EquiBind模型源码分析
使用提供的模型权重来预测你自己的蛋白质配体对的结合结构
- 第 1 步:你需要什么作为输入
mol2或.sdf或.pdbqt或.pdb格式的配体文件,其名称包含字符串配体(配体文件应包含所有氢)。
.pdb格式的受体文件,其名称包含字符串protein。我们运行reduce训练我们的蛋白质。也许你也想运行自己的蛋白质。
Reduce- 在 PDB 文件中添加和修正氢的工具
加载数据
读取配体信息
读取配体sdf文件信息
lig = read_molecule(os.path.join(args.inference_path, name, lig_name), sanitize=True)#
读取受体信息
主要包括全原子的三维坐标, CA, N, C主干上原子的三维坐标
## 读取受体的信息
rec, rec_coords, c_alpha_coords, n_coords, c_coords = get_receptor_inference(rec_path)
Equibind数据处理
预处理受体信息
rec: 受体对象
rec_coords 受体全原子坐标
c_alpha_coords CA坐标
n_coords N坐标
c_coords C坐标
use_rec_atoms是否使用残基原子
rec_graph_radius
surface_max_neighbors 最大邻节点个数
surface_graph_cutoff 距离cut off 多少埃
surface_mesh_cutoff
c_alpha_max_neighbors CA最大邻节点
rec_graph = get_rec_graph(rec, rec_coords, c_alpha_coords, n_coords, c_coords,
use_rec_atoms=dp['use_rec_atoms'], rec_radius=dp['rec_graph_radius'], #
surface_max_neighbors=dp['surface_max_neighbors'],
surface_graph_cutoff=dp['surface_graph_cutoff'],
surface_mesh_cutoff=dp['surface_mesh_cutoff'],
c_alpha_max_neighbors=dp['c_alpha_max_neighbors'])
将蛋白表示为结构
def get_calpha_graph(rec, c_alpha_coords, n_coords, c_coords, cutoff=20, max_neighbor=None):
################## Extract 3D coordinates and n_i,u_i,v_i vectors of representative residues 提取代表性残基的 3D 坐标和 n_i,u_i,v_i 向量################
residue_representatives_loc_list = []
n_i_list = []
u_i_list = []
v_i_list = []
for i, residue in enumerate(rec.get_residues()):
n_coord = n_coords[i] # N原子坐标
c_alpha_coord = c_alpha_coords[i] # CA原子坐标
c_coord = c_coords[i] # C原子坐标
u_i = (n_coord - c_alpha_coord) / np.linalg.norm(n_coord - c_alpha_coord) # N-CA 向量
t_i = (c_coord - c_alpha_coord) / np.linalg.norm(c_coord - c_alpha_coord) # C-CA 向量
n_i = np.cross(u_i, t_i) / np.linalg.norm(np.cross(u_i, t_i)) # N-CA 与 C-CA 叉乘法向量
v_i = np.cross(n_i, u_i) # N-CA 与 C-CA 叉乘法向量
assert (math.fabs(
np.linalg.norm(v_i) - 1.) < 1e-5), "protein utils protein_to_graph_dips, v_i norm larger than 1"
n_i_list.append(n_i)
u_i_list.append(u_i)
v_i_list.append(v_i)
residue_representatives_loc_list.append(c_alpha_coord)
residue_representatives_loc_feat = np.stack(residue_representatives_loc_list, axis=0) # (N_res, 3) CA原子坐标
n_i_feat = np.stack(n_i_list, axis=0)
u_i_feat = np.stack(u_i_list, axis=0)
v_i_feat = np.stack(v_i_list, axis=0)
num_residues = len(c_alpha_coords)
if num_residues <= 1:
raise ValueError(f"rec contains only 1 residue!")
################### Build the k-NN graph ##############################
assert num_residues == residue_representatives_loc_feat.shape[0]
assert residue_representatives_loc_feat.shape[1] == 3
distances = spa.distance.cdist(c_alpha_coords, c_alpha_coords) #计算距离, 默认欧几里得距离
src_list = []
dst_list = []
dist_list = []
mean_norm_list = []
for i in range(num_residues):
dst = list(np.where(distances[i, :] < cutoff)[0]) # 距离小于30的
dst.remove(i)
if max_neighbor != None and len(dst) > max_neighbor: # 最大的邻节点过滤,
dst = list(np.argsort(distances[i, :]))[1: max_neighbor + 1]
if len(dst) == 0:
dst = list(np.argsort(distances[i, :]))[1:2] # choose second because first is i itself
log(
f'The c_alpha_cutoff {cutoff} was too small for one c_alpha such that it had no neighbors. So we connected it to the closest other c_alpha')
assert i not in dst
src = [i] * len(dst)
src_list.extend(src)#
dst_list.extend(dst)#
valid_dist = list(distances[i, dst])
dist_list.extend(valid_dist)
valid_dist_np = distances[i, dst]
sigma = np.array([1., 2., 5., 10., 30.]).reshape((-1, 1))#
weights = softmax(- valid_dist_np.reshape((1, -1)) ** 2 / sigma, axis=1) # (sigma_num, neigh_num)
assert weights[0].sum() > 1 - 1e-2 and weights[0].sum() < 1.01
diff_vecs = residue_representatives_loc_feat[src, :] - residue_representatives_loc_feat[
dst, :] # (neigh_num, 3)起始就是向量
mean_vec = weights.dot(diff_vecs) # (sigma_num, neigh_num) @ (neigh_num, 3)->(sigma_num, 3)
denominator = weights.dot(np.linalg.norm(diff_vecs, axis=1)) # (sigma_num,)
mean_vec_ratio_norm = np.linalg.norm(mean_vec, axis=1) / denominator # (sigma_num,)
mean_norm_list.append(mean_vec_ratio_norm)
assert len(src_list) == len(dst_list)
assert len(dist_list) == len(dst_list)
graph = dgl.graph((torch.tensor(src_list), torch.tensor(dst_list)), num_nodes=num_residues, idtype=torch.int32)
graph.ndata['feat'] = rec_residue_featurizer(rec)
graph.edata['feat'] = distance_featurizer(dist_list, divisor=4) # avg distance = 7. So divisor = (4/7)*7 = 4
# Loop over all edges of the graph and build the various p_ij, q_ij, k_ij, t_ij pairs 在图的所有边上循环并构建各种p_ij、q_ij、k_ij、t_ij对
edge_feat_ori_list = []
for i in range(len(dist_list)):
src = src_list[i]
dst = dst_list[i]
# place n_i, u_i, v_i as lines in a 3x3 basis matrix
basis_matrix = np.stack((n_i_feat[dst, :], u_i_feat[dst, :], v_i_feat[dst, :]), axis=0)
p_ij = np.matmul(basis_matrix,
residue_representatives_loc_feat[src, :] - residue_representatives_loc_feat[
dst, :])
q_ij = np.matmul(basis_matrix, n_i_feat[src, :]) # shape (3,)
k_ij = np.matmul(basis_matrix, u_i_feat[src, :])
t_ij = np.matmul(basis_matrix, v_i_feat[src, :])
s_ij = np.concatenate((p_ij, q_ij, k_ij, t_ij), axis=0) # shape (12,)
edge_feat_ori_list.append(s_ij)
edge_feat_ori_feat = np.stack(edge_feat_ori_list, axis=0) # shape (num_edges, 4* 3)
edge_feat_ori_feat = torch.from_numpy(edge_feat_ori_feat.astype(np.float32))
graph.edata['feat'] = torch.cat([graph.edata['feat'], edge_feat_ori_feat], axis=1) # (num_edges, 27)
residue_representatives_loc_feat = torch.from_numpy(residue_representatives_loc_feat.astype(np.float32))
graph.ndata['x'] = residue_representatives_loc_feat
graph.ndata['mu_r_norm'] = torch.from_numpy(np.array(mean_norm_list).astype(np.float32))
return graph
重点–> 非常重要的处理细节
- 构建局部坐标

u i u_i ui是 α − C \alpha-C α−C原子指向N原子的向量; t i t_i ti是 α − C \alpha-C α−C原子指向C原子的向量;
n i n_i ni是垂直于 u i u_i ui和 t i t_i ti的向量; v i v_i vi是垂直于 n i n_i ni和 u i u_i ui的向量
那么 n i n_i ni、 v i v_i vi和 u i u_i ui两两垂直,构成了一个局部坐标系( u i , v i , n i u_i,v_i,n_i ui,vi,ni)
n_coord = n_coords[i] # N原子坐标
c_alpha_coord = c_alpha_coords[i] # CA原子坐标
c_coord = c_coords[i] # C原子坐标
u_i = (n_coord - c_alpha_coord) / np.linalg.norm(n_coord - c_alpha_coord) # N-CA 向量
t_i = (c_coord - c_alpha_coord) / np.linalg.norm(c_coord - c_alpha_coord) # C-CA 向量
n_i = np.cross(u_i, t_i) / np.linalg.norm(np.cross(u_i, t_i)) # N-CA 与 C-CA 叉乘法向量
v_i = np.cross(n_i, u_i) # N-CA 与 C-CA 叉乘法向量
- 构建KNN图表示
受体图 G ′ = ( V ′ , E ′ ) G' = (V', E') G′=(V′,E′)以残基作为节点,它们的 3D 坐标 X ′ ∈ R 3 × m X' \in R^{3 \times m} X′∈R3×m 由 α-碳位置给出。图中的每个节点都以小于 30 A ˚ 30Å 30A˚的距离连接到最近的 10 个其他节点。受体节点特征 F ′ ∈ R d × m F' \in R^{d \times m} F′∈Rd×m。
for i in range(num_residues):
dst = list(np.where(distances[i, :] < cutoff)[0]) # CA与CA距离小于30的
dst.remove(i)# 移除自己和自己本身
if max_neighbor != None and len(dst) > max_neighbor: # 最大的邻节点过滤,
dst = list(np.argsort(distances[i, :]))[1: max_neighbor + 1]
if len(dst) == 0:
dst = list(np.argsort(distances[i, :]))[1:2] # choose second because first is i itself
log(
f'The c_alpha_cutoff {cutoff} was too small for one c_alpha such that it had no neighbors. So we connected it to the closest other c_alpha')
assert i not in dst
src = [i] * len(dst)# 源节点
src_list.extend(src)#
dst_list.extend(dst)#目标节点
valid_dist = list(distances[i, dst])
dist_list.extend(valid_dist)
valid_dist_np = distances[i, dst]
sigma = np.array([1., 2., 5., 10., 30.]).reshape((-1, 1))#
weights = softmax(- valid_dist_np.reshape((1, -1)) ** 2 / sigma, axis=1) # (sigma_num, neigh_num), 计算目标节点的权重
assert weights[0].sum() > 1 - 1e-2 and weights[0].sum() < 1.01
diff_vecs = residue_representatives_loc_feat[src, :] - residue_representatives_loc_feat[
dst, :] # (neigh_num, 3)起始就是向量
mean_vec = weights.dot(diff_vecs) # (sigma_num, neigh_num) @ (neigh_num, 3)->(sigma_num, 3)
denominator = weights.dot(np.linalg.norm(diff_vecs, axis=1)) # (sigma_num,) 分母
mean_vec_ratio_norm = np.linalg.norm(mean_vec, axis=1) / denominator # (sigma_num,) 旋转均值
mean_norm_list.append(mean_vec_ratio_norm)
assert len(src_list) == len(dst_list)
assert len(dist_list) == len(dst_list)
graph = dgl.graph((torch.tensor(src_list), torch.tensor(dst_list)), num_nodes=num_residues, idtype=torch.int32)
同时使用了Surface Aware Node Features

表面接触建模对蛋白质对接很重要。这里设计了一种新的表面特征类型,将靠近蛋白质表面的残基与内部的残基区分开来。如上图所示,蛋白质内部的残基(左)被来自各个方向的矢量所包围,这些矢量相互抵消,而靠近表面的残基(右)只在一个较窄的锥体中有邻居,其孔径取决于表面的局部曲率。

通过上式得到5个表面感知节点特征,
λ
∈
{
1.
,
2.
,
5.
,
10.
,
30.
}
\lambda \in \{1.,2.,5.,10.,30.\}
λ∈{1.,2.,5.,10.,30.}。
sigma = np.array([1., 2., 5., 10., 30.]).reshape((-1, 1))#
weights = softmax(- valid_dist_np.reshape((1, -1)) ** 2 / sigma, axis=1) # (sigma_num, neigh_num), 计算目标节点的权重
assert weights[0].sum() > 1 - 1e-2 and weights[0].sum() < 1.01
diff_vecs = residue_representatives_loc_feat[src, :] - residue_representatives_loc_feat[
dst, :] # (neigh_num, 3)起始就是向量
mean_vec = weights.dot(diff_vecs) # (sigma_num, neigh_num) @ (neigh_num, 3)->(sigma_num, 3)
denominator = weights.dot(np.linalg.norm(diff_vecs, axis=1)) # (sigma_num,) 分母
mean_vec_ratio_norm = np.linalg.norm(mean_vec, axis=1) / denominator # (sigma_num,) 每个残基旋转均值
mean_norm_list.append(mean_vec_ratio_norm)
- 残基图上特征
节点特征使用残基类型、sasa(表面溶剂接触面积)和bfactor。
def rec_residue_featurizer(rec):
feature_list = []
sr.compute(rec, level="R")# 计算实体的表面辅助功能表面积。
for residue in rec.get_residues():
sasa = residue.sasa
for atom in residue:
if atom.name == 'CA':
bfactor = atom.bfactor
assert not np.isinf(bfactor)
assert not np.isnan(bfactor)
assert not np.isinf(sasa)
assert not np.isnan(sasa)
feature_list.append([safe_index(allowable_features['possible_amino_acids'], residue.get_resname()),
sasa,
bfactor])
return torch.tensor(feature_list, dtype=torch.float32) # (N_res, 1)
边特征使用具有 15 个不同方差的高斯基函数编码的原子间距离。
- Distance-Based Edge Features
距离也带有信息,这里使用距离的径向基函数作为边缘特征。

其中 R R R和缩放参数 { σ r } 1 ≤ r ≤ R \{\sigma_r\}_{1\leq r \leq R} {σr}1≤r≤R是超参,论文中使用的缩放参数为 { 1. 5 x ∣ x = 0 , 1 , 2 , . . . , 14 } \{1.5^x|x=0,1,2,...,14\} {1.5x∣x=0,1,2,...,14},因此,对于每条边有15个基于距离的边特征。
def distance_featurizer(dist_list, divisor) -> torch.Tensor: # 您希望使用一个约数,该约数接近要编码的平均距离的4/7倍
# you want to use a divisor that is close to 4/7 times the average distance that you want to encode
length_scale_list = [1.5 ** x for x in range(15)]
center_list = [0. for _ in range(15)]
num_edge = len(dist_list)
dist_list = np.array(dist_list)
transformed_dist = [np.exp(- ((dist_list / divisor) ** 2) / float(length_scale))
for length_scale, center in zip(length_scale_list, center_list)]
transformed_dist = np.array(transformed_dist).T
transformed_dist = transformed_dist.reshape((num_edge, -1))
return torch.from_numpy(transformed_dist.astype(np.float32))
边特征还是用局部骨架方向编码
- Relative Position Edge Features
边特征 p j → i p_{j \to i} pj→i,代表j相对于 i i i的相对位置

- Relative Orientation Edge Features
边缘特征 q j → i q_{j \to i} qj→i、 k j → i k_{j \to i} kj→i和 t j → i t_{j \to i} tj→i,表示 j j j相对于 i i i的相对方向。
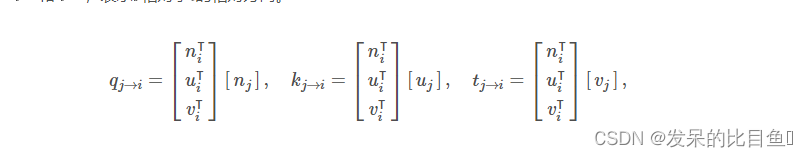
edge_feat_ori_list = []
for i in range(len(dist_list)):
src = src_list[i]
dst = dst_list[i]
# place n_i, u_i, v_i as lines in a 3x3 basis matrix
basis_matrix = np.stack((n_i_feat[dst, :], u_i_feat[dst, :], v_i_feat[dst, :]), axis=0)
p_ij = np.matmul(basis_matrix,
residue_representatives_loc_feat[src, :] - residue_representatives_loc_feat[
dst, :])
q_ij = np.matmul(basis_matrix, n_i_feat[src, :]) # shape (3,)
k_ij = np.matmul(basis_matrix, u_i_feat[src, :])
t_ij = np.matmul(basis_matrix, v_i_feat[src, :])
s_ij = np.concatenate((p_ij, q_ij, k_ij, t_ij), axis=0) # shape (12,)
edge_feat_ori_list.append(s_ij)
edge_feat_ori_feat = np.stack(edge_feat_ori_list, axis=0) # shape (num_edges, 4* 3)
edge_feat_ori_feat = torch.from_numpy(edge_feat_ori_feat.astype(np.float32))
graph.edata['feat'] = torch.cat([graph.edata['feat'], edge_feat_ori_feat], axis=1) # (num_edges, 27)
预处理配体信息
在配体中,边缘具有以与受体相同的方式编码的特征。这里不具体细讲
原子具有以下特征:原子数;手性;度;形式电荷;隐含价;连接氢的数量;自由基电子的数量;杂化类型;是否在芳环中;它有多少个环;最后,6 个特征表示它是否在大小为 3、4、5、6、7 或 8 的环中。
def get_lig_graph_revised(mol, name, radius=20, max_neighbors=None, use_rdkit_coords=False):
conf = mol.GetConformer()#前提,导入的原子必须带有坐标信息
true_lig_coords = conf.GetPositions()
if use_rdkit_coords:
try:
rdkit_coords = get_rdkit_coords(mol).numpy()
R, t = rigid_transform_Kabsch_3D(rdkit_coords.T, true_lig_coords.T)
lig_coords = ((R @ (rdkit_coords).T).T + t.squeeze())
log('kabsch RMSD between rdkit ligand and true ligand is ', np.sqrt(np.sum((lig_coords - true_lig_coords) ** 2, axis=1).mean()).item())
except Exception as e:
lig_coords = true_lig_coords
with open('temp_create_dataset_rdkit_timesplit_no_lig_or_rec_overlap_train.log', 'a') as f:
f.write('Generating RDKit conformer failed for \n')
f.write(name)
f.write('\n')
f.write(str(e))
f.write('\n')
f.flush()
print('Generating RDKit conformer failed for ')
print(name)
print(str(e))
else:
lig_coords = true_lig_coords
num_nodes = lig_coords.shape[0]
assert lig_coords.shape[1] == 3
distance = spa.distance.cdist(lig_coords, lig_coords)
src_list = []
dst_list = []
dist_list = []
mean_norm_list = []
for i in range(num_nodes):
dst = list(np.where(distance[i, :] < radius)[0])
dst.remove(i)
if max_neighbors != None and len(dst) > max_neighbors:
dst = list(np.argsort(distance[i, :]))[1: max_neighbors + 1] # closest would be self loop
if len(dst) == 0:
dst = list(np.argsort(distance[i, :]))[1:2] # closest would be the index i itself > self loop
log(
f'The lig_radius {radius} was too small for one lig atom such that it had no neighbors. So we connected {i} to the closest other lig atom {dst}')
assert i not in dst
assert dst != []
src = [i] * len(dst)
src_list.extend(src)
dst_list.extend(dst)
valid_dist = list(distance[i, dst])
dist_list.extend(valid_dist)
valid_dist_np = distance[i, dst]
sigma = np.array([1., 2., 5., 10., 30.]).reshape((-1, 1))
weights = softmax(- valid_dist_np.reshape((1, -1)) ** 2 / sigma, axis=1) # (sigma_num, neigh_num)
assert weights[0].sum() > 1 - 1e-2 and weights[0].sum() < 1.01
diff_vecs = lig_coords[src, :] - lig_coords[dst, :] # (neigh_num, 3)
mean_vec = weights.dot(diff_vecs) # (sigma_num, 3)
denominator = weights.dot(np.linalg.norm(diff_vecs, axis=1)) # (sigma_num,)
mean_vec_ratio_norm = np.linalg.norm(mean_vec, axis=1) / denominator # (sigma_num,)
mean_norm_list.append(mean_vec_ratio_norm)
assert len(src_list) == len(dst_list)
assert len(dist_list) == len(dst_list)
graph = dgl.graph((torch.tensor(src_list), torch.tensor(dst_list)), num_nodes=num_nodes, idtype=torch.int32)
graph.ndata['feat'] = lig_atom_featurizer(mol)
graph.edata['feat'] = distance_featurizer(dist_list, 0.75) # avg distance = 1.3 So divisor = (4/7)*1.3 = ~0.75
graph.ndata['x'] = torch.from_numpy(np.array(true_lig_coords).astype(np.float32))
graph.ndata['mu_r_norm'] = torch.from_numpy(np.array(mean_norm_list).astype(np.float32))
if use_rdkit_coords:
graph.ndata['new_x'] = torch.from_numpy(np.array(lig_coords).astype(np.float32))
return graph
节点特征
def lig_atom_featurizer(mol): # 在所有PDB结合中,它们是93个分子的Nan。我们在这种情况下打0。
ComputeGasteigerCharges(mol) # they are Nan for 93 molecules in all of PDBbind. We put a 0 in that case. 计算出的partial charge存储在每个原子的属性中
ringinfo = mol.GetRingInfo()
atom_features_list = []
for idx, atom in enumerate(mol.GetAtoms()):
g_charge = atom.GetDoubleProp('_GasteigerCharge') # 通过GetDoubleProp(浮点数)或GetProp(字符串)来获取。
atom_features_list.append([
safe_index(allowable_features['possible_atomic_num_list'], atom.GetAtomicNum()),
allowable_features['possible_chirality_list'].index(str(atom.GetChiralTag())),
safe_index(allowable_features['possible_degree_list'], atom.GetTotalDegree()),
safe_index(allowable_features['possible_formal_charge_list'], atom.GetFormalCharge()),
safe_index(allowable_features['possible_implicit_valence_list'], atom.GetImplicitValence()),
safe_index(allowable_features['possible_numH_list'], atom.GetTotalNumHs()),
safe_index(allowable_features['possible_number_radical_e_list'], atom.GetNumRadicalElectrons()),
safe_index(allowable_features['possible_hybridization_list'], str(atom.GetHybridization())),
allowable_features['possible_is_aromatic_list'].index(atom.GetIsAromatic()),
safe_index(allowable_features['possible_numring_list'], ringinfo.NumAtomRings(idx)),
allowable_features['possible_is_in_ring3_list'].index(ringinfo.IsAtomInRingOfSize(idx, 3)),
allowable_features['possible_is_in_ring4_list'].index(ringinfo.IsAtomInRingOfSize(idx, 4)),
allowable_features['possible_is_in_ring5_list'].index(ringinfo.IsAtomInRingOfSize(idx, 5)),
allowable_features['possible_is_in_ring6_list'].index(ringinfo.IsAtomInRingOfSize(idx, 6)),
allowable_features['possible_is_in_ring7_list'].index(ringinfo.IsAtomInRingOfSize(idx, 7)),
allowable_features['possible_is_in_ring8_list'].index(ringinfo.IsAtomInRingOfSize(idx, 8)),
g_charge if not np.isnan(g_charge) and not np.isinf(g_charge) else 0.
])
return torch.tensor(atom_features_list)
配体原子几何图
首先遍历分子原子,这些原子最为源节点, 然后找到两条跳内的邻居节点作为目标节点,边特征来自于节点间几何距离。
def get_geometry_graph(lig):
coords = lig.GetConformer().GetPositions()
edges_src = []
edges_dst = []
for i, atom in enumerate(lig.GetAtoms()):
src_idx = atom.GetIdx()
assert src_idx == i
one_hop_dsts = [neighbor for neighbor in list(atom.GetNeighbors())]
two_and_one_hop_idx = [neighbor.GetIdx() for neighbor in one_hop_dsts]
for one_hop_dst in one_hop_dsts:
for two_hop_dst in one_hop_dst.GetNeighbors():
two_and_one_hop_idx.append(two_hop_dst.GetIdx())
all_dst_idx = list(set(two_and_one_hop_idx))
if len(all_dst_idx) ==0: continue
all_dst_idx.remove(src_idx)
all_src_idx = [src_idx] *len(all_dst_idx)
edges_src.extend(all_src_idx)
edges_dst.extend(all_dst_idx)
graph = dgl.graph((torch.tensor(edges_src), torch.tensor(edges_dst)), num_nodes=lig.GetNumAtoms(), idtype=torch.long)
graph.edata['feat'] = torch.from_numpy(np.linalg.norm(coords[edges_src] - coords[edges_dst], axis=1).astype(np.float32))
return graph
Equibind模型
模型输入
- 配体图:
节点特征:原子相关化学特征、原子坐标(RDKIT重新生成)、Surface-aware node feature
边特征:距离特征 - 受体图:
节点特征:α-C原子坐标、surface-aware node feature、氨基酸名称位置索引,溶剂接触表面积,bfactor(晶体衍射因子)
边特征:距离、相对位置、相对角度特征 - 配体几何图:
边特征:距离(数据真实坐标计算得来)







![[数据结构复习]自用大纲](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c312aa0711b64f7c83fecdace5a2c978.png#pic_center)