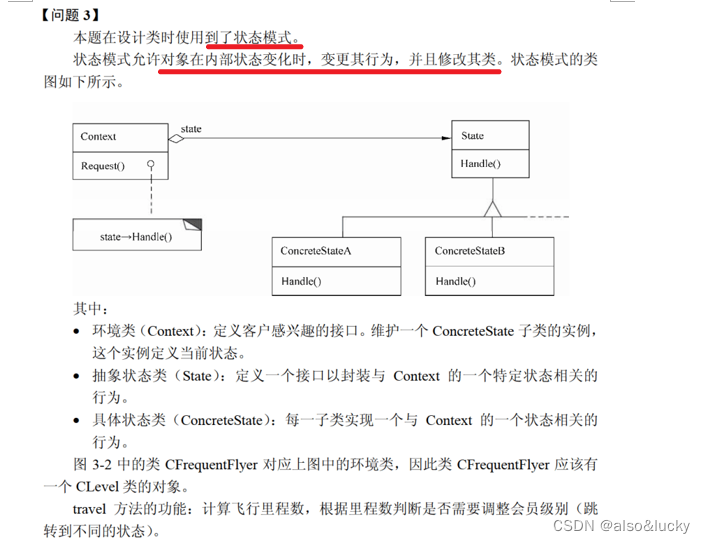
目录
- 1. 队列概念
- 2. 模拟实现队列
- 2.1 链式队列
- 2.2 循环队列
- 3. 双端队列
- 4. 队列的应用
- 4.1 用队列实现栈
- 4.2 用栈实现队列
1. 队列概念
队列是一种只能在一端进行插入数据操作,另一端进行删除数据操作的数据结构,插入数据的叫队尾,删除数据的叫队头。类似于生活中的排队打饭,进入队列中只能从队伍的后面进入,出队只能在队头出。队列是一种先进先出的数据结构。
2. 模拟实现队列
队列有链式结构和顺序结构两种,Java中的Queue接口底层是链式结构,包含方法如下:
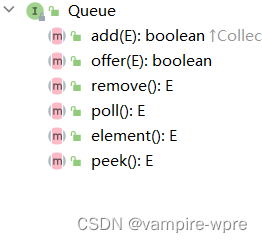
add和offer表示入队,remove和poll表示出队,element和peek表示获取队头的元素(不删除)。
2.1 链式队列
Java的Queue底层是用双向链表实现的,所以我们也用双向链表模拟实现
public class MyQueue<E> {
//使用双向链表
static class ListNode {
public ListNode next;//前驱
public ListNode prev;//后继
public Object val;//值
//构造方法用于初始化
public ListNode(Object val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public ListNode head;//头
public ListNode tail;//尾
//入队->只能从尾部入队(尾插)
public void offer(E val) {
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(val);
//第一次入队
if (tail == null) {
head = tail = newNode;
return;
}
tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = tail;
tail = newNode;
}
//出队->只能从头部出队(头删)
public E poll() {
if (empty()) {
return null;
}
Object ret = head.val;
head = head.next;
head.prev = null;
return (E) ret;
}
//获取队头元素
public E peek() {
if (empty()) {
return null;
}
return (E)head.val;
}
//判断队列是否为空
public boolean empty() {
return head == null;
}
}
2.2 循环队列
循环队列是使用数组实现的,循环队列的结果如图
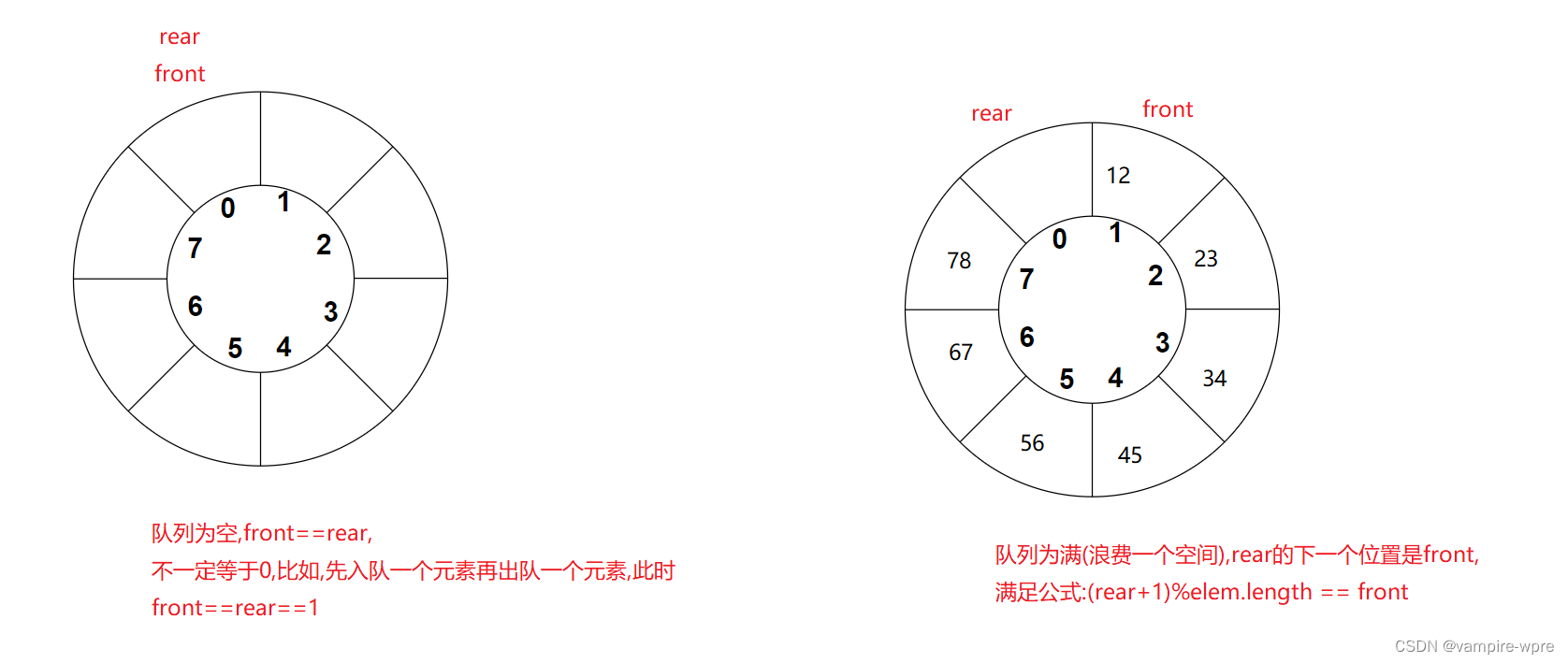
循环队列的原理: 循环队列看似乎结果成环,其实底层是连续的数组,实现循环的是队头(front)和队尾(rear)两个变量,front下标表示队列的第一个元素,rear下标则是队尾的下一个位置。队列为空的条件:front==rear,队列满了的条件:(rear+1)%数组长度 ==front
代码实现:
public class round_robinQueue<E> {
public Object[] elem;//数组
public int front;//队头
public int rear;//队尾
//k表示容量
public round_robinQueue(int k) {
this.elem = new Object[k + 1];//浪费一个空间,所以申请了k+1个空间
}
//入队一个元素
public boolean offer(E value) {
//满了不能插
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
elem[rear] = value;
rear = (rear + 1) % elem.length;
return true;
}
//出队一个元素
public boolean poll() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
front = (front + 1) % elem.length;
return true;
}
//获取队头元素
public E getFront() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return (E) elem[front];
}
//获取队尾元素
public E Rear() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
//rear指向的是下一个位置,不是最后一个元素,如果rear=0,会越界
if (rear == 0) {
return (E) elem[elem.length - 1];
}
return (E) elem[rear - 1];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == rear;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear + 1) % elem.length == front;
}
}
3. 双端队列
双端队列指允许两端都可以进行入队、出队操作的队列,Java中可以使用Deque这个接口,有顺序实现ArrayDeque和链式实现LinkedList
4. 队列的应用
4.1 用队列实现栈

题目链接:用队列实现栈
解题思路: 首先,只使用一个队列是不行的,需要两队列。
实现逻辑: 入栈操作:将元素放入不为空的队列(如果是第一次入栈,两个队列都可以)。出栈操作:将不为空的队列中的n-1个元素放入另一个队列中,最后将剩下的元素出队。获取栈顶元素:将不为空的队列中所有的元素放入另一个队列中,返回最后一个元素即可
代码:
class MyStack {
public Queue<Integer> q1;
public Queue<Integer> q2;
public MyStack() {
q1 = new LinkedList<>();
q2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
//入栈
public void push(int x) {
//如果都为空,在q1中添加
if (empty()) {
q1.offer(x);
return;
}
if (q1.isEmpty()) {
q2.offer(x);
} else {
q1.offer(x);
}
}
//出栈
public int pop() {
//如果模拟栈为空,返回
if (empty()) {
return -1;
}
if (!q1.isEmpty()) {
//q1不为空
int size = q1.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
q2.offer(q1.poll());
}
return q1.poll();
} else {
int size = q2.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
q1.offer(q2.poll());
}
return q2.poll();
}
}
//获取栈顶元素
public int top() {
//如果模拟栈为空,返回
if (empty()) {
return -1;
}
if (!q1.isEmpty()) {
//q1不为空
int size = q1.size();
int ret = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
ret = q1.poll();
q2.offer(ret);
}
return ret;
} else {
int size = q2.size();
int ret = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
ret = q2.poll();
q1.offer(ret);
}
return ret;
}
}
//判断模拟栈是否为空,如果两个队列都为空则为空
public boolean empty() {
return q1.isEmpty() && q2.isEmpty();
}
}
4.2 用栈实现队列

题目链接: 用栈实现队列
解题思路: 使用两个栈实现队列,入队和出队的逻辑:其中一个栈(s1)只进行入栈操作,表示入队列;另一个栈(s2)只进行出栈操作,表示出队,如果s2空了再将s1中所有元素都入s2这个栈
代码:
class MyQueue {
public Stack<Integer> s1;
public Stack<Integer> s2;
public MyQueue() {
s1 = new Stack<>();
s2 = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
s1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if (empty()) {
return -1;
}
//如果s2为空,把s1的所有元素拿过来
if (s2.empty()) {
while (!s1.empty()) {
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
}
return s2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if (empty()) {
return -1;
}
//如果s2为空,把s1的所有元素拿过来
if (s2.empty()) {
while (!s1.empty()) {
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
}
return s2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return s1.empty() && s2.empty();
}
}
今天的内容就到这里,感谢老铁们的点赞、收藏、评论~❤