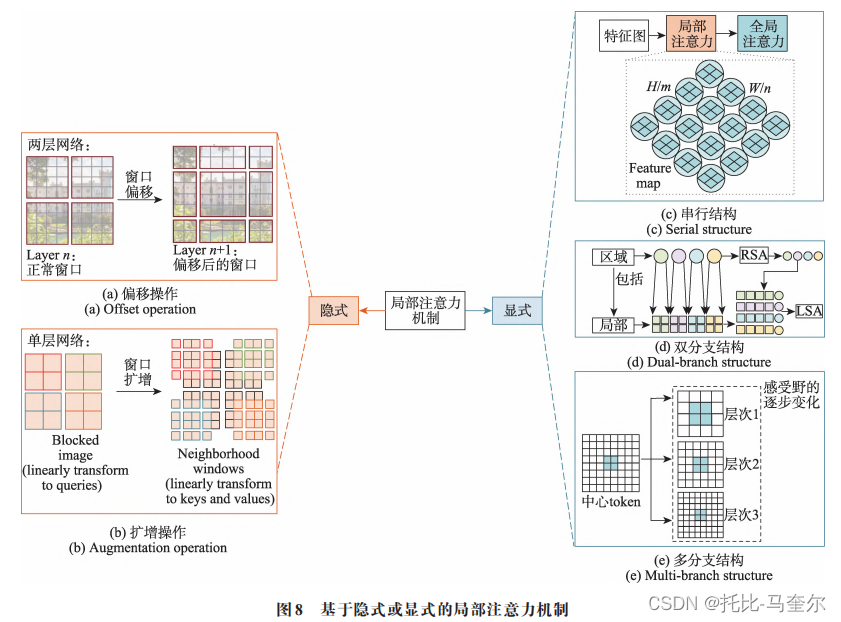
系列文章目录
手写SpringBoot(一)之简易版SpringBoot
手写SpringBoot(二)之动态切换Servlet容器
手写SpringBoot(二)之动态切换Servlet容器
文章目录
- 系列文章目录
- 手写SpringBoot(二)之动态切换Servlet容器
本节着重介绍@ConditionOnClass的由来
我们在切换serlvet容器的时候,会将SpringBoot默认的tomcat jar包给排除掉,换上我们需要的jar包,比如jetty。如下图所示
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>cn.axj</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-base</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<artifactId>user-service</artifactId>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.axj</groupId>
<artifactId>my-spring-boot</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-core</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.eclipse.jetty</groupId>
<artifactId>jetty-server</artifactId>
<version>9.4.43.v20210629</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
实现思路:
- 定义一个WebServer顶层接口
- 将tomcat和jetty的实现类加载到容器中,并根据条件判断,动态加载tomcat或者jetty的实现类
- 在servlet容器启动前动态获取WebServer,并通过WebServer启动
定义webServer
package cn.axj.springboot.my.web.container;
public interface WebServer {
void start(WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext);
}
实现WebServer
package cn.axj.springboot.my.web.container;
public class TomcatWebServer implements WebServer{
@Override
public void start(WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext) {
}
}
package cn.axj.springboot.my.web.container;
public class JettyWebServer implements WebServer{
@Override
public void start(WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext) {
}
}
定义WebServerAutoConfiguration类
package cn.axj.springboot.my.config;
import cn.axj.springboot.my.annnotation.MyConditionalOnClass;
import cn.axj.springboot.my.web.container.JettyWebServer;
import cn.axj.springboot.my.web.container.TomcatWebServer;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class WebServerAutoConfiguration {
/**
* 根据jar包是否有 org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat类来判断是否加载tomcatServer
* @return
*/
@Bean
@MyConditionalOnClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat")
public TomcatWebServer tomcatWebServer() {
return new TomcatWebServer();
}
/**
* 根据jar包是否有 org.eclipse.jetty.server.Server类来判断是否加载jettyServer
* @return
*/
@Bean
@MyConditionalOnClass("org.eclipse.jetty.server.Server")
public JettyWebServer jettyWebServer(){
return new JettyWebServer();
}
}
如何实现动态加载?
- 定义MyConditionalOnClass注解
- 利用Spring的@Conditional注解标记
- 定义Conditional条件判断类
定义MyConditionalOnClass注解,利用@Conditional注解定义动态加载逻辑
@Conditional源码如下,内部有一个Class对象需要实现Condition接口
public @interface Conditional {
Class<? extends Condition>[] value();
}
@Conditional(MyClassCondition.class) 逻辑是通过Condition接口里面的matches方法动态判断
package cn.axj.springboot.my.annnotation;
import cn.axj.springboot.my.condition.MyClassCondition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
@Conditional(MyClassCondition.class)
public @interface MyConditionalOnClass {
String value();
}
MyClassConditional如下
package cn.axj.springboot.my.condition;
import cn.axj.springboot.my.annnotation.MyConditionalOnClass;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Condition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* 定义一个自定义的条件类
* 该类主要用于根据条件动态加载Bean
**/
public class MyClassCondition implements Condition {
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
Map<String, Object> annotationAttributes = metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(MyConditionalOnClass.class.getName());
/**
* 获取{@link MyConditionalOnClass}注解中的属性值
* 例如:@MyConditionalOnClass(value = "com.example.MyBean")
* 则可以通过annotationAttributes.get("value")获取到"com.example.MyBean"
*/
String className = (String) annotationAttributes.get("value");
try {
Objects.requireNonNull(context.getClassLoader()).loadClass(className);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
//没有找到该类,则返回false
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
总体实现逻辑,由Spring提供的@Conditional条件注解动态加载bean机制,
- 封装@ConditionOnClass注解,并将@Conditional注解组合到该注解上面,@conditionOnClass的核心就是@Condition
- 通过定义value属性,来暴力传参,将tomcat或者jetty的核心类名传到Condition接口的matches方法下
- 通过Condition的matches方法匹配是否加载该bean
至此已实现在Spring中动态加载WebServer,在MyApplication.run方法中,从Spring容器中获取WebServer对象,并开启WebServer
public static void run(Class<?> clazz,String[] args) {
//启动Spring容器
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
annotationConfigApplicationContext.register(clazz);
annotationConfigApplicationContext.refresh();
//启动tomcat容器
WebServer webServer = getWebServer(annotationConfigApplicationContext);
webServer.start();
}
private static WebServer getWebServer(AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext) {
Map<String, WebServer> webServerMap = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBeansOfType(WebServer.class);
if(webServerMap.isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("web server is null");
}
if(webServerMap.size() > 1){
throw new RuntimeException("找到多个web server,只能有一个WebServer" + webServerMap.values());
}
return webServerMap.values().stream().findFirst().get();
}
至此,项目结构如下图

WebContainer已废弃
启动user-service模块,抛出异常
Exception in thread "main" org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'cn.axj.springboot.my.web.container.WebServer' available
由于Spring容器中不存在WebServer对象,这是为什么?
在 WebServerAutoConfiguration 中定义的WebServer两个对象不会被Spring扫描到,因为在@MySpringBootApplication中配置的@ComponentScan扫描的包路径并不包括my-spring-boot中的路径。所以不会被Spring容器扫描到,自然不会加载到容器中。
解决办法,
- 在UserApplication中使用
@Import(WebServerAutoConfiguration.class)将WebServerAutoConfiguration 配置类加载到Spring的Configuration中。但是这样对于用户来说,不太美好。 - 将
@Import(WebServerAutoConfiguration.class)加载到@MySpringbootApplication注解上,这样Spring在扫描该组合注解的时候,会扫描到Import标签,并将WebServerAutoConfiguration配置类解析并加载到容器中。
最后,实现TomcatWebServer和JettyWebServer的start()方法
tomcat
package cn.axj.springboot.my.web.container;
import org.apache.catalina.*;
import org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector;
import org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext;
import org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine;
import org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHost;
import org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet;
public class TomcatWebServer implements WebServer{
@Override
public void start(WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext) {
System.out.println("启动TomcatWeb容器");
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
Server server = tomcat.getServer();
Service service = server.findService("Tomcat");
Connector connector = new Connector();
connector.setPort(8080);
StandardEngine engine = new StandardEngine();
engine.setDefaultHost("localhost");
Host host = new StandardHost();
host.setName("localhost");
String contextPath = "";
Context context = new StandardContext();
context.setPath(contextPath);
context.addLifecycleListener(new Tomcat.FixContextListener());
host.addChild(context);
engine.addChild(host);
service.setContainer(engine);
service.addConnector(connector);
//配置dispatcherServlet,Springmvc专属
tomcat.addServlet(contextPath,"dispatcher",new DispatcherServlet(webApplicationContext));
context.addServletMappingDecoded("/*","dispatcher");
try {
tomcat.start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
jetty
这里先留个坑,这里实现应该不是由SpringBoot去实现。想一想,SpringBoot不可能将所有serlvet容器的jar包都引入,如果不引入,没有这个jar包如何实现?这里应该是由各servlet去适配。所以SpringBoot只需提供接口。