前言
map是golang中常用的一个基本数据结构,继上篇的channel源码学习之后,本文学习map的源码相关。
基础知识点
此部分参考自 https://www.zhihu.com/tardis/zm/art/423008350?source_id=1003
map的用法
通过make初始化分配容量,通过m[key] = value进行设置。
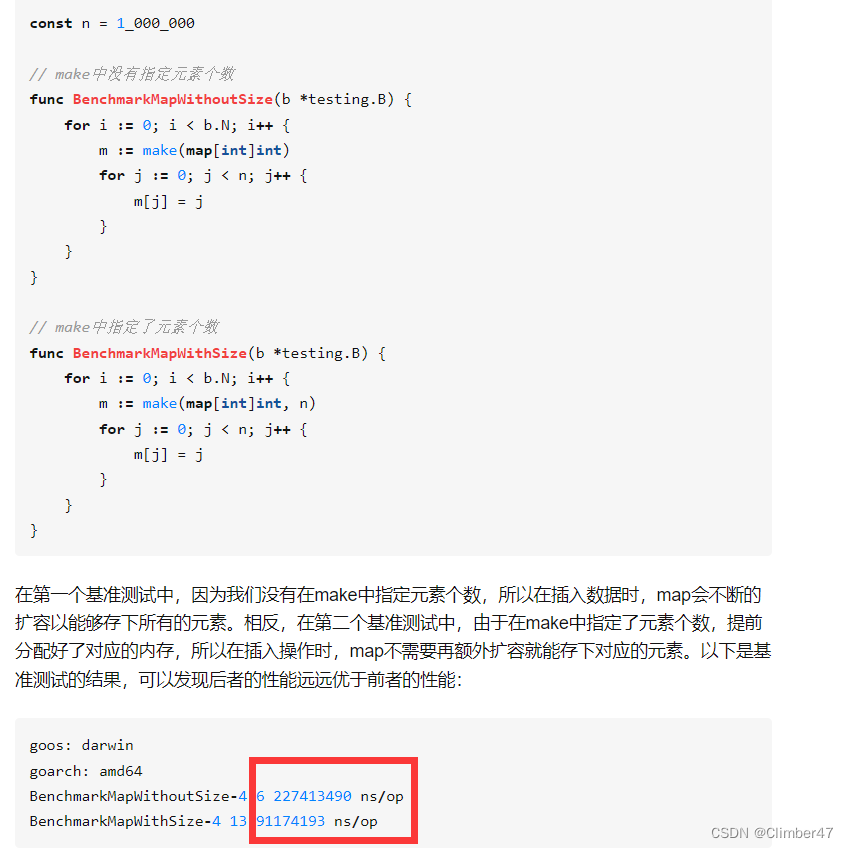
map初始化时为什么要关注容量
容量不够时候就需要涉及到扩容,所以一次分配够了,减少扩容次数,提高性能。
demo:
提升了两倍多的性能。
遍历时的无序性
具体自己先前文章中写过
对于map的操作
具体来说,就是边遍历边新增/删除。删除了的不可能再遍历到,新增的可能再遍历到(不一定)。
原因:map内部实现是一个链式hash表,为了保证无顺序,初始化时会随机一个遍历开始的位置,所以新增的元素被遍历到就变的不确定了,同样删除也是一个道理,但是删除元素后边就不会出现,所以一定不会被遍历到。
另一个点是,他随机并不是完全等概率的随机,第一个元素被选中的概率更高一些。
nil-map的写入操作会引发panic
扩容是在已申请的容量不够用时候,会触发。
但是直接0个容量,没有初始化。那就直接panic了。
map并发安全吗?不安全!
可以使用REMutex或者sync.Map去实现并发安全的map。
底层结构-源码
源码位于src\runtime\map.go中
源码
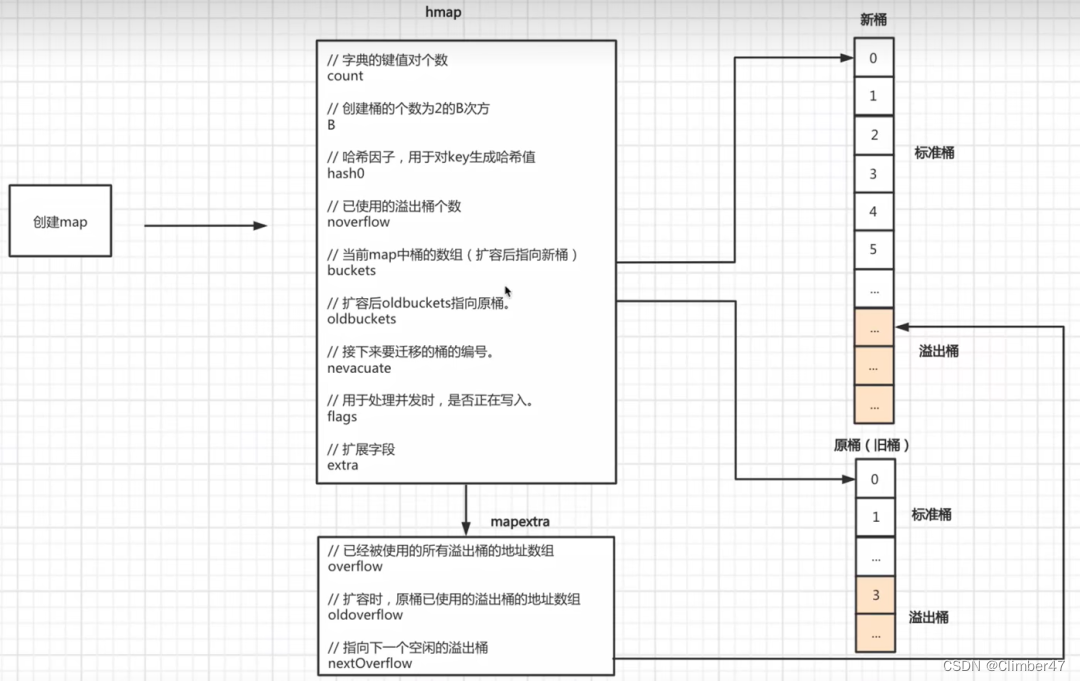
map底层是一个hmap,其中内容:
// A header for a Go map.
type hmap struct {
// Note: the format of the hmap is also encoded in cmd/compile/internal/reflectdata/reflect.go.
// Make sure this stays in sync with the compiler's definition.
count int // # live cells == size of map. Must be first (used by len() builtin)
flags uint8
B uint8 // log_2 of # of buckets (can hold up to loadFactor * 2^B items)
noverflow uint16 // approximate number of overflow buckets; see incrnoverflow for details
hash0 uint32 // hash seed
buckets unsafe.Pointer // array of 2^B Buckets. may be nil if count==0.
oldbuckets unsafe.Pointer // previous bucket array of half the size, non-nil only when growing
nevacuate uintptr // progress counter for evacuation (buckets less than this have been evacuated)
extra *mapextra // optional fields
}
含义:
count:map的当前长度,用len(m)输出的就是。
(可以理解为喝slice那边一样,一个len 一个cap)
B:和桶的多少相关,2^B = 桶的个数。
noverflow:表示近似溢出桶的数量。
hash0:哈希因子。
buckets unsafe.Pointer // array of 2^B Buckets. may be nil if count==0.
oldbuckets unsafe.Pointer // previous bucket array of half the size, non-nil only when growing
之后这两个对应的是hash桶,其中一个是扩容时候所用的。
提高效率的几处精妙设计
key hash值的后B位作为桶index查找桶
key hash值的前8位作为桶内结构体的三个数组(tophash,key,value)的index
桶结构体的tophash复用,既作为tophash使用,也作为标志位使用
灵活的扩容机制
工作流程-源码
创建
通过makemap函数进行创建。
// makemap implements Go map creation for make(map[k]v, hint).
// If the compiler has determined that the map or the first bucket
// can be created on the stack, h and/or bucket may be non-nil.
// If h != nil, the map can be created directly in h.
// If h.buckets != nil, bucket pointed to can be used as the first bucket.
func makemap(t *maptype, hint int, h *hmap) *hmap {
mem, overflow := math.MulUintptr(uintptr(hint), t.Bucket.Size_)
if overflow || mem > maxAlloc {
hint = 0
}
// initialize Hmap
if h == nil {
h = new(hmap)
}
h.hash0 = fastrand()
// Find the size parameter B which will hold the requested # of elements.
// For hint < 0 overLoadFactor returns false since hint < bucketCnt.
B := uint8(0)
for overLoadFactor(hint, B) {
B++
}
h.B = B
// allocate initial hash table
// if B == 0, the buckets field is allocated lazily later (in mapassign)
// If hint is large zeroing this memory could take a while.
if h.B != 0 {
var nextOverflow *bmap
h.buckets, nextOverflow = makeBucketArray(t, h.B, nil)
if nextOverflow != nil {
h.extra = new(mapextra)
h.extra.nextOverflow = nextOverflow
}
}
return h
}
扩容
扩容主要分为两种:
1、装载因子已经超过 6.5——放不下了;
2、哈希使用了太多溢出桶——链表太长 太乱了;
放不下了扩容
溢出桶过多整理
即sameSizeGrow 扩容,其本质并不是扩容,而是重新整理,减少链表。
放不下了扩容
即biggerSizeGrow扩容。当大于6.5时候,B+1,即翻倍桶的个数,之后进行迁移。
func hashGrow(t *maptype, h *hmap) {
// If we've hit the load factor, get bigger.
// Otherwise, there are too many overflow buckets,
// so keep the same number of buckets and "grow" laterally.
bigger := uint8(1)
if !overLoadFactor(h.count+1, h.B) {
bigger = 0
h.flags |= sameSizeGrow
}
oldbuckets := h.buckets
newbuckets, nextOverflow := makeBucketArray(t, h.B+bigger, nil)
flags := h.flags &^ (iterator | oldIterator)
if h.flags&iterator != 0 {
flags |= oldIterator
}
// commit the grow (atomic wrt gc)
h.B += bigger
h.flags = flags
h.oldbuckets = oldbuckets
h.buckets = newbuckets
h.nevacuate = 0
h.noverflow = 0
if h.extra != nil && h.extra.overflow != nil {
// Promote current overflow buckets to the old generation.
if h.extra.oldoverflow != nil {
throw("oldoverflow is not nil")
}
h.extra.oldoverflow = h.extra.overflow
h.extra.overflow = nil
}
if nextOverflow != nil {
if h.extra == nil {
h.extra = new(mapextra)
}
h.extra.nextOverflow = nextOverflow
}
// the actual copying of the hash table data is done incrementally
// by growWork() and evacuate().
}