AVL树是一种自平衡的二叉搜索树,它能够保持良好的平衡性质,使得在最坏情况下的时间复杂度也能保持在对数级别。本文将深入介绍AVL树的原理、实现和应用,并通过示例代码演示其基本操作。
文章目录
- 什么是AVL树?
- AVL树的实现
- 在AVL树中插入值为data的节点实现:
- AVL树的旋转
- 右单旋
- 左单旋
- 左右双旋
- 右左双旋
- AVL树的应用
- 完整代码
- 总结
什么是AVL树?
AVL树是由两位苏联数学家Adelson-Velsky和Landis于1962年发明的,它的特点是能够在插入和删除节点时自动调整树的结构,以保持树的平衡性。在AVL树中,任意节点的左右子树高度差不超过1,这就保证了整棵树的高度始终保持在对数级别,从而保证了插入、删除和查找等操作的高效性。
AVL树的实现
以下是一个C++实现的AVL树的基本结构和操作示例:
template<class T>
struct AVLTreeNode
{
AVLTreeNode(const T& data = T())
: _pLeft(nullptr)
, _pRight(nullptr)
, _pParent(nullptr)
, _data(data)
, _bf(0)
{}
AVLTreeNode<T>* _pLeft;
AVLTreeNode<T>* _pRight;
AVLTreeNode<T>* _pParent;
T _data;
int _bf; // 节点的平衡因子
};
// AVL: 二叉搜索树 + 平衡因子的限制
template<class T>
class AVLTree
{
typedef AVLTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
AVLTree()
: _pRoot(nullptr)
{}
// 在AVL树中插入值为data的节点
bool Insert(const T& data);
// AVL树的验证
bool IsAVLTree()
{
return _IsAVLTree(_pRoot);
}
private:
// 根据AVL树的概念验证pRoot是否为有效的AVL树
bool _IsAVLTree(Node* pRoot);
size_t _Height(Node* pRoot);
// 右单旋
void RotateR(Node* pParent);
// 左单旋
void RotateL(Node* pParent);
// 右左双旋
void RotateRL(Node* pParent);
// 左右双旋
void RotateLR(Node* pParent);
private:
Node* _pRoot;
};
在AVL树中插入值为data的节点实现:
// 在AVL树中插入值为data的节点
bool Insert(const T& data) {
// 插入节点
if (_pRoot == nullptr) {
_pRoot = new Node(data);
return true;
}
Node* pParent = nullptr;
Node* pCur = _pRoot;
while (pCur) {
pParent = pCur;
if (data < pCur->_data)
pCur = pCur->_pLeft; // 往左子树查找
else if (data > pCur->_data)
pCur = pCur->_pRight; // 往右子树查找
else
return false; // 重复值不插入
}
// 创建新节点
pCur = new Node(data);
if (data < pParent->_data)
pParent->_pLeft = pCur;
else
pParent->_pRight = pCur;
pCur->_pParent = pParent;
// 插入节点后,更新平衡因子并进行平衡处理
while (pParent) {
if (pCur == pParent->_pLeft) // 更新节点在左子树
--pParent->_bf; // 更新父节点的平衡因子
else
++pParent->_bf; // 更新父节点的平衡因子
if (0 == pParent->_bf) // 如果平衡旋转结束
break;
// 如果父节点的bf==1或-1,则不需要调整,直接向上更新即可
if (1 == pParent->_bf || -1 == pParent->_bf) {
pCur = pParent;
pParent = pParent->_pParent;
}
else { // 父节点不平衡,需要旋转调整
if (pParent->_bf == 2) {
if (pCur->_bf == 1) // LL型
// 左单旋
RotateL(pParent);
else // LR型
// 先左旋后右旋
RotateRL(pParent);
}
else {
if (pCur->_bf == -1) // RR型
// 右单旋
RotateR(pParent);
else // RL型
// 先左旋后右旋
RotateLR(pParent);
}
break;
}
}
return true;
}
AVL树的旋转
AVL树的平衡是通过维护每个节点的平衡因子来实现的。平衡因子指的是节点的左子树高度减去右子树高度的差值,其取值范围为-1、0和1。当平衡因子的绝对值超过1时,AVL树就需要进行旋转操作来重新平衡。
右单旋
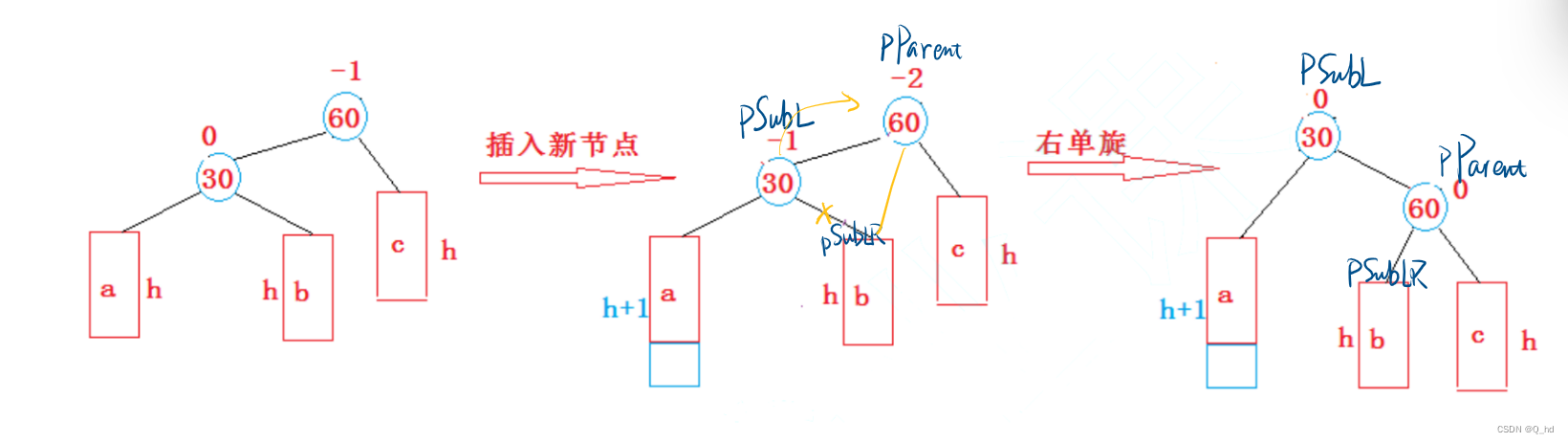
// 右单旋
void RotateR(Node* pParent) {
Node* pSubL = pParent->_pLeft;
Node* pSubLR = pSubL->_pRight;
// 右旋
pParent->_pLeft = pSubLR;
if (pSubLR)
pSubLR->_pParent = pParent;
pSubL->_pRight = pParent;
pSubL->_pParent = pParent->_pParent;
pParent->_pParent = pSubL;
if (pParent == _pRoot)
_pRoot = pSubL;
else {
if (pSubL->_pParent->_pLeft == pParent)
pSubL->_pParent->_pLeft = pSubL;
else
pSubL->_pParent->_pRight = pSubL;
}
pParent->_bf = pSubL->_bf = 0;
}
左单旋
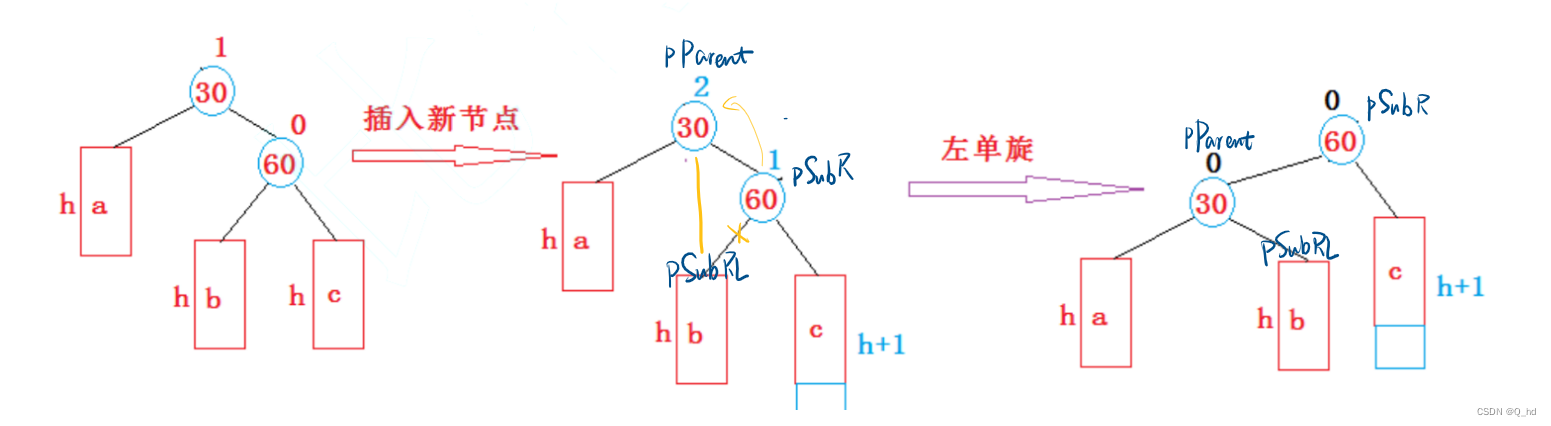
// 左单旋
void RotateL(Node* pParent) {
Node* pSubR = pParent->_pRight;
Node* pSubRL = pSubR->_pLeft;
// 左旋
pParent->_pRight = pSubRL;
if (pSubRL)
pSubRL->_pParent = pParent;
pSubR->_pLeft = pParent;
pSubR->_pParent = pParent->_pParent;
pParent->_pParent = pSubR;
if (pParent == _pRoot)
_pRoot = pSubR;
else
{
if (pSubR->_pParent->_pLeft == pParent)
pSubR->_pParent->_pLeft = pSubR;
else
pSubR->_pParent->_pRight = pSubR;
}
pParent->_bf = pSubR->_bf = 0;
}
左右双旋
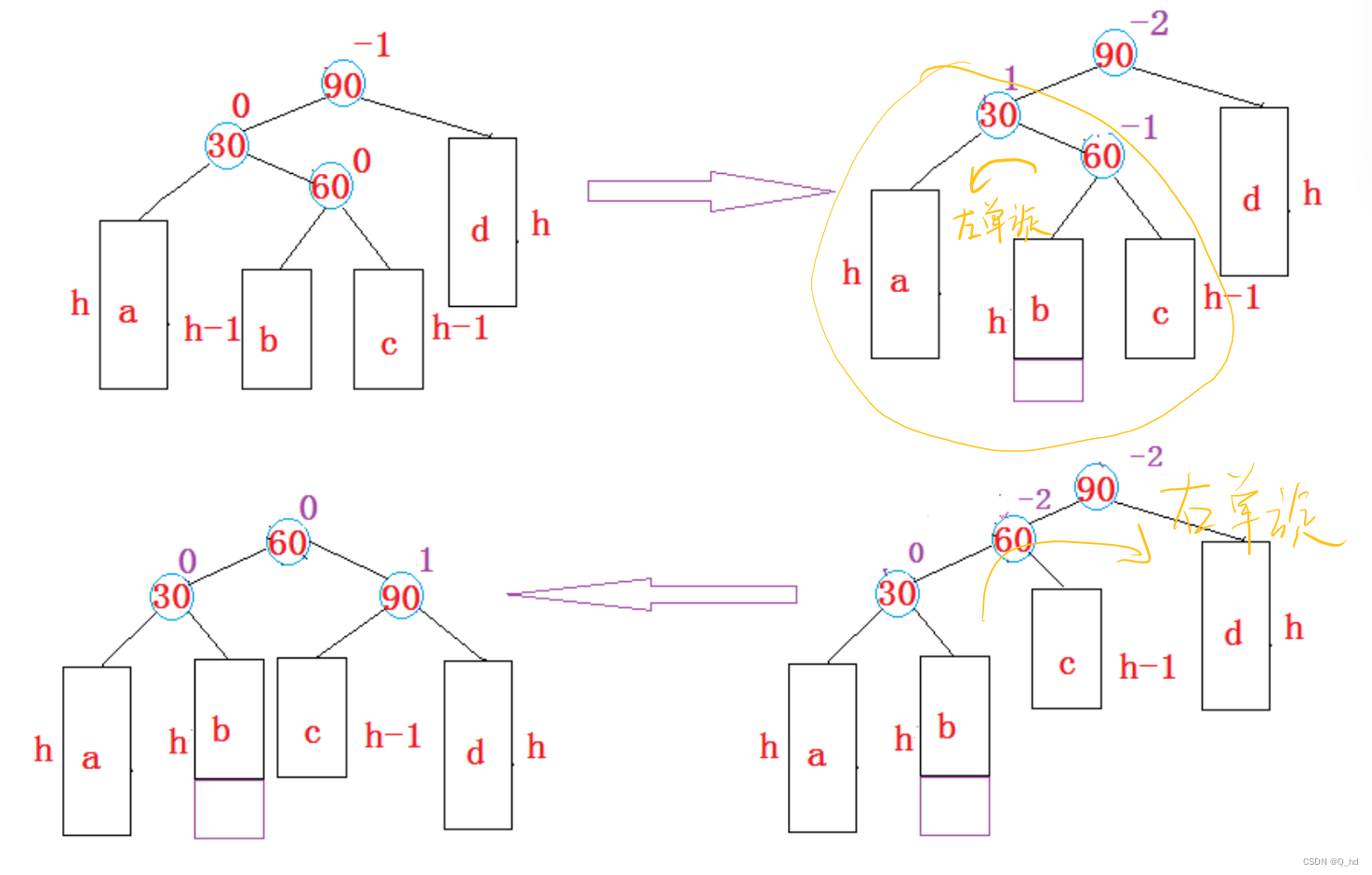
// 左右双旋
void RotateLR(Node* pParent) {
// 先左旋后右旋
Node* pSubL = pParent->_pLeft;
Node* pSubLR = pSubL->_pRight;
// 旋转之前,保存pSubLR的平衡因子,旋转完成之后,需要根据该平衡因子来调整其他节点的平衡因子
int bf = pSubLR->_bf;
// 进行左单旋
RotateL(pParent->_pLeft);
// 进行右单旋
RotateR(pParent);
if (1 == bf)
pSubL->_bf = -1;
else if (-1 == bf)
pParent->_bf = 1;
}
右左双旋
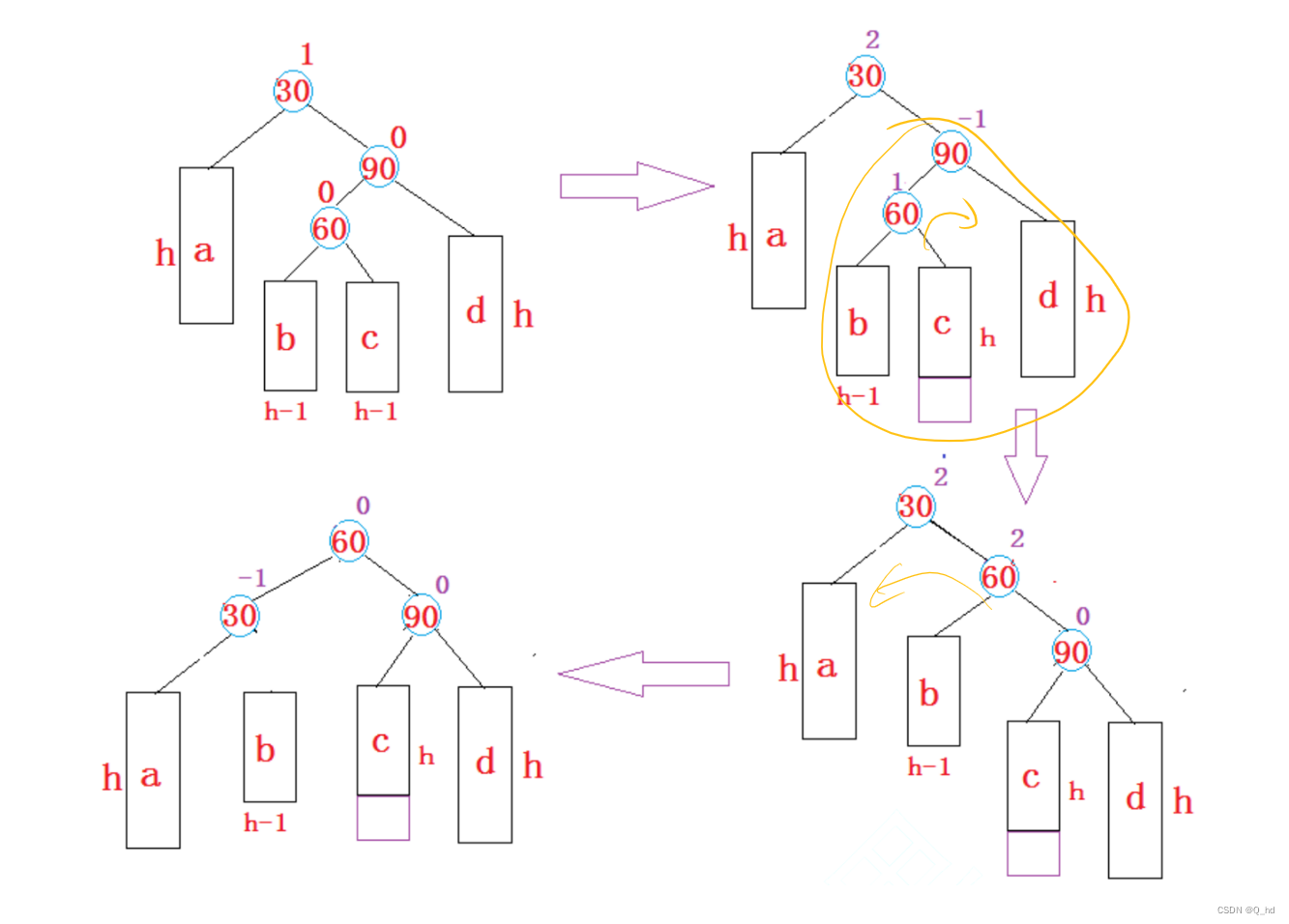
// 右左双旋
void RotateRL(Node* pParent) {
// 先右旋后左旋
Node* pSubR = pParent->_pRight;
Node* pSubRL = pSubR->_pLeft;
// 旋转之前,保存pSubRL的平衡因子,旋转完成之后,需要根据该平衡因子来调整其他节点的平衡因子
int bf = pSubRL->_bf;
// 进行右单旋
RotateR(pParent->_pRight);
//进行左单旋
RotateL(pParent);
if (1 == bf)
pParent->_bf = -1;
else if (-1 == bf)
pSubR->_bf = 1;
}
AVL树的应用
AVL树由于其高效的插入、删除和查找操作,在计算机科学领域有着广泛的应用。例如,在数据库系统中,AVL树常被用作索引结构,用于加速数据的检索操作;在编译器的符号表实现中,也可以使用AVL树来存储和查找变量信息。
完整代码
// AVLTree.h
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
struct AVLTreeNode
{
AVLTreeNode(const T& data = T())
: _pLeft(nullptr)
, _pRight(nullptr)
, _pParent(nullptr)
, _data(data)
, _bf(0)
{}
AVLTreeNode<T>* _pLeft;
AVLTreeNode<T>* _pRight;
AVLTreeNode<T>* _pParent;
T _data;
int _bf; // 节点的平衡因子
};
// AVL: 二叉搜索树 + 平衡因子的限制
template<class T>
class AVLTree
{
typedef AVLTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
AVLTree()
: _pRoot(nullptr)
{}
// 在AVL树中插入值为data的节点
bool Insert(const T& data) {
// 插入节点
if (_pRoot == nullptr) {
_pRoot = new Node(data);
return true;
}
Node* pParent = nullptr;
Node* pCur = _pRoot;
while (pCur) {
pParent = pCur;
if (data < pCur->_data)
pCur = pCur->_pLeft; // 往左子树查找
else if (data > pCur->_data)
pCur = pCur->_pRight; // 往右子树查找
else
return false; // 重复值不插入
}
// 创建新节点
pCur = new Node(data);
if (data < pParent->_data)
pParent->_pLeft = pCur;
else
pParent->_pRight = pCur;
pCur->_pParent = pParent;
// 插入节点后,更新平衡因子并进行平衡处理
while (pParent) {
if (pCur == pParent->_pLeft) // 更新节点在左子树
--pParent->_bf; // 更新父节点的平衡因子
else
++pParent->_bf; // 更新父节点的平衡因子
if (0 == pParent->_bf) // 如果平衡旋转结束
break;
// 如果父节点的bf==1或-1,则不需要调整,直接向上更新即可
if (1 == pParent->_bf || -1 == pParent->_bf) {
pCur = pParent;
pParent = pParent->_pParent;
}
else { // 父节点不平衡,需要旋转调整
if (pParent->_bf == 2) {
if (pCur->_bf == 1) // LL型
// 左单旋
RotateL(pParent);
else // LR型
// 先左旋后右旋
RotateRL(pParent);
}
else {
if (pCur->_bf == -1) // RR型
// 右单旋
RotateR(pParent);
else // RL型
// 先左旋后右旋
RotateLR(pParent);
}
break;
}
}
return true;
}
// AVL树的验证
bool IsAVLTree()
{
return _IsAVLTree(_pRoot);
}
private:
// 根据AVL树的概念验证pRoot是否为有效的AVL树
bool _IsAVLTree(Node* pRoot) {
if (pRoot == nullptr)
return true;
int leftHeight = _Height(pRoot->_pLeft);
int rightHeight = _Height(pRoot->_pRight);
if (abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1)
return false;
return _IsAVLTree(pRoot->_pLeft) && _IsAVLTree(pRoot->_pRight);
}
size_t _Height(Node* pRoot) {
if (pRoot == nullptr)
return 0;
int leftHeight = _Height(pRoot->_pLeft);
int rightHeight = _Height(pRoot->_pRight);
return 1 + max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
}
// 右单旋
void RotateR(Node* pParent) {
Node* pSubL = pParent->_pLeft;
Node* pSubLR = pSubL->_pRight;
// 右旋
pParent->_pLeft = pSubLR;
if (pSubLR)
pSubLR->_pParent = pParent;
pSubL->_pRight = pParent;
pSubL->_pParent = pParent->_pParent;
pParent->_pParent = pSubL;
if (pParent == _pRoot)
_pRoot = pSubL;
else {
if (pSubL->_pParent->_pLeft == pParent)
pSubL->_pParent->_pLeft = pSubL;
else
pSubL->_pParent->_pRight = pSubL;
}
pParent->_bf = pSubL->_bf = 0;
}
// 左单旋
void RotateL(Node* pParent) {
Node* pSubR = pParent->_pRight;
Node* pSubRL = pSubR->_pLeft;
// 左旋
pParent->_pRight = pSubRL;
if (pSubRL)
pSubRL->_pParent = pParent;
pSubR->_pLeft = pParent;
pSubR->_pParent = pParent->_pParent;
pParent->_pParent = pSubR;
if (pParent == _pRoot)
_pRoot = pSubR;
else
{
if (pSubR->_pParent->_pLeft == pParent)
pSubR->_pParent->_pLeft = pSubR;
else
pSubR->_pParent->_pRight = pSubR;
}
pParent->_bf = pSubR->_bf = 0;
}
// 右左双旋
void RotateRL(Node* pParent) {
// 先右旋后左旋
Node* pSubR = pParent->_pRight;
Node* pSubRL = pSubR->_pLeft;
// 旋转之前,保存pSubRL的平衡因子,旋转完成之后,需要根据该平衡因子来调整其他节点的平衡因子
int bf = pSubRL->_bf;
// 进行右单旋
RotateR(pParent->_pRight);
//进行左单旋
RotateL(pParent);
if (1 == bf)
pParent->_bf = -1;
else if (-1 == bf)
pSubR->_bf = 1;
}
// 左右双旋
void RotateLR(Node* pParent) {
// 先左旋后右旋
Node* pSubL = pParent->_pLeft;
Node* pSubLR = pSubL->_pRight;
// 旋转之前,保存pSubLR的平衡因子,旋转完成之后,需要根据该平衡因子来调整其他节点的平衡因子
int bf = pSubLR->_bf;
// 进行左单旋
RotateL(pParent->_pLeft);
// 进行右单旋
RotateR(pParent);
if (1 == bf)
pSubL->_bf = -1;
else if (-1 == bf)
pParent->_bf = 1;
}
private:
Node* _pRoot;
};
// test.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdlib>
#include "AVLTree.h"
int main() {
AVLTree<int> avlTree;
const int NUM_VALUES = 1000000;
// 生成并插入 10 万个随机整数值
srand(static_cast<unsigned int>(time(nullptr)));
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_VALUES; ++i) {
int randomValue = rand() % 1000000; // 生成 0 到 999999 之间的随机整数
avlTree.Insert(randomValue);
}
// 验证是否为 AVL 树
if (avlTree.IsAVLTree()) {
std::cout << "AVL Tree validation: This is an AVL tree." << std::endl;
}
else {
std::cout << "AVL Tree validation: This is not an AVL tree." << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
总结
本篇博客深入介绍了AVL树,包括其原理、实现和应用。通过C++代码示例展示了AVL树的基本结构和操作,以及探讨了在计算机科学领域的广泛应用。整体内容帮助读者更好地理解和应用AVL树这一自平衡的二叉搜索树。









![练习8 Web [GYCTF2020]Blacklist](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/1972477ac0484a039f5cf2d316365b65.png)