文章目录
- 1.迭代局部搜索(ILS)
- 2.用ILS解决TSP问题
- 2.1 函数模块
- 2.2 主函数
- 2.3 berlin52数据集测试
1.迭代局部搜索(ILS)
关于迭代局部搜索(ILS iterated local search)的框架和应用总结可以阅读文献Iterated Local Search: Framework and Applications
ILS的核心思想:找到一个局部最优解后,对当前解增加一个扰动,得到新解,从新解基础上再进行局部搜索找到新的局部最优。通过迭代不停的找到新的局部最优比较从而找到全局最优,避免的局部搜索容易陷入局部最优的缺点。

算法步骤如下:
- 生成初始解s(0)
- 对s0进行局部搜索得到一个局部最优解s*
- 循环以下过程直到迭代结束条件满足
- 对当前局部最优解s*进行扰动生成新解s’
- 对新解s’尽心局部搜索得到新的局部最优解s*’
- 判断是否接受新的局部最优解s*’
实现迭代局部搜索只需要写四个函数,生成初始解GenerateInitialSolution,局部搜索LocalSearch,扰动函数Perturbation,判断接收新解AcceptanceCriterion。这四个函数的设计方法都会影响最后的搜索解,不同的问题要针对性设计

2.用ILS解决TSP问题
2.1 函数模块
- 局部搜索方法
目前求解TSP的局部搜索方法比较好的是k-opt方法,在本人博客Discrete Optimization课程笔记(3)—局部搜索中的Case5:Traveling Salesman Problem(k-opt)有具体描述,此处代码使用2-opt
import numpy as np
import math
class Local2opt(object):
def __init__(self, points, init):
self.points = points
self.num_point = len(points)
self.init_path = init
self.best_path = []
self.best_dist = 0
def update(self, path, dist):
self.best_path = path
self.best_dist = dist
return self.best_path, self.best_dist
def two_opt(self, improvement_threshold=0.001):
self.best_path = self.init_path
self.best_dist = self.calculate_dist(self.best_path)
improvement_factor = 1
while improvement_factor > improvement_threshold:
pre_best = self.best_dist
for one in range(1, self.num_point - 2):
for two in range(one + 1, self.num_point - 1):
one_first_point = self.points[self.best_path[one - 1]]
one_end_point = self.points[self.best_path[one]]
two_first_point = self.points[self.best_path[two]]
two_end_point = self.points[self.best_path[two + 1]]
before = self.length(one_first_point, one_end_point) + self.length(two_first_point, two_end_point)
after = self.length(one_first_point, two_first_point) + self.length(one_end_point, two_end_point)
if after < before:
new_path = self.swap(self.best_path, one, two)
new_dist = self.best_dist + after - before
self.update(new_path, new_dist)
improvement_factor = 1 - self.best_dist / pre_best
return self.best_path, self.best_dist
def calculate_dist(self, path):
path_dist = 0
for i in range(len(path) - 1):
point1 = self.points[path[i]]
point2 = self.points[path[i+1]]
path_dist += self.length(point1, point2)
path_dist += self.length(self.points[path[-1]], self.points[path[0]])
return path_dist
def valid(self, path):
return (len(set(path)) == self.num_point) and (sorted(path) == list(range(self.num_point)))
@staticmethod
def swap(path, one, two):
a = np.concatenate((path[0:one], path[two:-len(path) + one - 1:-1], path[two + 1:])).astype(int)
return a.tolist()
@staticmethod
def length(point1, point2):
return math.sqrt((point1.x - point2.x) ** 2 + (point1.y - point2.y) ** 2)
- 扰动函数
用double-bridge move的方法,即将序列分成四段重组
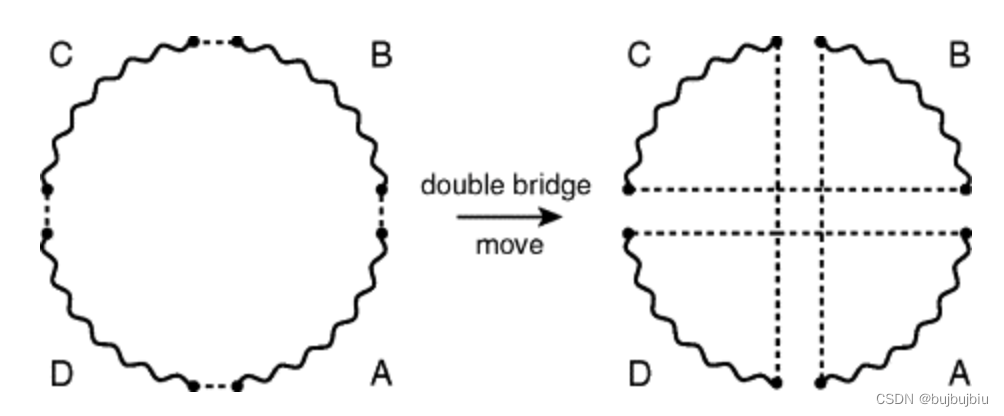
def perturb(path):
index = len(path) // 4
part_one = 1 + random.randint(0, index)
part_two = part_one + 1 + random.randint(0, index)
part_three = part_two + 1 + random.randint(0, index)
return path[:part_one] + path[part_three:] + path[part_two:part_three] + path[part_one:part_two]
- 判断接收新解
此处设置如果值更优,则接受新解,当然还有很多其它接受标准
- 生成初始解:随机生成
def generate_initial_solution(node_count):
return np.random.permutation(node_count)
2.2 主函数
确定好各个函数模块后,按照前面的算法步骤实现迭代局部搜索,max_search为最大迭代次数
def iterated_local_search(node_count, points, max_search):
init_path = generate_initial_solution(node_count)
opt = Local2opt(points, init_path)
best_path, best_dist = opt.two_opt()
for i in range(max_search):
current_path = perturb(best_path)
opt = Local2opt(points, current_path)
new_path, new_dist = opt.two_opt()
if new_dist < best_dist:
best_path = new_path
best_dist = new_dist
if i % 50 == 0:
print(f'number {i}, best:{best_dist}, new:{new_dist}')
return best_path, best_dist
2.3 berlin52数据集测试
首先读取数据,获取每个点的坐标,用namedtuple方式存储更方便
from collections import namedtuple
Point = namedtuple('Point', ['index', 'x', 'y'])
def read(path):
with open(path, 'r') as file:
data = file.read()
lines = data.split('\n')
node_count = int(lines[0])
points = []
for i in range(1, node_count + 1):
line = lines[i]
part = line.split()
points.append(Point(int(part[0]), float(part[1]), float(part[2])))
return node_count, points
运行主函数,获取迭代结果,绘制图像
def plot(path, points):
for i in range(len(path)-1):
node1 = path[i]
node2 = path[i + 1]
plt.plot([points[node1].x, points[node2].x], [points[node1].y, points[node2].y], c='r')
plt.scatter(points[node1].x, points[node1].y, c='black')
plt.plot([points[path[-1]].x, points[path[0]].x], [points[path[-1]].y, points[path[0]].y], c='r')
plt.scatter(points[path[-1]].x, points[path[-1]].y, c='black')
plt.show()
node_count, points = read('./berlin52.txt')
path, dist = iterated_local_search(node_count, points, 700)
plot(p, points)
迭代结果如下:berlin52求解器最优解为7542,此处最优解为7544,几乎最优
number 0, best:8619.660498923475, new:8619.660498923475
number 50, best:7778.703948691556, new:7778.703948691556
number 100, best:7778.703948691556, new:8287.326075493342
number 150, best:7721.773954616386, new:8401.535472141499
number 200, best:7588.382511657728, new:7957.109605398081
number 250, best:7580.155850970664, new:8034.869737864365
number 300, best:7580.155850970664, new:8224.925876727228
number 350, best:7580.155850970664, new:8108.147967255095
number 400, best:7580.155850970664, new:8227.789379075848
number 450, best:7580.155850970664, new:8206.208800876693
number 500, best:7580.155850970664, new:8014.874253178536
number 550, best:7566.832820859449, new:8496.26795729865
number 600, best:7544.365901904087, new:8390.292579324512
number 650, best:7544.365901904087, new:8113.830524951099
7544.365901904087 [38, 35, 34, 33, 43, 45, 15, 28, 49, 19, 22, 29, 1, 6, 41, 20, 16, 2, 17, 30, 21, 0, 48, 31, 44, 18, 40, 7, 8, 9, 42, 32, 50, 10, 51, 13, 12, 46, 25, 26, 27, 11, 24, 3, 5, 14, 4, 23, 47, 37, 36, 39]
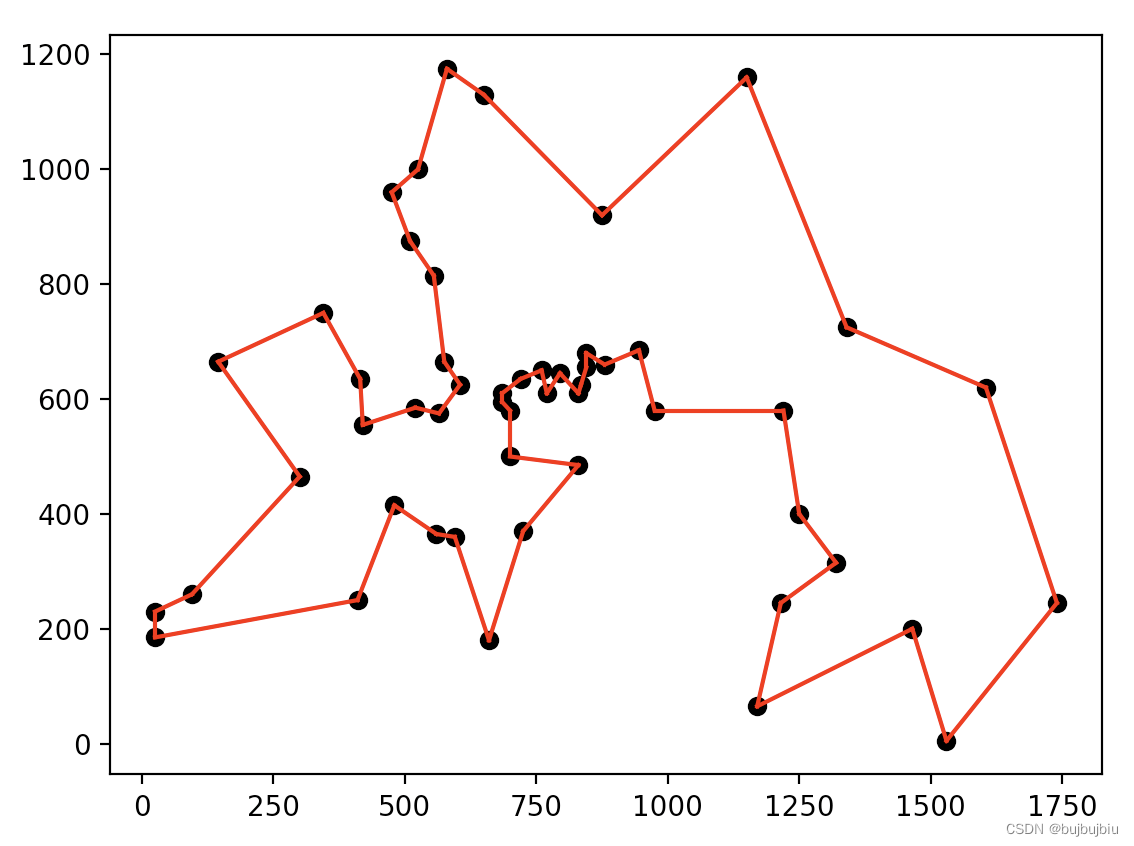
事实上,由于生成初始解时没有固定随机种子,因此每次运行结果都不同,有好有坏,后续可以改进四个重要的函数模块,让迭代过程更稳定。完整数据和代码见本人github
local-search-for-TSP

![LeetCode[373]查找和最小的K对数字](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/6a97303eaaaa4f4997fd504504638703.png)