一 完全二叉树的判断
1.1 描述
完全二叉树:他每一层都是满的,即使不满也是最后一层不满,最后一层不满也是从左到右变满的;话句话说就是
完全二叉树从根结点到倒数第二层满足完美二叉树,最后一层可以不完全填充,其叶子结点都靠左对齐
1.如果是最后一层,下一轮还有
2.不是从左往右排
判断的时候按层遍历
1、如果某个节点有右孩子,没有左孩子返回false;
2、当越到第一次越到左右孩子不双全的情况下说明这层已经是最后一层既叶子节点,那么接下来的遍历就不能再出现左节点或者有节点有的话就不是;
1.3 代码
public class Code01_IsCBT {
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
public static boolean isCBT1(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 是否遇到过左右两个孩子不双全的节点
boolean leaf = false;
Node l = null;
Node r = null;
queue.add(head);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
head = queue.poll();
l = head.left;
r = head.right;
if (
// 如果遇到了不双全的节点之后,又发现当前节点不是叶节点
(leaf && (l != null || r != null))
||
//如果某个节点有右孩子没有左孩子返回false;
(l == null && r != null)) {
return false;
}
if (l != null) {
queue.add(l);
}
if (r != null) {
queue.add(r);
}
if (l == null || r == null) {//如果有一个是null了,说明已经是最后一层了,
//不能再有下一层了,根据这个条件上面判断是否还有下一层,有的话一定就不是
leaf = true;
}
}
return true;
}
public static boolean isCBT2(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
return process(head).isCBT;
}二 平衡二叉树
2.1 描述
它是一 棵空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树
2.2 分析

2.3 代码
public static boolean isBalanced2(Node head) {
return process(head).isBalanced;
}
public static class Info{
public boolean isBalanced;
public int height;
public Info(boolean i, int h) {
isBalanced = i;
height = h;
}
}
public static Info process(Node x) {
if(x == null) {
return new Info(true, 0);
}
Info leftInfo = process(x.left);
Info rightInfo = process(x.right);
int height = Math.max(leftInfo.height, rightInfo.height) + 1;
boolean isBalanced = true;
if(!leftInfo.isBalanced) {
isBalanced = false;
}
if(!rightInfo.isBalanced) {
isBalanced = false;
}
if(Math.abs(leftInfo.height - rightInfo.height) > 1) {
isBalanced = false;
}
return new Info(isBalanced, height);
}
三 搜索二叉树
3.1 描述
若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值 若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值;
一颗左子树节点上的值都小于右子树上的值,并且左子树和右子树也要是颗二叉树
3.2 分析
1、 可以通过中序遍历,看是不是升序就可以判断;经典的搜索二叉树是没有重复值的;
2、分析如下,要信息的方法

使用递归收集信息的时候左右节点最大值最小值都要

3.3 代码
public static boolean isBST2(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
return process(head).isBST;
}
public static class Info {
public boolean isBST;
public int max;
public int min;
public Info(boolean i, int ma, int mi) {
isBST = i;
max = ma;
min = mi;
}
}
public static Info process(Node x) {
if (x == null) {
return null;
}
Info leftInfo = process(x.left);
Info rightInfo = process(x.right);
int max = x.value;
//找值要到他的子树中去全部找
if (leftInfo != null) {
max = Math.max(max, leftInfo.max);
}
if (rightInfo != null) {
max = Math.max(max, rightInfo.max);
}
int min = x.value;
if (leftInfo != null) {
min = Math.min(min, leftInfo.min);
}
if (rightInfo != null) {
min = Math.min(min, rightInfo.min);
}
boolean isBST = true;
if (leftInfo != null && !leftInfo.isBST) {
isBST = false;
}
if (rightInfo != null && !rightInfo.isBST) {
isBST = false;
}
if (leftInfo != null && leftInfo.max >= x.value) {
isBST = false;
}
if (rightInfo != null && rightInfo.min <= x.value) {
isBST = false;
}
return new Info(isBST, max, min);
}四 二叉树的最大距离
4.1 描述
给定一棵二叉树的头节点head,任何两个节点之间都存在距离,
返回整棵二叉树的最大距离
4.2 分析
情况一 和x有关是左右树的最大距离加上本身
情况二 与 x 无关的分别是左右树的最大距离
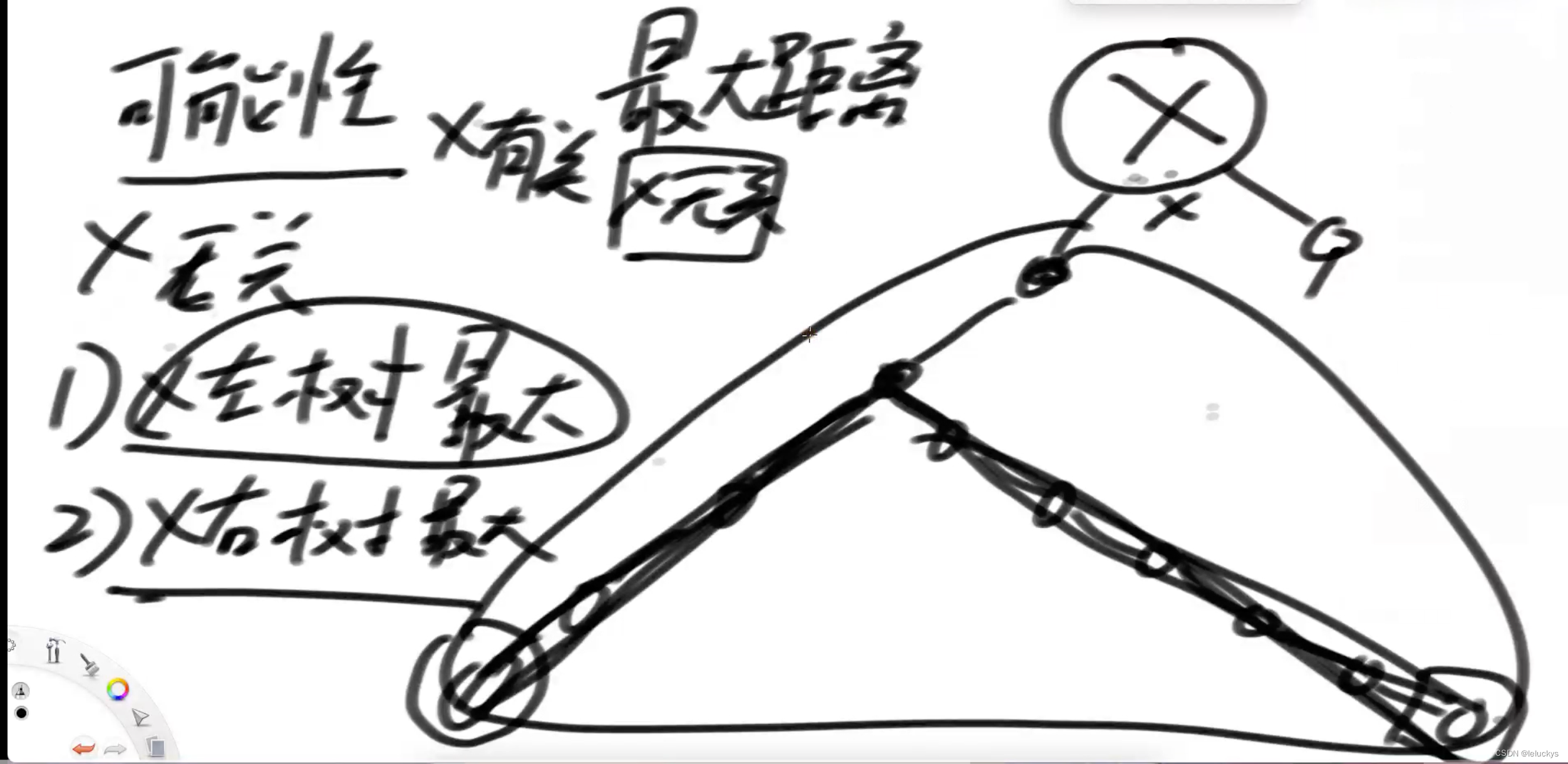 与x有关的最大距离
与x有关的最大距离
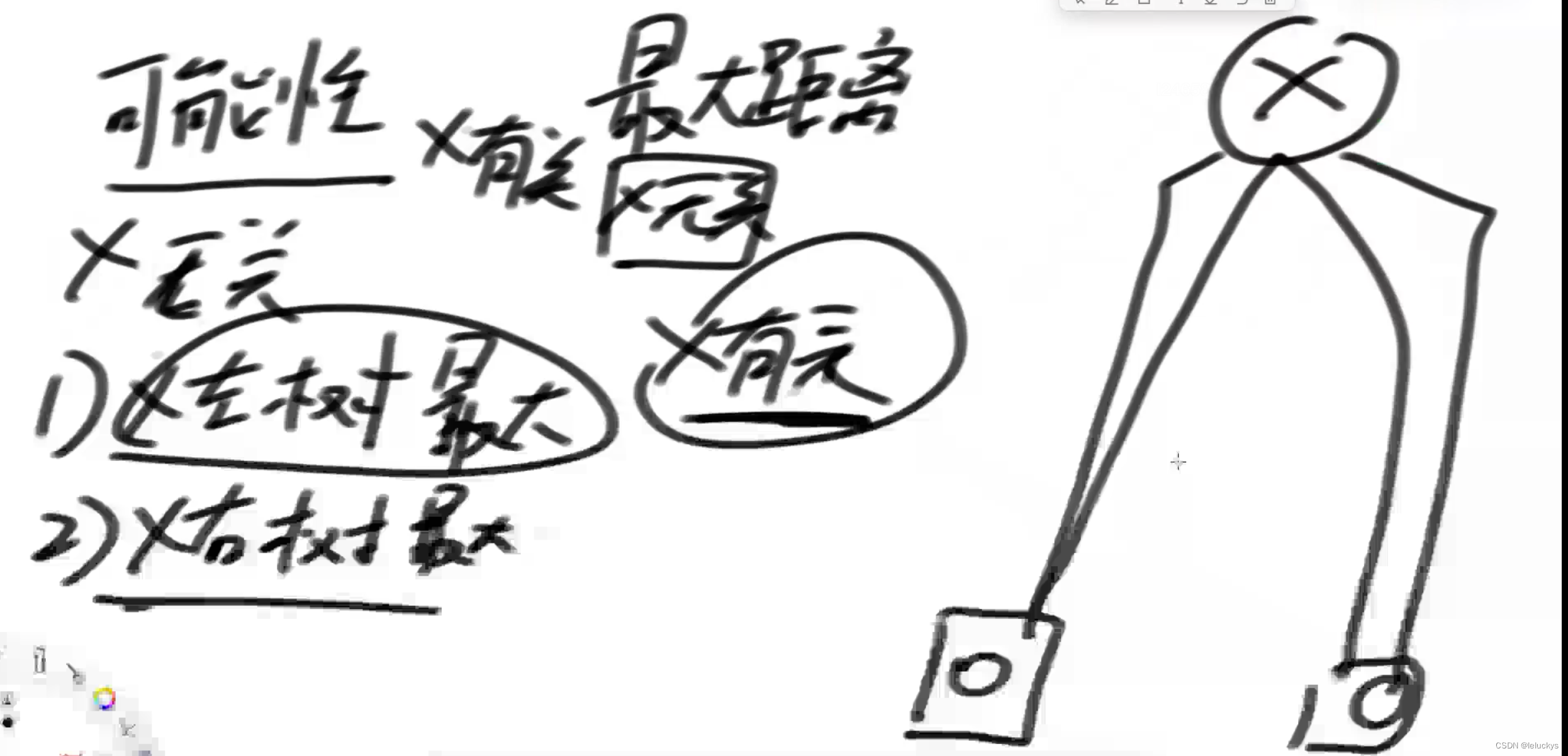 最大距离的三种情况
最大距离的三种情况

从上面分析:我们需要向子树要的信息就是最大距离和高度
4.3代码
public static int maxDistance2(Node head) {
return process(head).maxDistance;
}
public static class Info {
public int maxDistance;
public int height;
public Info(int m, int h) {
maxDistance = m;
height = h;
}
}
public static Info process(Node x) {
if (x == null) {
return new Info(0, 0);
}
Info leftInfo = process(x.left);
Info rightInfo = process(x.right);
int height = Math.max(leftInfo.height, rightInfo.height) + 1;
int p1 = leftInfo.maxDistance;
int p2 = rightInfo.maxDistance;
//与x有关
int p3 = leftInfo.height + rightInfo.height + 1;
int maxDistance = Math.max(Math.max(p1, p2), p3);
return new Info(maxDistance, height);
}五 满二叉树的判断
5.1 描述
如果一棵二叉树的结点要么是叶子结点,要么它有两个子结点,这样的树就是满二叉树;

5.2 分析
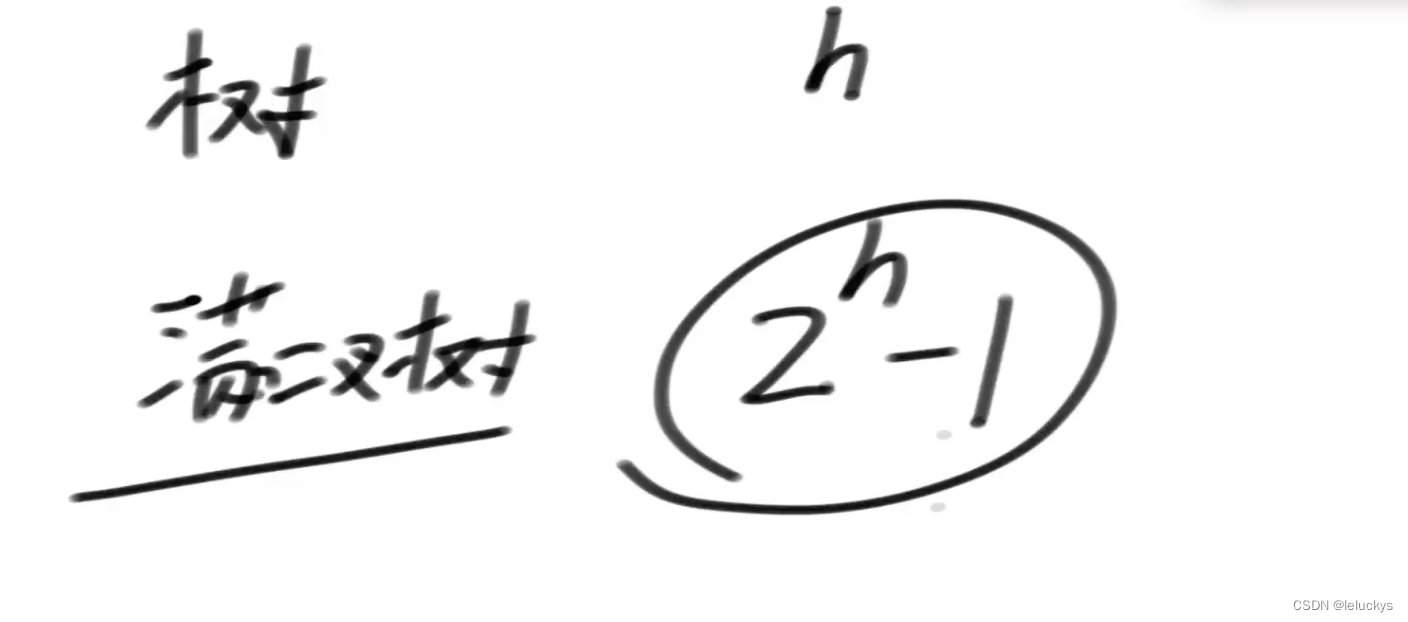 5.3 代码
5.3 代码
// 第一种方法
// 收集整棵树的高度h,和节点数n
// 只有满二叉树满足 : 2 ^ h - 1 == n
public static boolean isFull1(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
Info1 all = process1(head);
return (1 << all.height) - 1 == all.nodes;
}
public static class Info1 {
public int height;
public int nodes;
public Info1(int h, int n) {
height = h;
nodes = n;
}
}
public static Info1 process1(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return new Info1(0, 0);
}
Info1 leftInfo = process1(head.left);
Info1 rightInfo = process1(head.right);
int height = Math.max(leftInfo.height, rightInfo.height) + 1;
int nodes = leftInfo.nodes + rightInfo.nodes + 1;
return new Info1(height, nodes);
}
六 一颗二叉树中,整体不是搜索二叉树,可能某个子树是搜索二叉树,子树(某个头节点下所有的子树都要),在整颗二叉树中,有哪一颗子树是搜索二叉树,在所有的搜索二叉子树中找出所有最大的那颗子树有多少个节点并返回
6.1 描述
一颗二叉树中,整体不是搜索二叉树,可能某个子树是搜索二叉树,子树(某个头节点下所有的子树都要),在整颗二叉树中,有那一刻子树是搜索二叉树,在所有的子树中找出所有最大的那颗子树有多少个节点并返回
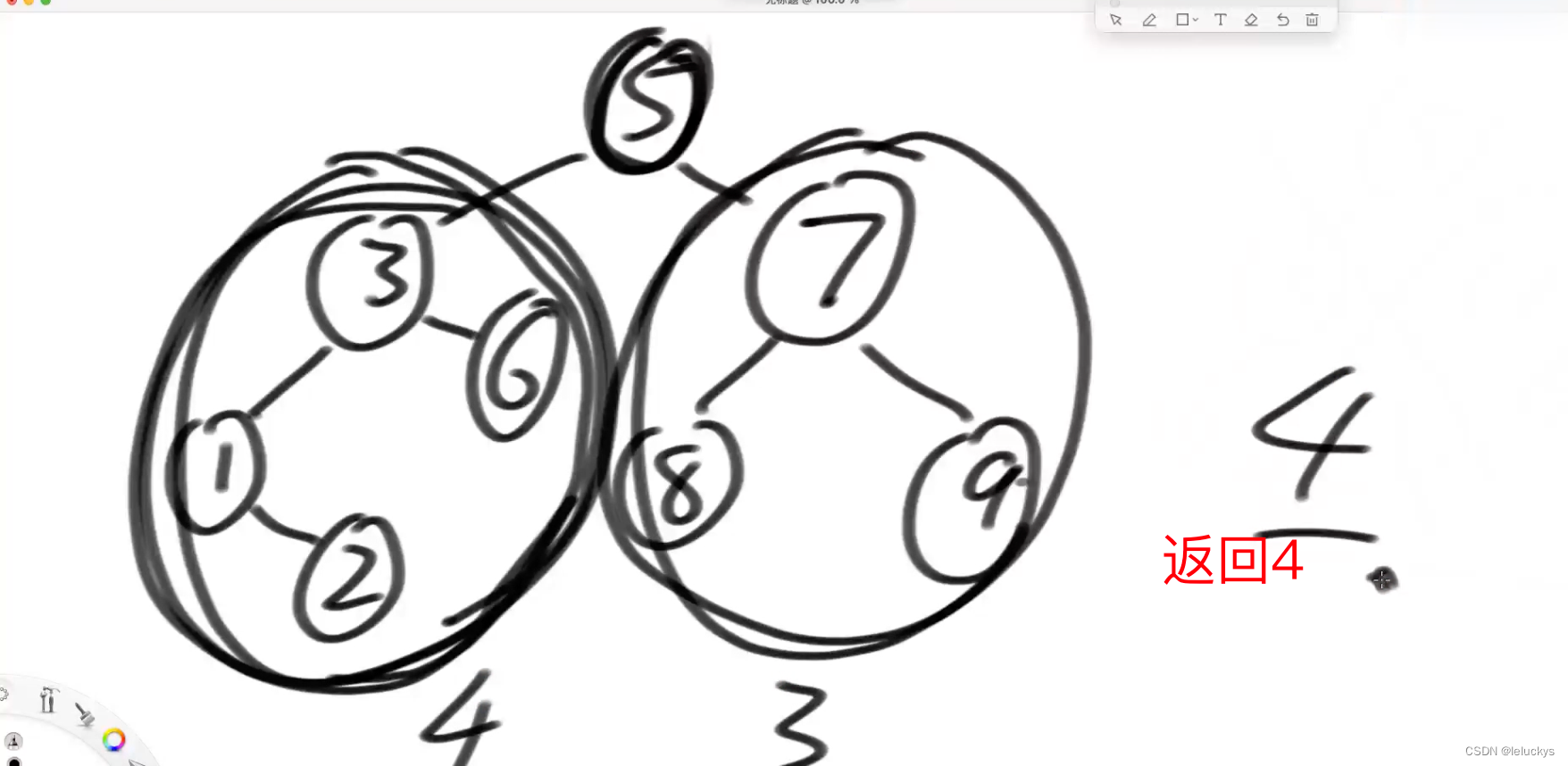
6.2 分析
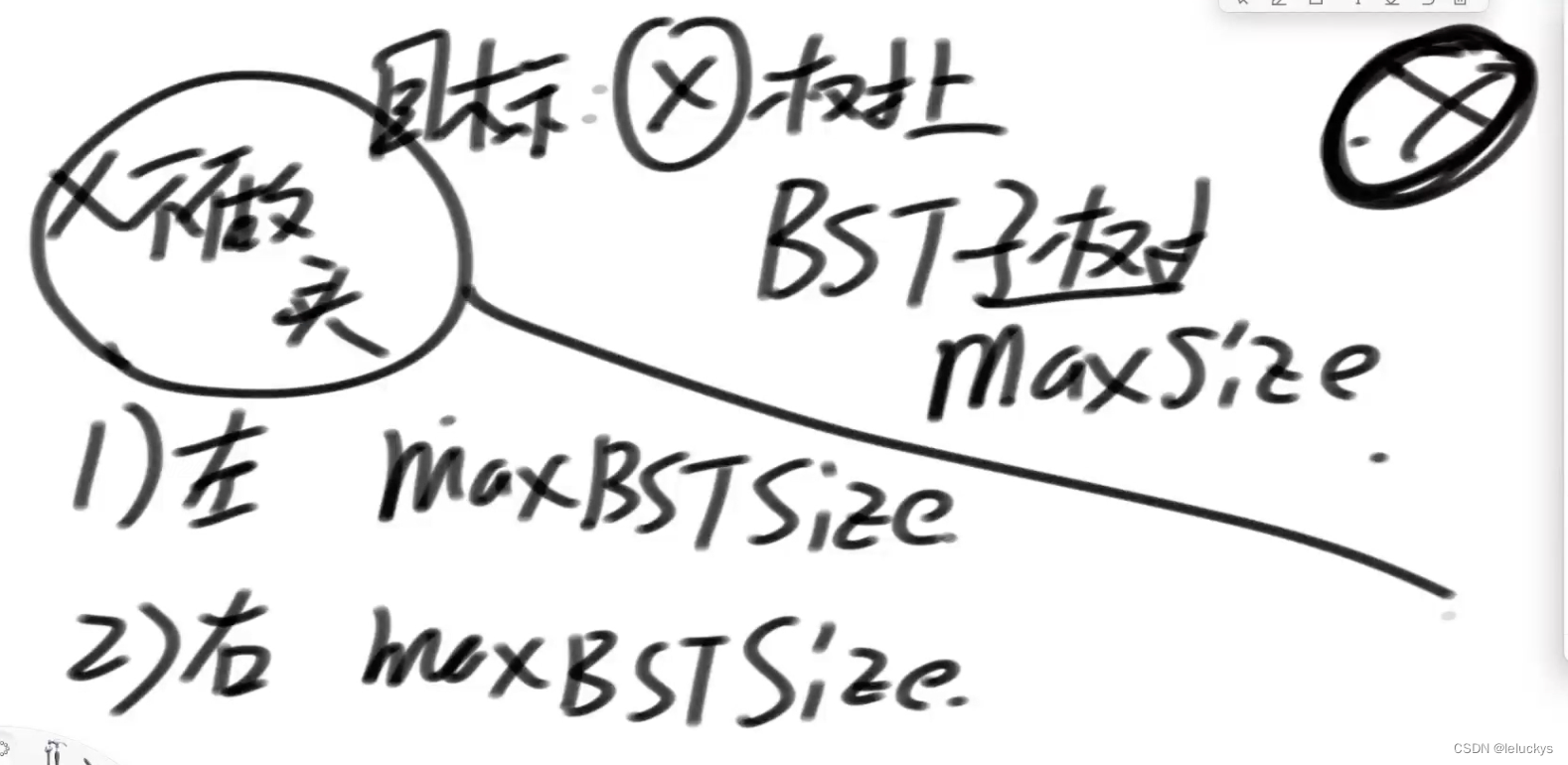

信息收集

信息合并 x左和x右就是maxBSTSubSize 左size和右size就是size
BST和size 两个可以合并,当maxBSTSubSize 和size相等的情况就是BST
6.3 代码
package class12;
// 在线测试链接 : https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-bst-subtree
public class Code05_MaxSubBSTSize {
// 提交时不要提交这个类
public static class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int value) {
val = value;
}
}
// 提交如下的代码,可以直接通过
public static int largestBSTSubtree(TreeNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return 0;
}
return process(head).maxBSTSubtreeSize;
}
public static class Info {
public int maxBSTSubtreeSize;
public int allSize;
public int max;
public int min;
public Info(int m, int a, int ma, int mi) {
maxBSTSubtreeSize = m;
allSize = a;
max = ma;
min = mi;
}
}
public static Info process(TreeNode x) {
if (x == null) {
return null;
}
Info leftInfo = process(x.left);
Info rightInfo = process(x.right);
int max = x.val;
int min = x.val;
int allSize = 1;
if (leftInfo != null) {
max = Math.max(leftInfo.max, max);
min = Math.min(leftInfo.min, min);
allSize += leftInfo.allSize;
}
if (rightInfo != null) {
max = Math.max(rightInfo.max, max);
min = Math.min(rightInfo.min, min);
allSize += rightInfo.allSize;
}
//不以x为头的情况
int p1 = -1;
if (leftInfo != null) {
p1 = leftInfo.maxBSTSubtreeSize;
}
int p2 = -1;
if (rightInfo != null) {
p2 = rightInfo.maxBSTSubtreeSize;
}
//以x为头的情况
int p3 = -1;
boolean leftBST = leftInfo == null ? true : (leftInfo.maxBSTSubtreeSize == leftInfo.allSize);
boolean rightBST = rightInfo == null ? true : (rightInfo.maxBSTSubtreeSize == rightInfo.allSize);
if (leftBST && rightBST) {
boolean leftMaxLessX = leftInfo == null ? true : (leftInfo.max < x.val);
boolean rightMinMoreX = rightInfo == null ? true : (x.val < rightInfo.min);
if (leftMaxLessX && rightMinMoreX) {
int leftSize = leftInfo == null ? 0 : leftInfo.allSize;
int rightSize = rightInfo == null ? 0 : rightInfo.allSize;
p3 = leftSize + rightSize + 1;
}
}
return new Info(Math.max(p1, Math.max(p2, p3)), allSize, max, min);
}
}
七 本节总结










![解决nginx报错nginx: [emerg] unknown log format main in 的方法](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/4ad75087aad9426bb851295795af9126.png)