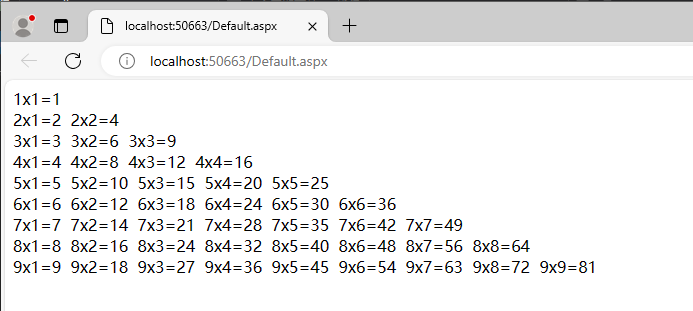
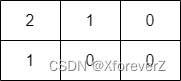
一、深入理解递归

二、递归vs迭代

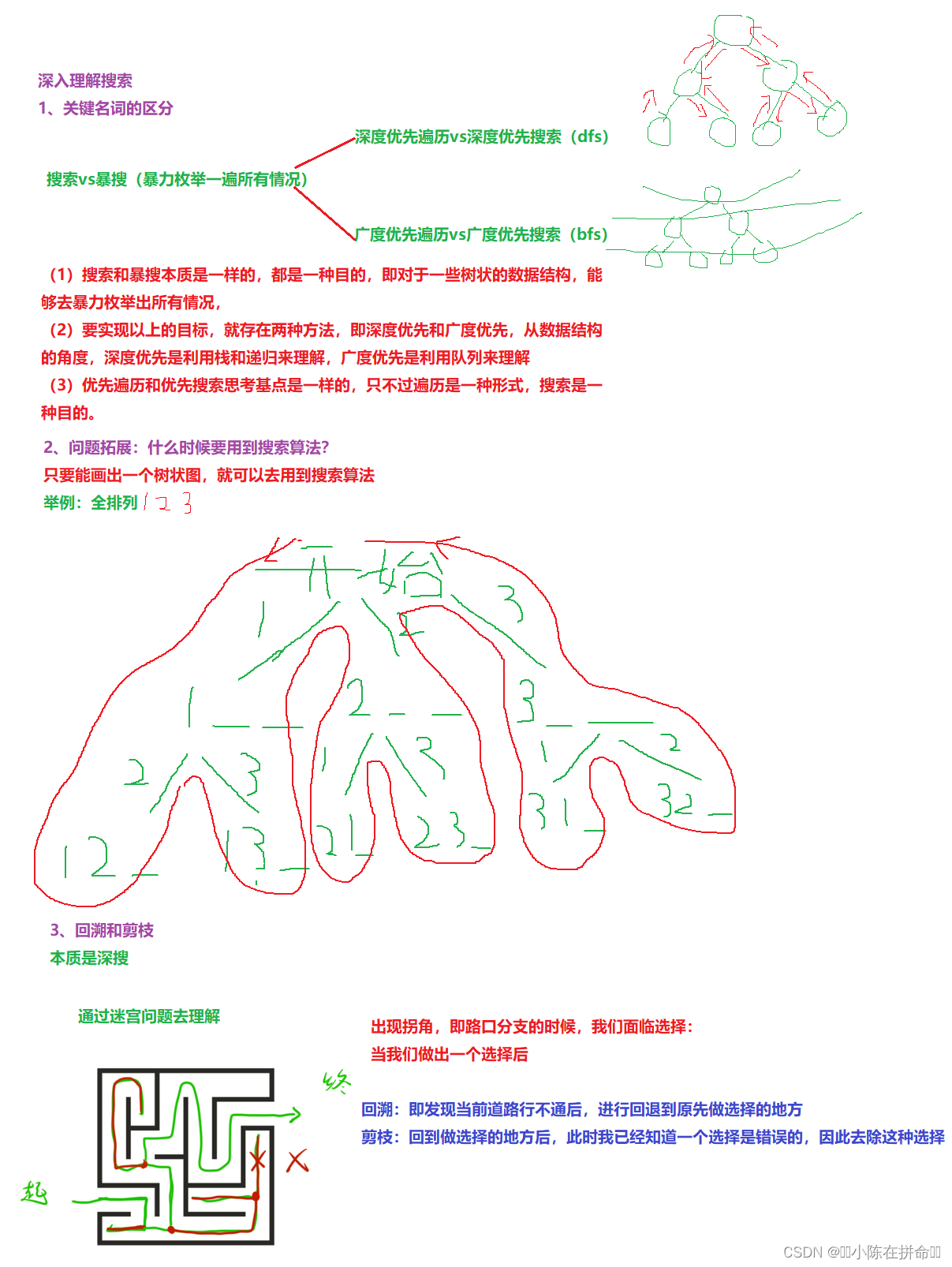
三、深入理解搜索、回溯和剪枝
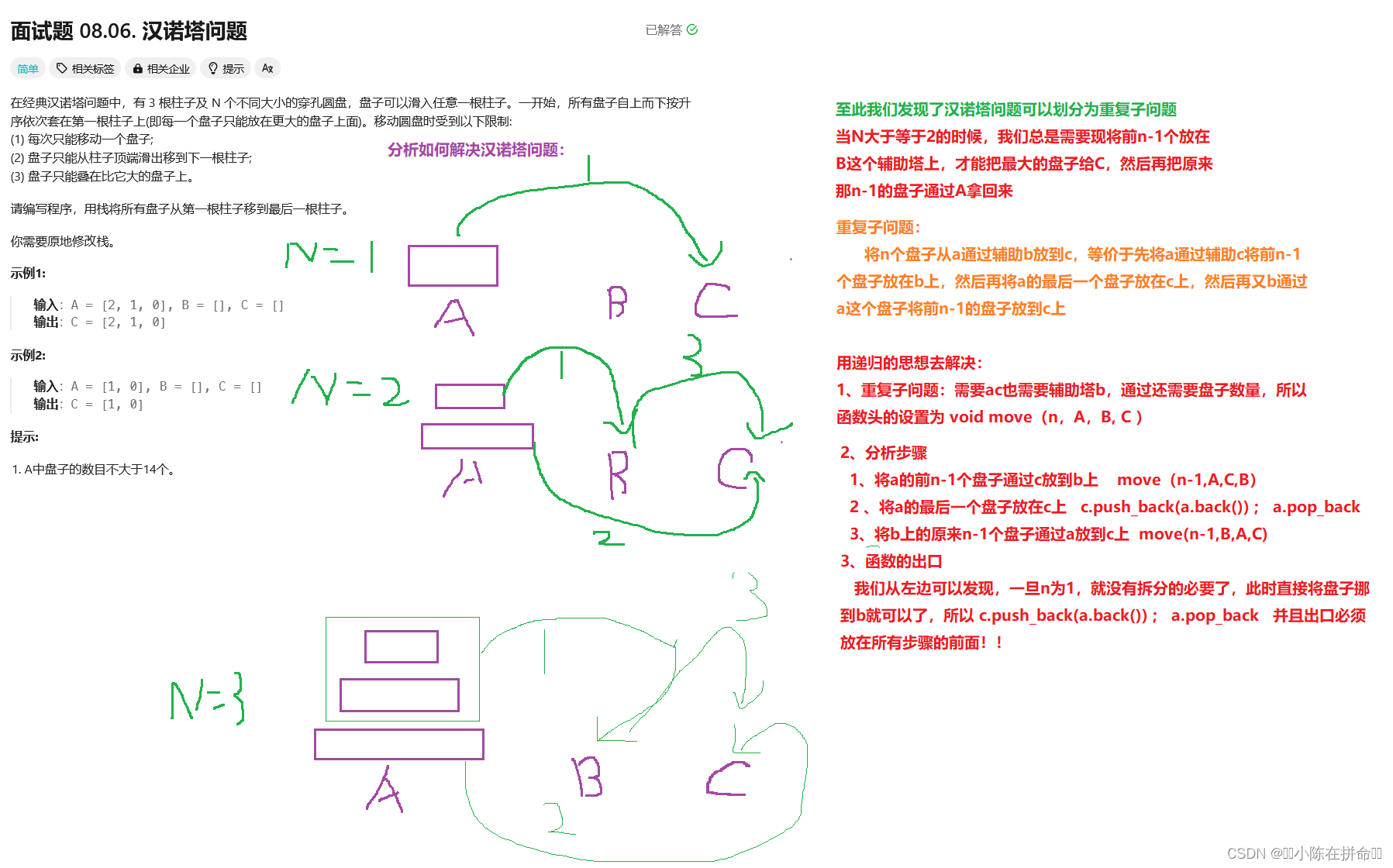
四、汉诺塔问题
. - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:
//笔试题,不讲武德,C=A
void move(int n,vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B, vector<int>& C)//实现从a经过b这个辅助盘子移到c
{
//设置函数出口
if(n==1) //此时不能再分割子问题了 直接给C即可
{
C.push_back(A.back());
A.pop_back();
return;
}
//先把a的前n-1个通过c移到b
move(n-1,A,C,B);
//然后将A的最后一个盘子移到C上
C.push_back(A.back());
A.pop_back();
//然后将b上的n-1个盘子通过A移到c
move(n-1,B,A,C);
}
void hanota(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B, vector<int>& C)
{
int n=A.size();
return move(n,A,B,C);
}
};五、合并两个有效链表
. - 力扣(LeetCode)

class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2)
{
if(list1==nullptr) return list2;
else if(list2==nullptr) return list1;
else if(list1->val<list2->val) {list1->next=mergeTwoLists(list1->next,list2);return list1;}
else {list2->next=mergeTwoLists(list2->next,list1);return list2;}
}
};六、反转链表
. - 力扣(LeetCode)

class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head)
{
if(head==nullptr||head->next==nullptr) return head;;
ListNode*ret=reverseList(head->next);
head->next->next=head;
head->next=nullptr;
return ret;
}
};七、两两交换链表
. - 力扣(LeetCode)
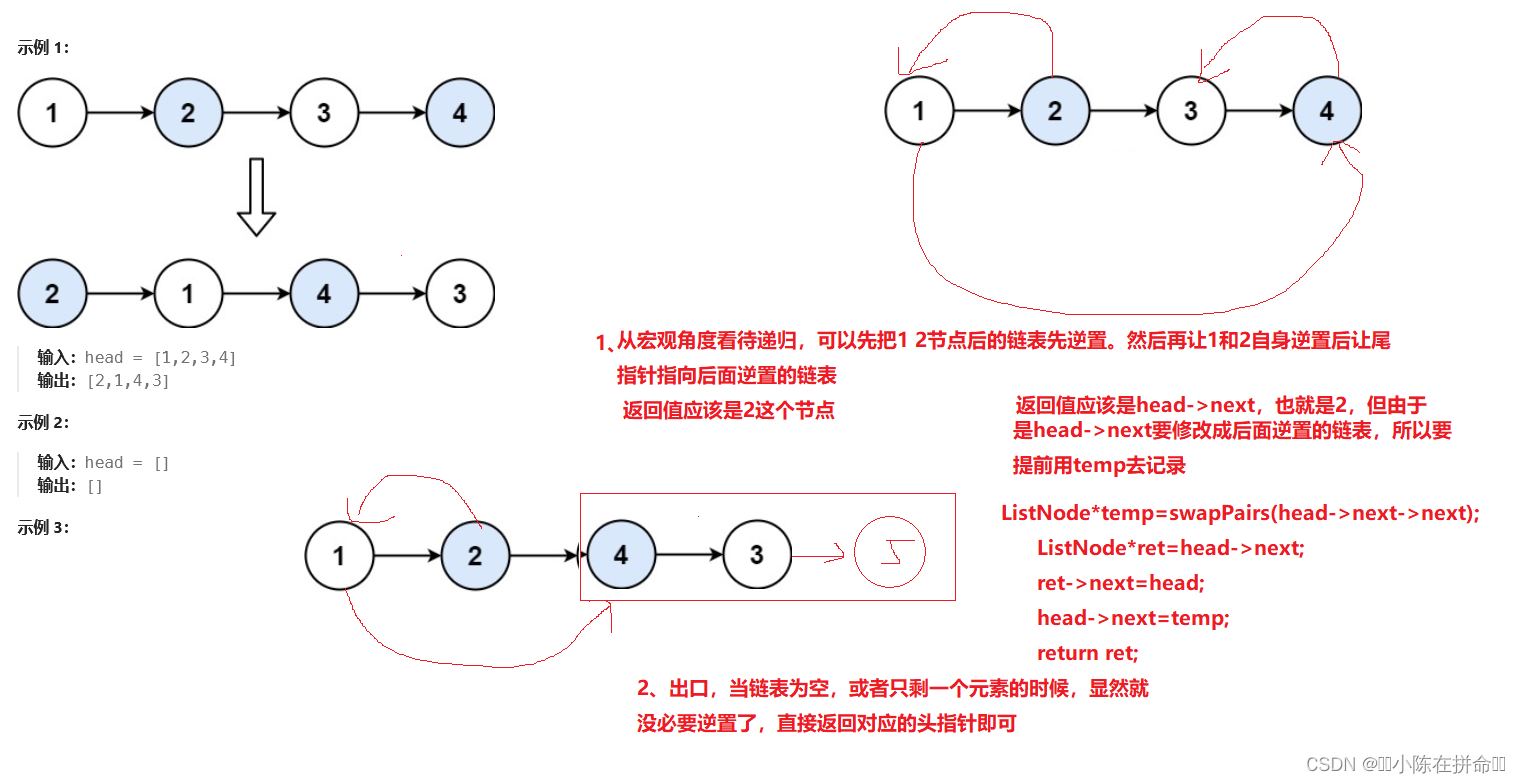
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head)
{
if(head==nullptr||head->next==nullptr) return head;
ListNode*temp=swapPairs(head->next->next);
ListNode*ret=head->next;
ret->next=head;
head->next=temp;
return ret;
}
};八、快速幂
. - 力扣(LeetCode)

1、迭代
class Solution {
public:
double myPow(double x, long long n) //修改参数,将传进来的值都转化成;long long 类型,避免溢出
{
if(n==0) return 1;
if(n<0) return myPow(1/x,-n) ;
double ans=1.0;
while(n)
{
if(n&1) ans*=x;//说明最低位为1,要乘以x
x*=x;
n>>=1;
}
return ans;
}
};2、递归
class Solution {
public:
double myPow(double x, long long n) //修改参数,将传进来的值都转化成;long long 类型,避免溢出
{
if(n==0) return 1;
if(n<0) return 1/myPow(x,-n);
double temp=myPow(x,n/2);//快速计算前一半的结果
return n%2==0?temp*temp:temp*temp*x;
}
};