目录
- 题目描述
- 思路及实现
- 方式一:递归
- 思路
- 代码实现
- Java版本
- C语言版本
- Python3版本
- Go语言版本
- 复杂度分析
- 方式二:广度优先搜索(BFS)
- 思路
- 代码实现
- Java版本
- C语言版本
- Python3版本
- 复杂度分析
- 总结
- 相似题目
- 标签(题目类型):树、深度优先搜索(DFS)、广度优先搜索(BFS)、递归、迭代
题目描述
给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
示例 1:
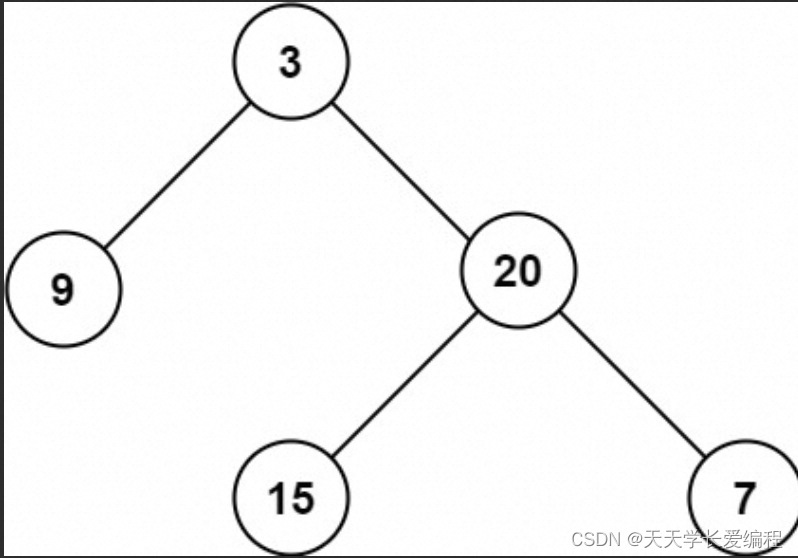
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:3
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2]
输出:2
提示:
树中节点的数量在 [0, 104] 区间内。
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
原题:LeetCode 104
思路及实现
方式一:递归
思路
对于递归方式,我们可以将问题分解为两个子问题:左子树的最大深度和右子树的最大深度。然后,二叉树的最大深度即为左右子树最大深度中的较大值加1(根节点的深度)。递归的终止条件是当节点为空时,返回深度0。
代码实现
Java版本
// Definition for a binary tree node.
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
public class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
}
说明:递归函数
maxDepth接收一个二叉树节点作为参数,如果节点为空,则返回深度0;否则分别计算左子树和右子树的最大深度,并返回二者中的较大值加1。
C语言版本
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Definition for a binary tree node.
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
};
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root->left);
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root->right);
return leftDepth > rightDepth ? leftDepth + 1 : rightDepth + 1;
}
// Helper function to create a new tree node
struct TreeNode* newNode(int data) {
struct TreeNode* node = (struct TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
node->val = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return(node);
}
// ... (driver code and main function)
说明:C语言版本的实现与Java版本类似,但需要注意内存分配和释放,以及节点创建函数
newNode的使用。
Python3版本
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
leftDepth = self.maxDepth(root.left)
rightDepth = self.maxDepth(root.right)
return max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1
说明:Python版本使用了类定义来构建二叉树节点,递归函数
maxDepth的实现与Java版本相同。
Go语言版本
package main
import "fmt"
// Definition for a binary tree node.
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
leftDepth := maxDepth(root.Left)
rightDepth := maxDepth(root.Right)
if leftDepth > rightDepth {
return leftDepth + 1
}
return rightDepth + 1
}
func main() {
// ... (driver code and main function)
}
说明:Go语言版本的实现也类似,只是语法稍有不同。
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中n为二叉树的节点数。因为每个节点只被访问一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(h),其中h为二叉树的高度。递归需要用到栈空间,最坏情况下,树完全不平衡,递归深度达到树的高度,因此空间复杂度为O(h)。但在平均情况下,由于二叉树的性质,递归调用的深度会相对较小,所以实际空间复杂度可能低于O(h)。
方式二:广度优先搜索(BFS)
思路
广度优先搜索(BFS)是另一种求解二叉树最大深度的方法。我们可以使用队列来进行层次遍历,每一层的节点数代表当前层的深度。当队列为空时,遍历结束,此时的深度即为二叉树的最大深度。
代码实现
Java版本
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int levelSize = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
depth++;
}
return depth;
}
}
说明:这里使用
LinkedList实现Queue接口,通过循环来逐层遍历二叉树。每遍历完一层,深度加1,直到队列为空。
C语言版本
在C语言中,没有内建的队列结构,所以我们需要手动实现一个队列。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_QUEUE_SIZE 100
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
};
struct QueueNode {
struct TreeNode *data;
struct QueueNode *next;
};
struct Queue {
struct QueueNode *front;
struct QueueNode *rear;
};
void enqueue(struct Queue *q, struct TreeNode *node) {
struct QueueNode *newNode = (struct QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct QueueNode));
newNode->data = node;
newNode->next = NULL;
if (q->rear == NULL) {
q->front = newNode;
q->rear = newNode;
} else {
q->rear->next = newNode;
q->rear = newNode;
}
}
struct TreeNode *dequeue(struct Queue *q) {
if (q->front == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
struct TreeNode *node = q->front->data;
struct QueueNode *temp = q->front;
q->front = q->front->next;
if (q->front == NULL) {
q->rear = NULL;
}
free(temp);
return node;
}
int isQueueEmpty(struct Queue *q) {
return q->front == NULL;
}
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
struct Queue q = {{NULL, NULL}};
enqueue(&q, root);
int depth = 0;
while (!isQueueEmpty(&q)) {
int levelSize = 0;
struct TreeNode *node;
// Count the number of nodes in current level
while ((node = dequeue(&q)) != NULL) {
levelSize++;
if (node->left) {
enqueue(&q, node->left);
}
if (node->right) {
enqueue(&q, node->right);
}
}
// All nodes of the current level are processed, move to the next level
depth++;
}
return depth;
}
// ... (driver code and main function)
说明:在C语言中,我们需要自己实现队列的数据结构,包括入队、出队和判断队列是否为空的操作。
Python3版本
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
queue = deque([root])
depth = 0
while queue:
level_size = len(queue)
for _ in range(level_size):
node = queue.popleft()
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
depth += 1
return depth
说明:在Python中,我们可以使用
collections.deque来实现队列,它提供了双端队列的功能,非常适合用于广度优先搜索。
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中n是二叉树的节点数。每个节点只会被访问和入队出队一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(n),在最坏情况下,当树完全不平衡时,所有节点都会被同时存储在队列中,因此需要额外的空间与节点数成正比。然而,在平均情况下,由于二叉树的性质,空间复杂度通常会低于O(n)。
总结:无论是递归的深度优先搜索还是非递归的广度优先搜索,它们都能有效地解决求二叉树最大深度的问题。深度优先搜索简洁直观,而广度优先搜索则更适合于层次结构的处理。在实际应用中,可以根据问题的特点和具体需求选择合适的方法。
总结
| 方式 | 优点 | 缺点 | 时间复杂度 | 空间复杂度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 递归深度优先搜索 | 代码直观,易于理解 | 递归可能导致栈溢出,对于深层树效率较低 | O(n) | O(h) |
| 非递归深度优先搜索 | 避免递归栈溢出,适用于深层树 | 需要手动维护栈,代码相对复杂 | O(n) | O(h) |
| 广度优先搜索 | 层次遍历,易于实现 | 需要额外的队列空间,空间复杂度较高 | O(n) | O(n) |
相似题目
| 相似题目 | 难度 | 链接 |
|---|---|---|
| leetcode 104 二叉树的最大深度 | 简单 | 力扣:力扣-104 |
| leetcode 110 平衡二叉树 | 简单 | 力扣:力扣-110 |
| leetcode 111 二叉树的最小深度 | 简单 | 力扣:力扣-111 |
| leetcode 543 二叉树的直径 | 简单 | 力扣:力扣-543 |
| leetcode 1654 到最近的人的最大距离 | 中等 | 力扣:力扣-1654 |
这些题目都涉及到二叉树的遍历和深度的概念,通过解决这些题目,可以加深对二叉树遍历和深度相关问题的理解和应用能力。



![[C++基础学习]----01-C++数据类型详解](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/2184a99373804f359de6397e1cfe71d1.png)