文章目录
- 1. ASC
- 2. 空间
- 3. 卡片
- 4. 相乘
- 5. 路径
- 6.时间显示
- 7.最少砝码
- 8. 杨辉三角形
- 9. 左孩子右兄弟
第12届蓝桥杯省赛,C/C++ C组真题,第10题不是很清楚,题解不敢乱放😁😁😁
1. ASC

额。。。。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
printf("%d\n",'L');
return 0;
}
2. 空间
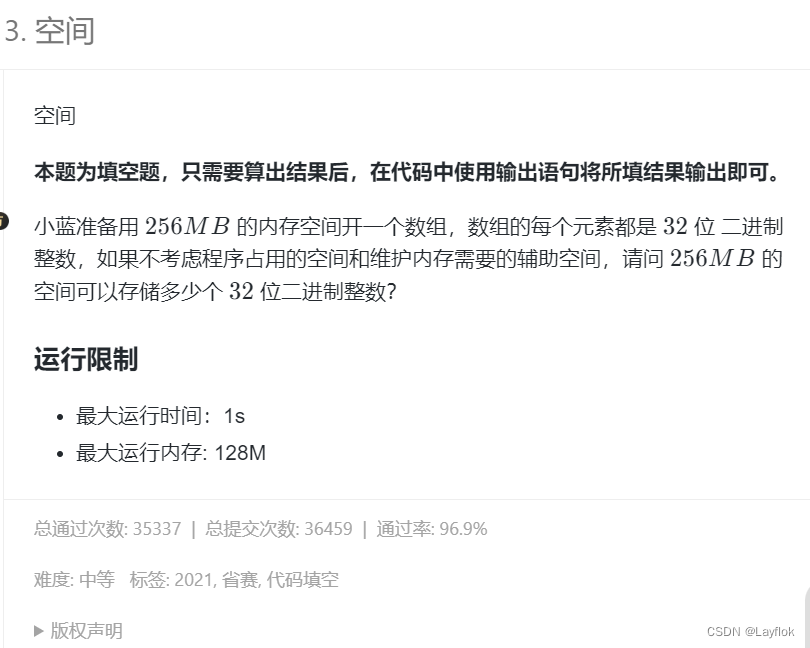
- 甲骨文(🤣🤣):一切的开始好吧。 – 一个字节等于8个比特位
- 1B = 8bit;
- 1KB = 1024B
- 1MB = 1024KB
- 1GB = 1024MB
- 1 TB = 1024GB
- …
- 打住吧,够用了。
在这道题中告诉我们256MB,我们知道32位,在C/C++中一个int是正好4个字节,也就是32个bit。
所以直接256 * 1024 * 1024 / 4就是答案。
当然也可以全部换算成bit位来算,256 * 1024 * 1024 * 8 / 32但要注意开long long。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//1个字节 = 8个bit位
//1B = 8个bit。
//1KB = 1024B。
//1MB = 1024KB
//1GB = 1024MB;
// int = 4个字节, = 32位
printf("%d\n",256 * 1024 * 1024 / 4);
//printf("%lld\n",(long long)256 * 1024 * 1024 * 8 / 32);
return 0;
}
3. 卡片

题目要求从给定的0~9 共2021张卡片,然后问我们最多能拼到哪里?
比如例子中1~9各有三张。 1 ~ 10 已经浪费了两个1, 11还需要两个1,所以拼不成,答案就是10.
填空题,不卡时间,也不用在意时间复杂度了,只要你程序没写死循环,你可以永远相信computer的速度,暴力就好了。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int h[10];
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
h[i] = 2021;
for (int i = 1; true; i++)
{
int t = i;
while (t)
{
int dig = t % 10;
if (!h[dig]) //卡片用完了 h[dig] == 0
{
printf("%d\n", i - 1); //注意是返回前一个构造好的,不是当前的
return 0;
}
h[dig]--; //减去这一位的次数。
t /= 10;
}
}
return 0;
}
4. 相乘
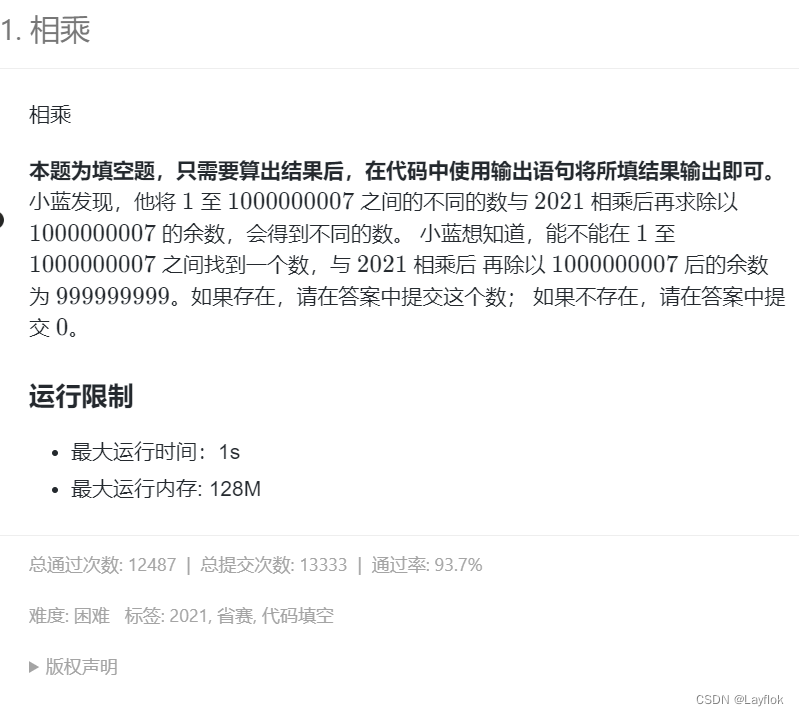
直接对题目进行模拟,看到这么大的数,我的建议是不管3721直接转long long
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
int main()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 1000000007; i++)
{
if ((LL)i * 2021 % 1000000007 == 999999999)
{
printf("%lld\n", i);
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
5. 路径

求1 ~ 2021直接的最短路,然后边的话,如果两点之间的绝对值小于21的话就是他俩的最小公倍数,如果大于21的话就没有边。
- 创图
- 求最短路
填空题,代码有点搓,海涵。
最小公倍数 = a * b / 最大公约数。
这一道题全是模板。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int h[N], e[N], w[N], ne[N], idx;
int dist[2100];
bool st[2100];
int gcd(int a, int b);
int lcm(int a, int b);
void Add(int a, int b, int c)
{
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}
void Dijkstra()
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1] = 0;
priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII> > heap;
heap.push({ 0, 1 });
while (heap.size())
{
auto t = heap.top();
heap.pop();
int v = t.second;
if (st[v]) continue;
st[v] = true;
for (int i = h[v]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (dist[j] > dist[v] + w[i])
{
dist[j] = dist[v] + w[i];
heap.push({ dist[j], j });
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
//创建图
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
for (int i = 1; i <= 2021; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j <= 2021; j++)
{
if (abs(i - j) <= 21)
{
int t = lcm(i, j);
Add(i, j, t);
}
}
}
//
Dijkstra();
if (dist[2021] == INF)
printf("找不到\n");
else
printf("%d\n", dist[2021]);
return 0;
}
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
int lcm(int a, int b)
{
return a * b / gcd(a, b);
}
6.时间显示

题目要求:
给我们一个毫秒数,因为不用管年份和毫秒,所以我们只需要计算出多余的东西就好了。
基础的时间换算知识就能解决这题
- 1秒 = 1000毫秒
- 1分钟 = 60秒
- 1 小时 = 60分钟
- 1 天 = 24小时。
要注意输出格式,小于10的数前面需要加0。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
int main()
{
LL sum;
scanf("%lld",&sum);
sum /= 1000; //
int h = sum % (60*60*24) / (60*60);
int t = sum % (60*60) / 60;
int s = sum % 60;
if (h < 10)
printf("0%d:", h);
else
printf("%d:",h);
if (t < 10)
printf("0%d:", t);
else
printf("%d:",t);
if (s < 10)
printf("0%d", s);
else
printf("%d",s);
return 0;
}
7.最少砝码
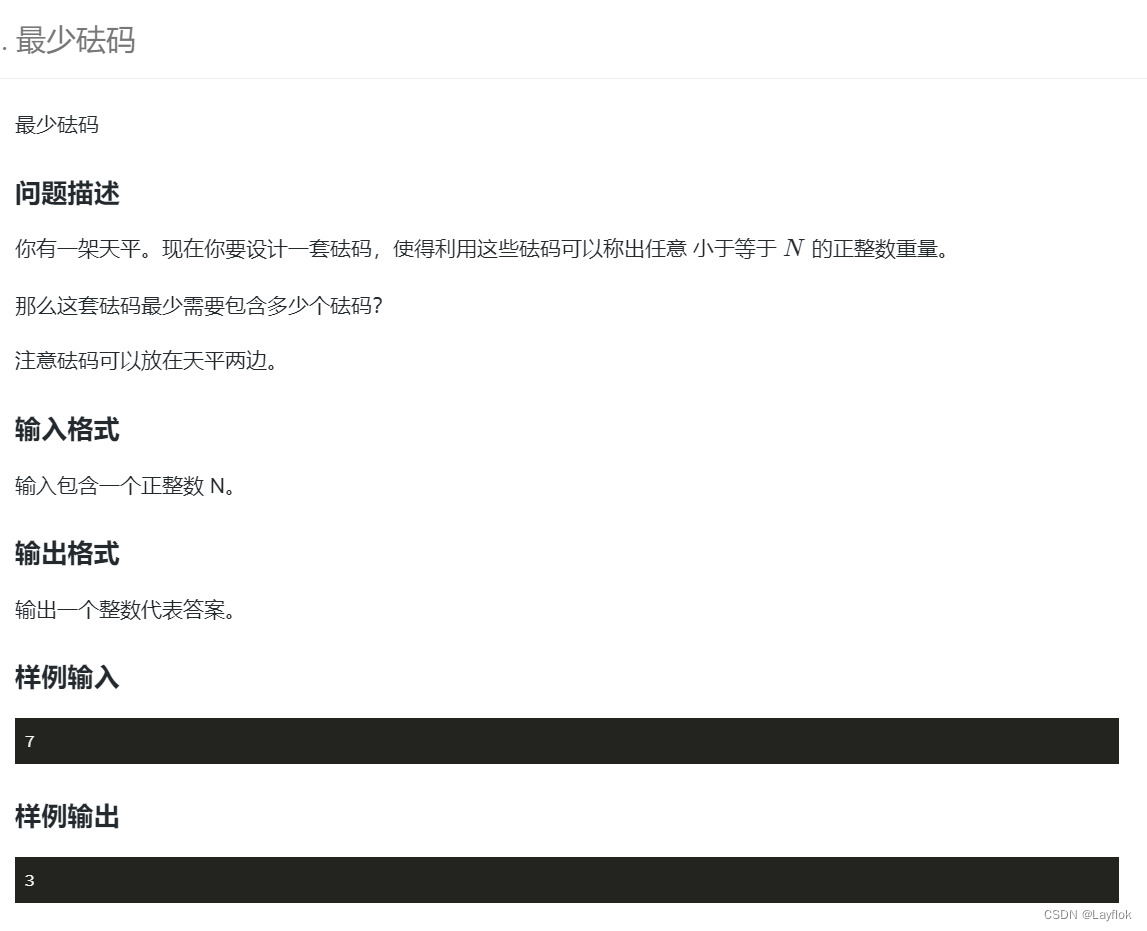

题目要求:
输入一个整数n,要求我们从1~n之内选出最少的数像一个天平那样表示其中的所有数。
思路:
水个题解把,3进制什么鬼,用三进制能表示的数只要 >= 所给定的范围,那么其的幂就是最少数的个数。
不行看看别人的题解,Acwing和蓝桥杯官网都有题解。
传送门~~~~~~~
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
int main()
{
LL x,sum = 0;
int res = 0;
scanf("%lld", &x);
while (sum < x)
{
sum += pow(3, res++);
}
printf("%d\n", res);
return 0;
}
8. 杨辉三角形

题目要求:
给我们一个数,然后求其在杨辉三角中的第几位。
思路:
暴力枚举:
杨辉三角都会构造,我们预处理出来前1000行的杨辉三角,最多1000行,多了会爆。
然后一一枚举就好了。可以过40%的测试用例
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e3 + 10;
int n = 1000;
int a[N][N];
int main()
{
a[1][1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++)
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j ++)
a[i][j] = a[i - 1][j] + a[i - 1][j - 1];
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j ++)
{
cnt ++;
if (a[i][j] == x) {
printf("%d\n",cnt);
return 0;
}
}
return 0;
}
二分 + 找规律
观察下图我们可以发现杨辉三角其实是一个对称的,所以我们只对其进行一半的操作就好了。
我们就可以对其进行二分的操作了,很妙!!!。
这个是视频题解y总真的讲的非常的详细。
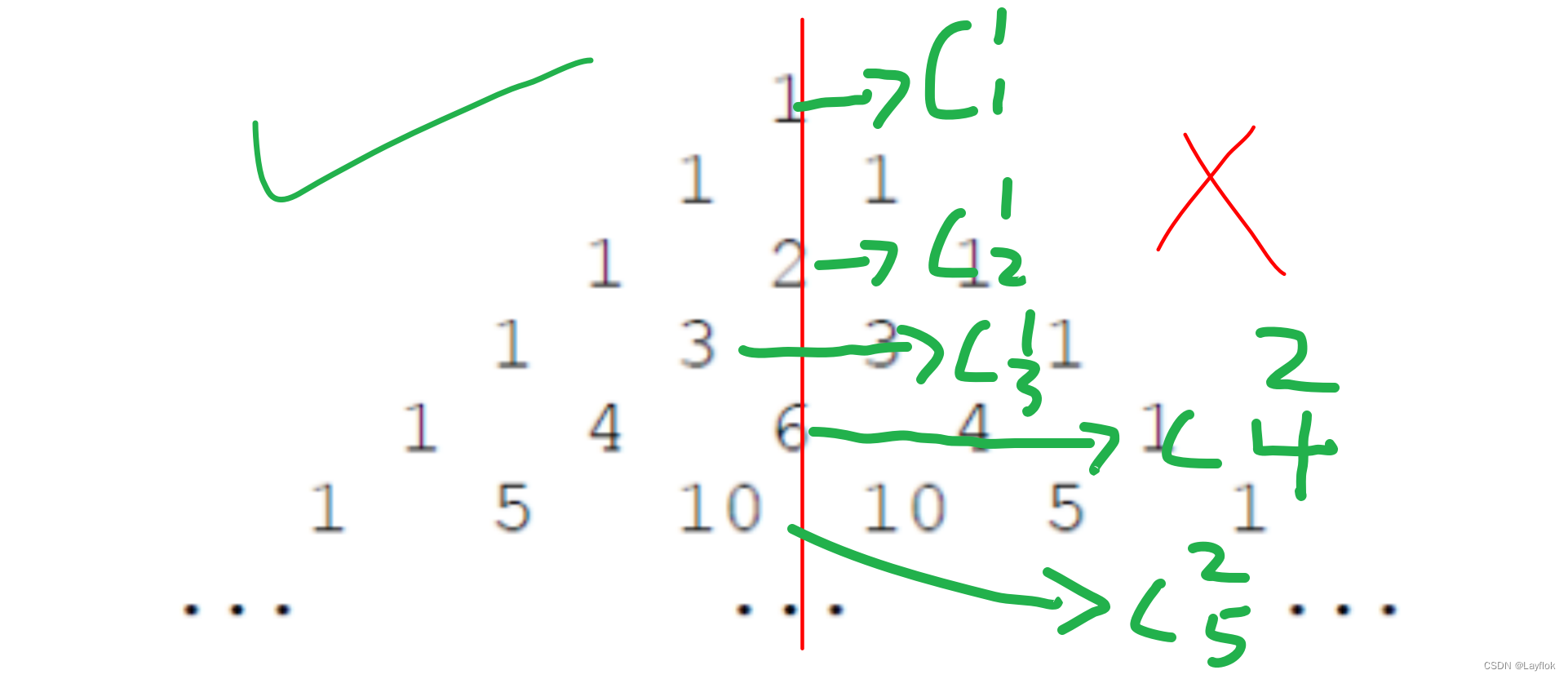
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
LL n;
LL C(int a, int b)
{
LL res = 1;
for (int i = a, j = 1; j <= b; i--, j++)
{
res = res * i / j;
if (res > n)
return res;
}
return res;
}
bool check(int k)
{
// l 是下限, r 是上限
LL l = 2 * k, r = max(l, n);
while (l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (C(mid,k) >= n)
r = mid;
else
l = mid + 1;
}
//二分完成之后r == l 是下限
if (C(r,k) != n) return false;
printf("%lld\n", r * (r + 1) / 2 + k + 1);
return true;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%lld", &n);
// k 枚举的上限
for (int k = 16; ; k--)
{
if (check(k))
break;
}
return 0;
}
9. 左孩子右兄弟

题目要求:
给我构造一棵树,然后将其转化为左孩子有兄弟的表示方式方式,使其的深度最大。
左孩子右兄弟,
- 左孩子,就是将
r节点的左孩子变成原本节点的孩子其中任意一个,没有的话就空着。 - 右兄弟呢,就是
r节点的兄弟,如果没有兄弟节点,右孩子也空着。
蓝桥的题目没有图片,可以去Acwing上也有这道题目,并且有图片。
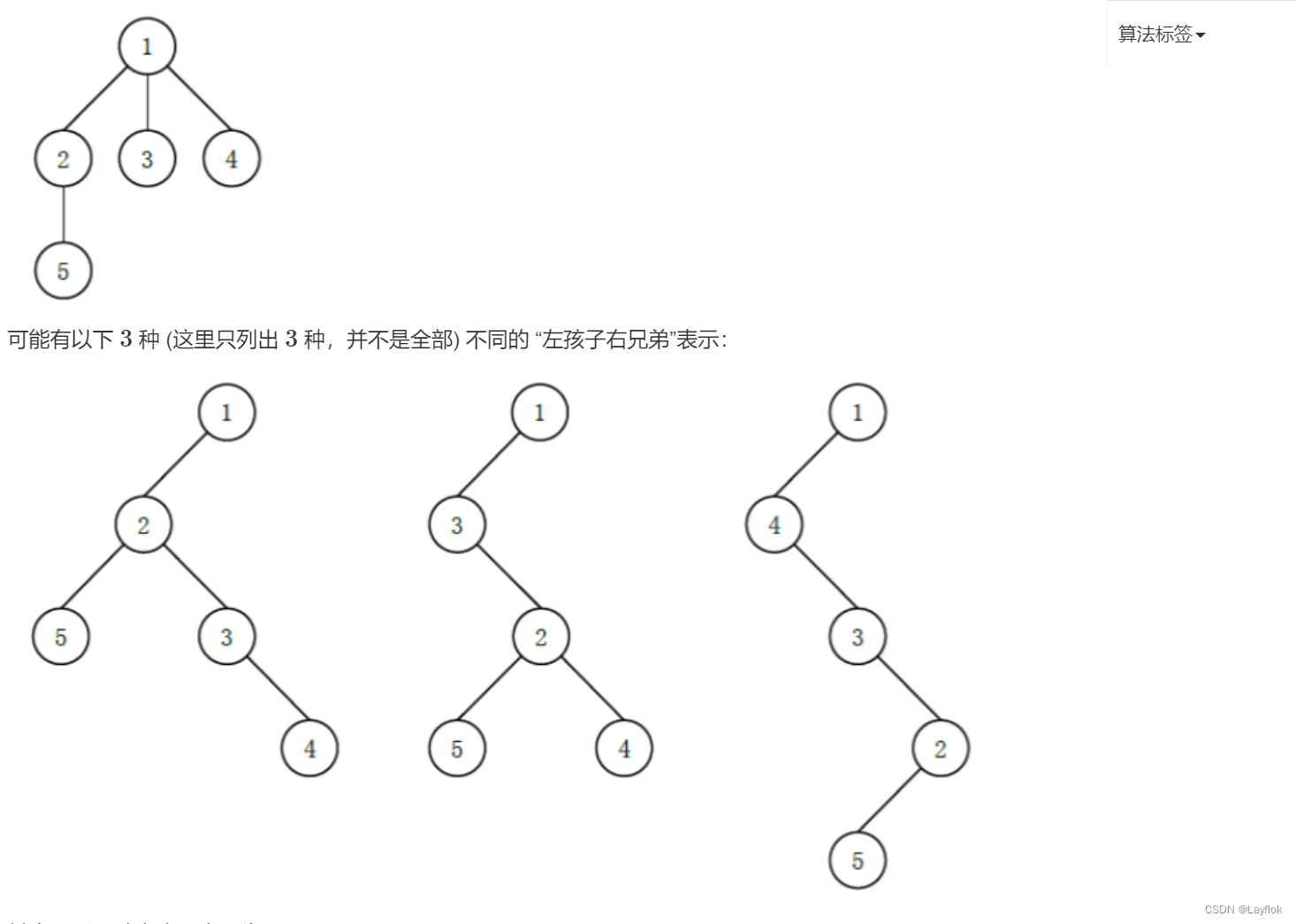
思路:
我们其实通过这张图就可以发现,只需要将其孩子最多的那个子树放在最后就可以是整棵树拉长了,而右孩子永远是右兄弟。
所以最大深度 = 子节点的数量 + 子节点所能形成的最大深度。
个人感觉有点那个树形dp的感觉。
另外注意题目中说只有一个节点的高度为0,这与我们平时所学的数据结构不一样,我们所学的只有一个节点,树的高度是1.
所以只需要在最后的时候将答案减去1就好了。
也可以在dfs函数中将高度最开始1赋值成0都可以。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n;
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
void Add(int a, int b)
{
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}
int dfs(int r)
{
int hmax = 1, cnt = 0; //hmax 为所子节点的最大高度, cnt为字节点的数量
for (int i = h[r]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
hmax = max(hmax, dfs(j));
cnt++;
}
return hmax + cnt;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
int p;
scanf("%d", &p);
Add(p, i);
}
printf("%d\n", dfs(1) - 1);
return 0;
}