1、Spring
IoC(Inversion of Controller)控制反转
使用对象时,由主动new产生对象转换为由外部提供对象,此过程中对象中创建控制权由程序转移到外部,此思想称为控制反转
Spring技术对IoC思想进行了实现
Spring提供了一个容器,称为IOC容器,用来充当IOC思想的外部
IoC容器负责对象的创建、初始化等一系列工作,被创建或被管理的对象在IoC容器中统称为Bean
DI(Dependency Injection)依赖注入
在容器中建立bean与bean之间的依赖关系的整个过程,称为依赖注入
1.1、IoC入门案例
导入Spring坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.23</version>
</dependency>创建UserService接口,和UserServiceImpl的实现类
public interface UserService {
void save();
}
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("user running...");
}
}创建Spring的配置文件 ---- resourse下右键new ---> XMLConfiguration File--->Spring Config --->applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 1.导入spring的坐标spring-context -->
<!-- 2.配置bean-->
<!-- bean标签标示配置bean id属性标识给bean起的名字 class属性标识给bean定义类型-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
</beans>新建测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
//3.获取IoC容器
ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//4.获取bean
UserService userService =(UserService) app.getBean("userService");
userService.save();
}1.2、DI入门案例
将BookServiceImpl注入到UserServiceImpl
修改UserServiceImpl的实现类,提供Set方法。创建BookService接口,和BookServiceImpl的实现类
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private BookService bookService;
public void setBookService(BookService bookService) {
this.bookService = bookService;
}
@Override
public void save() {
bookService.save();
System.out.println("user running...");
}
}
public interface BookService {
void save();
}
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("book running...");
}
}
配置Spring配置文件将其注入
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="bookService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.BookServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.UserServiceImpl">
<!-- 7.配置user和book的关系-->
<!-- property标签配置当前bean的属性-->
<!-- name属性标识配置哪一个的属性-->
<!-- ref属性标识参考那个bean-->
<property name="bookService" ref="bookService"></property>
</bean>
</beans>1.3、Bean基础配置
name:定义bean的别名,可定义多个,使用逗号(,)分号(;)空格( )分隔
<bean name="service1 service2" id="bookService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.BookServiceImpl"></bean>scope:定义bean作用范围,可选范围,singleton,prototype
<bean scope="singleton" name="service1 service2" id="bookService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.BookServiceImpl"></bean>
init-method:指定bean初始化方法名 destroy-method:指定bean销毁的方法 或者直接类实现InitializingBean DisposableBean(了解)
<bean init-method="save" destroy-method="save" id="bookService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.BookServiceImpl"></bean>
1.4、依赖注入的方式
setter注入------引用类型
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private BookService bookService;
public void setBookService(BookService bookService) {
this.bookService = bookService;
}
@Override
public void save() {
bookService.save();
System.out.println("user running...");
}
}
<bean id="bookService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.BookServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.UserServiceImpl">
<property name="bookService" ref="bookService" ></property>
</bean>setter注入-----基本类型
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private String name;
private int age;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("姓名:"+name+",年龄:"+age);
}
}
<bean id="userService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.UserServiceImpl">
<property name="name" value="zhangsan"/>
<property name="age" value="20"/>
</bean>构造器注入---引用类型
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private BookService bookService;
public UserServiceImpl(BookService bookService) {
this.bookService = bookService;
}
@Override
public void save() {
bookService.save();
System.out.println("user running...");
}
}
<bean id="bookService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.BookServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.UserServiceImpl">
<constructor-arg name="bookService" ref="bookService"/>
</bean>构造器注入---基本类型-----还有其他方法 type index
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private String name;
public UserServiceImpl(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("user running..."+name);
}
}
<bean id="userService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.UserServiceImpl">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="张三"/>
</bean>自动装配 --- autowire 可以根据类型和名称匹配 byType(主要用这个)
自动装配用于引用类型依赖注入,不能对简单类型进行操作
使用按类型装配时(byType)必须保障容器中相同类型的bean唯一,推荐使用
使用按类型装配时(byName)必须保障容器中具有指定名称的bean,因变量名与配置偶尔,不推荐使用
自动装配优先级低于setter注入与构造器注入,同时出现自动装配配置失效
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private BookService bookService;
public void setBookService(BookService bookService) {
this.bookService = bookService;
}
@Override
public void save() {
bookService.save();
System.out.println("user running...");
}
}
<bean id="bookService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.BookServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" autowire="byType"/>集合注入
<bean id="bookService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.BookServiceImpl">
<property name="array">
<array>
<value>1</value>
</array>
</property>
<property name="list">
<list>
<array>2</array>
</list>
</property>
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>3</value>
</set>
</property>
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="name" value="zhangsan"/>
</map>
</property>
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="age">18</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>1.5、容器
1.5.1、创建容器方式
方式一:类路径加载配置文件(常用)
ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");方式二:文件路径加载配置文件(了解)
ApplicationContext app = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("D://applicationContext.xml");
方式三::加载多个配置文件(了解)
ApplicationContext app = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml","bean2.xml");
1.5.2、获取bean
方式一:使用bean名称获取
UserService userService =(UserService) app.getBean("userService");方式二:使用bean名称获取并指定类型
UserService userService =app.getBean("userService",UserService.class);方式三:使用bean类型获取
UserService userService =app.getBean(UserService.class);1.5.3、总结


1.6、注解开发
1.6.1、注解开发定义bean
将配置文件下方代码的bean改为注释
<bean id="userService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"/>在类上面添加一个注解
Spring提供了@Component注解的三个衍生注解
@Controller:用于表现层bean定义
@Service:用于业务层bean定义
@Repository:用于数据层bean定义
@Component("userService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("user running...");
}
}创建java下com.itheima.config.SpringConfig配置文件
@Configuration:表明这个是配置类 @ComponentScan:包扫描com.itheima下的bean
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.itheima")
public class SpringConfig {
}
1.6.2、bean管理
bean的作用范围与bean的生命周期管理
@Component
@Scope("singleton")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("user running...");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){}
@PreDestroy
public void destory(){}
}1.6.3、依赖注入---自动装配
使用@Autowired注解将BookServiceImpl注入到UserServiceImpl(按类型) 找不到按名称加上@Qualifier("bookService"),一定要配上@Autowried
@Component
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
//@Qualifier("bookService")
private BookService bookService;
@Override
public void save() {
bookService.save();
System.out.println("user running...");
}
}注入简单类型的值
@Component
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Value("zhangsan")
private String name;
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("user’s"+name);
}
}注入properties的值
@PropertySource("jdbc.properties")加载一个 @PropertySource({"jdbc.properties","jdbc.properties"})加载多个
//在resource下创建jdbc.properties文件
name=lisi
//在SpringConfig配置文件中加上@PropertySource("jdbc.properties")
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.itheima")
@PropertySource("jdbc.properties")
public class SpringConfig {
}
//再使用@Value(${name})注入
@Component
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Value("${name}")
private String name;
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("user’s"+name);
}
}
1.6.4、管理第三方bean
开发管理第三方bena
//导入druid坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.12</version>
</dependency>
//1.再java下新建config.JDBCConfig的类
public class JDBCConfig {
//1.定义一个方法获得管理的对象
//2.添加@Bean,表示当前方法返回值是一个bean
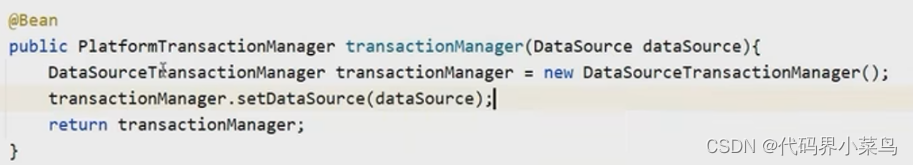
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("");
ds.setUrl("");
ds.setUsername("");
ds.setPassword("");
return ds;
}
}
//3.在java下新建config.SpringConfig的配置文件
@Configuration
@Import(JDBCConfig.class)
public class SpringConfig {
}
//4.测试文件
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext app = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
DataSource dataSource = app.getBean(DataSource.class);
System.out.println(dataSource);
}注解开发实现为第三方bean注入资源
简单类型
public class JDBCConfig {
@Value("com.itheima.com")
private String className;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName(className);
ds.setUrl("");
ds.setUsername("");
ds.setPassword("");
return ds;
}
}引用类型----他会根据类型自动装配,但注意SpringConfig加上@ComponentSan还有注意注入的类要加上@Component的注解
public class JDBCConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(UserService userService){
userService.save();
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("");
ds.setUrl("");
ds.setUsername("");
ds.setPassword("");
return ds;
}
}1.7、AOP
面向切面编程:在不惊动原始设计的基础上进行功能增强
1.7.1、AOP入门案例
在每一次执行方法之前输出当前时间
导入坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.4</version>
</dependency>制作连接点方法
@Component
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("book running...");
}
}制作共性功能,新建java下aop.MyAdvice
public class MyAdvice {
public void method(){
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}定义切入点
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(void com.itheima.service.UserService.save())")
private void pt(){}
@Before("pt()")
public void method(){
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
绑定切入点与通知关系 配置文件加上@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.itheima")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class SpringConfig {
}
1.7.2、AOP通知类型
@Before、@After、@BeforeThrowing、@BeforeThrowing
@Before("pt()")
public void method(){
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
}@Around:最常用环绕模式
@Around("pt()")
public void method(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
//表示对原始操作的调用
pjp.proceed();
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
}1.7.3、AOP通知获取数据
获取参数:
@After("pt()")
public void method(JoinPoint jp) throws Throwable {
//表示对原始操作的调用
Object[] args = jp.getArgs();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(args));
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
}1.8、Spring事务
事务作用:在数据层保障一系列的数据库操作同成功同失败
Spring事务作用:在数据层或业务层保障一系列的数据库操作同时成功同失败


2、SpringMVC
表现层功能的开发,Web框架
2.1、SpringMVC入门案例
(1)导入SpringMVC坐标与Servlet坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.23</version>
</dependency>(2)创建SpringMVC控制类(等同于Servlet功能) 在java下新建com.itheima.controller.UserController
@Controller
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/save")
@ResponseBody
public String save(){
System.out.println("user save...");
return "{'name':'zhangsan'}";
}
}(3)初始化SpringMVC环境(同Spring环境),设定SpringMVC加载对应的bean
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.itheima")
public class SpringConfig {
}
(4)定义一个servlet容器启动的配置类,在里面加载spring的配置 在com.itheima.config下新建
public class ServletContainerInitConfig extends AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
ctx.register(SpringConfig.class);
return ctx;
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"};
}
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() {
return null;
}
}
2.2、请求和响应
2.2.1、设置请求映射文件
名称:@RequestMapping 类型:方法注解 类注解 访问路径
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/save")
@ResponseBody
public String save(){
System.out.println("save....");
return "{'name':'zhangsan'}";
}
}
2.1.2、请求方式
处理中文乱码:在ServletContainnerConfig的配置文件中重写getServletFilters方法
//乱码处理
@Override
protected Filter[] getServletFilters() {
CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new CharacterEncodingFilter();
filter.setEncoding("UTF-8");
return new Filter[]{filter};
}get与post接收普通参数(参数名称与传递过来的key值一样)
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/save")
@ResponseBody
public String save(String name,int age){
System.out.println("save...."+name+age);
return "{'name':'zhangsan'}";
}
}2.1.2、5种类型参数传递
普通参数名字不同时:使用@RequestParam("name") name
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/save")
@ResponseBody
public String save(@RequestParam("name") String name, @RequestParam("age") int age){
System.out.println("save...."+name+age);
return "{'name':'zhangsan'}";
}
}
POJO类型参数:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/save")
@ResponseBody
public String save(User user){
System.out.println("save...."+user);
return "{'name':'zhangsan'}";
}
}数组:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/save")
@ResponseBody
public String save(@RequestParam("name") String[] name){
System.out.println("save...."+ Arrays.toString(name));
return "{'name':'zhangsan'}";
}
}集合类型参数:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/save")
@ResponseBody
public String save(@RequestParam List<String> name){
System.out.println("save...."+ name.toString());
return "{'name':'zhangsan'}";
}
}2.1.3、接收请求中的JSON数据
只能用于:JSON数组,JSON对象(POJO),JSON数组(POJO)
(1)添加JSON数据转化相关坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>(2)开启自动自动转换JSON数据的支持
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.itheima.controller")
//开启自动转换json数据支持
@EnableWebMvc
public class SpringMvcConfig {
}(3)接收数据加上@RequestBody
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/save")
@ResponseBody
public String save(@RequestBody User user){
System.out.println("save...."+ user);
return "{'name':'zhangsan'}";
}
}2.1.4、日期参数传递
加上@DateTimeFormat(pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") 2023-1-9 20:01:9
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/save")
@ResponseBody
public String save(@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") Date date){
System.out.println("save...."+ date);
return "{'name':'zhangsan'}";
}
}2.2、响应
响应页面/跳转页面
@Controller
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/user")
public String save(){
return "index.jsp";
}
}
响应文本
@Controller
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/user")
@ResponseBody
public String save(){
return "index hello";
}
}响应POJO
@Controller
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/user")
@ResponseBody
public User save(){
User user = new User("zhangsan", 18);
return user;
}
}
响应对象集合转JSON数组
@Controller
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/user")
@ResponseBody
public List<User> save(){
List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
users.add(new User("zhangsan", 18));
users.add(new User("lisi", 19));
return users;
}
}@ResponseBody 设置当前控制器返回值作为响应体
2.3、REST风格
REST(Representational State Transfer)表现形式状态转换 增删改查方法区别
简化代码开发:将@ResponseBody和@Controller合二为一@RestController
请求改为 @GetMapping @PostMapping @DeleteMapping @PutMapping
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping
public List<User> save(){
List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
users.add(new User("zhangsan", 18));
users.add(new User("lisi", 19));
return users;
}
}
2.4、SSM整合
2.4.1、表现层数据封装
新建com.itheima.util下的Result类
public class Result {
private Integer code;
private Object data;
private String msg;
public Result() {
}
public Result(Integer code, Object data) {
this.code = code;
this.data = data;
}
public Result(Integer code, Object data, String msg) {
this.code = code;
this.data = data;
this.msg = msg;
}
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(Integer code) {
this.code = code;
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
}
使用
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping
public Result save(){
List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
users.add(new User("zhangsan", 18));
users.add(new User("lisi", 19));
return new Result(200,users);
}
}2.4.2、异常处理器

异常一般处理在表现层。我们在controller下新建ProjectExceptionAdvice
@RestControllerAdvice
public class ProjectExceptionAdvice {
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public Result doException(Exception ex){
return new Result(401,null,"异常哪里走");
}
}
异常分类:业务异常、系统异常、其他异常
2.5、拦截器
拦截器(interceptor)是一种动态拦截方法调用的机制,在SpringMVC中动态拦截控制器方法的执行
作用:
在指定的放法调用前后执行预先设定的代码
组织原始方法的执行
2.5.1、入门案例
在表现层下新建interceptor.ProjectInterceptor
@Component
public class ProjectInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("preHandle");
return false;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("postHandle");
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("afterCompletion");
}
}在config下面的创建SpringMvcSupport文件
@Configuration
public class SpringMvcSupport extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
//注入冒红不是报错
@Autowired
private ProjectInterceptor projectInterceptor;
// 这个负责处理静态资源访问
@Override
protected void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/pages/**").addResourceLocations("/pages/");
}
// 这个是拦截器
@Override
protected void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(projectInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/user");
}
}在config的SpringMvcConfig配置文件扫描
@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.itheima.controller","com.itheima.config"})
//开启自动转换json数据支持
@EnableWebMvc
public class SpringMvcConfig {
}
preHandle是最常用的
2.5.2、配置多个拦截器
@Configuration
public class SpringMvcSupport extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
@Autowired
private ProjectInterceptor projectInterceptor1;
@Autowired
private ProjectInterceptor projectInterceptor2;
// 这个负责处理静态资源访问
@Override
protected void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/pages/**").addResourceLocations("/pages/");
}
// 这个是拦截器
@Override
protected void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(projectInterceptor1).addPathPatterns("/user");
registry.addInterceptor(projectInterceptor2).addPathPatterns("/user");
}
}
3、Maven
4、SpringBoot
4.1、spring项目快速启动
打成jar包->执行java -jar springboot.jar
4.2、配置文件格式
位置:resource下application.yml
三种:properties格式、yml格式(常用)、yaml格式 pro>yml>yaml
数据读取yml数据的三种方式:
city: china
user:
name: zhangsan
age: 19
方式一:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Value("${city}")
private String city;
@Value("${user.name}")
private String name;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String getUserbyId(@PathVariable Integer id){
return "hello.springboot"+id+city;
}
}
方式二:用一个对象进行全封装
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String getUserbyId(@PathVariable Integer id){
return "hello.springboot"+env.getProperty("city")+env.getProperty("user.name");
}
}
方式三:创建自定义对象封装指定数据
第一步创建:domain.User
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "user")
@Data
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
第二步:读取
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private User user;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String getUserbyId(@PathVariable Integer id){
return "hello.springboot"+user;
}
}
自定义对象封装数据警告解决方案-----加入坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>4.3、多环境开发
方式一:过时无所谓(推荐)
#设置启用的环境
spring:
profiles:
active: pro
---
#开发
spring:
profiles: dev
server:
port: 80
---
#生产
spring:
profiles: pro
server:
port: 81
---
#测试
spring:
profiles: test
server:
port: 82方式二:不过时
#设置环境
spring:
profiles:
active: pro
---
#开发
spring:
config:
activate:
on-profile: dev
server:
port: 80
---
#生产
spring:
config:
activate:
on-profile: pro
server:
port: 81
---
#测试
spring:
config:
activate:
on-profile: test
server:
port: 82多环境命令启动参数设置
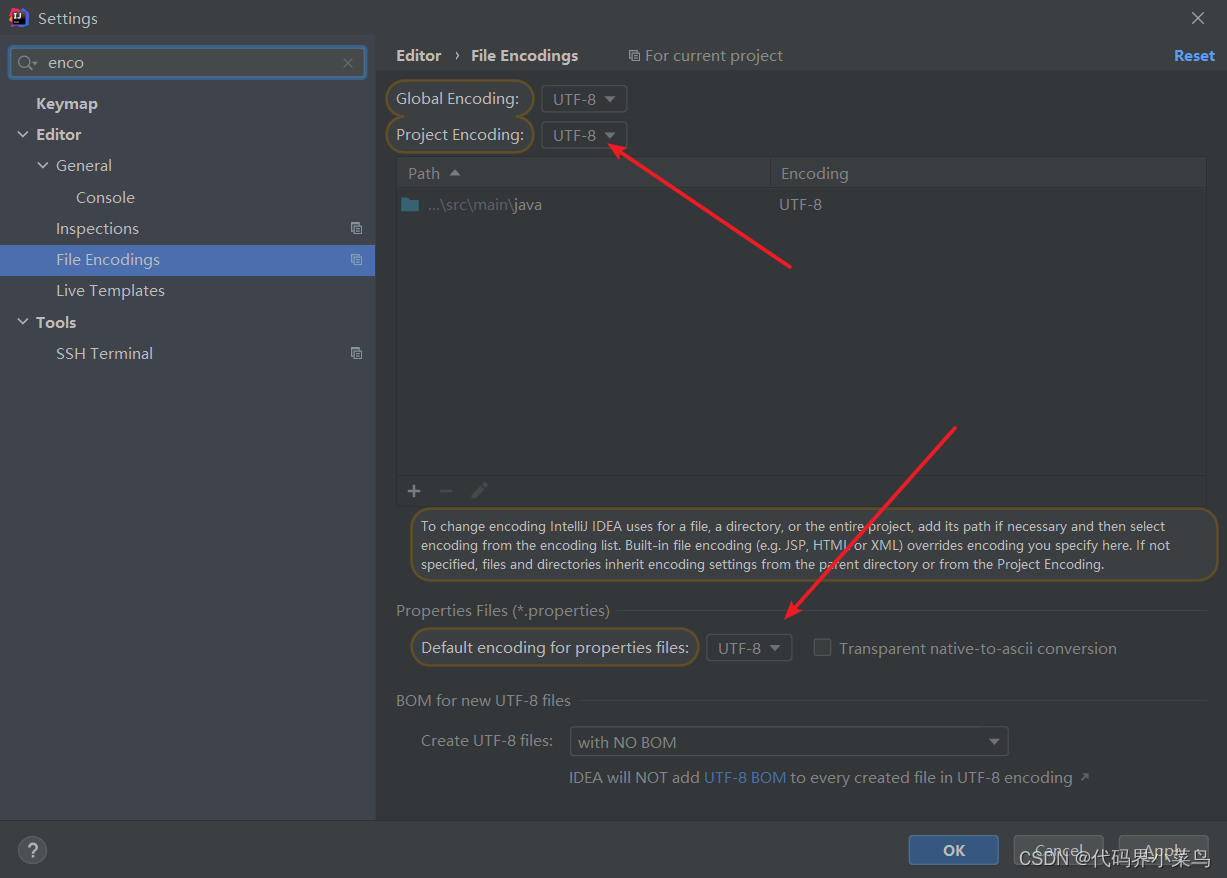
yml出现中文:先去设置,将编码改为UTF8
java -jar springboot.jar --spring.profiles.active=test
java -jar springboot.jar --server=88 --spring.profiles.active=test
1.SpringBoot整合第三方技术
整合MyBaties
导入坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.31</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.6</version>
</dependency>配置文件:properties.yml
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc?serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: root
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource创建实体类、domain.User
@Data
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Double balance;
}
创建接口方法
@Mapper
public interface UserDao {
@Select("select * from account where id = #{id}")
public User getById(Integer id);
}
编写测试类
@Test
void contextLoads() {
User user = userDao.getById(1);
System.out.println(user);
}5、Springboot整合MyBaties-plus
入门案例
MyBatisPlus(简称MP)是基于MyBatis框架基础上开发的增强型工具,旨在简化开发,提高效率
1.导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.31</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.12</version>
</dependency>设置配置文件
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc?serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: root
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource创建domian下User实体对象
@Data
public class Account{
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Double balance;
}创建UserDao让其继承BaseMapper<Account>
@Mapper
public interface UserDao extends BaseMapper<Account> {
}
测试类------他找表是根据你的BassMapper(类名) 类名小写的表名
@Test
void contextLoads() {
List<Account> users = userDao.selectList(null);
System.out.println(users);
}标准数据层开发
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot01QuickstartApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Test
//新增
public void insert(){
userDao.insert(new Account(null,"罗翔",15000.0));
}
@Test
//删除
public void delete(){
userDao.deleteById(10);
}
@Test
//修改
public void update(){
userDao.updateById(new Account(1,"罗翔",19000.0));
}
@Test
//根据id查询
public void getById(){
Account account = userDao.selectById(1);
System.out.println(account);
}
@Test
//查询所有
public void selectAll(){
List<Account> accounts = userDao.selectList(null);
System.out.println(accounts);
}
}lombok
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Account {
@TableId(value="id",type= IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Double balance;
}
标准分页功能制作
配置分页拦截器 创建MPConfig配置文件
@Configuration
public class MpConfig {
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mpInterceptor() {
//1.定义MP拦截器
MybatisPlusInterceptor mpInterceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
//2.添加具体的拦截器
mpInterceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new PaginationInnerInterceptor());
return mpInterceptor;
}
}测试
@Test
//分页
public void testGetByPage(){
IPage page = new Page(1, 2);
userDao.selectPage(page, null);
System.out.println("当前页码值"+page.getCurrent());
System.out.println("每页显示数"+page.getSize());
System.out.println("一共多少页"+page.getPages());
System.out.println("一共多少条数据"+page.getTotal());
System.out.println("数据"+page.getRecords());
}开启日志---不出问题一般不开
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl条件查询的三种格式
方式一:按条件查询
@Test
public void testGetByPage(){
QueryWrapper qw = new QueryWrapper();
qw.lt("balance", 1990);
List<Account> list = userDao.selectList(qw);
System.out.println(list);
}方式二:lamda格式按条件查询
@Test
public void testGetByPage(){
QueryWrapper<Account> qw = new QueryWrapper<>();
qw.lambda().lt(Account::getBalance, 1990);
List<Account> list = userDao.selectList(qw);
System.out.println(list);
}方式三:lamda格式按条件查询
@Test
public void testGetByPage(){
LambdaQueryWrapper<Account> lqw = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
lqw.lt(Account::getBalance,1231).ge(Account::getBalance,10);
List<Account> accounts = userDao.selectList(lqw);
System.out.println(accounts);
}条件查询---null值处理
@Test
public void testGetByPage(){
Account account = new Account();
account.setBalance(1233.0);
LambdaQueryWrapper<Account> lqw = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
lqw.lt(null != account.getBalance(),Account::getBalance,account.getBalance());
List<Account> accounts = userDao.selectList(lqw);
System.out.println(accounts);
}查询投影----只查询哪些字段
@Test
public void testGetByPage(){
LambdaQueryWrapper<Account> lqw = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
lqw.select(Account::getName,Account::getBalance);
List<Account> accounts = userDao.selectList(lqw);
System.out.println(accounts);
}查询条件设置
eq=:匹配 le ge between:区间 like tightLike lefiLike
映射匹配兼容性
问题一:表字段与编码属性设计不同步
@TableField(value = "username")
private String name;问题二:编码中添加了数据库中未定义的属性
@TableField(exist = false)
private String name;问题三:采用默认查询更多的字段查看权限
@TableField(select = false)
private String name;问题四:表名与编码开发设计不同步
@TableName("t_account")
public class Account{}2.DML编程控制
id生成策略
方法一:
AUTO(0):使用数据库id自增策略控制id生成
NONE(1):不设置id生成策略
INPUT(2):用户手工输入id
ASSIGN_ID(3):雪花算法生成id(可兼容数值型与字符型)
ASSIGN_UUID(4):以UUID生成算法作为id生成策略
@TableId(type= IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;方法二:全局配置
mybatis-plus:
global-config:
db-config:
id-type: auto #id生成策略
table-prefix: t_ble #前表缀多数据操作(删除与查询)
删除
@Test
public void testGetByPage(){
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(25);
list.add(26);
userDao.deleteBatchIds(list);
}查询
@Test
public void testGetByPage(){
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
List<Account> accounts = userDao.selectBatchIds(list);
System.out.println(accounts);
}逻辑删除
删除操作业务问题:业务数据从数据库中丢弃
逻辑删除:为数据设置是否可用状态字段,删除时设置状态字段为不可用状态,数据保留在数据库中
步骤一:注意这里的属性名和字段名不能命名为delete否则会报错
value:代表没删的值,delval:表示删除的值
@TableLogic(value = "0",delval = "1")
private Integer deleted;步骤二:测试
@Test
public void testGetByPage(){
userDao.deleteById(1);
}全局配置逻辑删除:
mybatis-plus:
global-config:
db-config:
logic-delete-field: deleted
logic-delete-value: 1 #删除的值
logic-not-delete-value: 0 #未删除的值乐观锁
业务并发现象带来的问题:秒杀
步骤一:添加字段--->version
步骤二:设定当前字段
@Version
private Integer version;步骤三:配置乐观锁拦截器机制对应的拼接
@Configuration
public class MpConfig {
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mpInterceptor() {
//1.定义MP拦截器
MybatisPlusInterceptor mpInterceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
//2.添加具体的拦截器----分页拦截
mpInterceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new PaginationInnerInterceptor());
//3.添加乐观锁
mpInterceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new OptimisticLockerInnerInterceptor());
return mpInterceptor;
}
}步骤四:使用乐观锁机制在修改前必须先获得对应数据的version方可正常进行
@Test
public void testGetByPage(){
//先查询数据,获取到version数据
Account account = userDao.selectById(2);
//执行数据修改操作
account.setName("jack");
userDao.updateById(account);
}代码生成器
这个还是自己查文档吧