【Java寒假打卡】Java基础-字符流
- 编码表
- 字符串中的编码和解码问题
- 字节流读取文本文件出现乱码的原因
- 字符流读取中文的过程
- 字符流写出数据
- 字符流输出数据注意事项
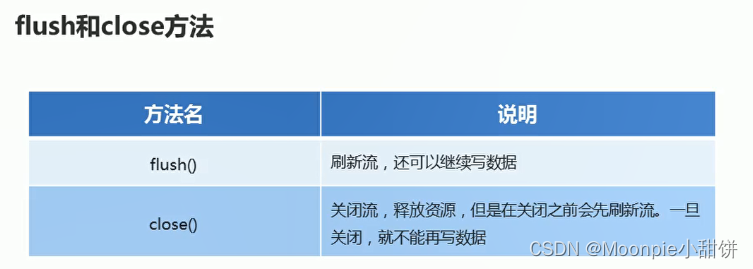
- flush和close方法
- 字符流读取数据
- 案例-保存键盘录入的数据
- 字符缓冲输入流
- 字符缓冲输出流
- 缓冲流的特有方法
- 案例-读取文件中的数据排序之后 写入本地
编码表

编码和解码的过程:
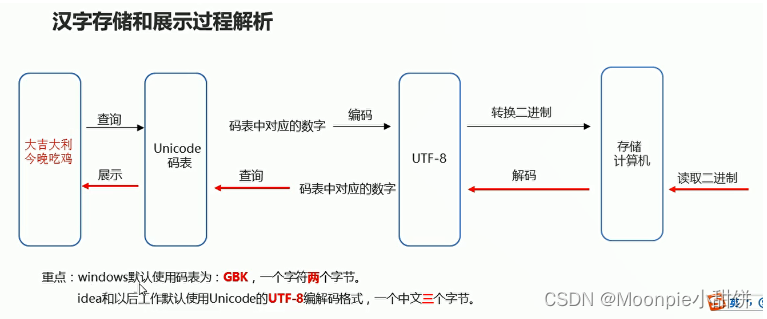
字符串中的编码和解码问题

- 字符串编码
package com.hfut.edu.test10;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
// 使用IDEA默认的字符集 UTF-8 将字符串编码为一些字节 然后将结果存储到字节数组中
String s = "黑马程序员";// 一个UTF-8字符 变为为三个字节
byte[] bytes = s.getBytes();// 将字符串存入字符数组中
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));// 将字节数组 转换为字符串
// 指定编码格式 GBK windows默认编码 一个字符使用两个字节
byte[] bytes1 = s.getBytes("GBK");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes1));// 将字节数组 转换为字符串
}
}
- 字符串解码
package com.hfut.edu.test10;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
// 使用IDEA默认的字符集 UTF-8 将字符串编码为一些字节 然后将结果存储到字节数组中
method1();
method2();
}
private static void method2() throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
byte[] bytes1 = {-23, -69, -111, -23, -87, -84, -25, -88, -117, -27, -70, -113, -27, -111, -104};
byte[] bytes2 = {-70, -38, -62, -19, -77, -52, -48, -14, -44, -79};
// 使用默认utf-8进行解码
String s1 = new String(bytes1);
System.out.println(s1);
// 使用指定的GBK进行解码
String s2 = new String(bytes2,"gbk");
System.out.println(s2);
}
private static void method1() throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
String s = "黑马程序员";// 一个UTF-8字符 变为为三个字节
byte[] bytes = s.getBytes();// 将字符串存入字符数组中
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));// 将字节数组 转换为字符串
// 指定编码格式 GBK windows默认编码 一个字符使用两个字节
byte[] bytes1 = s.getBytes("GBK");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes1));// 将字节数组 转换为字符串
}
}
字节流读取文本文件出现乱码的原因

字符流读取中文的过程
一次性读取多个字节

字符流写出数据
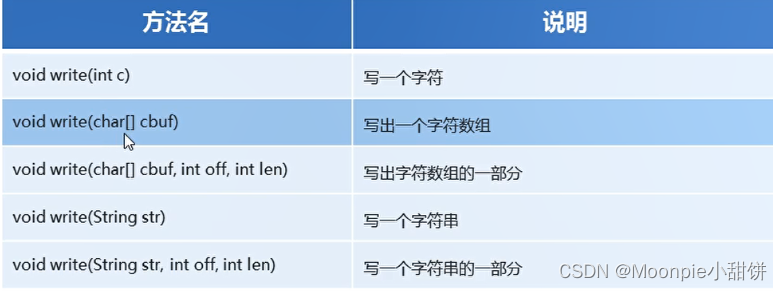
package com.hfut.edu.test10;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 字符流写出数据 FileWriter
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(new File("D:\\heima\\1.txt"));// 传入文件对象
// 写出数据
fw.write(97);
fw.write(98);
fw.write(99);
// 传入字符数组
char[] chars = {97,98,99};
fw.write(chars);
// 传入一个字符串数组
String line = "jcdsahfjdsghb";
fw.write(line);
String line1 = "字节跳动";
fw.write(line1,0,2);// 从0索引开始 读取两个字符
// 释放资源
fw.close();
}
}
字符流输出数据注意事项

flush和close方法
字符流读取数据
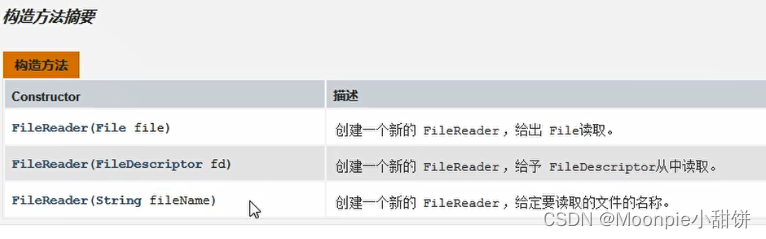
- 一次性读取一个字符
package com.hfut.edu.test10;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建字符输入流的对象
FileReader fr = new FileReader(new File("D:\\heima\\1.txt"));
// 读取数据
int ch;
while((ch = fr.read()) != -1){
System.out.println((char) ch);// 强制转换成字符
}
// 释放资源
fr.close();
}
}
- 一次性读取多个字节
package com.hfut.edu.test10;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 一次性读取多个字符
// 创建对象
FileReader fr = new FileReader(new File("D:\\heima\\1.txt"));
// 一次性读取多个字符
char[] chars = new char[1024];
int len;// 每次读取的字符个数
while((len = fr.read(chars)) != -1){
// 写入指定个数的字符
System.out.println(new String(chars,0,len));
}
fr.close();
}
}
案例-保存键盘录入的数据

package com.hfut.edu.test10;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 将键盘录入的用户的用户名和密码保存到本地实现永久化存储
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名");
String username = sc.next();
System.out.println("请输入密码");
String password = sc.next();
// 将用户名和密码写入本地文件
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(new File("D:\\heima\\1.txt"));
// 将用户名和密码写入文件中 参数传入字符串
fw.write(username);
fw.write("\r\n");// 添加回车换行
fw.write(password);
fw.close();
}
}
字符缓冲输入流
package com.hfut.edu.test10;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class test6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 字符缓冲输入流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\\heima\\1.txt"));
// 读取数据
char chars[] = new char[1024];
int len;// 每次读取的字符数据
while((len = br.read(chars)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(chars,0,len));// 打印输出的字符
}
}
}
字符缓冲输出流
package com.hfut.edu.test10;
import java.io.*;
public class test7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 字符缓冲输出流
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\\heima\\1.txt"));
// 将数据写入缓冲流
bw.write(97);
// 换行符
bw.write("\r\n");
char[] chars = {97,98,99,101};
bw.write(chars);
bw.flush();
bw.close();
}
}
缓冲流的特有方法

- newLine() 换行符
package com.hfut.edu.test10;
import java.io.*;
public class test7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 字符缓冲输出流
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\\heima\\1.txt"));
// 将数据写入缓冲流
bw.write(97);
// 换行符
bw.newLine();
char[] chars = {97,98,99,101};
bw.write(chars);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
bw.close();
}
}
- readLine() 读取一整行的数据
package com.hfut.edu.test10;
import java.io.*;
public class test8 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// readline 读取一整行数据
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\\heima\\1.txt"));
// 使用循环读取数据
String line;// 读不到数据 返回null
while((line = br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
}
}
案例-读取文件中的数据排序之后 写入本地
package com.hfut.edu.test10;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.Buffer;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class test9 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 读取文件中的数据排序之后写入本地文件
// 首先将文件中的数据读入到缓冲流中
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\\heima\\1.txt"));
// 文件中只有一行数据
String line = br.readLine();
System.out.println(line);
// 将数据字符串 按照空格进行分割 获得数组
String [] splits = line.split(" ");// 分割字符串数组
// 将字符串数组 转换成整数型数组
int[] arr = new int[splits.length];
// 遍历split数组 可以进行类型转换
for (int i = 0; i < splits.length; i++) {
String smallStr = splits[i];
int number = Integer.parseInt(smallStr);// 将字符串转换成 Integer对象 然后自动拆箱操作
arr[i] = number;// 存入数组
}
// 将整数进行排序
Arrays.sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(new File("D:\\heima\\2.txt")));
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
bw.write(arr[i] + " ");
bw.flush();
}
}
}