十三、授权
- 什么是授权
- 权限管理核心概念
- Spring Security 权限管理策略
- 基于 URL 地址的权限管理
- 基于方法的权限管理
- 实战
权限管理
身份认证,就是判断一个用户是否为合法用户的处理过程。SpringSecurity中支持多种不同方式的认证,但是无论开发者使用那种方式认证,都不会影响授权功能使用。因为Spring Security很好做到了认证和授权解耦
授权
授权,即访问控制,控制谁能访问哪些资源。简单的理解授权就是根据系统提前设置好的规则,给用户分配可以访问某一个资源的权限,用户根据自己所具有权限,去执行相应操作
授权核心概念
在前面学习认证过程中,我们得知认证成功之后会将当前登录用户信息保存到 Authentication 对象中,Authentication 对象中有一个 getAuthorities()方法,用来返回当前登录用户具备的权限信息,也就是当前用户具有权限信息。该方法的返回值为 Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority>,当需要进行权限判断时,就回根据集合返回权限信息调用相应方法进行判断

那么问题来了,针对于这个返回值 GrantedAuthority 应该如何理解呢?是角色还是权限?
我们针对于授权可以是基于角色权限管理和基于资源权限管理,从设计层面上来说,角色和权限是两个完全不同的东西:权限是一些具体操作,角色则是某些权限集合。如:
READ_BOOK 和 ROLE_ADMIN 是完全不同的。因此至于返回值是什么取决于你的业务设计情况:
- 基于角色权限设计就是:
用户<=>角色<=>资源三者关系返回就是用户的角色 - 基于资源权限设计就是:
用户<=>权限<=>资源三者关系返回就是用户的权限 - 基于角色和资源权限设计就是:
用户<=>角色<=>权限<=>资源返回统称为用户的权限
为什么可以统称为权限,因为从代码层面角色和权限没有太大不同,都是权限,特别是在 Spring Security 中,角色和权限处理方式基本上都是一样的。唯一区别 Spring Security 在很多时候会自动给角色添加一个ROLE_前缀,而权限则不会自动添加
13.1 权限管理策略
Spring Security 中提供的权限管理策略主要有两种类型
- 基于过滤器的权限管理(FilterSecurityInterceptor)
- 基于过滤器(URL)的权限管理主要是用来拦截 HTTP 请求,拦截下来之后,根据 HTTP 请求地址进行权限校验
- 基于 AOP 的权限管理(MethodSecruityInterceptor)
- 基于 AOP(方法)权限管理主要是用来处理方法级别的权限问题。当需要调用某一个方法时,通过 AOP 将操作拦截下来,然后判断用户是否具备相关的权限
基于 URL 权限管理
- controller
package com.vinjcent.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.provisioning.InMemoryUserDetailsManager;
/**
* 自定义 spring security 配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class WebSecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
public UserDetailsService userDetailsService() {
InMemoryUserDetailsManager inMemoryUserDetailsManager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();
inMemoryUserDetailsManager.createUser(User.withUsername("root").password("{noop}123").roles("ADMIN").build());
inMemoryUserDetailsManager.createUser(User.withUsername("lisi").password("{noop}123").roles("USER").build());
inMemoryUserDetailsManager.createUser(User.withUsername("win7").password("{noop}123").authorities("READ_INFO").build());
return inMemoryUserDetailsManager;
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService());
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.mvcMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN") // 访问 admin 角色
.mvcMatchers("/user/**").hasAnyRole("USER", "ADMIN") // 访问 user 角色
.mvcMatchers("/info/**").hasAuthority("READ_INFO") // 访问 READ_INFO 权限
.anyRequest()
.authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.and()
.csrf()
.disable();
}
}
- 权限表达式

| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| hasAuthority(String authority) | 当前用户是否具备指定权限 |
| hasAnyAuthority(String… authorities) | 当前用户是否具备指定权限中任意一个 |
| hasRole(String role) | 当前用户是否具备指定角色 |
| hasAnyRole(String… roles) | 当前用户是否具备指定角色中任意一个 |
| permitAll() | 放行所有请求/调用 |
| denyAll() | 拒绝所有请求/调用 |
| isAnonymous() | 当前用户是否是一个匿名用户 |
| isAuthenticated() | 当前用户是否已经认证成功 |
| isRememberMe() | 当前用户是否通过 RememberMe 自动登录 |
| isFullyAuthenticated() | 当前用户是否既不是匿名用户又不是通过 RememberMe 自动登录的 |
| hasPermission(Object target, Object permission) | 当前用户是否具备指定目标的指定权限信息 |
| hasPermission(Object targetId, String targetType, Object permission) | 当前用户是否具备指定目标的指定权限信息 |
基于方法的权限管理
基于方法的权限管理主要是通过 AOP 来实现,Spring Security 中通过 MethodSecurityInterceptor 来提供相关的实现。不同在于 FilterSecurityInterceptor 只是在请求之前进行前置处理,MethodSecurityInterceptor 除了前置处理之外还可以进行后置处理。前置处理就是在请求之前判断是否具备相应的权限,后置处理则是对方法的执行结果进行二次过滤。前置处理和后置处理分别对应了不同的实现类
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity 该注解是用来开启权限注解,用法如下
/**
* 自定义 spring security 配置类
*/
@Configuration
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true, securedEnabled = true, jsr250Enabled = true)
public class WebSecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {}
- perPostEnabled:开启Spring Security提供的四个权限注解,@PreAuthorize、@PreFilter、@PostAuthorize以及 @PostFilter
- securedEnabled:开启Spring Security提供的 @Secured 注解支持,该注解不支持权限表达式
- jsr250Enabled:开启 JSR-250 提供的注解,主要是 @DenyAll、@PermitAll、@RolesAllowed 同样这些注解也不支持权限表达式
以上注解含义如下
-
@PreAuthorize:在目标方法执行之前进行权限校验 -
@PreFiter:在目标方法执行之前对方法参数进行过滤 -
@PostAuthorize:在目标方法执行之后进行权限校验 -
@PostFiter:在目标方法执行之后对方法的返回结果进行过滤 -
@Secured:访问目标方法必须具备相应的角色 -
@DenyAll:拒绝所有访问 -
@PermitAll:允许所有访问 -
@RolesAllowed:访问目标方法必须具备相应的角色这些基于方法的权限管理相关的注解,一般来说只要设置
prePostEnable=true就够用了 -
用例测试(需要在自定义 Spring Security 配置类中添加@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity注解)
package com.vinjcent.controller;
import com.vinjcent.pojo.User;
import org.omg.CORBA.PUBLIC_MEMBER;
import org.springframework.security.access.annotation.Secured;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PostAuthorize;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PostFilter;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreFilter;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import javax.annotation.security.DenyAll;
import javax.annotation.security.PermitAll;
import javax.annotation.security.RolesAllowed;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
public class DemoController {
/**
* 方法执行前
* 角色必须是 "ADMIN" 并且用户名是 "root" 或有 "READ_INFO" 权限
* @return 字符串
*/
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN') and authentication.name == 'root' or hasAuthority('READ_INFO')")
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "admin ok!";
}
/**
* 方法执行前
* 当前认证的用户名必须与传递的参数username一致
* @param username 用户名
* @return 字符串
*/
@PreAuthorize("authentication.name == #username")
@GetMapping("/name")
public String hello(String username) {
return "hello: " + username;
}
/**
* 方法执行前
* 当前的过滤对象数组中,id 为 奇数的用户
* @param users 过滤后的用户
*/
@PreFilter(value = "filterObject.id % 2 != 0", filterTarget = "users")
@PostMapping("/users")
public void addUsers(@RequestBody List<User> users) { // filterTarget 必须是 数组、集合类型
System.out.println("users = " + users);
}
/**
* 方法执行后
* 返回的对象,id只能为"1"
* @param id 传递的id参数
* @return 返回一个对象
*/
@PostAuthorize("returnObject.id == 1")
@GetMapping("/userId")
public User getUserById(Integer id) {
return new User(id, "vinjcent");
}
/**
* 方法执行完后
* 将集合中用户id为偶数的用户进行过滤
* @return 用户集合
*/
@PostFilter("filterObject.id % 2 == 0")
@GetMapping("/users")
public List<User> getAllUsers() {
ArrayList<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
users.add(new User(i, "user" + i));
}
return users;
}
/**
* 当前认证的用户必须有指定角色,才能访问该方法
* @return 返回一个对象
*/
@Secured({"ROLE_USER", "ROLE_ADMIN"}) // 可以写多个角色,具有其中一个即可
@GetMapping("/secured")
public User getUserByUsername() {
return new User(99, "secured");
}
/**
* 允许所有访问
* @return 字符串
*/
@PermitAll
@GetMapping("/permitAll")
public String permitAll() {
return "permitAll";
}
/**
* 拒绝所有访问
* @return 字符串
*/
@DenyAll
@GetMapping("/denyAll")
public String denyAll() {
return "denyAll";
}
@RolesAllowed({"ROLE_USER", "ROLE_ADMIN"}) // 可以写多个角色,具有其中一个即可
@GetMapping("/rolesAllowed")
public String roleAllowed() {
return "rolesAllowed";
}
}
13.2 antMatchers()、mvcMatchers()、regexMatchers()
-
antMatchers:映射 AntPathRequestMatcher 实例 List
-
mvcMatchers:此匹配器将使用 Spring MVC 用于匹配的相同规则。例如,路径"/path"的映射通常匹配"/path"、“/path/”、“/path.html”
-
regexMatchers:正则表达式匹配器


13.3 授权之原理分析
授权 Debug
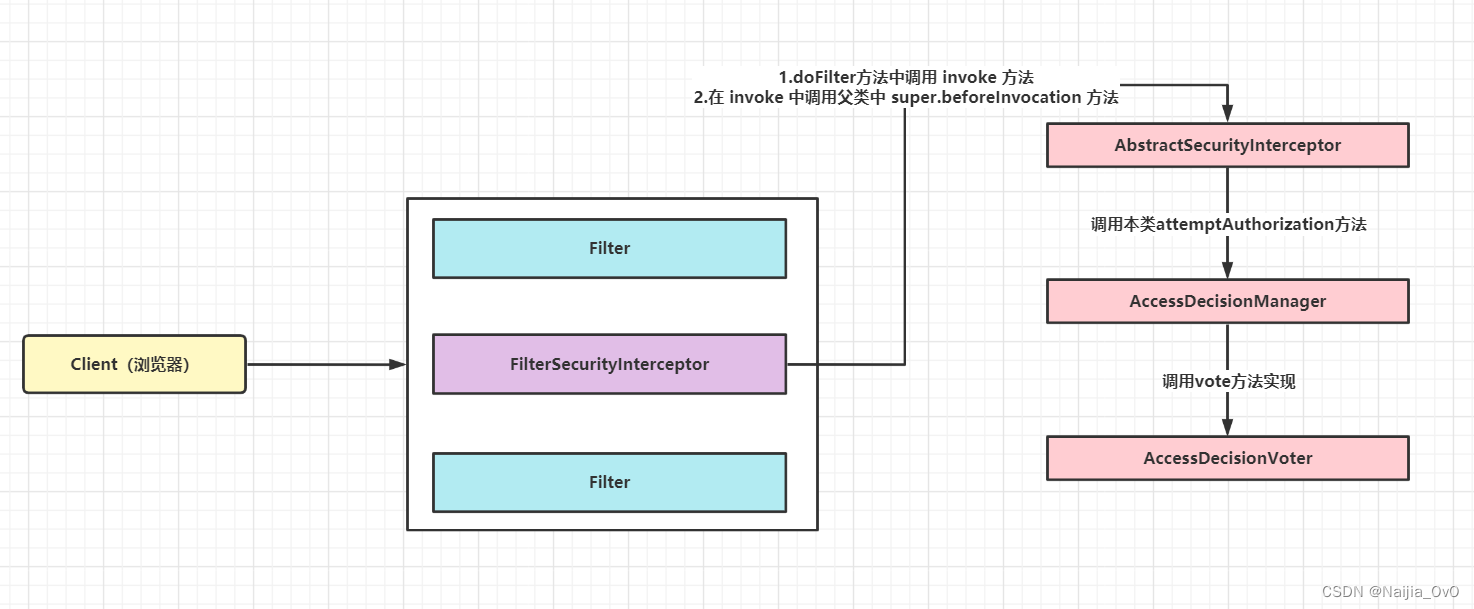
- 首先会经过 FilterSecurityInterceptor 类中的 doFilter() 方法

- 然后会经过父类的 super.beforeInvocation() 方法

- 接着走到了父类的 this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource().getAttributes(object) 获取对应的元数据(自定义资源的对应权限)

- 然后类似于认证,去尝试授权 attemptAuthorization()

- 授权当中,会进行 AccessDecisionManager 接口中的 decide() 方法进行投票

- 循环遍历认证后的用户所具有的权限

- 简要流程
- ConfigAttribute 在 Spring Security 中,用户请求一个资源(通常是一个接口或者一个 Java 方法)需要的角色会被封装成一个 ConfigAttribute 对象,在 ConfigAttribute 中只有一个 getAttribute 方法,该方法返回一个 String 字符串,就是角色的名称。一般来说,角色名称都带有一个
ROLE_前缀,投票器 AccessDecisionVoter 所做的事情,其实就是比较用户所具备的角色和请求某个资源所需的 ConfigAttribute 之间的关系 - AccessDecisionVoter 和 AccessDecisionManager 都有众多的实现类,在 AccessDecisionManager 中会挨个遍历 AccessDecisionVoter,进而决定是否允许用户访问,因而 AccessDecisionVoter 和 AccessDecisionManager 两者的关系类似于 AuthenticationProvider 和 ProviderManager 的关系
13.4 自定义资源权限实战
在前面的案例中,我们配置 URL 拦截规则和请求 URL 所需要的权限都是通过代码来配置的,这样就比较固定。如果想要调整访问某一个 URL 所需要的权限,就需要修改代码
动态管理权限规则就是我们将 URL 拦截规则和访问 URL 所需要的权限都保存在数据库中,这样,在不修改源代码的情况下,只需要修改数据库中的数据即可对权限进行调整
用户<--中间表-->角色<--中间表-->菜单
库表设计
-- menu 表
CREATE TABLE `menu` (
`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '菜单id',
`pattern` VARCHAR(128) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '路径映射',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
-- user 表
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '用户id',
`username` VARCHAR(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '用户名',
`password` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '密码',
`enabled` TINYINT(1) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '是否可用',
`locked` TINYINT(1) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '是否锁定',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
-- role 表
CREATE TABLE `role` (
`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '角色id',
`name` VARCHAR(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '角色英文名称',
`nameZh` VARCHAR(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '角色中文名称',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
-- menu_role 表
CREATE TABLE `menu_role` (
`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '菜单角色id',
`mid` INT(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '菜单id',
`rid` INT(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '角色id',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `mid` (`mid`),
KEY `rid` (`rid`),
CONSTRAINT `menu_role_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`mid`) REFERENCES `menu` (`id`),
CONSTRAINT `menu_role_ibfk_2` FOREIGN KEY (`rid`) REFERENCES `role` (`id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
-- user_role 表
CREATE TABLE `user_role` (
`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '用户角色id',
`uid` INT(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '用户id',
`rid` INT(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '角色id',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `uid` (`uid`),
KEY `rid` (`rid`),
CONSTRAINT `user_role_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`uid`) REFERENCES `user` (`id`),
CONSTRAINT `user_role_ibfk_2` FOREIGN KEY (`rid`) REFERENCES `role` (`id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=5 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
- 参考数据

依赖以及配置文件
- pom.xml
<dependencies>
<!--security-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--web-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--mysql-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.25</version>
</dependency>
<!--druid-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.8</version>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--lombok-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.20</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- application.yml
# 端口号
server:
port: 8080
spring:
application:
# 应用名称
name: SpringSecurity014
# 数据源
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springsecurity?useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: 123456
# mybatis
mybatis:
type-aliases-package: com.vinjcent.pojo
mapper-locations: classpath:com/vinjcent/mapper/*.xml
# 日志打印
logging:
level:
com:
vinjcent:
debug
代码设计
- 对应实体类

- Mapper 接口
1)UserMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.vinjcent.mapper.UserMapper">
<!--根据用户名查询用户信息-->
<select id="queryUserByUsername" resultType="User">
select id,
username,
password,
enabled,
locked
from user
where username = #{username}
</select>
</mapper>
2)RoleMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.vinjcent.mapper.RoleMapper">
<!--基础字段映射-->
<resultMap id="RoleResultMap" type="Role">
<id property="id" column="id" />
<result property="name" column="name" />
<result property="nameZh" column="nameZh" />
</resultMap>
<!--根据用户id查询角色信息-->
<select id="queryRolesByUid" resultMap="RoleResultMap">
select r.id id,
r.name name,
r.nameZh nameZh
from role r,
user_role ur
where r.id = ur.rid
and ur.uid = #{uid}
</select>
</mapper>
3)MenuMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybtais.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.vinjcent.mapper.MenuMapper">
<resultMap id="MenuResultMap" type="Menu">
<id column="id" property="id" />
<result column="pattern" property="pattern" />
<collection property="roles" ofType="Role">
<id column="rid" property="id" />
<result column="rname" property="name" />
<result column="rnameZh" property="nameZh" />
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="getAllMenus" resultMap="MenuResultMap">
select
m.id id,
m.pattern pattern,
r.id rid,
r.name rname,
r.nameZh rnameZh
from menu m
left join menu_role mr
on m.id = mr.mid
left join role r
on mr.rid = r.id
</select>
</mapper>
【注】service 层代码过于简单不在这里给出,根据 mapper 接口方法实现即可
- 测试接口 HelloController
package com.vinjcent.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
/**
* 资源 可访问的角色
* /admin/** ROLE_ADMIN
* /user/** ROLE_ADMIN ROLE_USER
* /guest/** ROLE_ADMIN ROLE_USER ROLE_GUEST
*
*
* 用户 具有的角色信息
* admin ADMIN USER GUEST
* user USER GUEST
* vinjcent GUEST
*
*/
@GetMapping("/admin/hello")
public String admin() {
return "hello admin";
}
@GetMapping("/user/hello")
public String user() {
return "hello user";
}
@GetMapping("/guest/hello")
public String guest() {
return "hello guest";
}
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
}
- 认证数据源 UserDetailsService
package com.vinjcent.config.security.service;
import com.vinjcent.pojo.Role;
import com.vinjcent.pojo.User;
import com.vinjcent.service.RoleService;
import com.vinjcent.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils;
import java.util.List;
@Component
public class DivUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
// dao ===> springboot + mybatis
private final UserService userService;
private final RoleService roleService;
@Autowired
public DivUserDetailsService(UserService userService, RoleService roleService) {
this.userService = userService;
this.roleService = roleService;
}
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
// 1.查询用户
User user = userService.queryUserByUsername(username);
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(user)) throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户名不存在!");
// 2.查询权限信息
List<Role> roles = roleService.queryRolesByUid(user.getId());
user.setRoles(roles);
return user;
}
}
- 自定义 url 权限元数据的数据源 FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource
package com.vinjcent.config.security.meta;
import com.vinjcent.pojo.Menu;
import com.vinjcent.pojo.Role;
import com.vinjcent.service.MenuService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.access.ConfigAttribute;
import org.springframework.security.access.SecurityConfig;
import org.springframework.security.web.FilterInvocation;
import org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.AntPathMatcher;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 自定义 url 权限元数据的数据源
*/
@Component
public class DivSecurityMetaSource implements FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource {
private final MenuService menuService;
@Autowired
public DivSecurityMetaSource(MenuService menuService) {
this.menuService = menuService;
}
// 用于路径对比
AntPathMatcher antPathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
/**
* 自定义动态资源权限数据源信息
* @param object
* @return
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
*/
@Override
public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAttributes(Object object) throws IllegalArgumentException {
// 1.获取请求资源路径
String requestURI = ((FilterInvocation) object).getRequest().getRequestURI();
// 2.获取数据库中所有菜单
List<Menu> menus = menuService.getAllMenus();
// 3.循环对比数据库中的路径与当前uri是否匹配
for (Menu menu : menus) {
// 如果匹配成功
if (antPathMatcher.match(menu.getPattern(), requestURI)) {
// 转链表为数组
String[] roles = menu.getRoles().stream().map(Role::getName).toArray(String[]::new);
// 返回角色集合
return SecurityConfig.createList(roles);
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAllConfigAttributes() {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) {
return FilterInvocation.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz);
}
}
- 自定义 security 配置类 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
package com.vinjcent.config.security;
import com.vinjcent.config.security.meta.DivSecurityMetaSource;
import com.vinjcent.config.security.service.DivUserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.ObjectPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configurers.UrlAuthorizationConfigurer;
import org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.FilterSecurityInterceptor;
/**
* 自定义 spring security 配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class WebSecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
// 注入认证数据源
private final DivUserDetailsService userDetailsService;
// 注入url元数据数据源
private final DivSecurityMetaSource securityMetaSource;
@Autowired
public WebSecurityConfiguration(DivUserDetailsService userDetailsService, DivSecurityMetaSource securityMetaSource) {
this.userDetailsService = userDetailsService;
this.securityMetaSource = securityMetaSource;
}
// 替换认证数据源
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService);
}
// 暴露AuthenticationManager,使得这个bean能在组件中进行注入
@Override
@Bean
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManager() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManager();
}
// http 拦截
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// 1.获取工厂对象
ApplicationContext context = http.getSharedObject(ApplicationContext.class);
// 2.设置自定义 url 权限元数据
http.apply(new UrlAuthorizationConfigurer<>(context))
.withObjectPostProcessor(new ObjectPostProcessor<FilterSecurityInterceptor>() {
@Override
public <O extends FilterSecurityInterceptor> O postProcess(O object) {
// 配置元数据信息
object.setSecurityMetadataSource(securityMetaSource);
// 是否拒绝公共资源的访问,设置为true,不允许访问公共资源
object.setRejectPublicInvocations(false);
return object;
}
});
// 开启表单验证
http.formLogin();
// 关闭csrf
http.csrf().disable();
}
}
- 测试对应接口
总结
用户对应角色具有指定的权限访问,admin 用户具有 ADMIN、USER、GUEST 角色,而 user 用户具有 USER、GUEST 角色,vinjcent 具有 GUEST 角色。发现/hello允许任何角色进行访问,/admin/hello只允许 ADMIN 角色进行访问;/user/hello 既可以是 USER 角色,又可以是 ADMIN 角色;而/guest/hello只允许 ADMIN、USER、GUEST 角色访问
角色可访问的资源
/**
* 资源 可访问的角色
* /admin/** ROLE_ADMIN
* /user/** ROLE_ADMIN ROLE_USER
* /guest/** ROLE_ADMIN ROLE_USER ROLE_GUEST
*/