar(1));
const int r = 21;
synthesizeFilterH(H, Point(705, 458), r);
synthesizeFilterH(H, Point(850, 391), r);
synthesizeFilterH(H, Point(993, 325), r);
//H calculation (stop)
// filtering (start)
Mat imgOut;
fftshift(H, H);
filter2DFreq(imgIn, imgOut, H);
// filtering (stop)函数 calcPSD()计算图像的功率谱密度:
void calcPSD(const Mat& inputImg, Mat& outputImg, int flag)
{
Mat planes[2] = { Mat_<float>(inputImg.clone()), Mat::zeros(inputImg.size(), CV_32F) };
Mat complexI;
merge(planes, 2, complexI);
dft(complexI, complexI);
split(complexI, planes); // planes[0] = Re(DFT(I)), planes[1] = Im(DFT(I))
planes[0].at<float>(0) = 0;
planes[1].at<float>(0) = 0;
// compute the PSD = sqrt(Re(DFT(I))^2 + Im(DFT(I))^2)^2
Mat imgPSD;
magnitude(planes[0], planes[1], imgPSD); //imgPSD = sqrt(Power spectrum density)
pow(imgPSD, 2, imgPSD); //it needs ^2 in order to get PSD
outputImg = imgPSD;
// logPSD = log(1 + PSD)
if (flag)
{
Mat imglogPSD;
imglogPSD = imgPSD + Scalar::all(1);
log(imglogPSD, imglogPSD);
outputImg = imglogPSD;
}
}函数 synthesizeFilterH()根据中心频率和半径形成理想圆形陷波抑制滤波器的传递函数:
void synthesizeFilterH(Mat& inputOutput_H, Point center, int radius)
{
Point c2 = center, c3 = center, c4 = center;
c2.y = inputOutput_H.rows - center.y;
c3.x = inputOutput_H.cols - center.x;
c4 = Point(c3.x,c2.y);
circle(inputOutput_H, center, radius, 0, -1, 8);
circle(inputOutput_H, c2, radius, 0, -1, 8);
circle(inputOutput_H, c3, radius, 0, -1, 8);
circle(inputOutput_H, c4, radius, 0, -1, 8);
}函数 filter2DFreq()过滤频域中的图像。函数 fftshift()和 filter2DFreq()是从教程 Out-of-focus Deblur Filter 中复制的。
结果
下图显示了被各种频率的周期性噪声严重损坏的图像。
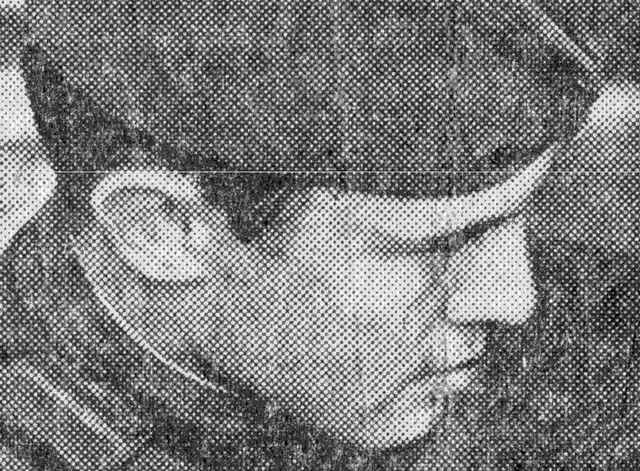

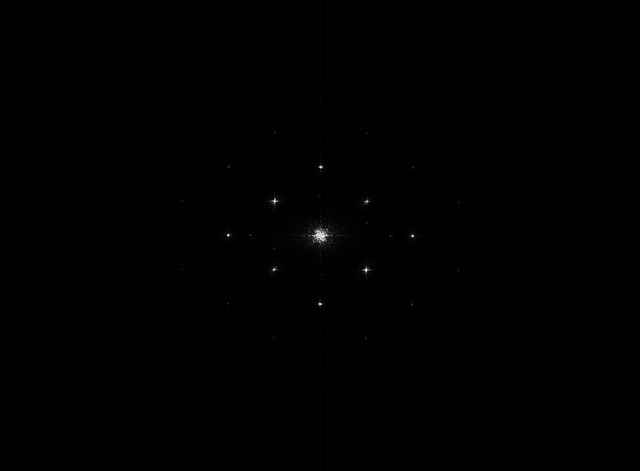
噪声分量很容易被看作是下图所示的功率谱密度中的亮点(尖峰)。
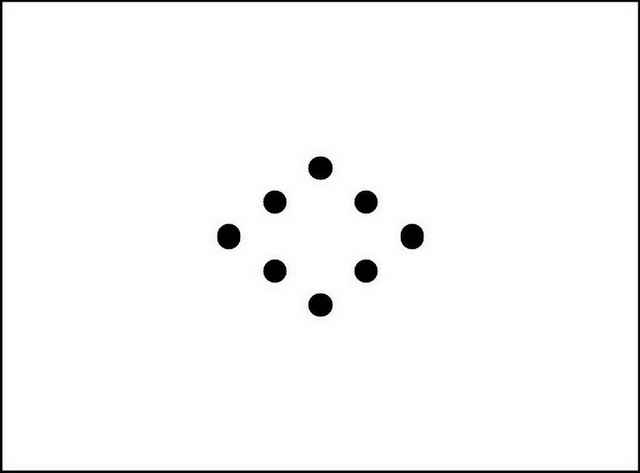
下图显示了具有适当半径的陷波抑制滤波器,以完全封闭噪声尖峰。
使用陷波抑制滤波器处理图像的结果如下所示。
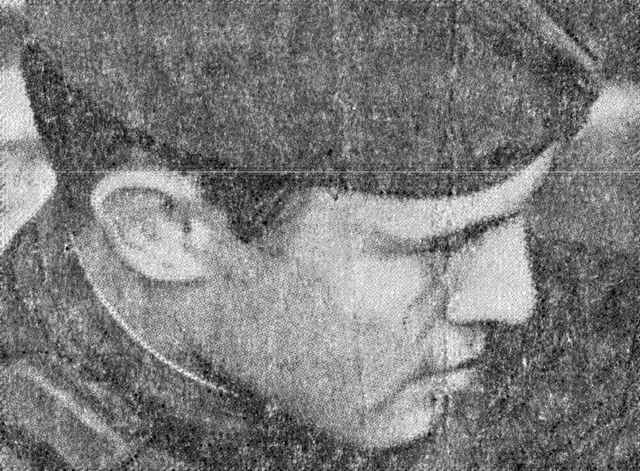

这种改进是显而易见的。与原始图像相比,此图像包含的可见周期性噪声要少得多。
您还可以在 YouTube 上找到此过滤理念的快速视频演示。