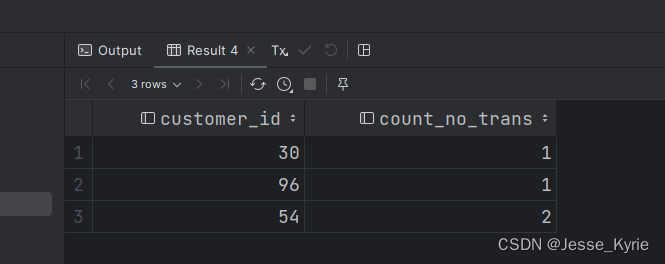
1.删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有结点。
. - 力扣(LeetCode)
思路一:遍历原链表,将值为val的节点释放掉
思路二:创建一个新链表,将值不为val的节点尾插到新链表中
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {
//创建一个新链表
ListNode*newhead,*newtail;
newhead=newtail=NULL;
ListNode*pcur=head;//用来遍历链表
while(pcur)
{
if(pcur->val!=val)
{
if(newhead==NULL)//链表为空
{
newhead=newtail=pcur;
}
else //尾插
{
newtail->next=pcur;
newtail=newtail->next;
}
}
pcur=pcur->next;
}
if(newtail)
{
newtail->next=NULL;
}
return newhead;
}2.反转一个单链表。
. - 力扣(LeetCode)
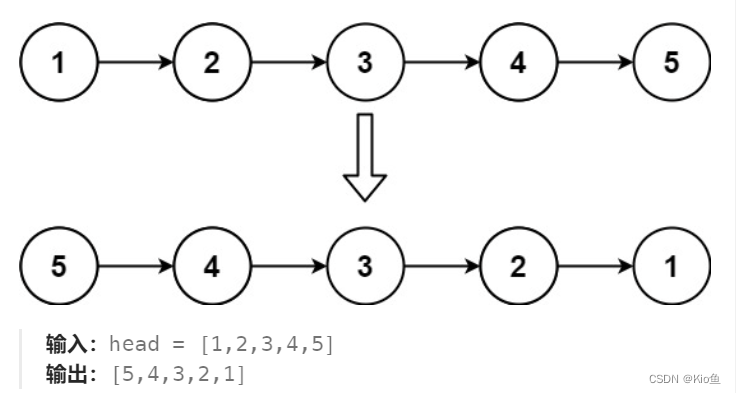
思路1:创建一个新链表,将新节点拿下来头插
思路2:创建三个指针完成链表的翻转


/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
if(head==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
ListNode*n1,*n2,*n3;
n1=NULL;
n2=head;
n3=head->next;
while(n2)
{
n2->next=n1;
n1=n2;
n2=n3;
if(n3)
{
n3=n3->next;
}
}
return n1;
}3.寻找链表的中间节点。
. - 力扣(LeetCode)
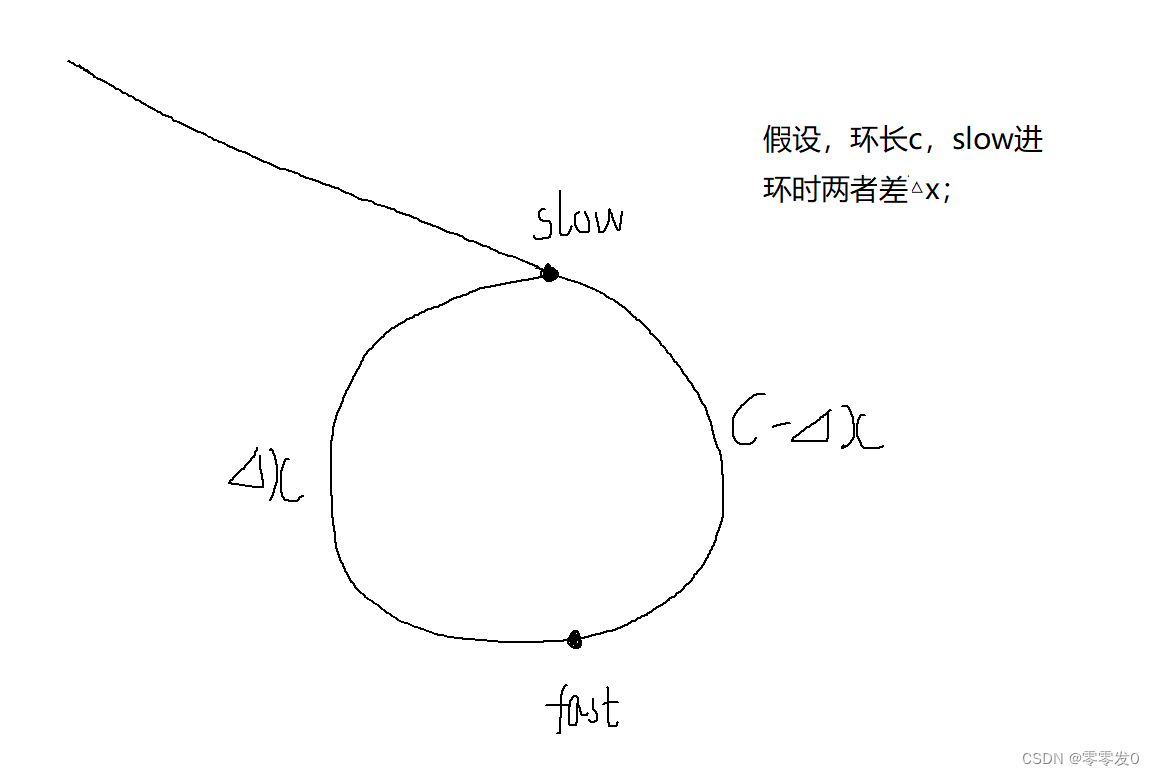
思路:使用快慢指针,快指针走2步,慢指针走1步,快指针走到空或者next指针为空时,慢指针指向的就是中间节点
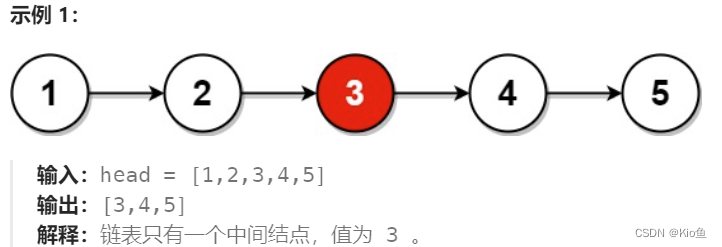
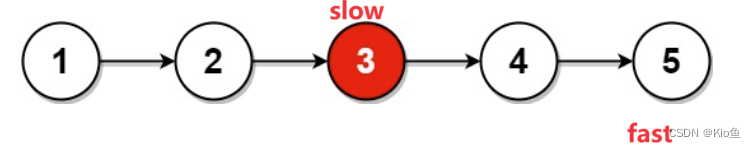
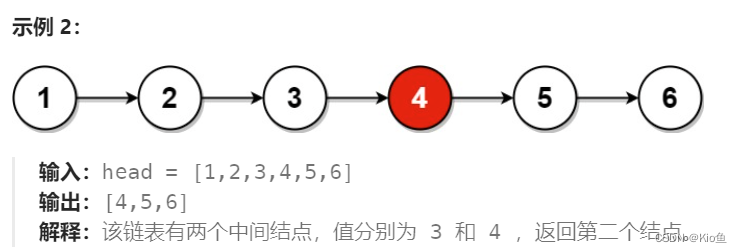

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {
//快慢指针
ListNode*slow,*fast;
slow=head;
fast=head;
while(fast&&fast->next)
{
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}4.输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
. - 力扣(LeetCode)

要求空间复杂度为O(1),只能遍历一遍链表
思路:快慢指针,快指针先走k步,然后快慢指针同时走,当快指针走到空时,slow指针指向的就是倒数第k个节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
int kthToLast(struct ListNode* head, int k){
ListNode*fast=head;
ListNode*slow=head;
while(k--)
{
fast=fast->next;
}
while(fast)
{
fast=fast->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
return slow->val;
}
5.将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。
. - 力扣(LeetCode)

思路:创建一个新的链表,遍历原链表,将链表中较小的节点尾插到新链表中
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {
if(list1==NULL)
{
return list2;
}
if(list2==NULL)
{
return list1;
}
ListNode*newhead,*newtail;
newhead=newtail=NULL;
ListNode*l1=list1;
ListNode*l2=list2;
while(l1&&l2)
{
if(l1->val<l2->val)
{
//将l1拿下来尾插
if(newhead==NULL)
{
newhead=newtail=l1;
}
else
{
newtail->next=l1;
newtail=newtail->next;
}
l1=l1->next;
}
else
{
//将l2拿下尾插
if(newhead==NULL)
{
newhead=newtail=l2;
}
else
{
newtail->next=l2;
newtail=newtail->next;
}
l2=l2->next;
}
}
//跳出循环,要不就是l1走到空,就是l2走到空
if(l1)//if(l1!=NULL)
{
newtail->next=l1;
}
if(l2)//if(l2!=NULL)
{
newtail->next=l2;
}
return newhead;
}6. 分割链表
链表分割_牛客题霸_牛客网

思路一:在原链表上进行修改,定义pcur从起始位置开始走,若pcur节点小于x,往后走:若pcur节点值大于等于x,尾插在链表之后。
思路二:创建一个新链表,若pcur节点的值小于x,头插在新链表中:若pcur节点的值大于等于x,尾插在新链表中。
思路三:创建两个链表,大链表和小链表。

/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class Partition {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {
if(pHead==NULL)
{
return pHead;
}
//创建两个带头链表
struct ListNode*lesshead,*lesstail;
struct ListNode*greaterhead,*greatertail;
lesshead=lesstail=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
greaterhead=greatertail=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
//遍历原链表
struct ListNode*pcur=pHead;
while(pcur)
{
if(pcur->val<x)
{
//尾插到小链表中
lesstail->next=pcur;
lesstail=lesstail->next;
}
else
{
//尾插到大链表中
greatertail->next=pcur;
greatertail=greatertail->next;
}
pcur=pcur->next;
}
greatertail->next=NULL;
lesstail->next=greaterhead->next;
return lesshead->next;
}
};7.判断链表是否为回文结构
链表的回文结构_牛客题霸_牛客网

/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class PalindromeList {
public:
//寻找链表的中间节点
struct ListNode *middleNode(struct ListNode*head)
{
struct ListNode*slow=head;
struct ListNode*fast=head;
while(fast&&fast->next)
{
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
//将中间节点和之后的节点逆置
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode*cur=head;
struct ListNode*newhead=NULL;
while(cur)
{
struct ListNode*next=cur->next;
//头插
cur->next=newhead;
newhead=cur;
cur=next;
}
return newhead;
}
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode*A)
{
struct ListNode*mid=middleNode(A);
struct ListNode*rmid=reverseList(mid);
while(A&&rmid)
{
if(A->val!=rmid->val)
{
return false;
}
A=A->next;
rmid=rmid->next;
}
return true;
}
};8.寻找两个链表的公共节点
. - 力扣(LeetCode)


/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
ListNode*curA=headA;
ListNode*curB=headB;
int lenA=1;
int lenB=1;
while(curA->next)
{
curA=curA->next;
lenA++;
}
while(curB->next)
{
curB=curB->next;
lenB++;
}
//尾节点不相等就不相交
if(curA!=curB)
{
return NULL;
}
//长的先走差距步,再同时走,第一个相等就是交点
//假设法
int gap=abs(lenA-lenB);
ListNode*longlist=headA;
ListNode*shortlist=headB;
if(lenB>lenA)
{
longlist=headB;
shortlist=headA;
}
while(gap--)
{
longlist=longlist->next;
}
while(longlist!=shortlist)
{
longlist=longlist->next;
shortlist=shortlist->next;
}
return longlist;
}9.随机链表的复制
. - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任一节点
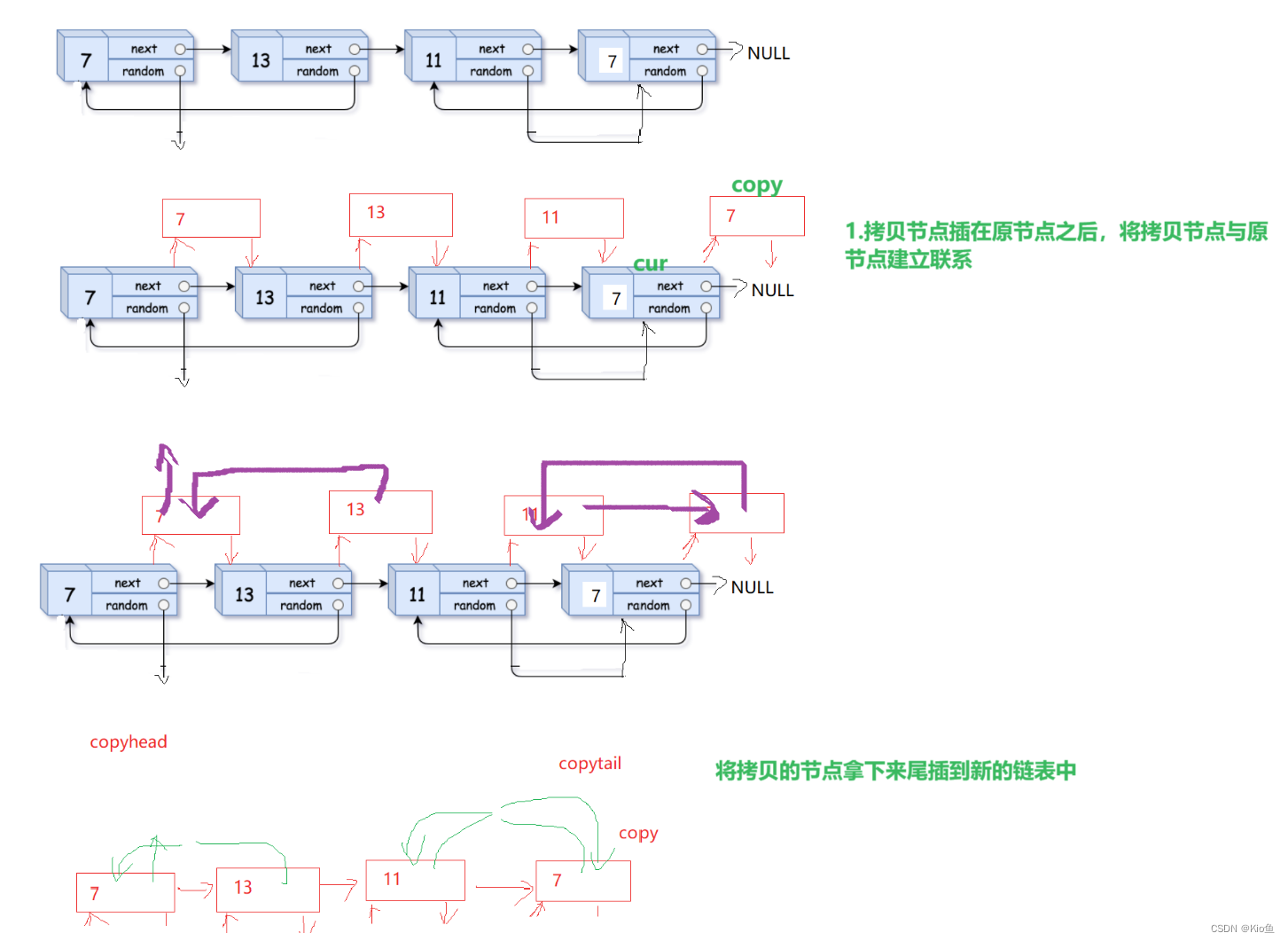
/**
* Definition for a Node.
* struct Node {
* int val;
* struct Node *next;
* struct Node *random;
* };
*/
typedef struct Node Node;
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
Node*cur=head;
//将拷贝节点插入在原节点的后面
while(cur)
{
Node*copy=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
copy->val=cur->val;
copy->next=cur->next;
cur->next=copy;
cur=copy->next;
}
//控制random
cur=head;
while(cur)
{
Node*copy=cur->next;
if(cur->random==NULL)
{
copy->random=NULL;
}
else
{
copy->random=cur->random->next;
}
cur=copy->next;
}
//把拷贝节点取下来尾插成为新链表
Node*copyhead=NULL;
Node*copytail=NULL;
cur=head;
while(cur)
{
Node*copy=cur->next;
Node*next=copy->next;
if(copyhead==NULL)
{
copyhead=copytail=copy;
}
else
{
copytail->next=copy;
copytail=copytail->next;
}
cur=next;
}
return copyhead;
}