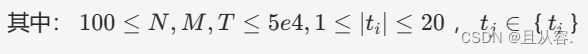Welcome to the third day of learning rust, I am referring to the book “The Rust Programming Language” by Steve Klabnik. Today we build a guessing game in rust.
欢迎来到学习Rust的第三天,基于Steve Klabnik的《The Rust Programming Language》一书。今天我们在rust中建立一个猜谜游戏。

Introduction 介绍
We will build a game that will pick a random number between 1 to 100 and the user has to guess the number on a correct guess the user wins.
我们将构建一个游戏,它将选择1到100之间的随机数字,用户必须猜测正确的猜测用户获胜的数字。
Algorithm 算法
This is what the pseudo code would look like
这就是伪代码的样子
secret_number = (Generate a random number)
loop {
Write “Please input your guess”
Read guess
Write "Your guess : ${guess}"
if(guess > secret_number){
Write "Too high!"
}else if(guess < secret_number){
Write "Too low!"
}else if(guess==number){
Write "You win"
break
}
}Step 1 : Set up a new project
步骤1:创建一个新项目
Use the cargo new command to set up a project
使用 cargo new 命令设置项目
$ cargo new guessing_game
$ cd guessing_gameStep 2 : Declaring variables and reading user input
步骤2:声明变量并阅读用户输入
Filename : main.rs Film:main.rs
use std::io;
fn main() {
println!("Guess the number");
println!("Please input your guess");
let mut guess = String::new();
io::stdin().read_line(&mut guess).expect("Failed to read line");
println!("Your guess: {}", guess);
}Let’s break the code down line by line :
让我们逐行分解代码:
use std::io;This line brings thestd::io(standard input/output) library into scope. Thestd::iolibrary provides a number of useful features for handling input/output.use std::io;此行将std::io(标准输入/输出)库带入范围。std::io库提供了许多用于处理输入/输出的有用特性。fn main(){...}This is the main function where the program execution begins.fn main(){...}这是程序开始执行的main函数。println!("Guess the number");println!is a macro that prints the text to the console.println!("Guess the number");println!是一个宏,它将文本打印到控制台。println!("Please input your guess");This line prompts the user to enter their guess.println!("Please input your guess");这一行提示用户输入他们的猜测。let mut guess = String::new();This line declares a mutable variableguessand initializes it to an empty string.*mutmeans the variable is mutable*, i.e., its value can be changed.String::new()creates a new, empty string.let mut guess = String::new();这一行声明了一个可变变量guess,并将其转换为空字符串。*mut表示变量是可变的 *,即,其值可以改变。String::new()创建一个新的空字符串。io::stdin().read_line(&mut guess).expect("Failed to read line");This line reads the user input from the standard input (keyboard). The entered input is put into theguessstring. If this process fails, the program will stop execution and display the message "Failed to read line".io::stdin().read_line(&mut guess).expect("Failed to read line");这一行从标准输入(键盘)读取用户输入。输入的输入被放入guess字符串中。如果此过程失败,程序将停止执行,并显示消息“读取行失败”。println!("Your guess : {guess}");This line prints out the string "Your guess: ", followed by whatever the user inputted.println!("Your guess : {guess}");这一行打印出字符串“Your guess:“,后跟用户输入的任何内容。
Step 3 : Generating a random number
步骤3:生成随机数
The number should be different each time for replayability. Rust’s standard library doesn’t include random number functionality, but the Rust team provides a rand crate for this purpose.
为了可重玩性,每次的数字应该不同。Rust的标准库不包含随机数功能,但Rust团队为此提供了一个 rand crate。
A Rust crate is like a neatly packaged box of code that you can easily use and share with others in the Rust programming language.
Rust crate就像一个整齐打包的代码盒,您可以轻松使用Rust编程语言并与其他人共享。
To use the rand crate :
使用 rand crate:
Filename: Cargo.toml Filtrate:Cargo.toml
[package]
name = "guessing_game"
version = "0.1.0"
edition = "2021"
[dependencies]
rand = "0.8.5" #append this lineUnderstanding the Cargo.toml file :
了解 Cargo.toml 文件:
- [package] [包]
name = "guessing_game": The name of the Rust package (or crate) is set to "guessing_game".name = "guessing_game":Rust包(或crate)的名称设置为“guessing_game”。version = "0.1.0": The version of the crate is specified as "0.1.0".version = "0.1.0":机箱的版本指定为“0.1.0”。edition = "2021": Specifies the Rust edition to use (in this case, the 2021 edition).edition = "2021":指定要使用的Rust版本(在本例中为2021版)。
2. [dependencies] 2. [依赖关系]
rand = "0.8.5": Adds a dependency on the "rand" crate with version "0.8.5". This means the "guessing_game" crate relies on the functionality provided by the "rand" crate, and version 0.8.5 specifically.rand = "0.8.5":在版本为“0.8.5”的“兰德”crate上添加依赖项。这意味着“guessing_game”crate依赖于“兰德”crate提供的功能,特别是0.8.5版本。
In simpler terms, this configuration file (Cargo.toml) is like a recipe for your Rust project, specifying its name, version, Rust edition, and any external dependencies it needs (in this case, the "rand" crate).
简单地说,这个配置文件( Cargo.toml )就像是Rust项目的配方,指定了它的名称、版本、Rust版本以及它需要的任何外部依赖(在本例中是“兰德”crate)。
After this without changing any code run cargo build , Why do we do that?
在此之后,不改变任何代码运行 cargo build ,为什么我们这样做?
- Fetch Dependencies:
cargo buildfetches and updates the project's dependencies specified inCargo.toml.
获取依赖项:cargo build获取并更新Cargo.toml中指定的项目依赖项。 - Dependency Resolution: It resolves and ensures the correct versions of dependencies are installed.
依赖项解析:它解析并确保安装了正确版本的依赖项。 - Build Process: Compiles Rust code and dependencies into executable artifacts or libraries.
构建过程:将Rust代码和依赖项编译为可执行工件或库。 - Check for Errors: Identifies and reports compilation errors, ensuring code consistency.
检查错误:检查并报告编译错误,确保代码一致性。 - Update lock file: Updates the
Cargo.lockfile to record the exact dependency versions for reproducibility.
更新锁定文件:更新Cargo.lock文件以记录精确的依赖性版本,以实现再现性。
Now let’s talk code 现在我们来谈谈代码
use std::io;
use rand::Rng;
fn main() {
println!("Guess the number!");
let secret_number = rand::thread_rng().gen_range(1..=100);
println!("Secret number: {}", secret_number);
println!("Please input your guess");
let mut guess = String::new();
io::stdin().read_line(&mut guess).expect("Failed to read line");
println!("Your guess: {}", guess);
}Running the program : 运行程序:
$ cargo run
Guess the number!
Secret number : 69
Please input your guess
32
Your guess : 32Let’s see what we did here :
让我们看看我们在这里做了什么:
use rand::Rng;: This line is an import statement that brings theRngtrait into scope, allowing you to use its methods.use rand::Rng;:这一行是一个import语句,它将Rngtrait带入作用域,允许你使用它的方法。rand::thread_rng(): This part initializes a random number generator specific to the current thread. Therand::thread_rng()function returns a type that implements theRngtrait.rand::thread_rng():这部分提供了一个特定于当前线程的随机数生成器。rand::thread_rng()函数返回一个实现了Rngtrait的类型。.gen_range(1..=100): Using the random number generator (Rngtrait), this code calls thegen_rangemethod to generate a random number within a specified range. The range is defined as1..=100, meaning the generated number should be between 1 and 100 (inclusive)..gen_range(1..=100):使用随机数生成器(Rngtrait),这段代码调用gen_range方法来生成指定范围内的随机数。范围被定义为1..=100,这意味着生成的数字应该在1和100之间(包括1和100)。
Step 4 : Comparing the guess to the user input
步骤4:将猜测与用户输入进行比较
Now that we have the input, the program compares the user’s guess to the secret number to determine if they guessed correctly. If the guess matches the secret number, the user is successful; otherwise, the program evaluates whether the guess is too high or too low.
现在我们有了输入,程序将用户的猜测与秘密数字进行比较,以确定他们是否猜对了。如果猜测与秘密数字匹配,则用户成功;否则,程序评估猜测是否过高或过低。
Let’s take a look at the code and then break it down :
让我们看看代码,然后分解它:
use std::io;
use std::cmp::Ordering;
use rand::Rng;
fn main() {
println!("Guess the number!");
let secret_number = rand::thread_rng().gen_range(1..=100);
println!("Secret number: {}", secret_number);
println!("Please input your guess");
let mut guess = String::new();
io::stdin().read_line(&mut guess).expect("Failed to read line");
let guess: u32 = guess.trim().parse().expect("Please type a number!");
println!("Your guess: {}", guess);
match guess.cmp(&secret_number) {
Ordering::Less => println!("Too small!"),
Ordering::Greater => println!("Too big!"),
Ordering::Equal => println!("You win!"),
}
}Running the program : 运行程序:
$ cargo run
Guess the number!
Secret number : 48
Please input your guess
98
Your guess : 98
Too big!Explanation : 说明:
let guess: u32 = guess.trim().parse().expect("Please type a number!");: Shadowing the variableguess, it parses the string into an unsigned 32-bit integer. If parsing fails, it prints an error message.let guess: u32 = guess.trim().parse().expect("Please type a number!");:隐藏变量guess,将字符串解析为无符号32位整数。如果解析失败,它将打印一条错误消息。match guess.cmp(&secret_number) { ... }: Compares the user's guess to the secret number using amatchstatement, handling three cases: less than, greater than, or equal to the secret number.
第0号:使用match语句将用户的猜测与秘密数字进行比较,处理三种情况:小于、大于或等于秘密数字。
Shadowing: 阴影:
- Shadowing is when a new variable is declared with the same name as an existing variable, effectively “shadowing” the previous one.
隐藏是当一个新变量与现有变量同名时,有效地“隐藏”前一个变量。 - In this code,
let guess: u32 = ...is an example of shadowing. The secondguessshadows the first one, changing its type fromStringtou32. Shadowing is often used to reassign a variable with a new value and type while keeping the same name.
在这段代码中,let guess: u32 = ...是阴影的一个例子。第二个guess隐藏第一个,将其类型从String更改为u32。隐藏通常用于为变量重新分配新的值和类型,同时保持名称不变。
Step 5 : Looping the guesses till the user wins
第5步:循环猜测,直到用户获胜
In Step 5, the program implements a loop structure to repeatedly prompt the user for guesses until they correctly guess the secret number as we saw in the algorithm
在步骤5中,程序实现了一个循环结构,反复提示用户进行猜测,直到他们正确地猜出密码,就像我们在算法中看到的那样
As always code then explanation :
一如既往的代码然后解释:
use std::io;
use std::cmp::Ordering;
use rand::Rng;
fn main() {
println!("Guess the number!");
let secret_number = rand::thread_rng().gen_range(1..=100);
println!("Secret number: {}", secret_number);
loop {
println!("Please input your guess");
let mut guess = String::new();
io::stdin().read_line(&mut guess).expect("Failed to read line");
let guess: u32 = guess.trim().parse().expect("Please type a number!");
println!("Your guess: {}", guess);
match guess.cmp(&secret_number) {
Ordering::Less => println!("Too small!"),
Ordering::Greater => println!("Too big!"),
Ordering::Equal => {
println!("You win!");
break;
},
}
}
}Running the program: 运行程序:
$ cargo run
Guess the number!
Secret number : 23
Please input your guess
4
Your guess : 4
Too small!
Please input your guess
76
Your guess : 76
Too big!
Please input your guess
23
Your guess : 4
You win!Explanation: 说明:
loop{...}statement is used to create an infinite looploop{...}语句用于创建无限循环- We are using the
breakstatement to exit out of the program when the variablesguessandsecret_numberare the same.
当变量guess和secret_number相同时,我们使用break语句退出程序。
Step 6 : Handling invalid input
步骤6:处理无效输入
In Step 6, we want to handle invalid inputs and errors because of them. For example : entering a string in the prompt
在第6步中,我们要处理无效输入和由此产生的错误。例如:在提示符中输入字符串
use std::io;
use std::cmp::Ordering;
use rand::Rng;
fn main() {
println!("Guess the number!");
let secret_number = rand::thread_rng().gen_range(1..=100);
println!("Secret number: {}", secret_number);
loop {
println!("Please input your guess");
let mut guess = String::new();
io::stdin().read_line(&mut guess).expect("Failed to read line");
let guess: u32 = match guess.trim().parse() {
Ok(num) => num,
Err(_) => continue,
};
println!("Your guess: {}", guess);
match guess.cmp(&secret_number) {
Ordering::Less => println!("Too small!"),
Ordering::Greater => println!("Too big!"),
Ordering::Equal => {
println!("You win!");
break;
},
}
}
}Running the program: 运行程序:
$ cargo run
Guess the number!
Secret number : 98
Please input your guess
meow
Please input your guess
43
Your guess : 43
Too small!Parse User Input: 解析用户输入:
- Attempts to parse the string in
guessinto an unsigned 32-bit integer.
尝试将guess中的字符串解析为无符号32位整数。 - Uses the
trimmethod to remove leading and trailing whitespaces from the user's input.
使用trim方法从用户输入中删除前导和尾随空格。
Match Statement: 匹配声明:
- The
matchstatement checks the result of the parsing operation.match语句检查解析操作的结果。 Ok(num) => num: If parsing is successful, assigns the parsed number to the variableguess.Ok(num) => num:如果解析成功,将解析后的数字赋给变量guess。
Error Handling: 错误处理:
Err(_) => continue: If an error occurs during parsing, the placeholder '_' matches any error, and the code inside the loop continues, prompting the user for input again.
第0号:如果在解析过程中出现错误,占位符'_'将匹配任何错误,循环中的代码将继续执行,提示用户再次输入。
Summary 总结
In this article, we embarked on our third day of learning Rust by building a guessing game. Here’s a summary of the key steps and concepts covered:Introduction
在本文中,我们通过构建一个猜谜游戏开始了学习Rust的第三天。以下是所涵盖的关键步骤和概念的摘要:简介
- The goal is to create a game where the user guesses a randomly generated number between 1 and 100.
我们的目标是创建一个游戏,让用户猜测1到100之间随机生成的数字。
Algorithm 算法
- A generic algorithm was outlined, providing a high-level overview of the game’s logic.
概述了一个通用算法,提供了游戏逻辑的高级概述。
Step 1: Set up a new project
步骤1:创建一个新项目
- Used
cargo newto create a new Rust project named "guessing_game."
使用cargo new创建一个名为“guessing_game”的新Rust项目。“
Step 2: Declaring variables and reading user input
步骤2:声明变量并阅读用户输入
- Introduced basic input/output functionality using
std::io.
使用std::io引入基本输入/输出功能。 - Demonstrated reading user input, initializing variables, and printing messages.
演示了阅读用户输入、初始化变量和打印消息。
Step 3: Generating a random number
步骤3:生成随机数
- Added the
randcrate as a dependency to generate random numbers.
添加了randcrate作为依赖项来生成随机数。 - Used
rand::thread_rng().gen_range(1..=100)to generate a random number between 1 and 100.
使用rand::thread_rng().gen_range(1..=100)生成1到100之间的随机数。
Step 4: Comparing the guess to the user input
步骤4:将猜测与用户输入进行比较
- Introduced variable shadowing and compared user input to the secret number.
引入了变量跟踪,并将用户输入与秘密数字进行比较。 - Used a
matchstatement to handle different comparison outcomes.
使用match语句处理不同的比较结果。
Step 5: Looping the guesses till the user wins
第5步:循环猜测,直到用户获胜
- Implemented a loop structure to allow the user to make repeated guesses until they correctly guess the secret number.
实现了一个循环结构,允许用户重复猜测,直到他们正确地猜测秘密数字。
Step 6: Handling invalid input
步骤6:处理无效输入
- Addressed potential errors by adding error handling to the user input parsing process.
通过向用户输入分析过程添加错误处理来解决潜在错误。 - Used the
continuestatement to skip the current iteration and prompt the user again in case of an error.
使用continue语句跳过当前迭代,并在出现错误时再次提示用户。
Final code : 最终代码:
use std::io;
use std::cmp::Ordering;
use rand::Rng;
fn main() {
println!("Guess the number!");
let secret_number = rand::thread_rng().gen_range(1..=100);
loop {
println!("Please input your guess");
let mut guess = String::new();
io::stdin().read_line(&mut guess).expect("Failed to read line");
let guess: u32 = match guess.trim().parse() {
Ok(num) => num,
Err(_) => continue,
};
println!("Your guess: {}", guess);
match guess.cmp(&secret_number) {
Ordering::Less => println!("Too small!"),
Ordering::Greater => println!("Too big!"),
Ordering::Equal => {
println!("You win!");
break;
},
}
}
}