本人在B站上关于vue3的尚硅谷的课程,以下是整理一些笔记。
1.两个知识点
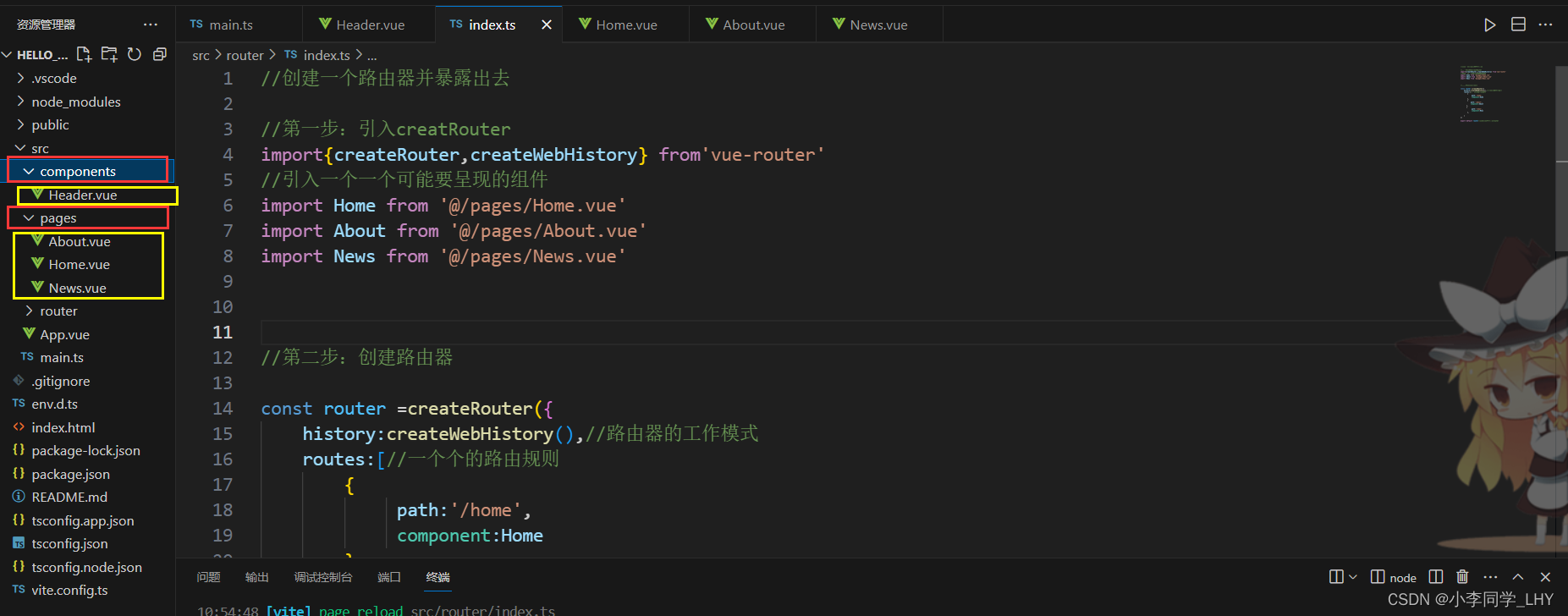
1.路由组件通常存放在pages 或 views文件夹,一般组件通常存放在components文件夹。
组件可以分为:
1. 一般组件:亲手写标签出来的
2. 路由组件:靠路由的规则渲染出来的
比如:
routes:[//一个个的路由规则 { path:'/home', component:Home }, { path:'/about', component:About }, { path:'/news', component:News }, ]
遵循vue中的规则:
一般组件放在components文件夹中,路由组件放在pages 或 views文件夹。
2.通过点击导航,视觉效果上“消失” 了的路由组件,默认是被卸载掉的,需要的时候再去挂载。
比如我在路由组件About中使用生命周期钩子来输出日志信息来观察展示区是如何"消失的"
<template>
<div class="about">
<h2>大家好,欢迎来到小李同学的博客</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts" name="About">
import {onMounted,onUnmounted} from 'vue'
onMounted(()=>{
console.log('About组件挂载了')
})
onUnmounted(()=>{
console.log('About组件卸载了')
})
</script>
<style scoped>
.about {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
height: 100%;
color: rgb(85, 84, 84);
font-size: 18px;
}
</style> 


2.路由器工作模式
1.History模式:就像你在浏览器中打开一个新的网页一样。当你在应用程序中切换页面时,URL会更新,但页面不会重新加载。这样的URL看起来更加友好和自然,就像传统的网页链接一样。
比如:我现在写的博客的网址也是

优点:URL更加美观,不带有#,更接近传统的网站URL。
缺点:后期项目上线,需要服务端配合处理路径问题,否则刷新会有404错误。
2.Hash模式:就像你在一个长网页中滚动到不同的章节。当你在应用程序中切换页面时,URL会在#符号后面加上一段标识,但浏览器不会发送请求到服务器。这样的URL看起来有点奇怪,但它对于一些特殊的环境(比如旧版浏览器)是有效的。
比如:这段代码的使用
//创建一个路由器并暴露出去
//第一步:引入creatRouter
import{createRouter,createWebHistory,createWebHashHistory} from'vue-router'
//引入一个一个可能要呈现的组件
import Home from '@/pages/Home.vue'
import About from '@/pages/About.vue'
import News from '@/pages/News.vue'
//第二步:创建路由器
const router =createRouter({
history:createWebHashHistory(),//路由器的Hash工作模式
routes:[//一个个的路由规则
{
path:'/home',
component:Home
},
{
path:'/about',
component:About
},
{
path:'/news',
component:News
},
]
})
export default router//定义好后暴露出去router
优点:兼容性更好,因为不需要服务器端处理路径。
缺点:URL带有#不太美观,且在SEO优化方面相对较差。
两者的应用场景:
如果你的应用程序主要在现代浏览器中运行,并且你希望URL看起来更加友好和自然,那么可以选择使用history模式。如果你需要在旧版浏览器中兼容,或者你的应用程序是一个单页应用(SPA),可以选择使用hash模式。
3.to的两者写法
在用于生成导航链接的标签<router-link>组件中to的两种常见使用方式,分别是字符串写法和对象写法。
<!-- App.vue 有三种标签,html(结构标签) ,script(交互标签) ,style(样式,用于好看) -->
<template>
<div class = 'app'>
<Header/>
<!-- 导航区 -->
<div class = 'navigate'>
<RouterLink to = '/home'active-class="active" >首页</RouterLink>
<RouterLink to = '/news'active-class="active" >新闻</RouterLink>
<RouterLink to = '/about'active-class="active " >关于</RouterLink>
</div>
<!-- 展示区 -->
<div class = 'main-content'>
<RouterView></RouterView>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup name = "App">
import { RouterView,RouterLink} from 'vue-router';
import Header from './components/Header.vue'
</script>
<style>
/* App */
.navigate {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
margin: 0 100px;
}
.navigate a {
display: block;
text-align: center;
width: 90px;
height: 40px;
line-height: 40px;
border-radius: 10px;
background-color: gray;
text-decoration: none;
color: white;
font-size: 18px;
letter-spacing: 5px;
}
.navigate a.active {
background-color: #64967E;
color: #ffc268;
font-weight: 900;
text-shadow: 0 0 1px black;
font-family: 微软雅黑;
}
.main-content {
margin: 0 auto;
margin-top: 30px;
border-radius: 10px;
width: 90%;
height: 400px;
border: 1px solid;
}
</style>
第一种:to的字符串写法

第二种:to的对象写法

两者的区别:
使用字符串写法时,你可以直接将目标路由的路径作为字符串传递给to属性,例如to="/home"。
使用对象写法时,你可以通过一个对象来指定目标路由的各种属性,例如{ path: '/home' }。除了path属性,你还可以在对象中指定其他路由属性,如name、params、query等,以满足更复杂的路由导航需求。
4.命名路由
作用:可以简化路由跳转及传参。
routes:[
{
name:'zhuye',
path:'/home',
component:Home
},
{
name:'xinwen',
path:'/news',
component:News,
},
{
name:'guanyu',
path:'/about',
component:About
}跳转路由:
<!--简化前:需要写完整的路径(to的字符串写法) -->
<router-link to="/news/detail">跳转</router-link><!--简化后:直接通过名字跳转(to的对象写法配合name属性) -->
<router-link :to="{name:'guanyu'}">跳转</router-link>5.嵌套路由
我们在关于新闻的组件中可以再嵌套一个子路由,用来展示不同新闻的不同详情。
此时,新闻的标题成为导航区,点击后详情出现展示区内。

下面是嵌套路由的步骤:
1.编写News的子路由:Detail.vue组件

代码如下:
<template>
<ul class="news-list">
<li>编号:xxx</li>
<li>标题:xxx</li>
<li>内容:xxx</li>
</ul>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts" name="About">
</script>
<style scoped>
.news-list {
list-style: none;
padding-left: 20px;
}
.news-list>li {
line-height: 30px;
}
</style> 2.在index.ts文件配置路由规则,使用children配置项:

代码如下:
// 创建一个路由器,并暴露出去
// 第一步:引入createRouter
import {createRouter,createWebHistory,createWebHashHistory} from 'vue-router'
// 引入一个一个可能要呈现组件
import Home from '@/pages/Home.vue'
import News from '@/pages/News.vue'
import About from '@/pages/About.vue'
import Detail from '@/pages/Detail.vue'
// 第二步:创建路由器
const router = createRouter({
history:createWebHistory(), //路由器的工作模式(稍后讲解)
routes:[ //一个一个的路由规则
{
name:'zhuye',
path:'/home',
component:Home
},
{
name:'xinwen',
path:'/news',
component:News,
children:[
{
path:'detail',
component:Detail
}
]
},
{
name:'guanyu',
path:'/about',
component:About
},
]
})
// 暴露出去router
export default router
3.在关于新闻的"News"组件添加子路
注意:
在新闻的导航区里面,再写入展示区div

代码如下:
<template>
<div class="news">
<!-- 导航区 -->
<ul>
<li v-for="news in newsList" :key="news.id">
<RouterLink to="/news/detail">{{news.title}}</RouterLink>
</li>
</ul>
<!-- 展示区 -->
<div class="news-content">
<RouterView></RouterView>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts" name="News">
import {reactive} from 'vue'
import {RouterView,RouterLink} from 'vue-router'
const newsList = reactive([
{id:'title01',title:'很好的抗癌食物',content:'西篮花'},
{id:'title02',title:'如何一夜暴富',content:'学IT'},
{id:'title03',title:'震惊,万万没想到',content:'明天是周一'},
{id:'title04',title:'好消息!好消息!',content:'快过年了'}
])
</script>
<style scoped>
/* 新闻 */
.news {
padding: 0 20px;
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
height: 100%;
}
.news ul {
margin-top: 30px;
list-style: none;
padding-left: 10px;
}
.news li>a {
font-size: 18px;
line-height: 40px;
text-decoration: none;
color: #64967E;
text-shadow: 0 0 1px rgb(0, 84, 0);
}
.news-content {
width: 70%;
height: 90%;
border: 1px solid;
margin-top: 20px;
border-radius: 10px;
}
</style>展示: