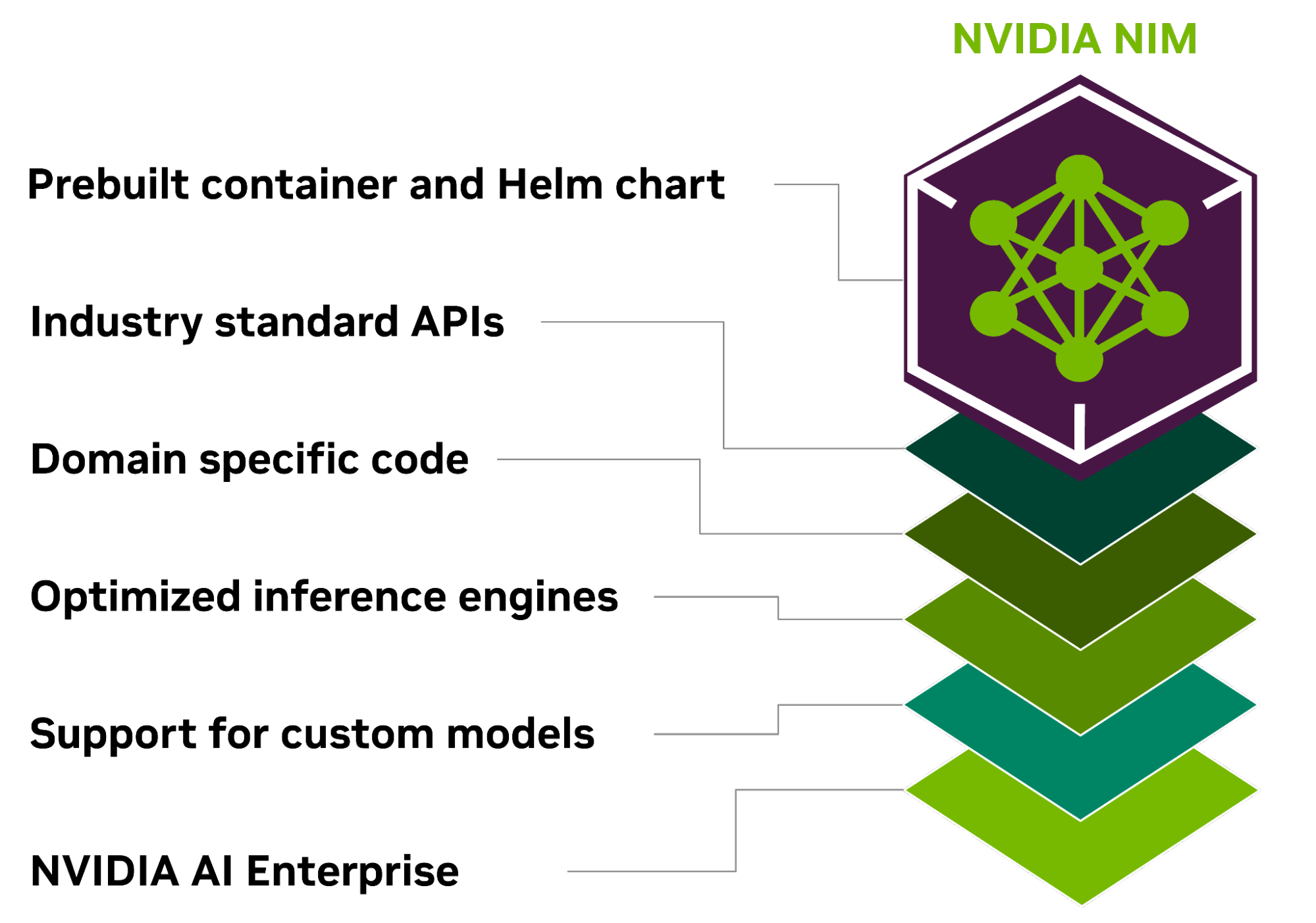
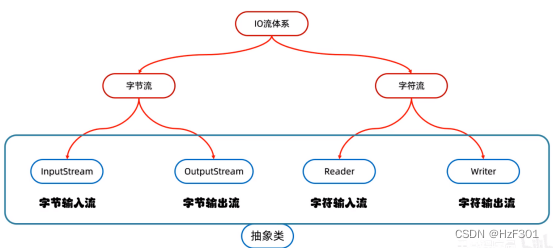
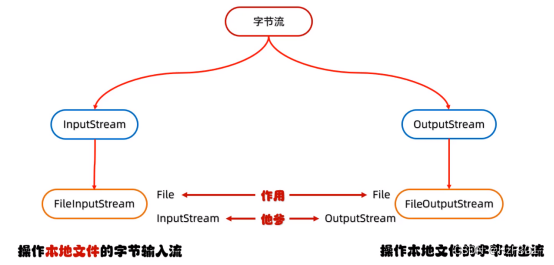
IO流


字节流 字符流
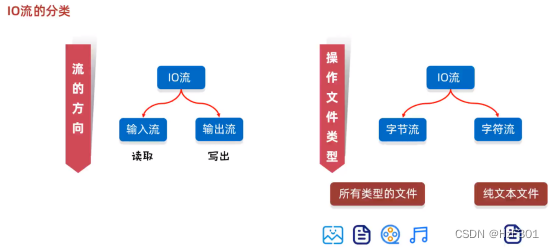
纯文本文件


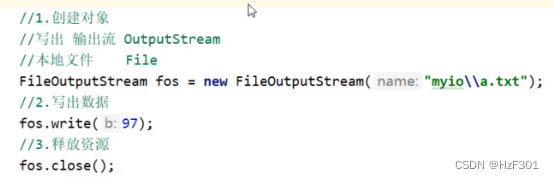
Fileoutputstream
注意点

如果不释放资源,java会一直占用该文件,外部无法删除掉该文件
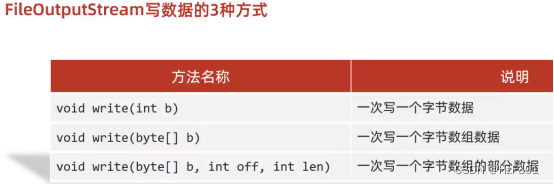
写数据
换行写
用字符串的getBytes()得到字符数组
\r\n

续写

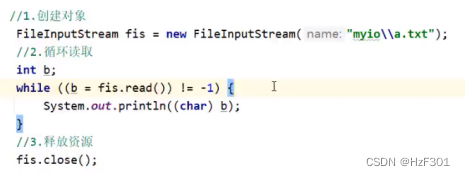
Fileinputstream
Read
一次只读一个字符,返回int类型,对应ASCII码表,如果读不到,返回-1
没读一次,读取的指针就会移动到下一个字符

循环读取
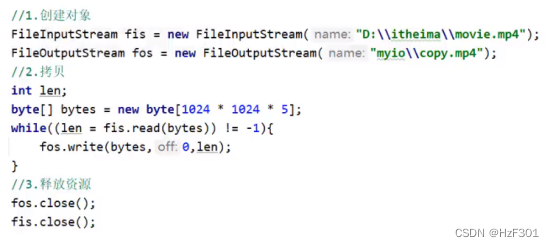
文件拷贝
注意先开的,最后关闭
一次读一个字节
拷贝小文件快一点,大文件很慢
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("day28\\a.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("day28\\b.txt");
int b;
while ((b = fis.read()) != -1){
fos.write(b);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}一次读多个字节

注意数组会残留数据
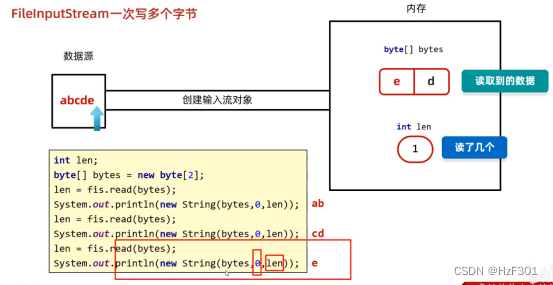
数组中会残留d
所以在写的时候,写入新读取到的数据
Try catch 释放资源太麻烦

注意创建流对象一定是autocloseable接口的实现类


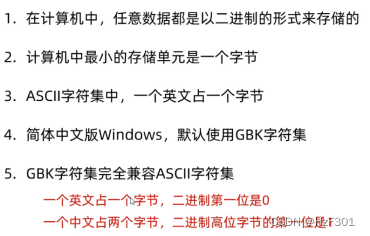
GBK字符集 国产


为什么一定以1开头?
区分开中英文
直接解码

Unicode字符集
UTF-8编码规则
英文 一个字节存
中文 三个字节存



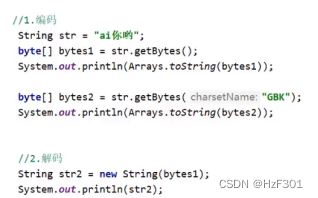
字节流读中文出现乱码



读取的时候,可能由于解码和编码所使用的不是同一种方式,所以会乱码
但拷贝的时候,是把所有字节都复制下来了,不会有数据的丢失,不会有乱码
Idea默认UTF-8

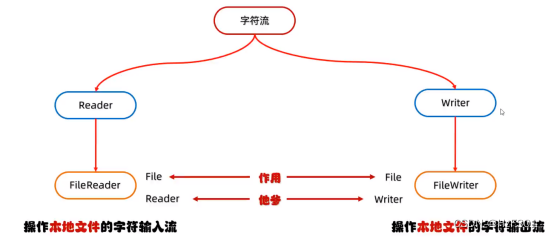
字符流
底层是字节流

Filereader filewriter
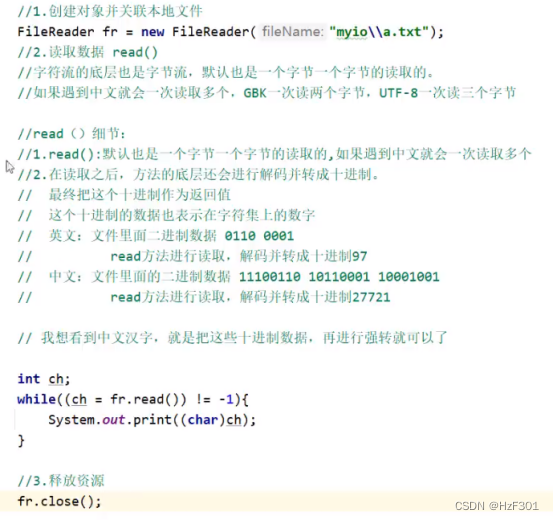
Filereader



要记得强转
不强转就返回解码完的十进制数字,这个数字就是对应字符集上的数字
空参read()原理:要手动强转
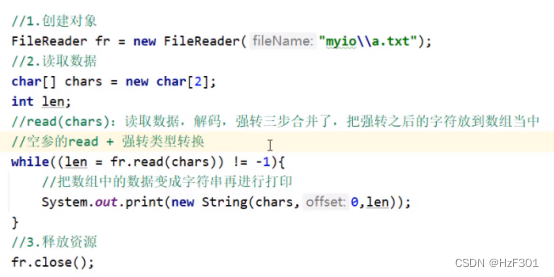
带参read()原理:空参read+自动类型转换
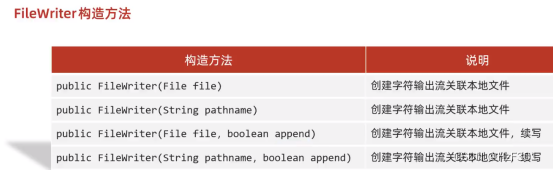
Filewriter
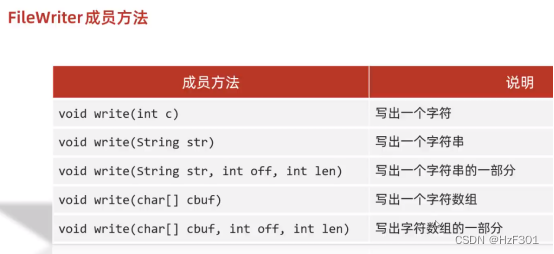

字符流底层原理
输入流
创建缓冲区(长度为8192的字节数组),字节流没有缓冲区
缓冲区:提高读取效率


如果此时已经读到缓冲区没有数据,会再次回到文件里看还有没有剩余的数据,如果也没有,则返回-1;
如果有,则继续读取数据,装缓冲区,会把之前的数据直接覆盖掉,有多少数据就覆盖多少,如果剩下的数据不够覆盖8192个字节,则剩下的数据还是之前已经读到的数据,这些就不会被覆盖。
98~104是新数据,97是上一次存入缓冲区的数据
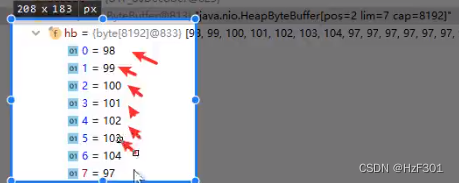
缓冲区中的数据不会随着文件清空而消失
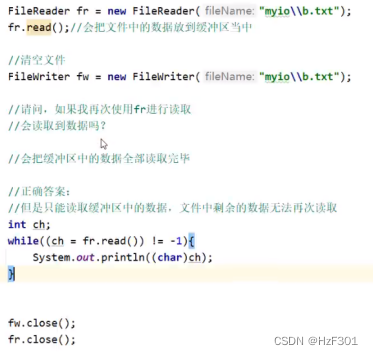
字符输出流底层原理
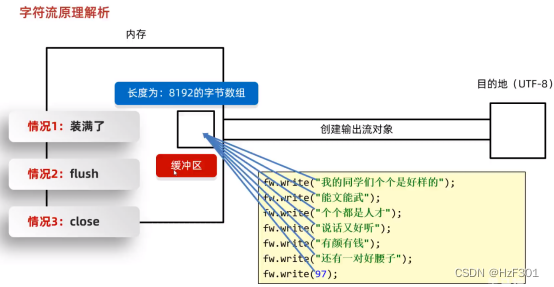
情况1:
缓冲区装第8193个数据时,就会自动输出缓冲区中的所有数据
如果不够8193个,就不会输出

字节流和字符流的使用场景


package exercise;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class exercise5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
copyFile("day27\\src\\aaa", "day28\\src");
}
private static void copyFile(String path, String copyPath) throws IOException {
File f = new File(path);
File newFile = new File(copyPath, f.getName());
boolean bb = newFile.mkdir();
File[] files = f.listFiles();
if (files != null) {
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isFile()) {
//如果是文件,直接拷贝
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file.getPath());
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(newFile.getPath(), file.getName()));
byte[] b = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 5];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(b)) != -1) {
fos.write(b, 0, len);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
} else {
//如果是文件夹,拷贝新的文件夹
copyFile(file.getPath(), new File(copyPath, f.getName()).getPath());
}
}
}
}
}
一个字节异或一个数字两次,就会得到原数字,利用这个特性进行加密解密
异或:^
package exercise;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class exercise6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("day28\\src\\aaa\\a.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("day28\\src\\aaa\\aEnc.txt");
// FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("day28\\src\\aaa\\aDec.txt");
byte[] b = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 5];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read()) != -1) {
fos.write(len ^ 10);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
}
package exercise;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class exercise7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("day28\\src\\aaa\\b.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("day28\\src\\c.txt");
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int ch;
while ((ch = fr.read()) != -1) {
sb.append((char) ch);
}
Integer[] arr = Arrays.stream(sb.toString().split("-"))
.map(Integer::parseInt).sorted().toArray(Integer[]::new);
String s = Arrays.toString(arr).replace(", ", "-");
fw.write(s.substring(1, s.length() - 1));
fw.close();
fr.close();
}
}