文章目录
- 1. 前言
- 2. softirq 实现
- 2.1 softirq 初始化
- 2.1.1 注册各类 softirq 处理接口
- 2.1.2 创建 softirq 处理线程
- 2.2 softirq 的 触发 和 处理
- 2.1.1 softirq 触发
- 2.1.2 softirq 处理
- 2.1.2.1 在 中断上下文 处理 softirq
- 2.1.2.2 在 ksoftirqd 内核线程上下文 处理 softirq
- 3. softirq 之 tasklet
- 3.1 定义初始化 tasklet
- 3.2 使能调度 tasklet
- 3.3 执行 tasklet
- 4. softirq 同步
- 5. softirq 观测
- 6. softirq 的未来
1. 前言
2. softirq 实现
2.1 softirq 初始化
2.1.1 注册各类 softirq 处理接口
start_kernel() /* init/main.c */
...
sched_init(); /* kernel/sched/core.c */
...
init_sched_fair_class(); /* kernel/sched/fair.c */
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
open_softirq(SCHED_SOFTIRQ, run_rebalance_domains); /* 调度均衡处理 软中断 */
...
#endif
...
...
/* 注册 RCU 软中断 处理接口 */
rcu_init(); /* kernel/rcu/tree.c */
...
open_softirq(RCU_SOFTIRQ, rcu_process_callbacks);
...
...
/*
* 所有 CPU 的 软件 timer 管理数据初始化,
* 以及 软件 timer 软中断处理接口注册.
*/
init_timers(); /* kernel/time/timer.c */
init_timer_cpus();
/* 注册软件 timer 处理接口: 在 softirq 中处理 每个 CPU 上的 软件 timer */
open_softirq(TIMER_SOFTIRQ, run_timer_softirq);
...
/* tasklet 软中断 初始化 */
softirq_init(); /* kernel/softirq.c */
int cpu;
/* 初始每 CPU 的 tasklet, tasklet hi 队列为空 */
for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) {
per_cpu(tasklet_vec, cpu).tail =
&per_cpu(tasklet_vec, cpu).head;
per_cpu(tasklet_hi_vec, cpu).tail =
&per_cpu(tasklet_hi_vec, cpu).head;
}
/* 注册 taslet(TASKLET_SOFTIRQ), tasklet hi(HI_SOFTIRQ) 软中断 处理接口 */
open_softirq(TASKLET_SOFTIRQ, tasklet_action);
open_softirq(HI_SOFTIRQ, tasklet_hi_action);start_kernel()
...
rest_init();
/* 在 BOOT CPU 上启动初始化线程, 处理剩下的初始化工作 */
pid = kernel_thread(kernel_init, NULL, CLONE_FS);
/* 初始化线程入口 */
kernel_init()
kernel_init_freeable();
do_basic_setup();
do_initcalls();
do_initcall_level(level);
do_one_initcall(*fn);
/*
* block/blk-softirq.c, blk_softirq_init()
* lib/irq_poll.c, irq_poll_setup()
* net/core/dev.c, net_dev_init()
*/
fn()
blk_softirq_init() /* block/blk-softirq.c */
...
open_softirq(BLOCK_SOFTIRQ, blk_done_softirq);
...
irq_poll_setup() /* lib/irq_poll.c */
...
open_softirq(IRQ_POLL_SOFTIRQ, irq_poll_softirq);
...
net_dev_init() /* net/core/dev.c */
...
/* 注册 网络设备 收、发 软中断 处理接口 */
open_softirq(NET_TX_SOFTIRQ, net_tx_action);
open_softirq(NET_RX_SOFTIRQ, net_rx_action);
...从上面的代码分析中,我们看到了如下列表中、各类型软中断处理接口的注册:
/* include/linux/interrupt.h */
enum
{
HI_SOFTIRQ=0,
TIMER_SOFTIRQ,
NET_TX_SOFTIRQ,
NET_RX_SOFTIRQ,
BLOCK_SOFTIRQ,
IRQ_POLL_SOFTIRQ,
TASKLET_SOFTIRQ,
SCHED_SOFTIRQ,
HRTIMER_SOFTIRQ, /* Unused, but kept as tools rely on the
numbering. Sigh! */
RCU_SOFTIRQ, /* Preferable RCU should always be the last softirq */
NR_SOFTIRQS
};注册软中端处理接口的函数 open_softirq() 实现如下:
/* kernel/softirq.c */
static struct softirq_action softirq_vec[NR_SOFTIRQS] __cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
void open_softirq(int nr, void (*action)(struct softirq_action *))
{
softirq_vec[nr].action = action;
}2.1.2 创建 softirq 处理线程
open_softirq() 注册的各类软中断处理接口,可能运行于两种上下文:
1. 中断上下文,软中断处理接口在中断处理过程退出时被 irq_exit() 调用。
2. 每 CPU 的软中断线程 ksoftirqd 上下文。本小节描述软中断接口运行的第2种上下文建立的过程,即 每 CPU 的软中断线程 ksoftirqd 的建立过程。ksoftirqd 的建立,是在内核初始化线程中完成:
kernel_init()
kernel_init_freeable();
do_pre_smp_initcalls();
for (fn = __initcall_start; fn < __initcall0_start; fn++)
do_one_initcall(*fn);
/* 调用 early_initcall(spawn_ksoftirqd); */
spawn_ksoftirqd() /* kernel/softirq.c */static struct smp_hotplug_thread softirq_threads = {
.store = &ksoftirqd,
.thread_should_run = ksoftirqd_should_run,
.thread_fn = run_ksoftirqd,
.thread_comm = "ksoftirqd/%u",
};
static __init int spawn_ksoftirqd(void)
{
...
/* 注册每 CPU 软中断线程 ksoftirqd */
BUG_ON(smpboot_register_percpu_thread(&softirq_threads));
return 0;
}上面的代码,为每个 CPU 创建了一个名为 ksoftirqd 的内核线程,内核线程的入口函数为 run_ksoftirqd() 。我们可以用 ps 命令观察到它们:
# ps -ef | grep ksoftirqd
10 root [ksoftirqd/0]
16 root [ksoftirqd/1]
21 root [ksoftirqd/2]
26 root [ksoftirqd/3]我们看到,在这个带 4 核 CPU 的硬件上,Linux 内核创建了 4 个 ksoftirqd 内核线程。
2.2 softirq 的 触发 和 处理
2.1.1 softirq 触发
Linux 系统提供下列接口 抛出 或 生成 softirq:
/* include/linux/interrupt.h */
extern void raise_softirq_irqoff(unsigned int nr);
extern void raise_softirq(unsigned int nr);
extern void __raise_softirq_irqoff(unsigned int nr);来看下它们的实现:
/* kernel/softirq.c */
#ifndef __ARCH_IRQ_STAT
irq_cpustat_t irq_stat[NR_CPUS] ____cacheline_aligned; /* 每 CPU 的 softirq 挂起状态 */
EXPORT_SYMBOL(irq_stat);
#endif
void raise_softirq(unsigned int nr)
{
unsigned long flags;
/* ARMv7: 读取 CPSR 寄存器的值到 @flags, 同时关闭 CPU IRQ 中断 */
local_irq_save(flags);
raise_softirq_irqoff(nr);
/* ARMv7: CPSR = flags */
local_irq_restore(flags);
}
/*
* This function must run with irqs disabled!
*/
inline void raise_softirq_irqoff(unsigned int nr)
{
__raise_softirq_irqoff(nr);
/*
* If we're in an interrupt or softirq, we're done
* (this also catches softirq-disabled code). We will
* actually run the softirq once we return from
* the irq or softirq.
*
* Otherwise we wake up ksoftirqd to make sure we
* schedule the softirq soon.
*/
if (!in_interrupt())
wakeup_softirqd(); /* 唤醒 当前 CPU 的 ksoftirq 线程, 处理 softirq */
}
void __raise_softirq_irqoff(unsigned int nr)
{
trace_softirq_raise(nr);
or_softirq_pending(1UL << nr); /* 标记 [当前 CPU] 有挂起的、@x 类型的 softirq */
}
/* include/linux/interrupt.h */
#ifndef __ARCH_SET_SOFTIRQ_PENDING
#define set_softirq_pending(x) (local_softirq_pending() = (x))
#define or_softirq_pending(x) (local_softirq_pending() |= (x))
#endif
/* include/linux/irq_cpustat.h */
#ifndef __ARCH_IRQ_STAT
extern irq_cpustat_t irq_stat[]; /* defined in asm/hardirq.h */
#define __IRQ_STAT(cpu, member) (irq_stat[cpu].member)
#endif
#define local_softirq_pending() \
__IRQ_STAT(smp_processor_id(), __softirq_pending)2.1.2 softirq 处理
/* arch/arm/kernel/entry-armv.S */
/*
* 中断向量表。
* 这里是第1级,每项是各模式下第2级向量表的指针,
* 即中断向量表是按 vector[8][16] 的形式组织。
* 第1级是各中断类型的入口: reset, undef, swi, ...
* 第2级是各中断类型下,各CPU模式的入口: usr, svc, irq, fiq, ...
*/
.section .vectors, "ax", %progbits
.L__vectors_start:
W(b) vector_rst /* 复位 */
W(b) vector_und /* 未定义指令异常向量表指针: vector_stub und, UND_MODE */
...
/* IRQ 中断 各 CPU 模式处理接口 组成 */
W(b) vector_irq /* IRQ: vector_stub irq, IRQ_MODE, 4 */
...
/*
* Interrupt dispatcher
*/
/* IRQ 中断 各 CPU 模式处理接口 组成 */
vector_stub irq, IRQ_MODE, 4 /* vector_irq */
// CPU User 模式 IRQ 中断处理入口
.long __irq_usr @ 0 (USR_26 / USR_32)
.long __irq_invalid @ 1 (FIQ_26 / FIQ_32)
.long __irq_invalid @ 2 (IRQ_26 / IRQ_32)
// CPU SVC 模式 IRQ 中断处理入口
.long __irq_svc @ 3 (SVC_26 / SVC_32)
......
.align 5
__irq_svc: // CPU SVC 模式 IRQ 中断处理入口 (中断发生在 内核态)
...
irq_handler
...
.align 5
__irq_usr: // CPU User 模式 IRQ 中断处理入口 (中断发生在 用户态)
...
irq_handler
...我们看到,不管是内核态,还是用户态,中断处理都调用 irq_handler,看它的定义:
/*
* Interrupt handling.
*/
.macro irq_handler
#ifdef CONFIG_MULTI_IRQ_HANDLER
ldr r1, =handle_arch_irq /* r1 = gic_handle_irq() */
mov r0, sp
badr lr, 9997f
ldr pc, [r1]
#else
...
#endif
9997:
.endmirq_handler 是个汇编宏,它调用了 ARM GIC 芯片的中断处理接口 gic_handle_irq(),这个接口是在初始化 GIC 中断芯片时注册的。gic_handle_irq() 在其处理中断即将退出前,处理 softirq:
gic_handle_irq(regs) /* drivers/irqchip/irq-gic.c */
/* 处理 SPI, PPI */
if (likely(irqnr > 15 && irqnr < 1020)) { /* 处理 PPI, SPI */
handle_domain_irq(gic->domain, irqnr, regs); /* include/linux/irqdesc.h */
__handle_domain_irq(domain, hwirq, true, regs);
__handle_domain_irq(domain, hwirq, true, regs); /* kernel/irq/irqdesc.c */
irq_enter();
// 处理中断:这里不关心中断处理的细节
...
irq_exit(); /* 软中断, RCU 等等处理 */
set_irq_regs(old_regs);
return ret;
...
}
if (irqnr < 16) { /* 处理 SGI */
...
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
...
handle_IPI(irqnr, regs); /* arch/arm/kernel/smp.c */
// 除了用来唤醒 CPU 的 IPI_WAKEUP 中断外,都会有 irq_enter() + irq_exit()。
// 至于要被唤醒的 CPU ,都还在睡大觉,就别指望它来处理 softirq 了。
irq_enter();
// 处理 IPI 中断
...
irq_exit();
...
#endif
...
}先看下 irq_enter(),因为它会更新一个和 sotfirq 处理相关的计数:
irq_enter() /* kernel/softirq.c */
...
__irq_enter(); /* include/linux/hardirq.h */
...
/* HARDIRQ_OFFSET 计数加 1 */
preempt_count_add(HARDIRQ_OFFSET); /* include/linux/preempt.h */
__preempt_count_add(HARDIRQ_OFFSET) /* include/asm-generic/preempt.h */
//*preempt_count_ptr() += HARDIRQ_OFFSET;
¤t_thread_info()->preempt_count += HARDIRQ_OFFSET;
...这里的 current_thread_info()->preempt_count 有必要再展开下:
/* arch/arm/include/asm/thread_info.h */
struct thread_info {
...
/*
* 以下类型的计数, 分别占用 @preempt_count 不同 bits:
* PREEMPT_OFFSET, SOFTIRQ_OFFSET, SOFTIRQ_OFFSET, NMI_OFFSET
*/
int preempt_count; /* 0 => preemptable, <0 => bug */
...
/* thread_info 所属的 进程(对象) */
struct task_struct *task; /* main task structure */
...
};
...
/*
* how to get the current stack pointer in C
*/
register unsigned long current_stack_pointer asm ("sp");
/*
* how to get the thread information struct from C
*/
static inline struct thread_info *current_thread_info(void) __attribute_const__;
static inline struct thread_info *current_thread_info(void)
{
/* current_stack_pointer: SP 寄存器的值 */
return (struct thread_info *)
(current_stack_pointer & ~(THREAD_SIZE - 1));
}看到了吧,preempt_count_add(HARDIRQ_OFFSET) 修改的计数值,是当前 CPU 上被 IRQ 中断进程的 struct thread_info 的 preempt_count 成员变量。后面的讨论和这个计数变量密切相关,我们需要提前了解它的来源。
前面讲到,softirq 会在 中断上下文 或 ksoftirqd 内核线程上下文 被处理,先来看在 中断上下文 处理 softirq 的细节。
2.1.2.1 在 中断上下文 处理 softirq
irq_exit()
...
/* 这里减去 irq_enter() 增加的 HARDIRQ_OFFSET 计数,将 HARDIRQ_OFFSET 计数 归 0 */
preempt_count_sub(HARDIRQ_OFFSET);
...
if (!in_interrupt() && local_softirq_pending())
invoke_softirq(); /* 处理当前 CPU 挂起待处理 softirq 事件 */
/*
* 如果 ksoftirqd 当前正在运行状态, 并且没有要求同步处理的
* tasklet, tasklet hi softirq 事件, 则将挂起的 softirq 交给
* ksoftirqd 处理, 而不是在这里的 IRQ 中断上下文处理.
*/
if (ksoftirqd_running(local_softirq_pending()))
return;
if (!force_irqthreads) { /* 如果 不是强制要求使用 ksoftirqd 处理 softirq, */
#ifdef CONFIG_HAVE_IRQ_EXIT_ON_IRQ_STACK
/*
* We can safely execute softirq on the current stack if
* it is the irq stack, because it should be near empty
* at this stage.
*/
__do_softirq();
#else
/*
* Otherwise, irq_exit() is called on the task stack that can
* be potentially deep already. So call softirq in its own stack
* to prevent from any overrun.
*/
/*
* 在 IRQ 中断处理即将结束时, 如果 在 IRQ 中断上下文处理 softirq.
* 当前 CPU 的本地中断处于禁用状态.
*/
do_softirq_own_stack();
__do_softirq();
#endif
} else { /* 强制通过 ksoftirqd 处理 softirq, 则唤醒 ksoftirqd 处理 softirq */
wakeup_softirqd();
}
.../* 中断上下文 和 ksoftirqd 内核线程上下文 处理 softirq 的公共逻辑 */
__do_softirq() /* kernel/softirq.c */
unsigned long end = jiffies + MAX_SOFTIRQ_TIME; /* softirq 处理超时时间: 2ms */
unsigned long old_flags = current->flags;
int max_restart = MAX_SOFTIRQ_RESTART; /* softirq 处理最大轮次 */
struct softirq_action *h;
...
__u32 pending;
int softirq_bit;
...
pending = local_softirq_pending(); /* 读取当前 CPU 挂起的 softirq 事件 */
...
/*
* 禁用 softirq,防止 __do_softirq() 当前 CPU 上的重入。
* 譬如中断抢占、嵌套的情形,可以避免 ksoftirqd 上下文 和 中断上下处理上下文
* 并发的问题,这可以让我们编写 softirq action 接口时,不必考虑所有的竞争场景,
* 这将在后面的章节 4. softirq 同步里面细述。
*/
__local_bh_disable_ip(_RET_IP_, SOFTIRQ_OFFSET);
...
restart:
/* Reset the pending bitmask before enabling irqs */
set_softirq_pending(0); /* 清除当前 CPU 挂起的 softirq */
local_irq_enable(); /* 启用 CPU 本地中断,避免 softirq 耗时太长,使得中断得不到响应 */
h = softirq_vec;
/*
* 返回当前 CPU 挂起未处理的、最高优先级 softirq 类型,
* 按 softirq 优先级 从高到低 进行处理.
*/
while ((softirq_bit = ffs(pending))) {
unsigned int vec_nr;
...
h += softirq_bit - 1; /* 软中断向量: softirq_vec[vec_nr] */
vec_nr = h - softirq_vec; /* softirq 类型: HI_SOFTIRQ, ..., RCU_SOFTIRQ */
...
/*
* 统计当前 CPU @vec_nr 类型中断的发生次数。
* 用户空间可通过文件 /proc/softirqs
* 查看, 实现于代码文件 fs/proc/softirqs.c
*/
kstat_incr_softirqs_this_cpu(vec_nr);
trace_softirq_entry(vec_nr);
/*
* 各类型 softirq 处理接口, 优先级 从高到低:
* HI_SOFTIRQ: tasklet_hi_action()
* TIMER_SOFTIRQ: run_timer_softirq()
* NET_TX_SOFTIRQ: net_tx_action()
* NET_RX_SOFTIRQ: net_rx_action()
* BLOCK_SOFTIRQ: blk_done_softirq()
* IRQ_POLL_SOFTIRQ: irq_poll_softirq()
* TASKLET_SOFTIRQ: tasklet_action()
* SCHED_SOFTIRQ: run_rebalance_domains()
* HRTIMER_SOFTIRQ: 没用到, 占位符, 工具依赖的编号顺序
* RCU_SOFTIRQ: rcu_process_callbacks()
*/
h->action(h);
trace_softirq_exit(vec_nr);
...
h++;
pending >>= softirq_bit;
}
...
/*
* 重新禁用 CPU 本地中断.
* 在 接下来的一轮 (跳到 restart 处) softirq 处理
* 或
* 退出中断处理时
* 会重新启用.
*/
local_irq_disable();
/*
* 软中断处理接口有可能又抛出了 softirq 事件.
* 譬如有未启用的 tasklet, 后续需要在启用调度后得到机会
* 执行, 需要重新抛出 TASKLET_SOFTIRQ, 详见 tasklet_action().
* tasklet hi 也是类似的.
*/
pending = local_softirq_pending();
if (pending) {
/*
* 如果处理 softirq 期间, 又有新的 softirq 挂起,
* 且 同时满足下列条件:
* . 软中断处理没有超时 (MAX_SOFTIRQ_TIME == 2ms)
* . 没有挂起调度请求
* . 没有超过 softirq 处理轮数 (MAX_SOFTIRQ_RESTART == 10)
* 则接着发起新的一轮 softirq 处理.
*/
if (time_before(jiffies, end) && !need_resched() && --max_restart)
goto restart;
/*
* 不满足在此立刻发起新的 softirq 处理的条件, 则唤醒
* ksoftirqd, 将挂起 softirq 交给该内核线程处理.
*/
wakeup_softirqd();
}
...
__local_bh_enable(SOFTIRQ_OFFSET); /* 使能 softirq */
...可能在中断上下文处理 softirq ,昭示着一个很重要的事实,那就是所有的 softirq 的处理代码,都不能有导致睡眠、调度的代码。
2.1.2.2 在 ksoftirqd 内核线程上下文 处理 softirq
/* kernel/softirq.c */
static void run_ksoftirqd(unsigned int cpu)
{
local_irq_disable();
if (local_softirq_pending()) {
/*
* We can safely run softirq on inline stack, as we are not deep
* in the task stack here.
*/
__do_softirq(); /* 在 线程上下文 处理本地 CPU 上的 softirq 事件,细节同中断上下文的分析 */
local_irq_enable();
...
return;
}
local_irq_enable();
}3. softirq 之 tasklet
3.1 定义初始化 tasklet
/* include/linux/interrupt.h */
struct tasklet_struct
{
struct tasklet_struct *next;
/*
* bit-0: 1 表示 tasklet 为调度状态.
* 被 tasklet_trylock() 设置, tasklet_unlock() 清除.
* bit-1: 1 表示 tasklet 为运行态(仅用于 SMP),
* 被 tasklet_schedule() 设置, 被 __do_softirq()
* 执行过后清除.
*/
unsigned long state;
atomic_t count; /* 0 表示 tasklet 为启用状态,非 0 表示 tasklet 为禁用状态 */
void (*func)(unsigned long);
unsigned long data;
};/* include/linux/interrupt.h */
/* 方法一: 静态定义 tasklet 对象 */
#define DECLARE_TASKLET(name, func, data) \
struct tasklet_struct name = { NULL, 0, ATOMIC_INIT(0), func, data }
DECLARE_TASKLET(my_tasklet, my_tasklet_function, (unsigned long)my_tasklet_data);
/* 方法二:动态定义 tasklet 对象 */
/* include/linux/interrupt.h */
struct tasklet_struct my_tasklet;
tasklet_init(&my_tasklet, my_tasklet_function, (unsigned long)my_tasklet_data); /* kernel/softirq.c */
t->next = NULL;
t->state = 0;
atomic_set(&t->count, 0);
t->func = func;
t->data = data;3.2 使能调度 tasklet
/* include/linux/interrupt.h */
static inline void tasklet_schedule(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{
/*
* 标记 tasklet 为 TASKLET_STATE_SCHED 状态:
* TASKLET_STATE_SCHED 态的 tasklet 将在 softirq 里面被调度执行.
*/
if (!test_and_set_bit(TASKLET_STATE_SCHED, &t->state)) /* 不能对 tasklet 重复调度 */
__tasklet_schedule(t);
}
/* kernel/softirq.c */
/*
* Tasklets
*/
struct tasklet_head {
struct tasklet_struct *head;
struct tasklet_struct **tail;
};
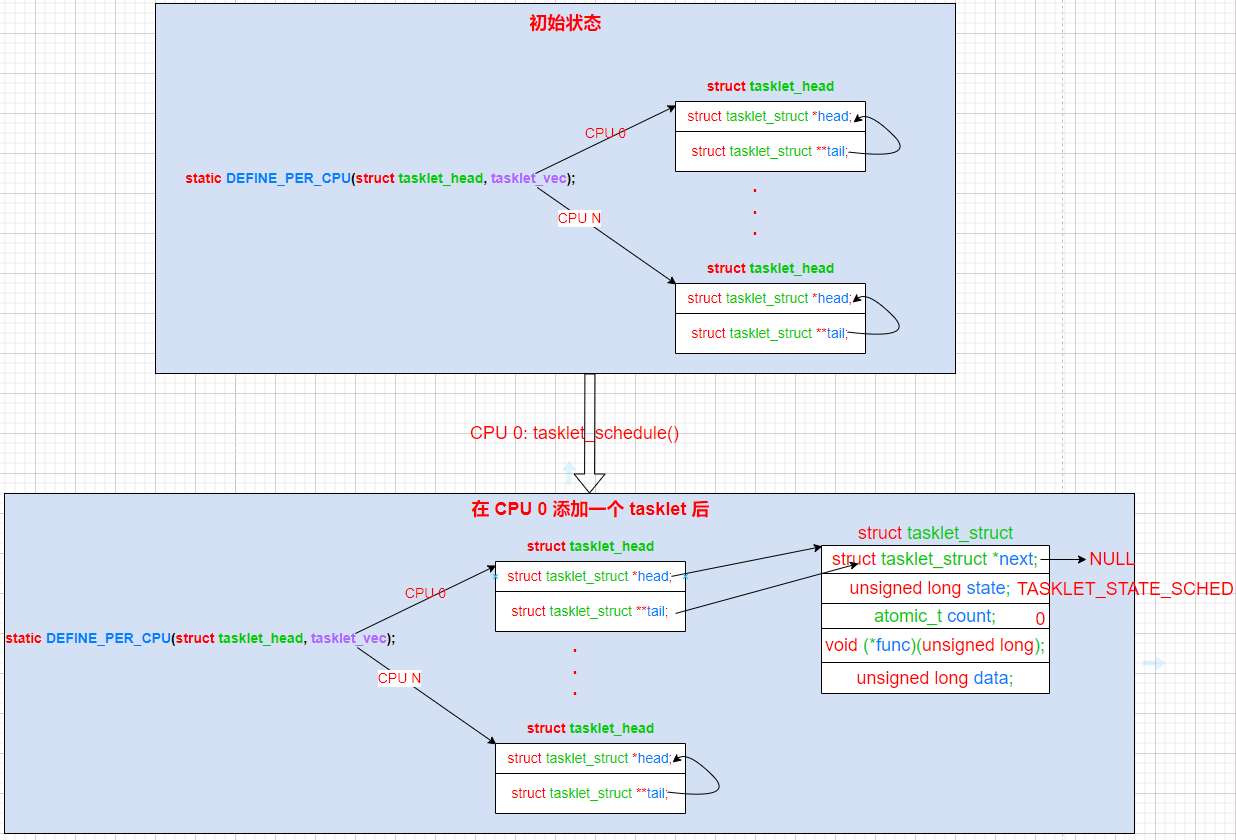
static DEFINE_PER_CPU(struct tasklet_head, tasklet_vec); /* 每 CPU 的 tasklet 队列 (TASKLET_SOFTIRQ) */
static DEFINE_PER_CPU(struct tasklet_head, tasklet_hi_vec); /* 每 CPU 的 tasklet hi 队列 (HI_SOFTIRQ) */
void __tasklet_schedule(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{
unsigned long flags;
local_irq_save(flags);
t->next = NULL;
*__this_cpu_read(tasklet_vec.tail) = t;
__this_cpu_write(tasklet_vec.tail, &(t->next));
raise_softirq_irqoff(TASKLET_SOFTIRQ); /* 抛出 tasklet 软中断 */
local_irq_restore(flags);
}用一张图来看下 tasklet 组织数据结构,有助于我们理解后面对 tasklet 执行过程 的分析:
3.3 执行 tasklet
/* kernel/softirq.c */
__do_softirq()
...
h->action(h);
tasklet_action()
...这里只分析 tasklet_action() ,tasklet_hi_action() 的逻辑几乎完全一样,这里就不再赘述,感兴趣的读者可自行阅读相关源码。
static __latent_entropy void tasklet_action(struct softirq_action *a)
{
struct tasklet_struct *list;
/* 一次性处理当前 CPU 上所有挂起的 tasklet */
local_irq_disable();
list = __this_cpu_read(tasklet_vec.head); /* @list -> 当前 tasklet 列表的第 1 个 tasklet */
/*
* 清空当前 CPU 的 tasklet 列表:
* .head -> NULL
* .tail -> &.head
*/
__this_cpu_write(tasklet_vec.head, NULL);
__this_cpu_write(tasklet_vec.tail, this_cpu_ptr(&tasklet_vec.head));
local_irq_enable();
/* 处理列表 @list 中所有启用的、被调度的 tasklet */
while (list) {
struct tasklet_struct *t = list;
list = list->next;
/*
* 标记 tasklet 为 TASKLET_STATE_RUN 态锁定 tasklet:
* . 如果返回 false 表示 tasklet 已经处于 TASKLET_STATE_RUN,
* 锁定 tasklet 失败;
* . 否则返回 true 表示锁定 tasklet 成功.
*/
if (tasklet_trylock(t)) {
if (!atomic_read(&t->count)) { /* tasklet 为启用状态 */
if (!test_and_clear_bit(TASKLET_STATE_SCHED,
&t->state)) /* 已执行的 tasklet 清除调度标记 */
/*
* 如果
* !test_and_clear_bit(TASKLET_STATE_SCHED, &t->state)
* 成立, 表示 tasklet 没有被设置 TASKLET_STATE_SCHED 位:
* 非 TASKLET_STATE_SCHED 态的 tasklet 出现在 tasklet_vec
* 中,被认为是一个 BUG.
* 程序代码通过 tasklet_schedule() 设置 TASKLET_STATE_SCHED.
*/
BUG();
t->func(t->data);
tasklet_unlock(t);
/*
* 继续执行下一个 tasklet.
*
* 可以看到, 启用并被调度的 tasklet 的执行是一次性的,
* 要想反复执行 tasklet, 需要重新通过 tasklet_schedule()
* 调度 tasklet 执行.
*/
continue;
}
/*
* tasklet 没有启用, 清除 tasklet 的 TASKLET_STATE_RUN 态释放
* tasklet, 接着将该 tasklet 归还到当前 CPU 的 队列, 以备后续
* 启用了再执行.
*/
tasklet_unlock(t);
}
/*
* tasklet 当前从当前 CPU 的 tasklet 队列中移除了,
* 而且 tasklet 没有被启用, 仍然归还到当前 CPU 的
* tasklet 队列中, 以备后续启用了再执行.
*/
local_irq_disable();
/* 将没有执行的 tasklet 归还到当前 CPU 的 tasklet 队列 */
t->next = NULL;
*__this_cpu_read(tasklet_vec.tail) = t;
__this_cpu_write(tasklet_vec.tail, &(t->next));
/*
* 当前 CPU 有未启用的、未被执行的 tasklet,
* 重新抛出 TASKLET_SOFTIRQ, 让这些未启用的
* tasklet 后续在启用并调度后有机会被执行.
*/
__raise_softirq_irqoff(TASKLET_SOFTIRQ);
local_irq_enable();
}
}4. softirq 同步
对于 tasklet hi (HI_SOFTIRQ) 和 tasklet (TASKLET_SOFTIRQ) ,因为它们有每 CPU 独立的队列,所以它们总是在(通过 tasklet_schedule() )提交的 CPU 上执行,同一 CPU 队列上的 tasklet 也按提交的顺序串行的执行;另外,同一个 tasklet,无法同时提交到多个 CPU 上去执行,看 tasklet_schedule() 的实现:
static inline void tasklet_schedule(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{
/*
* 标记 tasklet 为 TASKLET_STATE_SCHED 状态:
* TASKLET_STATE_SCHED 态的 tasklet 将在 softirq 里面被调度执行.
*/
if (!test_and_set_bit(TASKLET_STATE_SCHED, &t->state)) /* 不能对 tasklet 重复调度 */
__tasklet_schedule(t);
}而对于剩余其它类型的 softirq ,虽然它们也总是在提交的 CPU 上执行,但不同于 tasklet 的是,它们可能在多个 CPU 上并行,如 支持硬件多队列的网卡驱动,可能导致 net_rx_action() 在多个 CPU 上同时运行。
了解 softirq 的同步,有助于我们写出正确的代码,这是很重要的。
5. softirq 观测
# cat /proc/softirqs
CPU0 CPU1 CPU2 CPU3
HI: 0 0 0 0
TIMER: 6817 6083 8633 5130
NET_TX: 0 0 0 0
NET_RX: 2 16 6 10
BLOCK: 11161 11269 5199 4379
IRQ_POLL: 0 0 0 0
TASKLET: 1 1 8 1
SCHED: 4522 3375 3217 2745
HRTIMER: 0 0 0 0
RCU: 5661 5083 6497 4399第 1 行示了系统中 CPU,接下来的每一行显示了每种类型 softirq 在每个 CPU 上发生的次数。另外,从下面的代码:
static void __local_bh_enable(unsigned int cnt)
{
...
if (softirq_count() == (cnt & SOFTIRQ_MASK))
trace_softirqs_on(_RET_IP_);
...
}
asmlinkage __visible void __softirq_entry __do_softirq(void)
{
...
while ((softirq_bit = ffs(pending))) {
...
trace_softirq_entry(vec_nr);
h->action(h);
trace_softirq_exit(vec_nr);
...
}
...
}看到,Linux 内核也提供 tracepoint / traceevent 来跟踪 softirq 的执行情况。
6. softirq 的未来
softirq 虽然存在发展很多年,但一直存在一些让人诟病的东西,社区有要移除 softirq (一部分) 的声音,感兴趣的读者,可以阅读这边文章 The end of tasklets。该篇文章的一些参考链接,也值得阅读一下。
![[lesson26]类的静态成员函数](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/262806a4430249788c1aa35414dbd67c.png#pic_center)