发文章是为了证明自己真的掌握了一个知识,同时给他人带来帮助,如有问题,欢迎指正,祝大家万事胜意!
目录
前言
openGauss数据库维护管理
1 操作系统参数检查
1.1 实验介绍
1.2 场景设置及操作步骤
2 openGauss 运行健康状态检查
2.1 实验介绍
2.2 场景设置及操作步骤
3 数据库性能检查
3.1 实验介绍
3.2 通过 gs_checkperf 工具来检查数据库性能
3.3 通过 EXPLAIN 进行 SQL 语句优化
4 日志检查
4.1 实验介绍
4.2 通过 gs_collector 工具来收集日志信息
5 最大连接数设置
5.1 实验介绍
5.2 场景设置及操作步骤
6 例行表、索引的维护
6.1 实验介绍
6.2 场景设置及操作步骤
前言
| 设备名称 | 设备型号 | 软件版本 |
| 虚拟机 | VMware | VMware-workstation-full-17.5.1 |
| 操作系统 | openEuler | openEuler 22.3LTS |
| 数据库 | openGauss | openGauss 5.0.0 |
需要的工具,大家不用现在下,后面用到了再下也可以,如果需要相关文件,可以评论,其实大多数都是可以去官网下的哈,因为我只能通过网盘给大家,文件又有点大,网盘的速度大家都是清楚的哈哈,所以还是推荐大家去官网,如果实在找不到可以找我

openGauss数据库维护管理
1 操作系统参数检查
1.1 实验介绍
1.2 场景设置及操作步骤
步骤 1 用 ROOT 用户登录装有 openGauss 数据库服务的操作系统,登录后信息如下:
Welcome to 5.10.0-153.12.0.92.oe2203sp2.x86_64
System information as of time: 2024年 03月 25日 星期一 19:09:30 CST
System load: 0.02
Processes: 195
Memory used: 39.3%
Swap used: 13.3%
Usage On: 25%
IP address: 192.168.28.131
Users online: 1
步骤 2 在 ROOT 用户下执行 gs_checkos 先对系统参数进行检查。
[root@node0 ~]# gs_checkos -i A
Checking items:
A1. [ OS version status ] : Normal
A2. [ Kernel version status ] : Normal
A3. [ Unicode status ] : Normal
A4. [ Time zone status ] : Normal
A5. [ Swap memory status ] : Warning
A6. [ System control parameters status ] : Warning
A7. [ File system configuration status ] : Normal
A8. [ Disk configuration status ] : Normal
A9. [ Pre-read block size status ] : Normal
BondMode Null
A11.[ Network card configuration status ] : Normal
A12.[ Time consistency status ] : Warning
A13.[ Firewall service status ] : Normal
A14.[ THP service status ] : Normal
Total numbers:13. Abnormal numbers:0. Warning numbers:3.
2 openGauss 运行健康状态检查
2.1 实验介绍
2.2 场景设置及操作步骤
[root@node0 ~]# su - omm
Last login: Mon Mar 25 18:47:31 CST 2024 on pts/0
Welcome to 5.10.0-153.12.0.92.oe2203sp2.x86_64
System information as of time: 2024年 03月 25日 星期一 19:31:35 CST
System load: 0.30
Processes: 195
Memory used: 39.0%
Swap used: 14.3%
Usage On: 25%
IP address: 192.168.28.131
Users online: 1
To run a command as administrator(user "root"),use "sudo <command>".
[omm@node0 ~]$ gs_om -t status
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
cluster_name : dbCluster
cluster_state : Normal
redistributing : No
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
[omm@node0 ~]$ gs_om -t stop
Stopping cluster.
=========================================
Successfully stopped cluster.
=========================================
End stop cluster.
[omm@node0 ~]$ gs_check -i CheckDBConnection -L
2024-03-25 19:37:53 [NAM] CheckDBConnection
2024-03-25 19:37:53 [STD] 检查能否连接数据库,如果连接成功则检查项通过,否则检查项不通过
2024-03-25 19:37:53 [RST] NG
The database can not be connected.
2024-03-25 19:37:53 [RAW]
步骤 5 启动 openGauss 数据库服务。
[omm@node0 ~]$ gs_om -t start
Starting cluster.
=========================================
[SUCCESS] node0
......
=========================================
Successfully started.
[omm@node0 ~]$ gs_om -t status;
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
cluster_name : dbCluster
cluster_state : Normal
redistributing : No
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
[omm@node0 ~]$ gs_check -i CheckDBConnection -L
2024-03-25 19:46:27 [NAM] CheckDBConnection
2024-03-25 19:46:27 [STD] 检查能否连接数据库,如果连接成功则检查项通过,否则检查项不通过
2024-03-25 19:46:27 [RST] OK
The database connection is normal.
2024-03-25 19:46:27 [RAW]
source '/home/omm/.bashrc' && gsql -m -d postgres -p 15400 -c 'select pg_sleep(1);'
3 数据库性能检查
3.1 实验介绍
3.2 通过 gs_checkperf 工具来检查数据库性能
[root@node0 ~]# su - omm
Last login: Mon Mar 25 18:47:31 CST 2024 on pts/0
Welcome to 5.10.0-153.12.0.92.oe2203sp2.x86_64
System information as of time: 2024年 03月 25日 星期一 19:31:35 CST
System load: 0.30
Processes: 195
Memory used: 39.0%
Swap used: 14.3%
Usage On: 25%
IP address: 192.168.28.131
Users online: 1
To run a command as administrator(user "root"),use "sudo <command>".
[omm@node0 ~]$ gs_om -t start
Starting cluster.
=========================================
[SUCCESS] node0:
[2024-03-25 19:53:25.112][42128][][gs_ctl]: gs_ctl started,datadir is /opt/huawei/install/data/dn
[2024-03-25 19:53:25.129][42128][][gs_ctl]: another server might be running; Please use the restart command
=========================================
Successfully started.
[omm@node0 ~]$ gs_checkperf
Cluster statistics information:
Host CPU busy time ratio : 1.79 %
MPPDB CPU time % in busy time : 8.68 %
Shared Buffer Hit ratio : 99.56 %
In-memory sort ratio : 0
Physical Reads : 759
Physical Writes : 124
DB size : 50 MB
Total Physical writes : 124
Active SQL count : 4
Session count : 8
[omm@node0 ~]$ gsql -d postgres -p 15400 -r
gsql ((openGauss 5.0.0 build a07d57c3) compiled at 2023-03-29 03:37:13 commit 0 last mr )
Non-SSL connection (SSL connection is recommended when requiring high-security)
Type "help" for help.
openGauss=# analyze pmk.pmk_configuration;
ANALYZE
openGauss=# analyze pmk.pmk_meta_data;
ANALYZE
openGauss=# analyze pmk.pmk_snapshot;
ANALYZE
openGauss=# analyze pmk.pmk_snapshot_datanode_stat;
ANALYZE
openGauss=# \q
[omm@node0 ~]$ gs_checkperf
Cluster statistics information:
Host CPU busy time ratio : 2.02 %
MPPDB CPU time % in busy time : 16.25 %
Shared Buffer Hit ratio : 99.67 %
In-memory sort ratio : 0
Physical Reads : 777
Physical Writes : 335
DB size : 51 MB
Total Physical writes : 335
Active SQL count : 4
Session count : 8
[omm@node0 ~]$ gs_checkperf --detail
Cluster statistics information:
Host CPU usage rate:
Host total CPU time : 26998790.000 Jiffies
Host CPU busy time : 594830.000 Jiffies
Host CPU iowait time : 5920.000 Jiffies
Host CPU busy time ratio : 2.20 %
Host CPU iowait time ratio : .02 %
MPPDB CPU usage rate:
MPPDB CPU time % in busy time : 16.57 %
MPPDB CPU time % in total time : .37 %
Shared buffer hit rate:
Shared Buffer Reads : 1232
Shared Buffer Hits : 430218
Shared Buffer Hit ratio : 99.71 %
In memory sort rate:
In-memory sort count : 0
In-disk sort count : 0
In-memory sort ratio : 0
I/O usage:
Number of files : 121
Physical Reads : 785
Physical Writes : 492
Read Time : 168726 ms
Write Time : 5694 ms
Disk usage:
DB size : 51 MB
Total Physical writes : 492
Average Physical write : 86406.74
Maximum Physical write : 492
Activity statistics:
Active SQL count : 4
Session count : 8
Node statistics information:
dn_6001:
MPPDB CPU Time : 98590 Jiffies
Host CPU Busy Time : 594830 Jiffies
Host CPU Total Time : 26998790 Jiffies
MPPDB CPU Time % in Busy Time : 16.57 %
MPPDB CPU Time % in Total Time : .37 %
Physical memory : 1497370624 Bytes
DB Memory usage : 5200146432 Bytes
Shared buffer size : 284164096 Bytes
Shared buffer hit ratio : 99.71 %
Sorts in memory : 0
Sorts in disk : 0
In-memory sort ratio : 0
Number of files : 121
Physical Reads : 785
Physical Writes : 492
Read Time : 168726
Write Time : 5694
Session statistics information(Top 10):
Session CPU statistics:
1 dn_6001-postgres-omm:
Session CPU time : 3
Database CPU time : 98680
Session CPU time % : 0.00 %
2 dn_6001-postgres-omm:
Session CPU time : 0
Database CPU time : 98680
Session CPU time % : 0.00 %
3 dn_6001-postgres-omm:
Session CPU time : 0
Database CPU time : 98680
Session CPU time % : 0.00 %
4 dn_6001-postgres-omm:
Session CPU time : 0
Database CPU time : 98680
Session CPU time % : 0.00 %
Session Memory statistics:
1 dn_6001-postgres-omm:
Buffer Reads : 303
Shared Buffer Hit ratio : 100.00
In Memory sorts : 0
In Disk sorts : 0
In Memory sorts ratio : 0
Total Memory Size : 7002360
Used Memory Size : 5792184
2 dn_6001-postgres-omm:
Buffer Reads : 300
Shared Buffer Hit ratio : 99.01
In Memory sorts : 0
In Disk sorts : 0
In Memory sorts ratio : 0
Total Memory Size : 6994168
Used Memory Size : 5790576
3 dn_6001-postgres-omm:
Buffer Reads : 303
Shared Buffer Hit ratio : 100.00
In Memory sorts : 0
In Disk sorts : 0
In Memory sorts ratio : 0
Total Memory Size : 6961400
Used Memory Size : 5782816
4 dn_6001-postgres-omm:
Buffer Reads : 1113
Shared Buffer Hit ratio : 100.00
In Memory sorts : 1
In Disk sorts : 0
In Memory sorts ratio : 100.00
Total Memory Size : 12467920
Used Memory Size : 10249640
Session IO statistics:
1 dn_6001-postgres-omm:
Physical Reads : 3
Read Time : 11883
2 dn_6001-postgres-omm:
Physical Reads : 0
Read Time : 0
3 dn_6001-postgres-omm:
Physical Reads : 0
Read Time : 0
4 dn_6001-postgres-omm:
Physical Reads : 0
Read Time : 0
3.3 通过 EXPLAIN 进行 SQL 语句优化
[root@node0 ~]# su - omm
Last login: Mon Mar 25 19:31:35 CST 2024 on pts/0
Welcome to 5.10.0-153.12.0.92.oe2203sp2.x86_64
System information as of time: 2024年 03月 25日 星期一 20:21:39 CST
System load: 0.02
Processes: 195
Memory used: 38.6%
Swap used: 13.9%
Usage On: 25%
IP address: 192.168.28.131
Users online: 1
To run a command as administrator(user "root"),use "sudo <command>".
[omm@node0 ~]$ gs_om -t start
Starting cluster.
=========================================
[SUCCESS] node0:
......
=========================================
Successfully started.[omm@node0 ~]$ gsql -d postgres -p 15400 -r
gsql ((openGauss 5.0.0 build a07d57c3) compiled at 2023-03-29 03:37:13 commit 0 last mr )
Non-SSL connection (SSL connection is recommended when requiring high-security)
Type "help" for help.
openGauss=# CREATE TABLE student
openGauss-# ( std_id INT NOT NULL,
openGauss(# std_name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
openGauss(# std_sex VARCHAR(6),
openGauss(# std_birth DATE,
openGauss(# std_in DATE NOT NULL,
openGauss(# std_address VARCHAR(100)
openGauss(# );
CREATE TABLE
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (1,'张一','男
','1993-01-01','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (2,'张二','男
','1993-01-02','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (3,'张三','男
','1993-01-03','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (4,'张四','男
','1993-01-04','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (5,'张五','男
','1993-01-05','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (6,'张六','男
','1993-01-06','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (7,'张七','男
','1993-01-07','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (8,'张八','男
','1993-01-08','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (9,'张九','男
','1993-01-09','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (10,'李一','男
','1993-01-10','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (11,'李二','男
','1993-01-11','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (12,'李三','男
','1993-01-12','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (13,'李四','男
','1993-01-13','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (14,'李五','男
','1993-01-14','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (15,'李六','男
','1993-01-15','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (16,'李七','男
','1993-01-16','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (17,'李八','男
','1993-01-17','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (18,'李九','男
','1993-01-18','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (19,'王一','男
','1993-01-19','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (20,'王二','男
','1993-01-20','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (21,'王三','男
','1993-01-21','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (22,'王四','男
','1993-01-22','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (23,'王五','男
','1993-01-23','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (24,'王六','男
','1993-01-24','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (25,'王七','男
','1993-01-25','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (26,'王八','男
','1993-01-26','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (27,'王九','男
','1993-01-27','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (28,'钱一','男
','1993-01-28','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (29,'钱二','男
','1993-01-29','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (30,'钱三','男
','1993-01-30','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (31,'钱四','男
','1993-02-01','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (32,'钱五','男
','1993-02-02','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (33,'钱六','男
','1993-02-03','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (34,'钱七','男
','1993-02-04','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (35,'钱八','男
','1993-02-05','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (36,'钱九','男
','1993-02-06','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (37,'吴一','男
','1993-02-07','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (38,'吴二','男
','1993-02-08','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (39,'吴三','男
','1993-02-09','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (40,'吴四','男
','1993-02-10','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (41,'吴五','男
','1993-02-11','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (42,'吴六','男
','1993-02-12','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (43,'吴七','男
','1993-02-13','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (44,'吴八','男
','1993-02-14','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (45,'吴九','男
','1993-02-15','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (46,'柳一','男
','1993-02-16','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (47,'柳二','男
','1993-02-17','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (48,'柳三','男
','1993-02-18','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (49,'柳四','男
','1993-02-19','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (50,'柳五','男
','1993-02-20','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');openGauss=# select count(*) from student;
count
-------
50
(1 row)
openGauss=# select * from student order by std_id;
std_id | std_name | std_sex | std_birth | std_in |
std_address
--------+----------+---------+---------------------+---------------------+----
------------------
1 | 张一 | 男 +| 1993-01-01 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
| | | | |
2 | 张二 | 男 +| 1993-01-02 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
| | | | |
3 | 张三 | 男 +| 1993-01-03 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
| | | | |
4 | 张四 | 男 +| 1993-01-04 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
| | | | |
5 | 张五 | 男 +| 1993-01-05 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
| | | | |
6 | 张六 | 男 +| 1993-01-06 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
| | | | |
7 | 张七 | 男 +| 1993-01-07 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
| | | | |
8 | 张八 | 男 +| 1993-01-08 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
| | | | |
9 | 张九 | 男 +| 1993-01-09 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
| | | | |
10 | 李一 | 男 +| 1993-01-10 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
| | | | |
11 | 李二 | 男 +| 1993-01-11 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
| | | | |
12 | 李三 | 男 +| 1993-01-12 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
| | | | |
13 | 李四 | 男 +| 1993-01-13 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
| | | | |
14 | 李五 | 男 +| 1993-01-14 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
| | | | |
15 | 李六 | 男 +| 1993-01-15 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
……(部分粘贴,有省略)
//注:就是查询结果,我就不完全粘贴了(我尽量减少一些无用的代码,不然影响观看)注:就是查询结果,我就不完全粘贴了(我尽量减少一些无用的代码,不然影响观看)
openGauss=# \d student
Table "public.student"
Column | Type | Modifiers
-------------+--------------------------------+-----------
std_id | integer | not null
std_name | character varying(20) | not null
std_sex | character varying(6) |
std_birth | timestamp(0) without time zone |
std_in | timestamp(0) without time zone | not null
std_address | character varying(100) |
openGauss=# ANALYZE VERBOSE student;
INFO: analyzing "public.student"(dn_6001 pid=3982)
INFO: ANALYZE INFO : "student": scanned 1 of 1 pages, containing 50 live rows and 0 dead rows; 50 rows in sample, 50 estimated total rows(dn_6001 pid=3982)
ANALYZE
openGauss=# explain select * from student where std_id = 30;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------
Seq Scan on student (cost=0.00..1.62 rows=1 width=63)
Filter: (std_id = 30)
(2 rows)
openGauss=# alter table student add primary key(std_id);
NOTICE: ALTER TABLE / ADD PRIMARY KEY will create implicit index "student_pkey" for table "student"
ALTER TABLE
openGauss=# \d student
Table "public.student"
Column | Type | Modifiers
-------------+--------------------------------+-----------
std_id | integer | not null
std_name | character varying(20) | not null
std_sex | character varying(6) |
std_birth | timestamp(0) without time zone |
std_in | timestamp(0) without time zone | not null
std_address | character varying(100) |
Indexes:
"student_pkey" PRIMARY KEY, btree (std_id) TABLESPACE pg_default
openGauss=# explain select /*+indexscan(student student_pkey)*/ * from student where std_id=30;
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
[Bypass]
Index Scan using student_pkey on student (cost=0.00..8.27 rows=1 width=63)
Index Cond: (std_id = 30)
(3 rows)
4 日志检查
4.1 实验介绍
4.2 通过 gs_collector 工具来收集日志信息
openGauss=# \q
[omm@node0 ~]$ pwd
/home/omm
[omm@node0 ~]$ vi collector.json
{
"Collect":
[
{"TypeName": "System", "Content":"RunTimeInfo, HardWareInfo","Interval":"0", "Count":"1"},
{"TypeName": "Log", "Content" : "Coordinator,DataNode,Gtm,ClusterManager",
"Interval":"0", "Count":"1"},
{"TypeName": "Database", "Content":
"pg_locks,pg_stat_activity,pg_thread_wait_status","Interval":"0", "Count":"1"},
{"TypeName": "Config", "Content": "Coordinator,DataNode,Gtm", "Interval":"0", "Count":"1"}
]
}[omm@node0 ~]$ gs_collector --begin-time="20240301 23:00" --end-time="20240325 18:00"
Successfully parsed the configuration file.
create Dir.
Successfully create dir.
do system check interval 0 : count 1
Collecting OS information.
The cmd is source /home/omm/.bashrc; python3 '/opt/huawei/install/om/script/local/LocalCollect.py' -t system_check -U omm -l /var/log/omm/omm/om/gs_local.log -C '{#TypeName#: #System#, #Content#: #ps,ioStat,netFlow,spaceUsage,cpuInfo,memInfo,disk,#, #Interval#: #0#, #Count#: #1#}'
Failed to collect OS information.
do database check interval 0 : count 1
Collecting catalog statistics.
Successfully collected catalog statistics.
do log check interval 0 : count 1
Collecting Log files.
Successfully collected Log files.
do Config check 0:1
Collecting Config files.
Successfully collected Config files.
Collecting files.
Successfully collected files.
All results are stored in /var/log/omm/omm/collector_20240328_213601.tar.gz.
[omm@node0 ~]$ cd /var/log/omm/omm/
[omm@node0 omm]$ ll
total 324
drwxr-x--- 3 omm dbgrp 4096 Mar 16 09:51 asp_data
drwxr-x--- 7 omm dbgrp 4096 Mar 15 17:44 bin
drwxr-x--- 3 omm dbgrp 4096 Mar 15 20:37 cm
-rw------- 1 omm dbgrp 136455 Mar 25 19:02 collector_20240325_190144.tar.gz
-rw------- 1 omm dbgrp 150982 Mar 28 21:36 collector_20240328_213601.tar.gz
drwx------ 3 omm dbgrp 4096 Mar 16 09:51 gs_profile
drwxr-x--- 3 omm dbgrp 4096 Mar 16 09:51 mem_log
drwxr-x--- 2 omm dbgrp 4096 Mar 28 21:36 om
drwxr-x--- 3 omm dbgrp 4096 Mar 15 17:44 pg_audit
drwxr-x--- 3 omm dbgrp 4096 Mar 15 17:44 pg_log
drwxr-x--- 3 omm dbgrp 4096 Mar 16 09:51 pg_perf
drwxr-x--- 3 omm dbgrp 4096 Mar 16 09:51 sql_monitor
[omm@node0 omm]$ tar -zxvf collector_20240328_213601.tar.gz
collector_20240328_213601/
collector_20240328_213601/node0.tar.gz
collector_20240328_213601/Summary.log
collector_20240328_213601/Detail.log
接下来,进入解压后的文件夹 collector_20240328_213601(这个每个人可能不一样,不要完全复制,观察一下,和你的解压时间挂钩,大家仔细看看),并对 node0.tar.gz (这个也是,和主机名挂钩)包进一步解压。
[omm@node0 omm]$ cd collector_20240328_213601
[omm@node0 collector_20240328_213601]$ ll
total 156
-rw------- 1 omm dbgrp 2870 Mar 28 21:36 Detail.log
-rw------- 1 omm dbgrp 150043 Mar 28 21:36 node0.tar.gz
-rw------- 1 omm dbgrp 1055 Mar 28 21:36 Summary.log
[omm@node0 collector_20240328_213601]$ tar -zxvf node0.tar.gz
node0/
node0/gstackfiles/
node0/configfiles/
node0/configfiles/config_20240328_213613624181/
node0/configfiles/config_20240328_213613624181/dn_6001/
node0/configfiles/config_20240328_213613624181/dn_6001/pg_ident.conf
node0/configfiles/config_20240328_213613624181/dn_6001/gaussdb.state
node0/configfiles/config_20240328_213613624181/dn_6001/pg_replslot/
node0/configfiles/config_20240328_213613624181/dn_6001/pg_hba.conf
node0/configfiles/config_20240328_213613624181/dn_6001/postgresql.conf
node0/systemfiles/
node0/systemfiles/OS_information_20240328_213603621784.txt
node0/systemfiles/database_system_info_20240328_213603672555.txt
node0/coreDumpfiles/
node0/planSimulatorfiles/
node0/catalogfiles/
node0/catalogfiles/dn_6001_pg_locks_20240328_213608752242.csv
node0/catalogfiles/dn_6001_pg_stat_activity_20240328_213609154400.csv
node0/catalogfiles/gs_clean_20240328_213610016028.txt
node0/catalogfiles/dn_6001_pg_thread_wait_status_20240328_213609607570.csv
node0/logfiles/
node0/logfiles/log_20240328_213611730074.tar.gz
node0/xlogfiles/
在解压的 node0(指的是服务器名/主机名,各自的不一样,请注意观察)下有各种定制收集的日志
[omm@node0 collector_20240328_213601]$ cd node0
[omm@node0 node0]$ ll
total 32
drwx------ 2 omm dbgrp 4096 Mar 28 21:36 catalogfiles
drwx------ 3 omm dbgrp 4096 Mar 28 21:36 configfiles
drwx------ 2 omm dbgrp 4096 Mar 28 21:36 coreDumpfiles
drwx------ 2 omm dbgrp 4096 Mar 28 21:36 gstackfiles
drwx------ 2 omm dbgrp 4096 Mar 28 21:36 logfiles
drwx------ 2 omm dbgrp 4096 Mar 28 21:36 planSimulatorfiles
drwx------ 2 omm dbgrp 4096 Mar 28 21:36 systemfiles
drwx------ 2 omm dbgrp 4096 Mar 28 21:36 xlogfiles
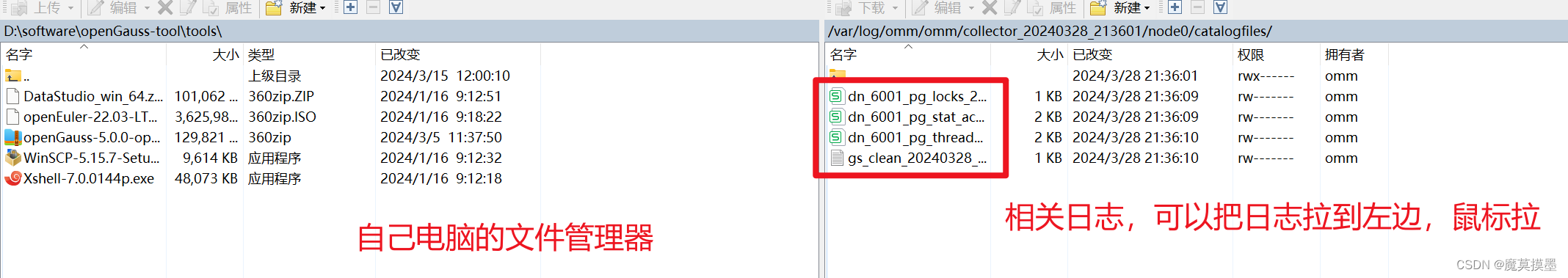
[omm@node0 node0]$ cd catalogfiles/
[omm@node0 catalogfiles]$ ll
total 16
-rw------- 1 omm dbgrp 392 Mar 28 21:36 dn_6001_pg_locks_20240328_213608752242.csv
-rw------- 1 omm dbgrp 1851 Mar 28 21:36 dn_6001_pg_stat_activity_20240328_213609154400.csv
-rw------- 1 omm dbgrp 1945 Mar 28 21:36 dn_6001_pg_thread_wait_status_20240328_213609607570.csv
-rw------- 1 omm dbgrp 286 Mar 28 21:36 gs_clean_20240328_213610016028.txt
[omm@node0 catalogfiles]$
5 最大连接数设置
5.1 实验介绍
5.2 场景设置及操作步骤
[root@node0 ~]# su - omm
Last login: Thu Mar 28 21:10:18 CST 2024 on pts/0
Welcome to 5.10.0-153.12.0.92.oe2203sp2.x86_64
System information as of time: 2024年 03月 28日 星期四 22:03:30 CST
System load: 0.02
Processes: 199
Memory used: 39.1%
Swap used: 21.8%
Usage On: 25%
IP address: 192.168.28.131
Users online: 2
To run a command as administrator(user "root"),use "sudo <command>".
[omm@node0 ~]$ gs_om -t status;
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
cluster_name : dbCluster
cluster_state : Normal
redistributing : No
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
[omm@node0 ~]$ gsql -d postgres -p 15400 -r
gsql ((openGauss 5.0.0 build a07d57c3) compiled at 2023-03-29 03:37:13 commit 0 last mr )
Non-SSL connection (SSL connection is recommended when requiring high-security)
Type "help" for help.
openGauss=# select count(1) from pg_stat_activity;
count
-------
8
(1 row)
openGauss=# SHOW max_connections;
max_connections
-----------------
5000
(1 row)
openGauss=# \q
[omm@node0 ~]$ gs_guc reload -I all -c "max_connections= 6000";
The gs_guc run with the following arguments: [gs_guc -I all -c max_connections= 6000 reload ].
expected instance path: [/opt/huawei/install/data/dn/postgresql.conf]
gs_guc reload: max_connections=6000: [/opt/huawei/install/data/dn/postgresql.conf]
server signaled
Total instances: 1. Failed instances: 0.
Success to perform gs_guc!
[omm@node0 ~]$ gs_om -t stop;
Stopping cluster.
=========================================
Successfully stopped cluster.
=========================================
End stop cluster.
[omm@node0 ~]$ gs_om -t start;
Starting cluster.
=========================================
[SUCCESS] node0
2024-03-28 22:26:31.558 66057e17.1 [unknown] 140368399876032 [unknown] 0 dn_6001 01000 0 [BACKEND] WARNING: could not create any HA TCP/IP sockets
2024-03-28 22:26:31.558 66057e17.1 [unknown] 140368399876032 [unknown] 0 dn_6001 01000 0 [BACKEND] WARNING: could not create any HA TCP/IP sockets
2024-03-28 22:26:31.561 66057e17.1 [unknown] 140368399876032 [unknown] 0 dn_6001 01000 0 [BACKEND] WARNING: Failed to initialize the memory protect for g_instance.attr.attr_storage.cstore_buffers (1024 Mbytes) or shared memory (2314 Mbytes) is larger.
=========================================
Successfully started.
[omm@node0 ~]$ gsql -d postgres -p 15400 -r
gsql ((openGauss 5.0.0 build a07d57c3) compiled at 2023-03-29 03:37:13 commit 0 last mr )
Non-SSL connection (SSL connection is recommended when requiring high-security)
Type "help" for help.
openGauss=# SHOW max_connections;
max_connections
-----------------
6000
(1 row)
6 例行表、索引的维护
6.1 实验介绍
6.2 场景设置及操作步骤
[root@node0 ~]# su - omm
Last login: Thu Mar 28 22:03:30 CST 2024 on pts/0
Welcome to 5.10.0-153.12.0.92.oe2203sp2.x86_64
System information as of time: 2024年 03月 28日 星期四 22:33:00 CST
System load: 0.08
Processes: 198
Memory used: 37.1%
Swap used: 9.4%
Usage On: 25%
IP address: 192.168.28.131
Users online: 2
To run a command as administrator(user "root"),use "sudo <command>".
[omm@node0 ~]$ gs_om -t start;
Starting cluster.
=========================================
[SUCCESS] node0
2024-03-28 22:35:55.148 6605804b.1 [unknown] 140256478302144 [unknown] 0 dn_6001 01000 0 [BACKEND] WARNING: could not create any HA TCP/IP sockets
2024-03-28 22:35:55.148 6605804b.1 [unknown] 140256478302144 [unknown] 0 dn_6001 01000 0 [BACKEND] WARNING: could not create any HA TCP/IP sockets
2024-03-28 22:35:55.150 6605804b.1 [unknown] 140256478302144 [unknown] 0 dn_6001 01000 0 [BACKEND] WARNING: Failed to initialize the memory protect for g_instance.attr.attr_storage.cstore_buffers (1024 Mbytes) or shared memory (2314 Mbytes) is larger.
=========================================
Successfully started.
[omm@node0 ~]$ gsql -d postgres -p 15400 -r;
gsql ((openGauss 5.0.0 build a07d57c3) compiled at 2023-03-29 03:37:13 commit 0 last mr )
Non-SSL connection (SSL connection is recommended when requiring high-security)
Type "help" for help.openGauss=# drop table student;
DROP TABLE
openGauss=# CREATE TABLE student
openGauss-# ( std_id INT NOT NULL,
openGauss(# std_name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
openGauss(# std_sex VARCHAR(6),
openGauss(# std_birth DATE,
openGauss(# std_in DATE NOT NULL,
openGauss(# std_address VARCHAR(100)
openGauss(# );
CREATE TABLE
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (1,'张一','男
','1993-01-01','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (2,'张二','男
','1993-01-02','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (3,'张三','男
','1993-01-03','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (4,'张四','男
','1993-01-04','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (5,'张五','男
','1993-01-05','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (6,'张六','男
','1993-01-06','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (7,'张七','男
','1993-01-07','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (8,'张八','男
','1993-01-08','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (9,'张九','男
','1993-01-09','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (10,'李一','男
','1993-01-10','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (11,'李二','男
','1993-01-11','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (12,'李三','男
','1993-01-12','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (13,'李四','男
','1993-01-13','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (14,'李五','男
','1993-01-14','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (15,'李六','男
','1993-01-15','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (16,'李七','男
','1993-01-16','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (17,'李八','男
','1993-01-17','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (18,'李九','男
','1993-01-18','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (19,'王一','男
','1993-01-19','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (20,'王二','男
','1993-01-20','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (21,'王三','男
','1993-01-21','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (22,'王四','男
','1993-01-22','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (23,'王五','男
','1993-01-23','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (24,'王六','男
','1993-01-24','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (25,'王七','男
','1993-01-25','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (26,'王八','男
','1993-01-26','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (27,'王九','男
','1993-01-27','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (28,'钱一','男
','1993-01-28','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (29,'钱二','男
','1993-01-29','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (30,'钱三','男
','1993-01-30','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (31,'钱四','男
','1993-02-01','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (32,'钱五','男
','1993-02-02','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (33,'钱六','男
','1993-02-03','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (34,'钱七','男
','1993-02-04','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (35,'钱八','男
','1993-02-05','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (36,'钱九','男
','1993-02-06','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (37,'吴一','男
','1993-02-07','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (38,'吴二','男
','1993-02-08','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (39,'吴三','男
','1993-02-09','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (40,'吴四','男
','1993-02-10','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (41,'吴五','男
','1993-02-11','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (42,'吴六','男
','1993-02-12','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (43,'吴七','男
','1993-02-13','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (44,'吴八','男
','1993-02-14','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (45,'吴九','男
','1993-02-15','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (46,'柳一','男
','1993-02-16','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (47,'柳二','男
','1993-02-17','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (48,'柳三','男
','1993-02-18','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (49,'柳四','男
','1993-02-19','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');
INSERT INTO student(std_id,std_name,std_sex,std_birth,std_in,std_address) VALUES (50,'柳五','男
','1993-02-20','2011-09-01','江苏省南京市雨花台区');openGauss=# select count(*) from student;
count
-------
50
(1 row)
openGauss=# select * from student order by std_id;
std_id | std_name | std_sex | std_birth | std_in |
std_address
--------+----------+---------+---------------------+---------------------+----
------------------
1 | 张一 | 男 +| 1993-01-01 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
| | | | |
2 | 张二 | 男 +| 1993-01-02 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
| | | | |
3 | 张三 | 男 +| 1993-01-03 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
| | | | |
4 | 张四 | 男 +| 1993-01-04 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
| | | | |
5 | 张五 | 男 +| 1993-01-05 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
| | | | |
6 | 张六 | 男 +| 1993-01-06 00:00:00 | 2011-09-01 00:00:00 | 江
省南京市雨花台区
openGauss=# \d student
Table "public.student"
Column | Type | Modifiers
-------------+--------------------------------+-----------
std_id | integer | not null
std_name | character varying(20) | not null
std_sex | character varying(6) |
std_birth | timestamp(0) without time zone |
std_in | timestamp(0) without time zone | not null
std_address | character varying(100) |
openGauss=# vacuum student;
VACUUM
openGauss=# delete from student where std_id>30;
DELETE 20
openGauss=# vacuum full student;
VACUUM
openGauss=# analyze student;
ANALYZE
openGauss=# analyze verbose student;
INFO: analyzing "public.student"(dn_6001 pid=3999)
INFO: ANALYZE INFO : "student": scanned 1 of 1 pages, containing 30 live rows and 20 dead rows; 30 rows in sample, 30 estimated total rows(dn_6001 pid=3999)
ANALYZE
openGauss=# vacuum analyze student;
VACUUM
openGauss=# select relname,n_tup_ins,n_tup_upd,n_tup_del,last_analyze,vacuum_count from PG_STAT_ALL_TABLES where relname='student';
relname | n_tup_ins | n_tup_upd | n_tup_del | last_analyze |
vacuum_count
---------+-----------+-----------+-----------+------------------------------+-
-------------
student | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2024-03-29 11:14:46.38435+08 |
1
(1 row)
openGauss=# create index inx_stu01 on student(std_name);
CREATE INDEX
openGauss=# reindex table student;
REINDEX
openGauss=# drop index inx_stu01;
DROP INDEX
openGauss=# create index inx_stu01 on student(std_name);
CREATE INDEX
openGauss=# \d student;
Table "public.student"
Column | Type | Modifiers
-------------+--------------------------------+-----------
std_id | integer | not null
std_name | character varying(20) | not null
std_sex | character varying(6) |
std_birth | timestamp(0) without time zone |
std_in | timestamp(0) without time zone | not null
std_address | character varying(100) |
Indexes:
"inx_stu01" btree (std_name) TABLESPACE pg_default
![练习 16 Web [极客大挑战 2019]LoveSQL](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/cbbfc9d58e95478b89b119b7e6ee77ff.png)