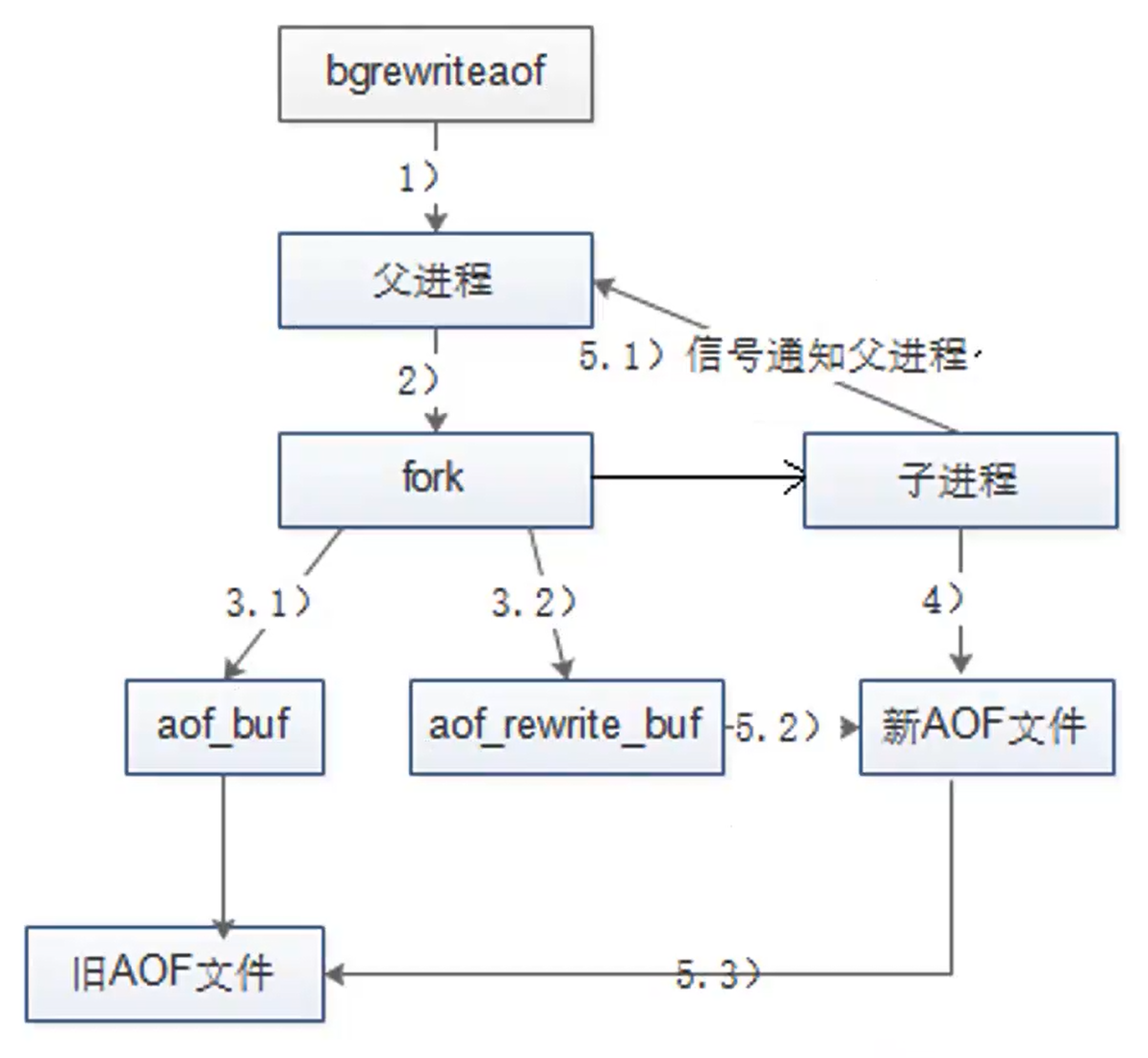
零.前言
本篇文章主要阐述CSS常见属性、复合属性,更多前置知识请见作者其它文章:
CSS(一)---【CSS简介、导入方式、八种选择器、优先级】-CSDN博客
1.CSS属性
CSS的属性有上百个,但是我们并不需要全部学习,只要我们学习一部分,就可以知微见著明白绝大部分的CSS属性使用了。至于很少使用的属性,等需要的时候再查就好。
一.复合属性
通过复合属性可以一次性的设置多个属性(原子属性)。
比如,我们可以在font属性里面设置字体大小、字体、宽度等等,这分别对应了“font-size”、“font-style”、“font-weight”三个属性。
例如:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<p style="font: bolder 50px heiti;">这是一个复合属性案例</p>
</body>
</html>效果:

二.常见属性
2.0前言
对于字体大小、字体高度、窗口宽度等等,只要涉及大小的都需要我们给定一个属性值单位。
那么属性值的单位可以是:“px(像素)”、“%(百分比)”。
其中,百分比是相较于整个窗口的大小。
2.1line-height【行高】
当我们有一串很密集的数据时候,它可能是下面这个样子的:

可以看到,这些文本在浏览器中呈现效果是:“挤在一起”
这样非常影响观感,这个时候我们就可以使用“line-height”属性来设置行高,从而有层次感。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<p style="line-height: 40px;">这是一段话这是一段话这是一段话这是一段话这是一段话这是一段话这是一段话这是一段话这是一段话这是一段话这是一段话这是一段话这是一段话这是一段话这是一段话这是一段话这是一段话这是一段话这是一段话这是一段话这是一段话这是一段话</p>
</body>
</html>
效果:

是不是好看了一点点
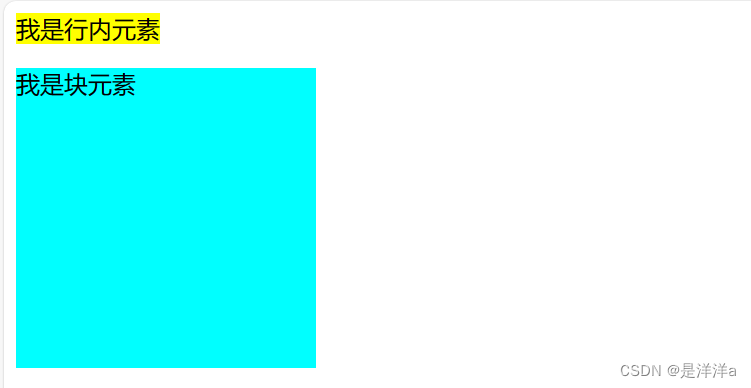
2.2width(宽度)和height(高度)属性
注意:只有块元素和行内块元素可以设置“宽度”和“高度”,对于行内元素不可以设置“宽度”和“高度”,即使设置了也是无效的!!
因为行内元素的高度和宽度取决于它的内容!!
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- span是行内元素,设置宽度高度均无效 -->
<span style="width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: yellow;">我是行内元素</span>
<!-- p是块元素,可以设置宽度高度 -->
<p style="width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: aqua;">我是块元素</p>
</body>
</html>效果:
2.3display【块元素、行元素、块内元素切换】
使用display属性,可以将一个标签强制转换成【块元素、行元素、块内元素】。
- “块元素”:block
- “行元素”:inline
- “行内块元素”:inline-block
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<span style="width: 100px;height: 100px;background-color: brown;">我是行内元素,宽度高度对我无效</span>
<span style="width: 100px;height: 100px;background-color: yellow; display: block;">我是块元素,宽度高度对我有效</span>
<span style="width: 100px;height: 100px;background-color: blueviolet; display: inline-block;">我是行内块元素,宽度高度对我有效</span>
</body>
</html>
效果:

2.4background-color(背景颜色)
使用background-color可以设置标签的背景颜色,可以是:“英文单词代指颜色”、“十六进制值”、“RGB值”。
同时还可以使用“opacity”属性来指定标签的透明度,取值范围为:“0.0 - 1.0”,值越低,越透明。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
div {
background-color: green;
}
div.first {
opacity: 0.1;
}
div.second {
opacity: 0.3;
}
div.third {
opacity: 0.6;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>透明框</h1>
<p>当使用 opacity 属性为元素背景添加透明度时,其所有子元素也会变为透明。这可能会使完全透明的元素内的文本难以阅读:</p>
<div class="first">
<h1>opacity 0.1</h1>
</div>
<div class="second">
<h1>opacity 0.3</h1>
</div>
<div class="third">
<h1>opacity 0.6</h1>
</div>
<div>
<h1>opacity 1(默认)</h1>
</div>
</body>
</html>效果:

2.5background-image【背景图像相关】
使用background-image可以设置标签的背景图像,如果需要设置整个页面的背景图像,可以使用在<body>设置background-image属性。
body {
background-image: url("paper.gif");
}效果:

但在默认情况下,如果图片的大小小于页面的大小,那么图片就会以重复的方式堆叠,直到铺满整个页面。
例如:

这显然是不对的,为此我们可以使用“background-repeat”属性来设置图片是否重复堆叠,或者只在某些方向上重复堆叠。
“background-repeat”的取值:
- “repeat-x”:水平方向堆叠
- “repeat-y”:竖直方向堆叠
- “no-repeat”:不堆叠图片
除此之外,我们还可以使用“background-position”属性来设置图片的摆放位置。
属性值可以是:“left”、“right”、“top”、“bottom”、“具体的坐标值(像素单位)”。
例如:
background-position: right top; //右上角
background-position: 40px 20px; 摆放在屏幕(40px,20px)处[x,y]坐标对于坐标来言,屏幕的左上方为(0,0),向右为x增加,向下为y增加,x、y均无负值。
当我们需要指定背景图像是否随鼠标滚轮同步滚动时,我们可以使用:“background-attachment”属性。
background-attachment属性值:
- “fixed”:背景图像不随鼠标滚轮同步滚动,也就是固定在屏幕中
- “scroll”:背景图像随鼠标滚轮同步滚动,不会固定在屏幕中
body {
background-image: url("tree.png");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: right top;
background-attachment: fixed;
}
//固定在屏幕.
body {
background-image: url("tree.png");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: right top;
background-attachment: scroll;
}
//随鼠标滚轮移动,不固定在屏幕.2.6background(背景复合属性)
background属性是一个复合属性,可以在该属性中一次性指定background下的所有子属性。
background下的子属性按照顺序有:
- “background-color”:背景颜色
- “background-image”:背景图片
- “background-repeat”:背景图片是否重复堆叠
- “background-attachment”:背景图片是否附着于页面上(是否随鼠标滚动而滚动)
- “background-position”:背景图片的摆放位置
若当中某一条属性值缺失,可以不用管它,继续按照顺序书写剩余属性即可。
例如,我们想要设置一个无背景颜色、有背景图片、背景图片不堆叠、摆放位置为右上角,我们可以这样书写:
<style>
body{
background:url(./photo/image.jpg) no-repeat right top;
}</style>
即可,不需要担心属性值会被赋给不对应的属性,因为系统会自动识别。