零、文章目录
文章地址
- 个人博客-CSDN地址:https://blog.csdn.net/liyou123456789
- 个人博客-GiteePages:https://bluecusliyou.gitee.io/techlearn
代码仓库地址
- Gitee:https://gitee.com/bluecusliyou/TechLearn
- Github:https://github.com/bluecusliyou/TechLearn
CSS入门五、定位
1、为什么需要定位
- 某个元素可以自由的在一个盒子内移动位置,并且压住其他盒子。
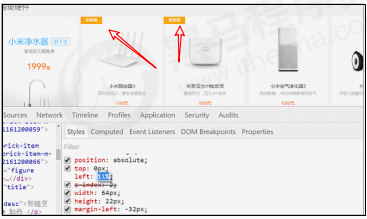
- 当我们滚动窗口的时候,盒子是固定屏幕某个位置的。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-UufJXA5O-1673421752068)(http://cdn.bluecusliyou.com/202212301728027.png)]
-
以上效果,标准流或浮动都无法快速实现,此时需要定位来实现。
-
浮动和定位区别:
-
浮动:可以让多个块级盒子一行没有缝隙排列显示, 经常用于横向排列盒子。
- 定位:可以让盒子
自由的在某个盒子内移动位置或者固定屏幕中某个位置,并且可以压住其他盒子。
- 定位:可以让盒子
-
2、定位组成
定位将盒子定在某一个位置,所以定位也是在摆放盒子,按照定位的方式移动盒子。- 定位 = 定位模式 + 边偏移 。
(1)定位模式
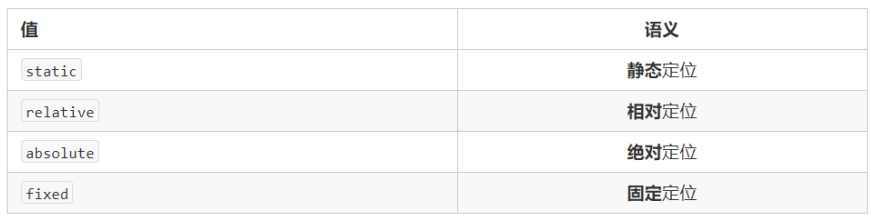
定位模式决定元素的定位方式 ,它通过 position 属性来设置,其值可以分为四个:
(2)边偏移
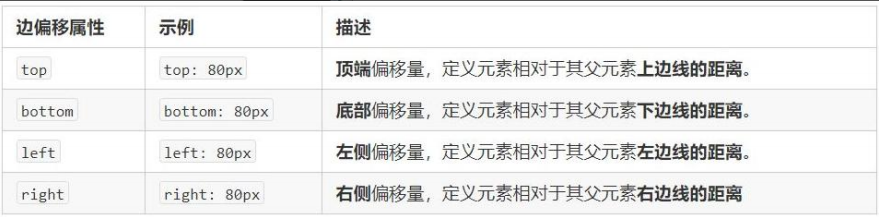
边偏移就是定位的盒子移动到最终位置。有 top、bottom、left 和 right 4 个属性。
3、静态定位 static(了解)
- 静态定位是元素的
默认定位方式,无定位的意思。 - 静态定位按照标准流特性摆放位置,它没有边偏移。
- 静态定位在布局时很少用到。
选择器 { position: static; }
4、相对定位 relative(重要)
相对定位是元素在移动位置的时候,是相对于它原来的位置来说的(自恋型)。- 相对定位的特点:(务必记住)
移动位置的时候参照点是自己原来的位置。原来在标准流的位置继续占有,后面的盒子仍然以标准流的方式对待它。
- 因此,相对定位并没有脱标。它最典型的应用是给绝对定位当爹的。
选择器 { position: relative; }
案例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>相对定位</title>
<style>
.box1 {
position: relative;
top: 100px;
left: 100px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
.box2 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: deeppink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
</div>
<div class="box2">
</div>
</body>
</html>

5、绝对定位 absolute(重要)
-
绝对定位是元素在移动位置的时候,是相对于它祖先元素来说的(拼爹型)。 -
绝对定位的特点:(务必记住)
-
如果
没有祖先元素或者祖先元素没有定位,则以浏览器为准定位的。 -
如果祖先元素有定位(相对、绝对、固定定位),则以
最近一级的有定位祖先元素为参考点定位。 -
绝对定位
不再占有原先的位置。(脱标)
-
选择器 { position: absolute; }
绝对定位-无父亲或者父亲无定位:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>绝对定位-无父亲或者父亲无定位</title>
<style>
.father {
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
.son {
position: absolute;
/* top: 10px;
left: 10px; */
/* top: 100px;
right: 200px; */
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
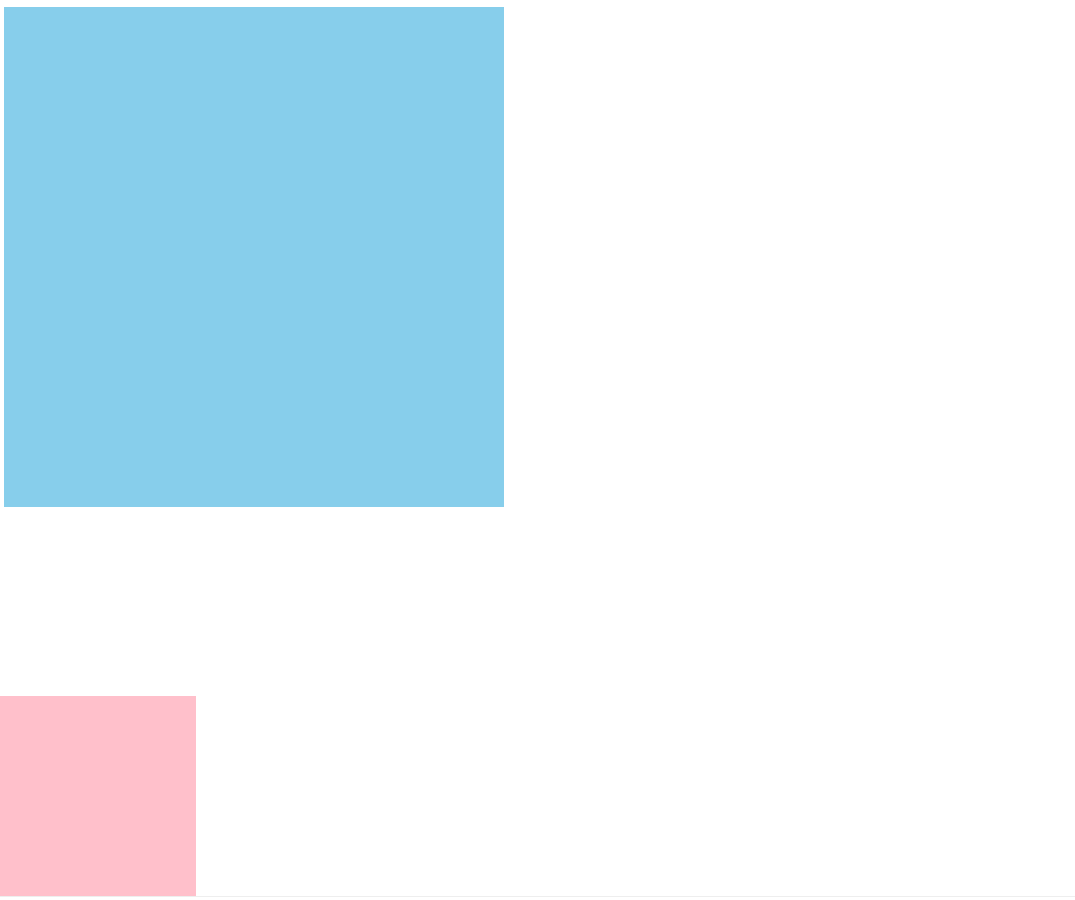
绝对定位-父级有定位:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>绝对定位-父级有定位</title>
<style>
.yeye {
position: relative;
width: 800px;
height: 800px;
background-color: hotpink;
padding: 50px;
}
.father {
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
.son {
position: absolute;
left: 30px;
bottom: 10px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="yeye">
<div class="father">
<div class="son"></div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

6、子绝父相的由来
-
子级是绝对定位的话,父级要用相对定位。-
子级绝对定位,不会占有位置,可以放到父盒子里面的任何一个地方,不会影响其他的兄弟盒子。
-
父盒子需要加定位限制子盒子在父盒子内显示。
-
父盒子布局时,需要占有位置,因此父亲只能是相对定位。
-
-
当然,子绝父相不是永远不变的,如果父元素不需要占有位置,子绝父绝也会遇到。
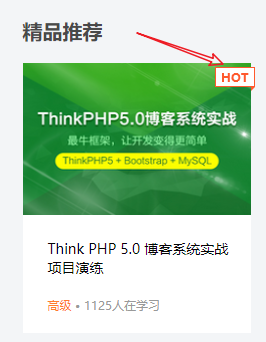
学成网综合案例加上hot
.box-bd ul li {
/* 子绝父相 */
position: relative;
float: left;
width: 228px;
height: 270px;
background-color: #fff;
margin-right: 15px;
margin-bottom: 15px;
}
.box-bd ul li > img {
width: 100%;
}
.box-bd ul li h4 {
margin: 20px 20px 20px 25px;
font-size: 14px;
color: #050505;
font-weight: 400;
}
.box-bd ul li em {
position: absolute;
top: 4px;
right: -4px;
}
<li>
<em>
<img src="images/hot.png" alt="">
</em>
<img src="images/pic.png" alt="">
<h4>
Think PHP 5.0 博客系统实战项目演练
</h4>
<div class="info">
<span>高级</span> • 1125人在学习
</div>
</li>
7、固定定位 fixed (重要)
固定定位是元素固定于浏览器可视区(浏览器显示内容的窗口)的位置。- 主要使用场景: 在浏览器页面滚动时元素的位置不变(广告栏之类)。
- 固定定位的特点:(务必记住)
- 以浏览器的可视窗口为参照点移动元素。跟父元素没有任何关系,不随滚动条滚动。
- 固定定位
不占有原先的位置。固定定位也是脱标的,其实固定定位也可以看做是一种特殊的绝对定位。
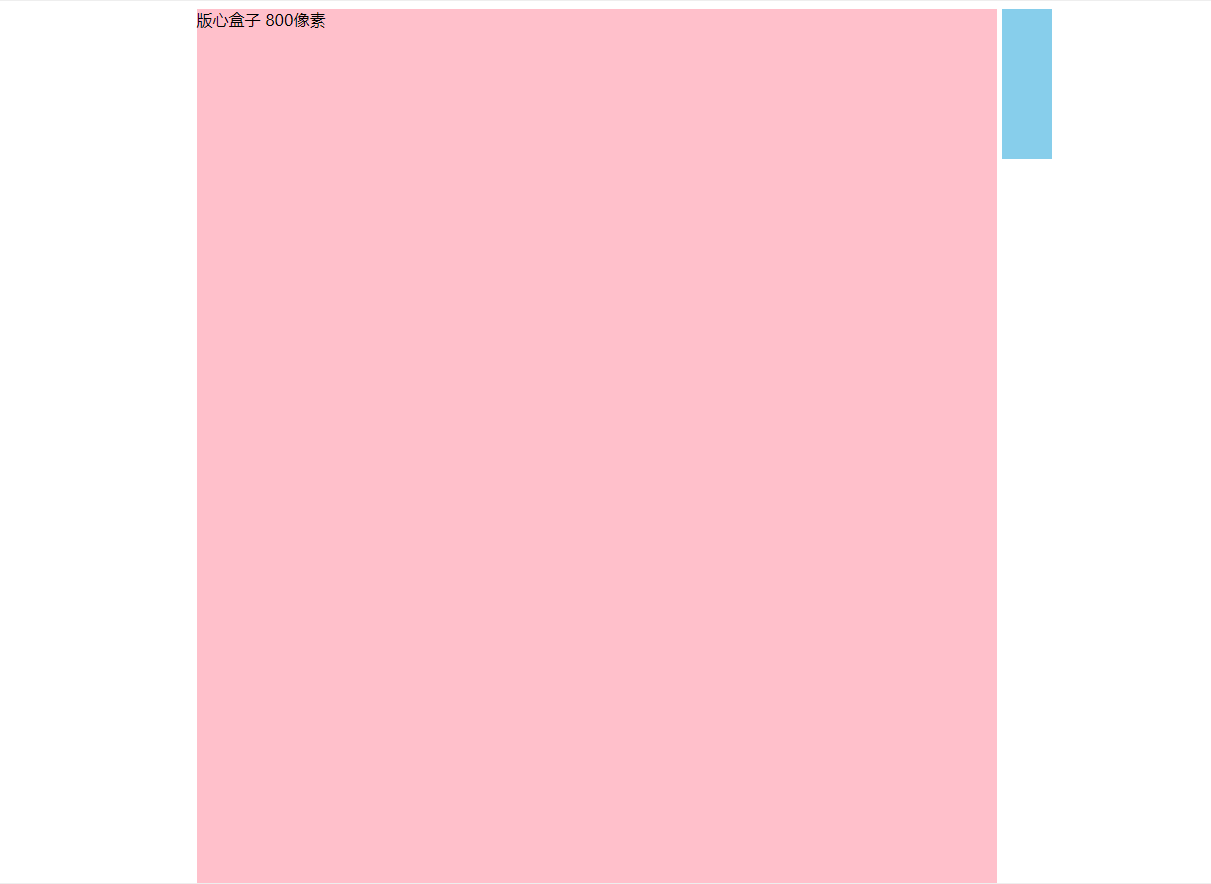
固定定位小技巧: 固定在版心右侧位置。- 让固定定位的盒子 left: 50%. 走到浏览器可视区(也可以看做版心) 的一半位置。
- 让固定定位的盒子 margin-left: 版心宽度的一半距离。多走版心宽度的一半位置就可以让固定定位的盒子贴着版心右侧对齐了。
固定定位案例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>固定定位</title>
<style>
.dj {
position: fixed;
top: 100px;
left: 40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="dj">
<img src="images/pvp.png" alt="">
</div>
<p>页面内容来衬托图片位置</p>
<p>页面内容来衬托图片位置</p>
<p>页面内容来衬托图片位置</p>
<p>页面内容来衬托图片位置</p>
<p>页面内容来衬托图片位置</p>
<p>页面内容来衬托图片位置</p>
<p>页面内容来衬托图片位置</p>
<p>页面内容来衬托图片位置</p>
<p>页面内容来衬托图片位置</p>
<p>页面内容来衬托图片位置</p>
<p>页面内容来衬托图片位置</p>
</body>
</html>

固定到版心右侧:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>固定定位小技巧-固定到版心右侧</title>
<style>
.w {
width: 800px;
height: 1400px;
background-color: pink;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.fixed {
position: fixed;
/* 1. 走浏览器宽度的一半 */
left: 50%;
/* 2. 利用margin 走版心盒子宽度的一半距离 */
margin-left: 405px;
width: 50px;
height: 150px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="fixed"></div>
<div class="w">版心盒子 800像素</div>
</body>
</html>
8、粘性定位 sticky(了解)
粘性定位可以被认为是相对定位和固定定位的混合。 Sticky 粘性的。- 粘性定位的特点:
- 以浏览器的可视窗口为参照点移动元素(固定定位特点)。
- 粘性定位
占有原先的位置(相对定位特点)。 - 必须添加 top 、left、right、bottom 其中一个才有效。
- 跟页面滚动搭配使用。 兼容性较差,IE 不支持。
案例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>粘性定位</title>
<style>
body {
height: 3000px;
}
.nav {
/* 粘性定位 */
position: sticky;
top: 0;
width: 800px;
height: 50px;
background-color: pink;
margin: 100px auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="nav">我是导航栏</div>
</body>
</html>
滚轮向下,内容保持不动。

9、 定位的总结
-
一定记住相对定位、固定定位、绝对定位两个大的特点:
-
是否占有位置(脱标否)
-
以谁为基准点移动位置。
-
-
学习定位重点学会子绝父相。
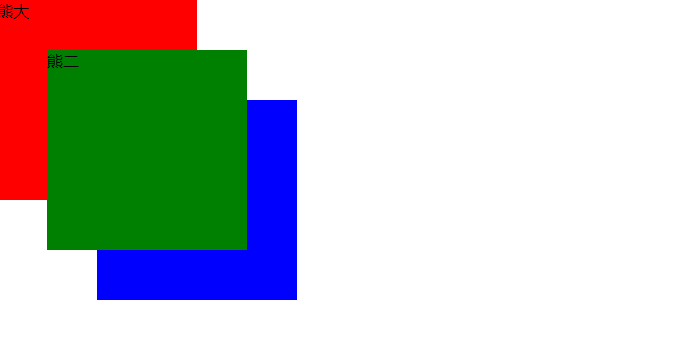
10、定位叠放次序 z-index
- 在使用定位布局时,可能会出现盒子重叠的情况。此时,可以使用
z-index来控制盒子的前后次序 (z轴)。 - 数值可以是正整数、负整数或 0, 默认是 auto,数值越大,盒子越靠上。
- 如果属性值相同,则按照书写顺序,后来居上。
- 数字后面
不能加单位。 - 只有
定位的盒子才有 z-index 属性。
选择器 { z-index: 1; }
案例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>定位的堆叠顺序</title>
<style>
.box {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
}
.xiongda {
background-color: red;
z-index: 1;
}
.xionger {
background-color: green;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
z-index: 2;
}
.qiangge {
background-color:blue;
left: 100px;
top: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box xiongda">熊大</div>
<div class="box xionger">熊二</div>
<div class="box qiangge">光头强</div>
</body>
</html>
11、绝对定位的盒子居中
- 加了绝对定位的盒子不能通过
margin:0 auto水平居中,但是可以通过以下计算方法实现水平和垂直居中。- left: 50%;:让盒子的左侧移动到父级元素的水平中心位置。
- margin-left: -100px;:让盒子向左移动自身宽度的一半。
案例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>绝对定位水平垂直居中</title>
<style>
.box {
position: absolute;
/* 1. left 走 50% 父容器宽度的一半 */
left: 50%;
/* 2. margin 负值 往左边走 自己盒子宽度的一半 */
margin-left: -100px;
top: 50%;
margin-top: -100px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
/* margin: auto; */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"></div>
</body>
</html>
12、定位元素特殊特性
-
绝对定位和固定定位也和浮动类似。
块级元素添加绝对或者固定定位,不设宽度或者高度,默认大小是内容的大小。
-
行内元素添加绝对或者固定定位,可以直接设置高度和宽度。
案例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>定位元素特殊特性</title>
<style>
div {
position: absolute;
background-color: skyblue;
}
span {
position: absolute;
top: 300px;
width: 200px;
height: 150px;
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>abcd</div>
<span>123</span>
</body>
</html>
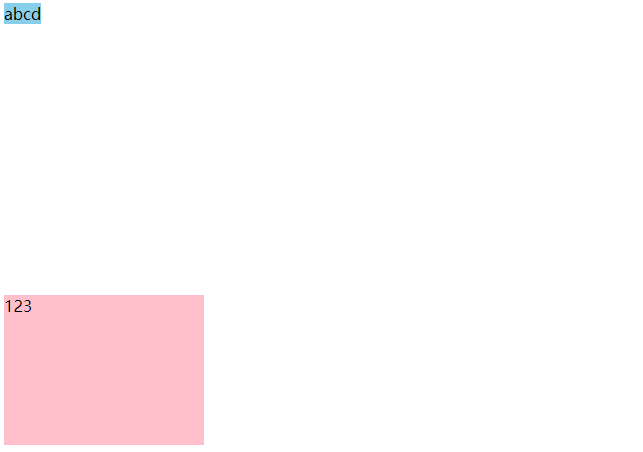
13、脱标盒子不会外边距塌陷
- 浮动元素、绝对定位(固定定位)元素的都不会触发外边距合并的问题。
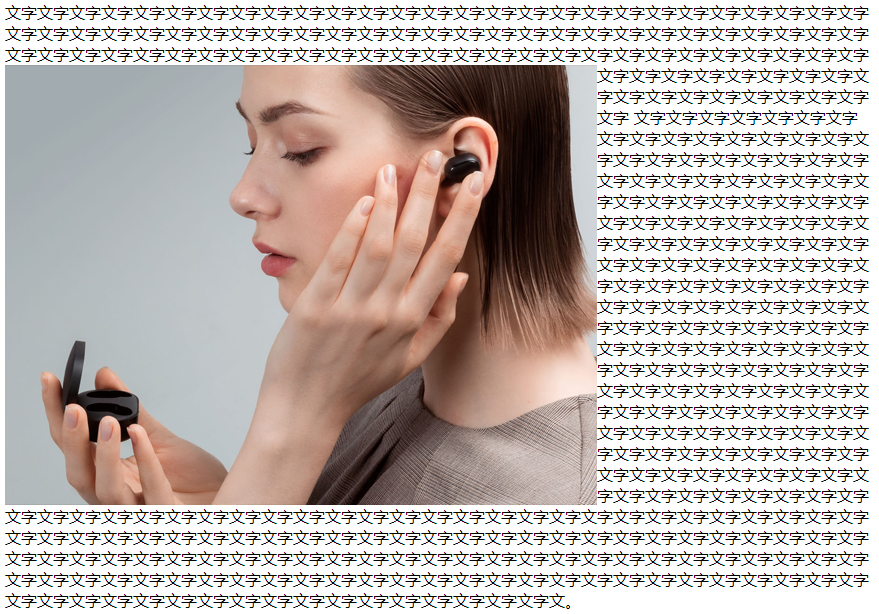
14、绝对定位和浮动的区别
浮动元素不同,只会压住它下面标准流的盒子,但是不会压住下面标准流盒子里面的文字(图片)。- 但是
绝对定位(固定定位)会压住下面标准流所有的内容。 浮动之所以不会压住文字,因为浮动产生的目的最初是为了做文字环绕效果的。 文字会围绕浮动元素。
浮动产生原来的目的是做文字环绕效果案例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>浮动产生原来的目的是做文字环绕效果</title>
<style>
img {
float: left;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文<img src="images/img.jpg" alt="">字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字 文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文字文。
</body>
</html>

绝对定位会完全压住标准流盒子内容案例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>绝对定位会完全压住标准流盒子内容</title>
<style>
.box {
/* 1.浮动的元素不会压住下面标准流的文字 */
/* float: left; */
/* 2. 绝对定位(固定定位) 会压住下面标准流所有的内容。 */
position: absolute;
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"></div>
<p>阁下何不同风起,扶摇直上九万里</p>
</body>
</html>

15、综合案例–轮播图

(1)布局制作
-
大盒子我们类名为 tb-promo 淘宝广告。
-
里面先放一张图片。
-
左右两个按钮 用链接就好了。 左箭头 prev 右箭头 next 。
-
底侧小圆点用ul 做。 类名为 promo-nav 。
(2)代码实现
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>淘宝轮播图</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
li {
list-style: none;
}
.tb-promo {
position: relative;
width: 520px;
height: 280px;
background-color: pink;
margin: 100px auto;
}
.tb-promo img {
width: 520px;
height: 280px;
}
/* 并集选择器可以集体声明相同的样式 */
.prev,
.next {
position: absolute;
/* 绝对定位的盒子垂直居中 */
top: 50%;
margin-top: -15px;
/* 加了绝对定位的盒子可以直接设置高度和宽度 */
width: 20px;
height: 30px;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, .3);
text-align: center;
line-height: 30px;
color: #fff;
text-decoration: none;
}
.prev {
left: 0;
/* border-radius: 15px; */
border-top-right-radius: 15px;
border-bottom-right-radius: 15px;
}
.next {
/* 如果一个盒子既有left属性也有right属性,则默认会执行 left属性 同理 top bottom 会执行 top */
right: 0;
/* border-radius: 15px; */
border-top-left-radius: 15px;
border-bottom-left-radius: 15px;
}
.promo-nav {
position: absolute;
bottom: 15px;
left: 50%;
margin-left: -35px;
width: 70px;
height: 13px;
/* background-color: pink; */
background: rgba(255,255,255, .3);
border-radius: 7px;
}
.promo-nav li {
float: left;
width: 8px;
height: 8px;
background-color: #fff;
border-radius: 50%;
margin: 3px;
}
/* 不要忘记选择器权重的问题 */
.promo-nav .selected {
background-color: #ff5000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="tb-promo">
<img src="images/tb.jpg" alt="">
<!-- 左侧按钮箭头 -->
<a href="#" class="prev"> < </a>
<!-- 右侧按钮箭头 -->
<a href="#" class="next"> > </a>
<!-- 小圆点 -->
<ul class="promo-nav">
<li class="selected"></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>

16、网页布局总结
- 通过盒子模型,清楚知道大部分html标签是一个盒子。
- 一个完整的网页,是标准流、浮动、定位一起完成布局的,每个都有自己的专门用法。
- 标准流:可以让盒子上下排列或者左右排列,
垂直的块级盒子显示就用标准流布局。 - 浮动:可以让多个块级元素一行显示或者左右对齐盒子,
多个块级盒子水平显示就用浮动布局。 - 定位:定位最大的特点是有层叠的概念,就是可以让多个盒子前后叠压来显示。
如果元素自由在某个盒子内移动就用定位布局。