目录
- 一 INSERT 语句
- 1.1 参数的对应解析convertArgsToSqlCommandParam
- 1.2 ID获取对应的MappedStatement
- 1.3 MappedStatement交给执行器执行
- 1.4 不同的执行器获取不同的StatementHandler
- 1.5 根据参数获取BoundSql
- 1.6 执行器配置参数处理器ParameterHandler
- 1.7 拿到StatementHandler具体的执行
官网:mybatis – MyBatis 3 | 简介
参考书籍:《通用源码阅读指导书:MyBatis源码详解》 易哥
参考文章:
- Mybatis源码解析
上一篇文章我们分析到了MapperMethod的执行流程,我们回顾一下?
/**
* 执行映射接口中的方法
* @param sqlSession sqlSession接口的实例,通过它可以进行数据库的操作
* @param args 执行接口方法时传入的参数
* @return 数据库操作结果
*/
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) { // 根据SQL语句类型,执行不同操作
case INSERT: { // 如果是插入语句
// 将参数顺序与实参对应好
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 执行操作并返回结果
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: { // 如果是更新语句
// 将参数顺序与实参对应好
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 执行操作并返回结果
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: { // 如果是删除语句MappedStatement
// 将参数顺序与实参对应好
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 执行操作并返回结果
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT: // 如果是查询语句
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) { // 方法返回值为void,且有结果处理器
// 使用结果处理器执行查询
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) { // 多条结果查询
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) { // Map结果查询
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) { // 游标类型结果查询
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else { // 单条结果查询
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH: // 清空缓存语句
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default: // 未知语句类型,抛出异常
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
// 查询结果为null,但返回类型为基本类型。因此返回变量无法接收查询结果,抛出异常。
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
下面我们具体来分析一下执行流程?
一 INSERT 语句
// 如果是插入语句
case INSERT: {
// 将参数顺序与实参对应好
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 执行操作并返回结果
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
// 参数与实参对应好
public Object convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(Object[] args) {
return paramNameResolver.getNamedParams(args);
}
/**
* <p>
* The key is the index and the value is the name of the parameter.
* The name is obtained from {@link Param} if specified. When {@link Param} is not specified,
* the parameter index is used. Note that this index could be different from the actual index
* when the method has special parameters (i.e. {@link RowBounds} or {@link ResultHandler}).
* </p>
* <ul>
* <li>aMethod(@Param("M") int a, @Param("N") int b) -> {{0, "M"}, {1, "N"}}</li>
* <li>aMethod(int a, int b) -> {{0, "0"}, {1, "1"}}</li>
* <li>aMethod(int a, RowBounds rb, int b) -> {{0, "0"}, {2, "1"}}</li>
* </ul>
*
* 凡是加了@Param注解的会单独处理,特殊参数也会单独处理
*/
// 方法入参的参数次序表。键为参数次序,值为参数名称或者参数@Param注解的值
private final SortedMap<Integer, String> names;
// 该方法入参中是否含有@Param注解
private boolean hasParamAnnotation;
/**
*
* 将被解析的方法中的参数名称列表与传入的`Object[] args`进行对应,返回对应关系。
*
*
* 如果只有一个参数,直接返回参数
* 如果有多个参数,则进行与之前解析出的参数名称进行对应,返回对应关系
*
*/
public Object getNamedParams(Object[] args) {
final int paramCount = names.size();
if (args == null || paramCount == 0) {
return null;
// 是否拥有@Param注解
} else if (!hasParamAnnotation && paramCount == 1) {
return args[names.firstKey()];
} else {
final Map<String, Object> param = new ParamMap<>();
int i = 0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : names.entrySet()) {
// 首先按照类注释中提供的key,存入一遍 【参数的@Param名称 或者 参数排序:实参值】
// 注意,key和value交换了位置
param.put(entry.getValue(), args[entry.getKey()]);
// add generic param names (param1, param2, ...)
final String genericParamName = GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX + String.valueOf(i + 1);
// ensure not to overwrite parameter named with @Param
// 再按照param1, param2, ...的命名方式存入一遍
if (!names.containsValue(genericParamName)) {
param.put(genericParamName, args[entry.getKey()]);
}
i++;
}
return param;
}
}
测试代码
@Test
public void InsertTest(){
// 第一阶段:MyBatis的初始化阶段
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
// 得到配置文件的输入流
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 得到SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// 第二阶段:数据读写阶段
try (SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
// 找到接口对应的实现
UserMapper userMapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 组建查询参数
User userParam = new User();
userParam.setSchoolname("Sunny School");
// 调用接口展开数据库操作
int insert = userMapper.insert(userParam);
System.out.println(insert);
}
}
1.1 参数的对应解析convertArgsToSqlCommandParam
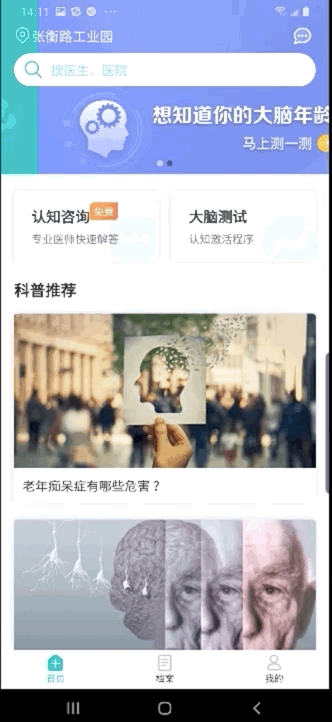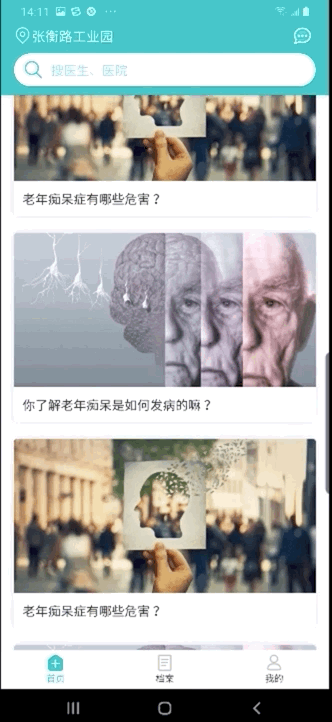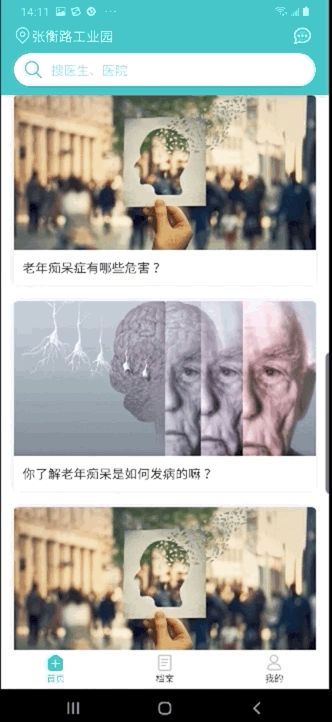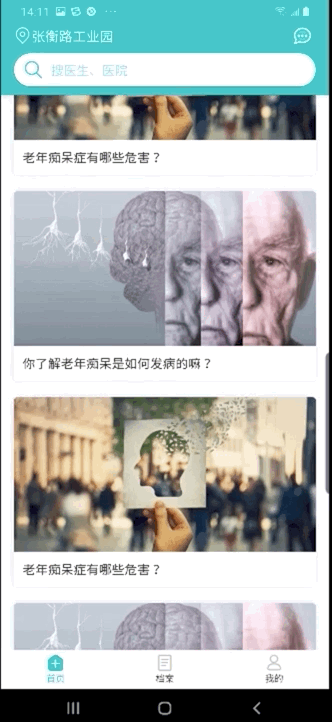
- 打上断点,调试一手,我们可以看到首先判断SqlCommand的类型是INSERT
- 通过convertArgsToSqlCommandParam方法转换参数,下面我们来看看具体的convertArgsToSqlCommandParam的方法,这就需要ParamNameResolver的方法来帮助解析
public static final String GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX = "param";
// 是否使用实际参数
private final boolean useActualParamName;
// name的map
private final SortedMap<Integer, String> names;
// 是否使用@Param注解
private boolean hasParamAnnotation;
// 构造器
public ParamNameResolver(Configuration config, Method method) {
// Configuration中是否使用实际参数
this.useActualParamName = config.isUseActualParamName();
// 方法参数类型
final Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
// 方法的注解
final Annotation[][] paramAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
final SortedMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
int paramCount = paramAnnotations.length;
// get names from @Param annotations
for (int paramIndex = 0; paramIndex < paramCount; paramIndex++) {
if (isSpecialParameter(paramTypes[paramIndex])) {
// skip special parameters
continue;
}
String name = null;
// 遍历方法注解,查找是否拥有@Param注解
for (Annotation annotation : paramAnnotations[paramIndex]) {
if (annotation instanceof Param) {
hasParamAnnotation = true;
// 注解的值
name = ((Param) annotation).value();
break;
}
}
if (name == null) {
// @Param was not specified.
if (useActualParamName) {
// 通过Stream流的方式获取name
name = getActualParamName(method, paramIndex);
}
if (name == null) {
// use the parameter index as the name ("0", "1", ...)
// gcode issue #71
name = String.valueOf(map.size());
}
}
//
map.put(paramIndex, name);
}
names = Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap(map);
}
// 获取参数
public Object getNamedParams(Object[] args) {
final int paramCount = names.size();
if (args == null || paramCount == 0) {
return null;
}
// 不是注解且参数个数为1 aMethod(@Param("M") int a, @Param("N") int b) -> {{0, "M"}, {1, "N"}}
else if (!hasParamAnnotation && paramCount == 1) {
// 就返回第一个值
Object value = args[names.firstKey()];
// 判断是否需要返回集合类型
return wrapToMapIfCollection(value, useActualParamName ? names.get(0) : null);
}
// 注解的方式
else {
final Map<String, Object> param = new ParamMap<>();
int i = 0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : names.entrySet()) {
param.put(entry.getValue(), args[entry.getKey()]);
// add generic param names (param1, param2, ...)
final String genericParamName = GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX + (i + 1);
// ensure not to overwrite parameter named with @Param
if (!names.containsValue(genericParamName)) {
param.put(genericParamName, args[entry.getKey()]);
}
i++;
}
return param;
}
}
我们可以看到通过convertArgsToSqlCommandParam的调用,参数完成了对应的转换
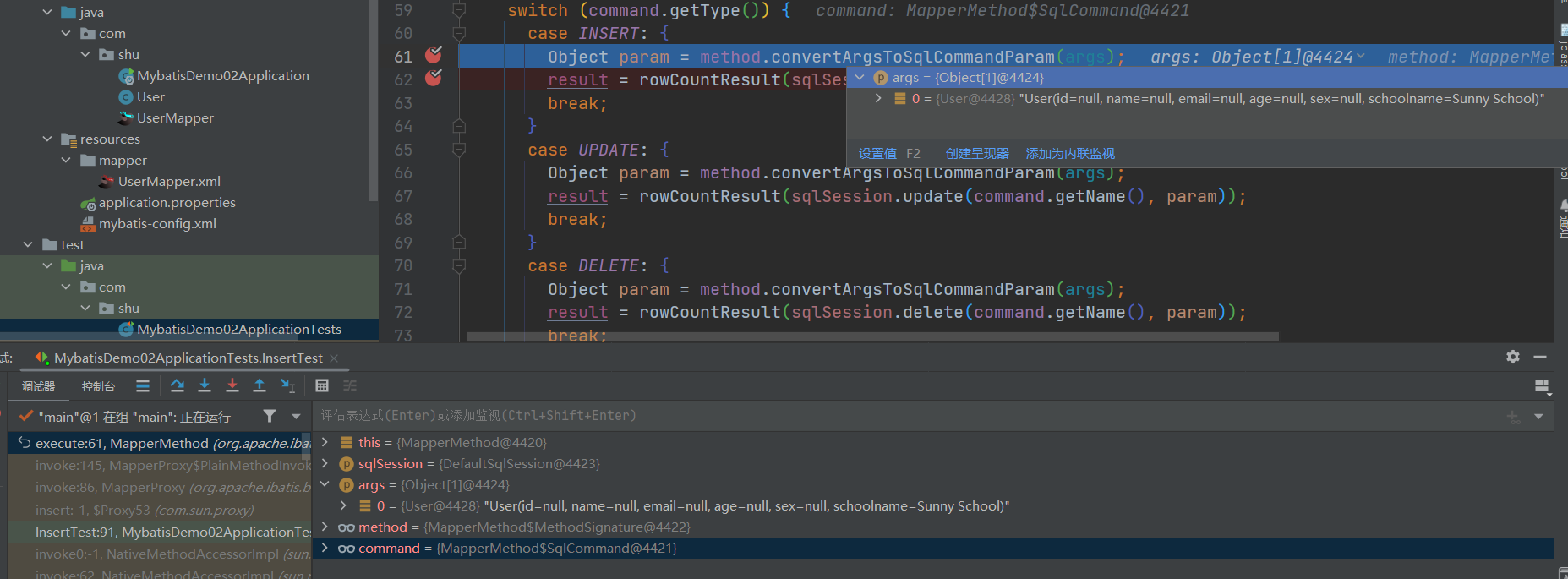
1.2 ID获取对应的MappedStatement
- 下面的步骤,通过id获取到我们解析好的Sql语句,比如com.shu.UserMapper.insert
- 交给相应的执行器,执行sql语句
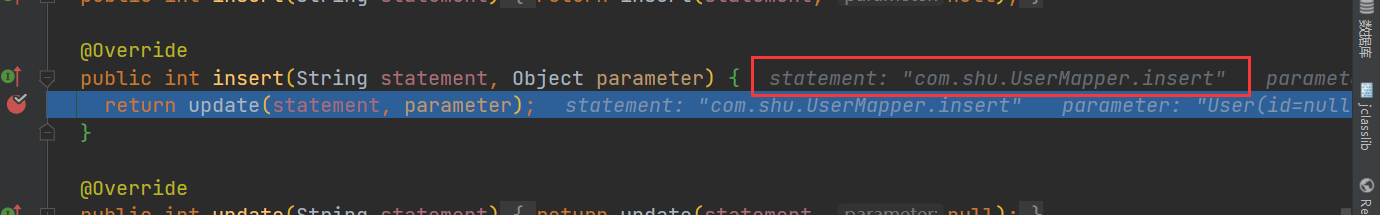
// 执行语句的插入
@Override
public int insert(String statement, Object parameter) {
return update(statement, parameter);
}
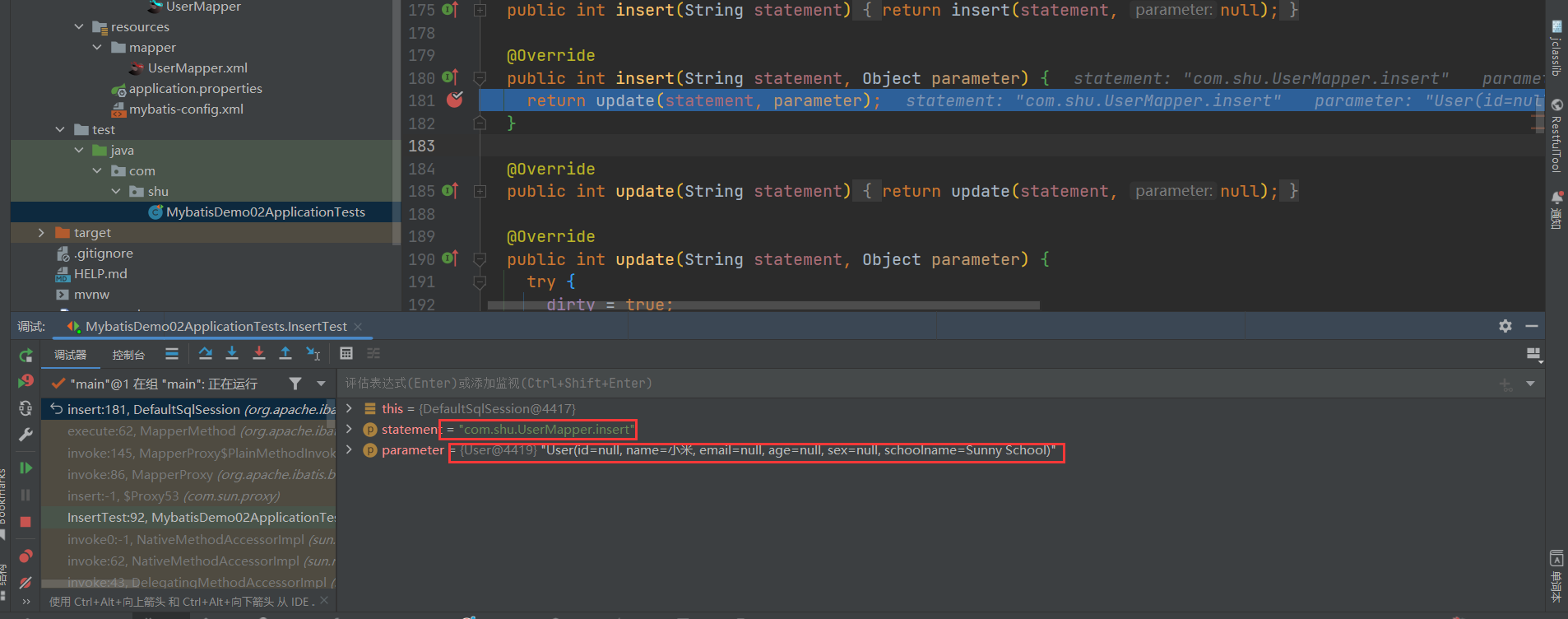
具体的执行
// 映射的数据库操作语句
protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new StrictMap<MappedStatement>("Mapped Statements collection")
.conflictMessageProducer((savedValue, targetValue) ->
". please check " + savedValue.getResource() + " and " + targetValue.getResource());
@Override
public int update(String statement, Object parameter) {
try {
// 是否缓存过了
dirty = true;
// 通过id获取执行的sql语句
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// 把具体的执行sql与参数交给执行器执行返回执行结果
return executor.update(ms, wrapCollection(parameter));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error updating database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
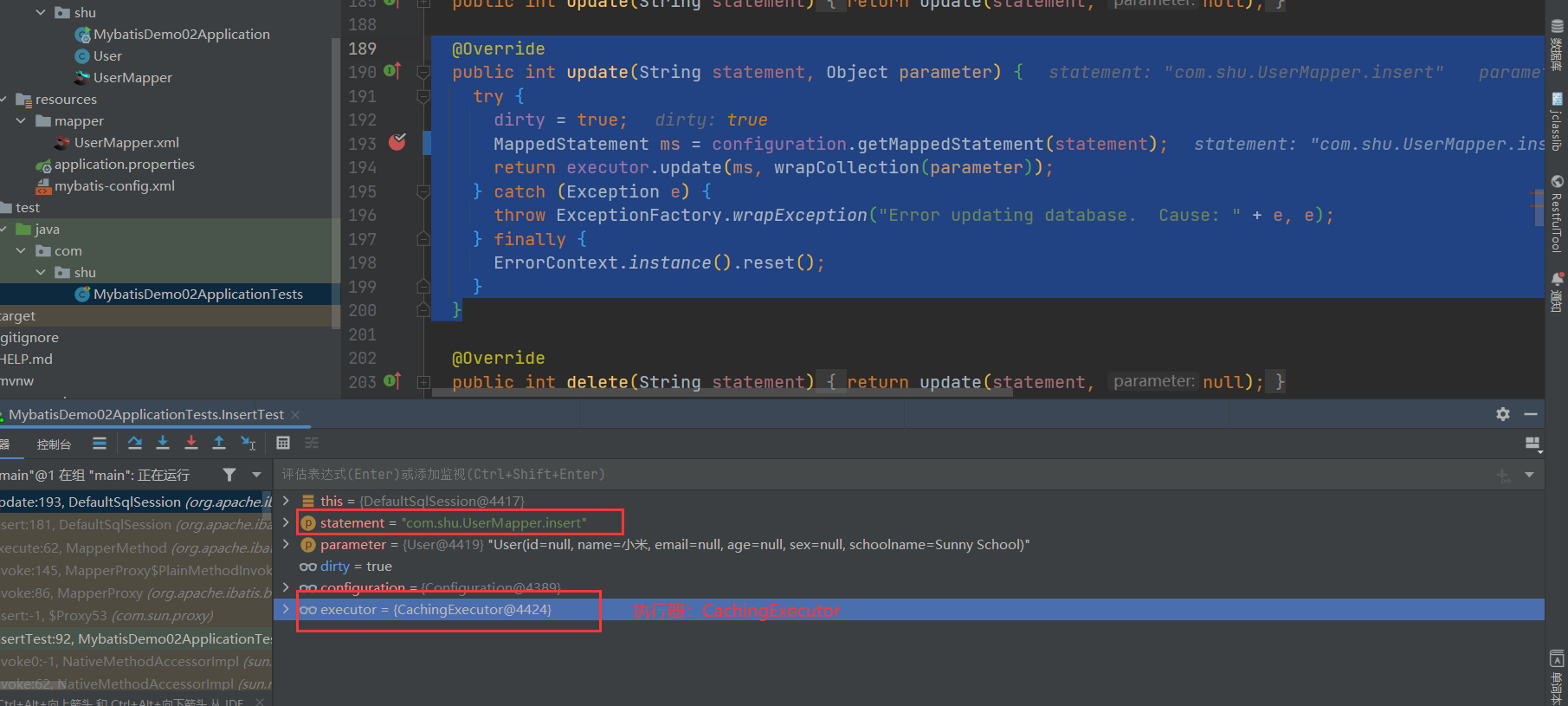
- 通过id获取需要执行的Sql语句以及配置信息,MappedStatement的构建参考前面的解析:Mybatis源码分析(四)Mapper文件的解析_长安不及十里的博客-CSDN博客_mybatis如何解析mapper文件
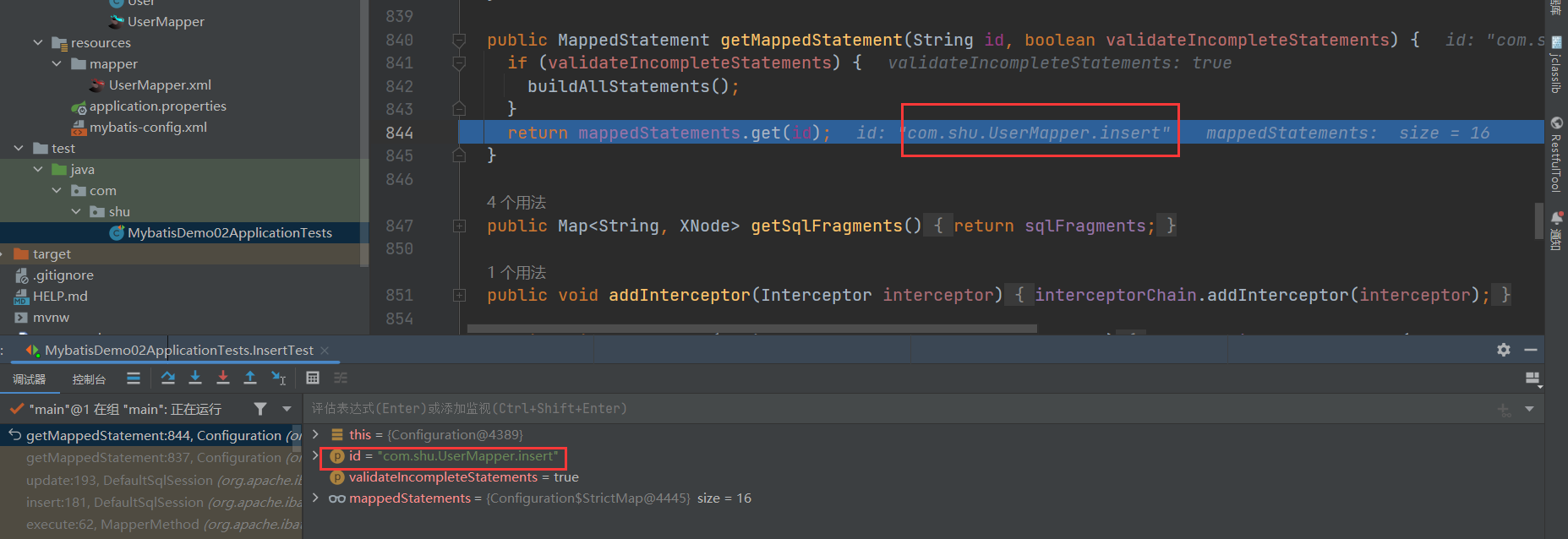
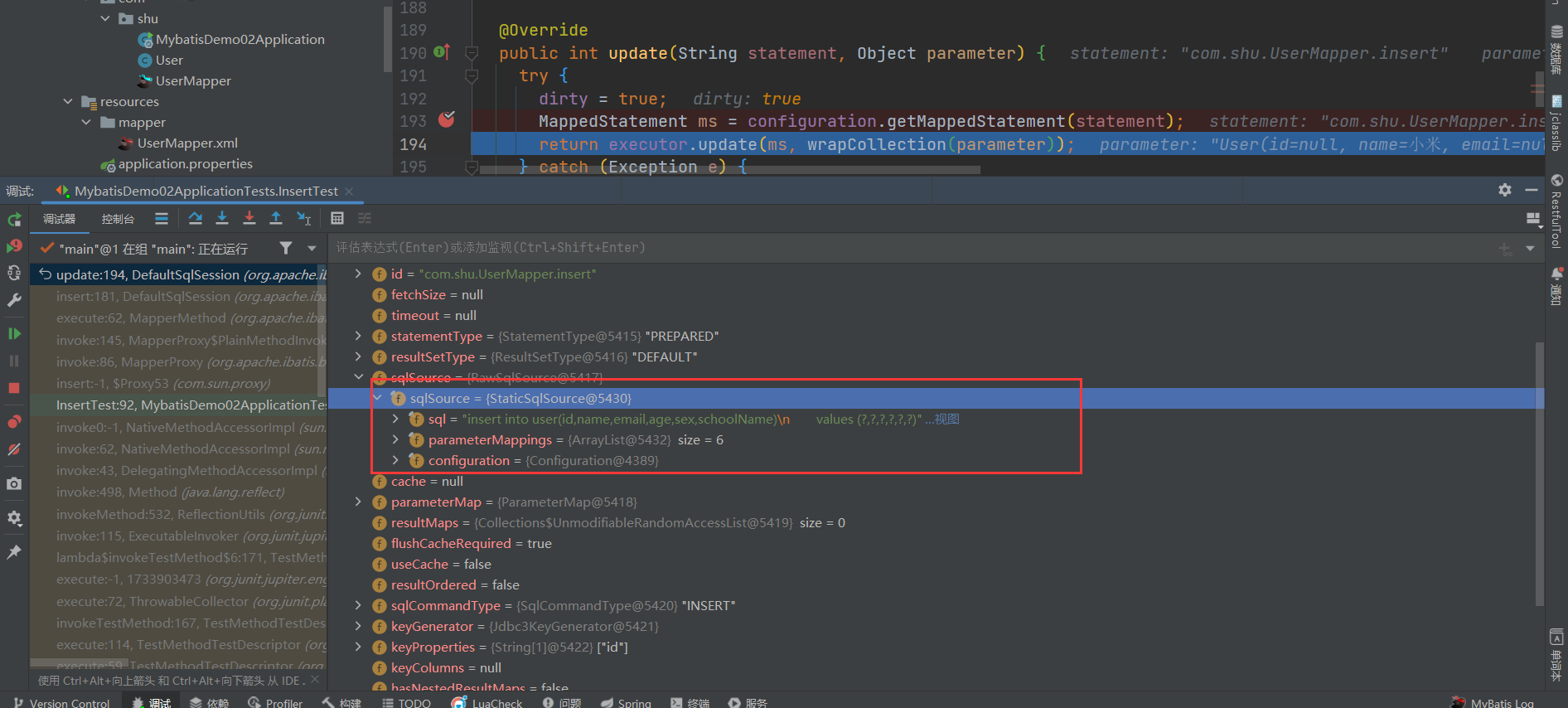
1.3 MappedStatement交给执行器执行
- 在上面,我们通过id获取到了configuration中具体的MappedStatement
- 下面我们交给具体的执行器负责处理对应的SQL语句,而Executor采用模板模式进行设计
首先我们来看看执行器
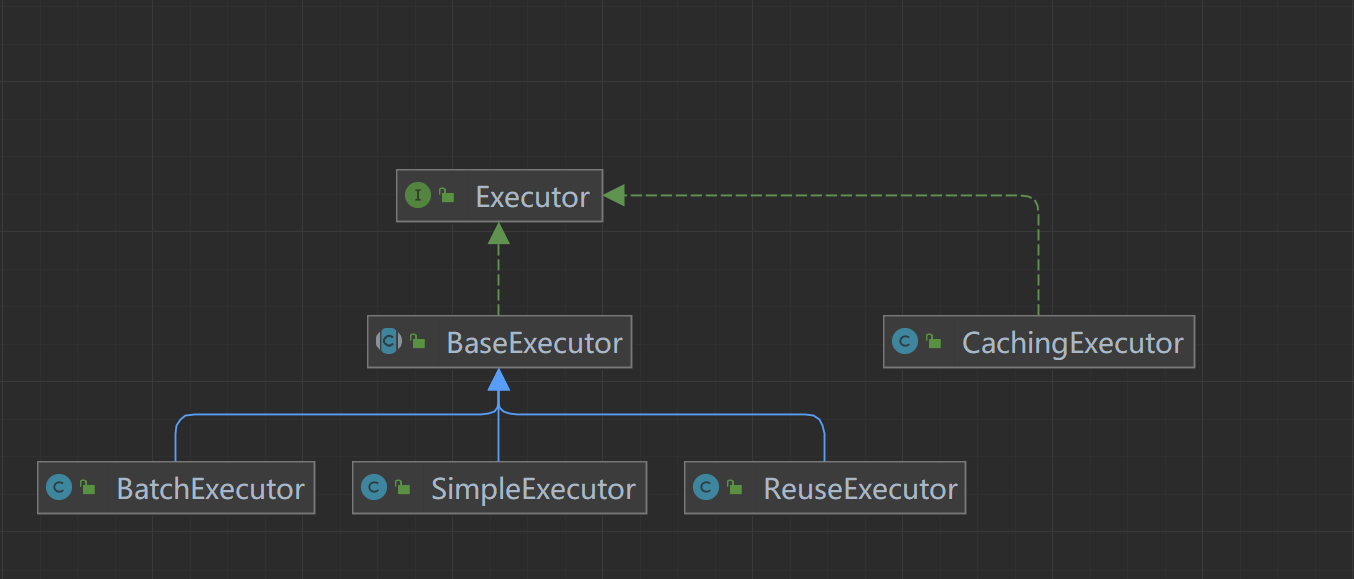
- ExecutorType.SIMPLE(默认执行器)
可以返回自增键,只需要在mapper文件中,增加属性: useGeneratedKeys=“true” keyProperty=“productId”,那么自增键会在事务提交后,自动设置到传入的 user对象中
这个类型不做特殊的事情,它只为每个语句创建一个PreparedStatement。
- ExecutorType.REUSE
这种类型将重复使用PreparedStatements。
- ExecutorType.BATCH
这个类型批量更新,且必要地区别开其中的select 语句,确保动作易于理解。
// 在我们这默认使用CachingExecutor
- 更新数据库数据,INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE三种操作都会调用该方法
// 事务缓存管理器
private final TransactionalCacheManager tcm = new TransactionalCacheManager();
/**
* 更新数据库数据,INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE三种操作都会调用该方法
* @param ms 映射语句
* @param parameterObject 参数对象
* @return 数据库操作结果
* @throws SQLException
*/
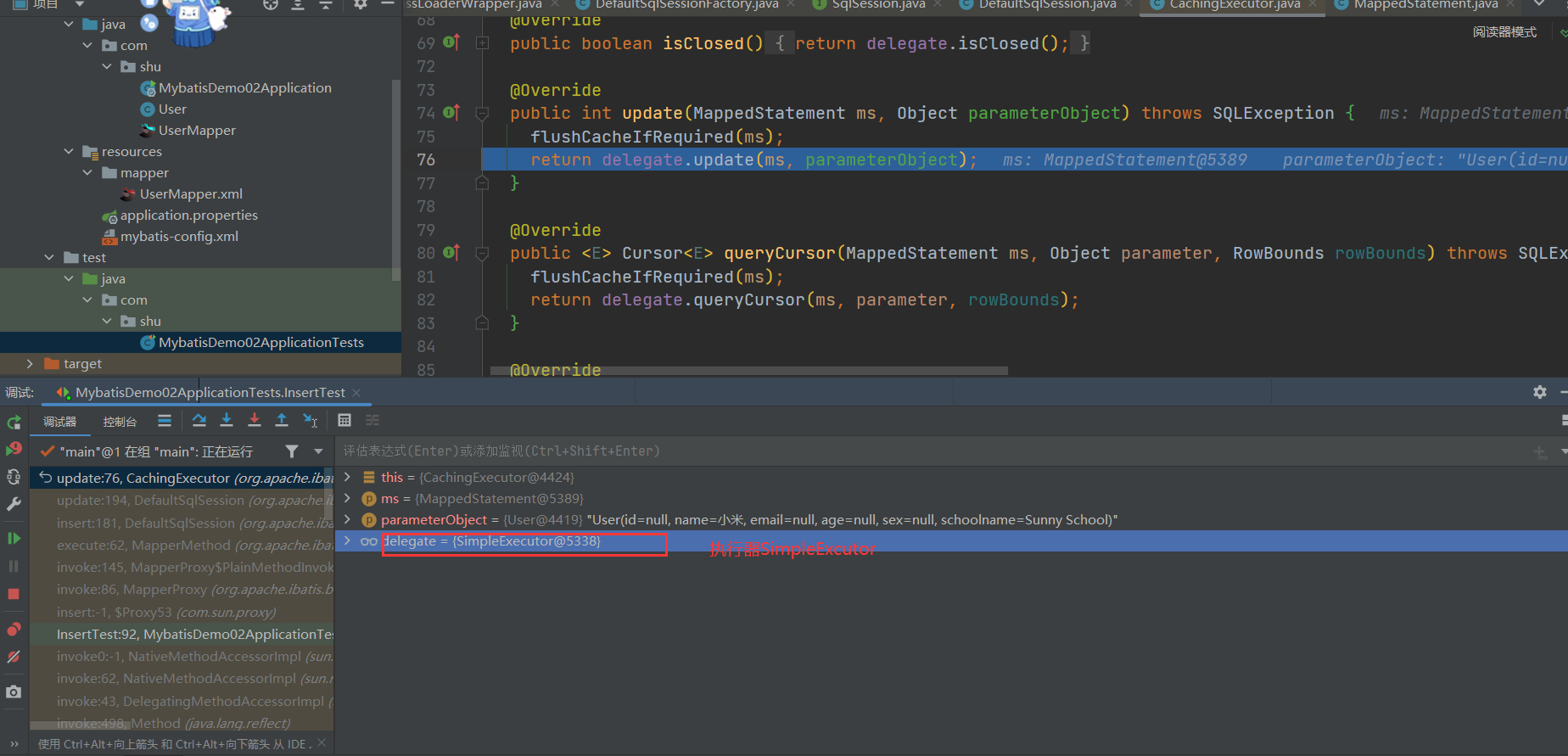
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException {
// 根据要求判断语句执行前是否要清除二级缓存,如果需要,清除二级缓存
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
return delegate.update(ms, parameterObject);
}
/**
* 根据要求判断语句执行前是否要清除二级缓存,如果需要,清除二级缓存
* 注意:默认情况下,非SELECT语句的isFlushCacheRequired方法会返回true
* @param ms MappedStatement
*/
private void flushCacheIfRequired(MappedStatement ms) {
// 获取MappedStatement对应的缓存
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) { // 存在缓存且该操作语句要求执行前清除缓存
// 清除事务中的缓存
tcm.clear(cache);
}
}
- 更新数据库数据,INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE三种操作都会调用该方法
/**
* 更新数据库数据,INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE三种操作都会调用该方法
* @param ms 映射语句
* @param parameter 参数对象
* @return 数据库操作结果
* @throws SQLException
*/
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource())
.activity("executing an update").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
// 执行器已经关闭
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
// 清理本地缓存
clearLocalCache();
// 返回调用子类进行操作
return doUpdate(ms, parameter);
}
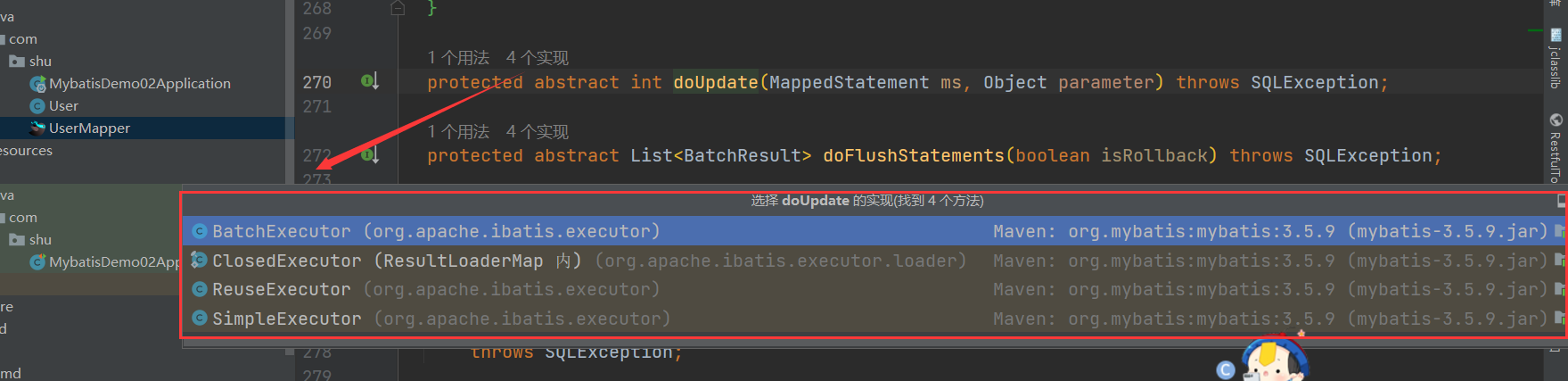
// 调用SimpleExecutor的方法
@Override
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// 获取配置文件
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 处理器
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.update(stmt);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
1.4 不同的执行器获取不同的StatementHandler
StatementHandler 是四大组件中最重要的一个对象,负责操作 Statement 对象与数据库进行交流
- 首先我们来看看StatementHandler接口
// 从Connection中创建一个Statement
Statement prepare(Connection connection, Integer transactionTimeout)
throws SQLException;
// 为Statement绑定实参
void parameterize(Statement statement)
throws SQLException;
// 批量执行操作
void batch(Statement statement)
throws SQLException;
// 执行增、删、改操作
int update(Statement statement)
throws SQLException;
// 执行查找操作,返回list
<E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler)
throws SQLException;
// 执行查询操作,返回迭代游标
<E> Cursor<E> queryCursor(Statement statement)
throws SQLException;
// 获取BoundSql对象
BoundSql getBoundSql();
// 获取参数处理器
ParameterHandler getParameterHandler();
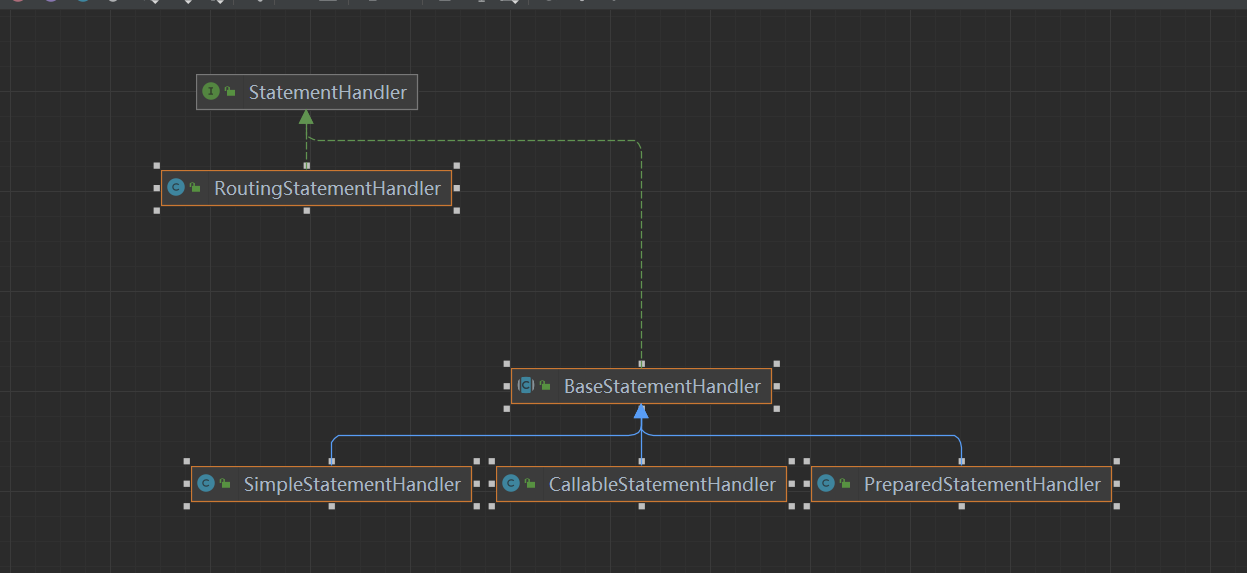
- 对应是实现类
// 根据语句类型选取出的被代理类的对象
private final StatementHandler delegate;
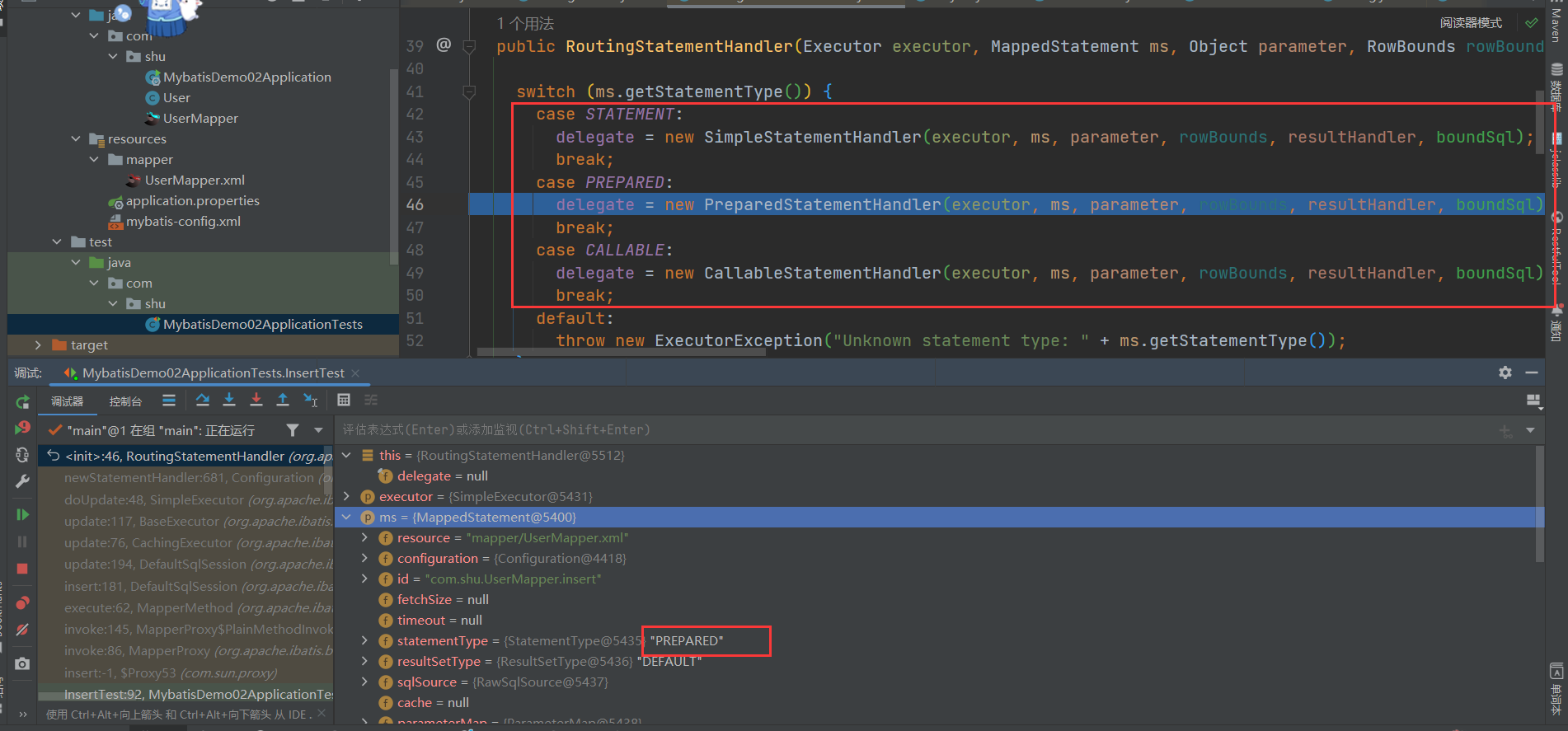
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
// 根据语句类型选择被代理对象
switch (ms.getStatementType()) {
case STATEMENT:
delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case PREPARED:
delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case CALLABLE:
delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
default:
throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType());
}
}
- RoutingStatementHandler: RoutingStatementHandler 并没有对 Statement 对象进行使用,只是根据StatementType 来创建一个代理,代理的就是对应Handler的三种实现类。在MyBatis工作时,使用的StatementHandler 接口对象实际上就是 RoutingStatementHandler 对象。
- BaseStatementHandler: 是 StatementHandler 接口的另一个实现类.本身是一个抽象类.用于简化StatementHandler 接口实现的难度,属于适配器设计模式体现,它主要有三个实现类
- SimpleStatementHandler: 管理 Statement 对象并向数据库中推送不需要预编译的SQL语句。
- PreparedStatementHandler: 管理 Statement 对象并向数据中推送需要预编译的SQL语句。
- CallableStatementHandler:管理 Statement 对象并调用数据库中的存储过程。
/**
* 主要定义了从Connection中获取Statement的方法,而对于具体的Statement操作则未定义
*/
public abstract class BaseStatementHandler implements StatementHandler {
// 配置文件
protected final Configuration configuration;
// 对象工厂
protected final ObjectFactory objectFactory;
// 类型注册机
protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry;
// 结果处理器
protected final ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler;
// 参数处理器
protected final ParameterHandler parameterHandler;
// 执行器
protected final Executor executor;
// 隐射语句
protected final MappedStatement mappedStatement;
// 行范围
protected final RowBounds rowBounds;
// 绑定的sql
protected BoundSql boundSql;
}
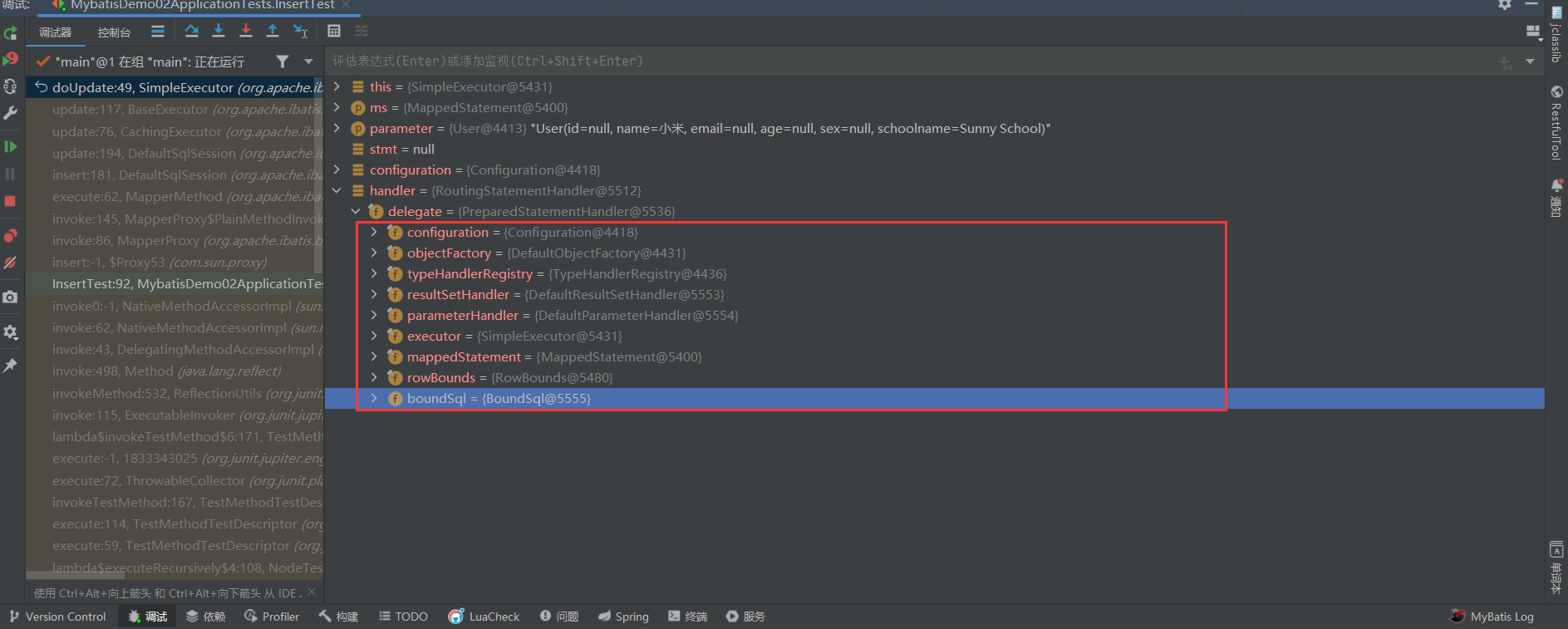
- 再来看看他的构造器方法
protected BaseStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
// 配置文件
this.configuration = mappedStatement.getConfiguration();
// 执行器
this.executor = executor;
// 隐射语句
this.mappedStatement = mappedStatement;
this.rowBounds = rowBounds;
// 类型处理器
this.typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
// 对象工厂
this.objectFactory = configuration.getObjectFactory();
if (boundSql == null) { // issue #435, get the key before calculating the statement
// 如果是前置主键自增,则在这里进行获得自增的键值
generateKeys(parameterObject);
// 获取BoundSql对象
boundSql = mappedStatement.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
}
// 需要绑定的sql
this.boundSql = boundSql;
// 参数处理器
this.parameterHandler = configuration.newParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
// 结果处理器
this.resultSetHandler = configuration.newResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, rowBounds, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql);
}
- 在他的构造器中我们需要关注到两个方法generateKeys(parameterObject)方法,mappedStatement.getBoundSql(parameterObject)方法,首先让我们来看看generateKeys()方法
// 前置自增主键的生成
protected void generateKeys(Object parameter) {
// 从隐射语句中获取KeyGenerator
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator();
ErrorContext.instance().store();
keyGenerator.processBefore(executor, mappedStatement, null, parameter);
ErrorContext.instance().recall();
}
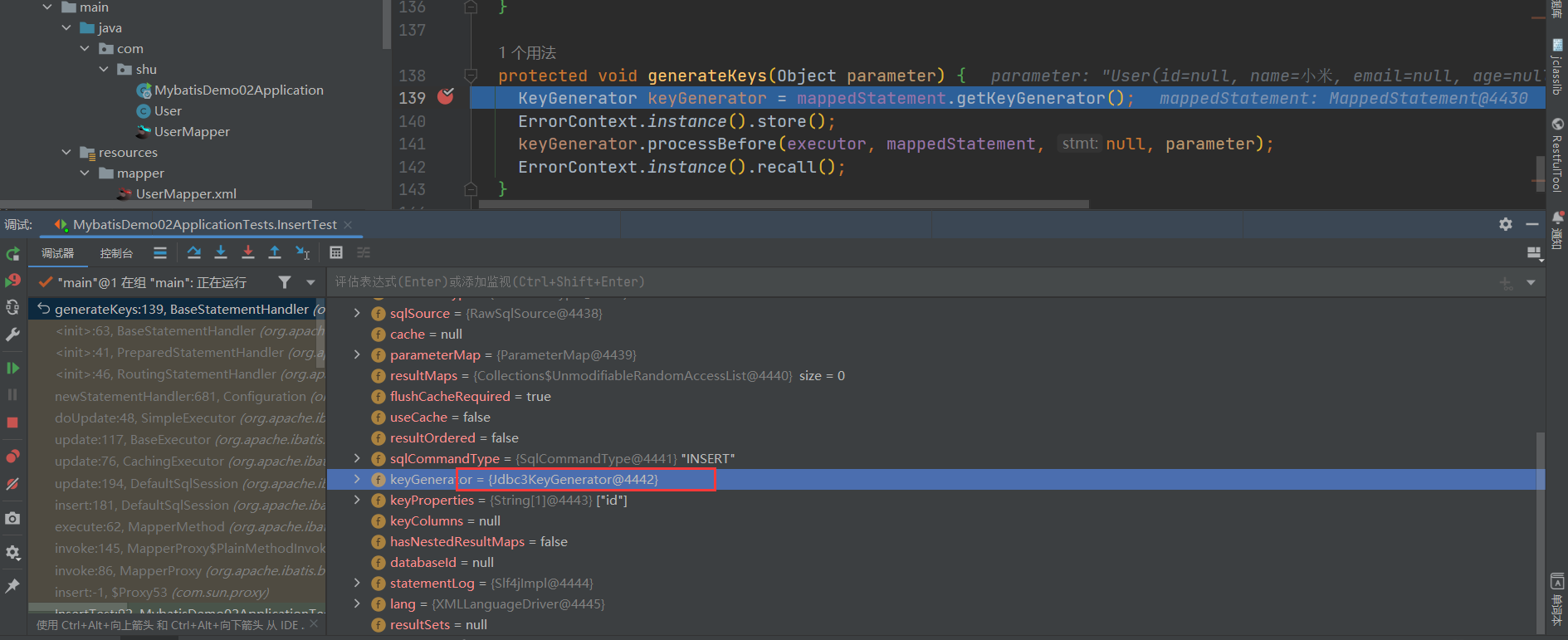
- 我们可以看到用于实现数据插入时主键自增的主键编号生成器有三种实现,而决定用那种在于MappedStatement的Builder方法中
// 全局启用主键生成且是插入语句,则设置主键生成器
mappedStatement.keyGenerator = configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType) ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
1.5 根据参数获取BoundSql
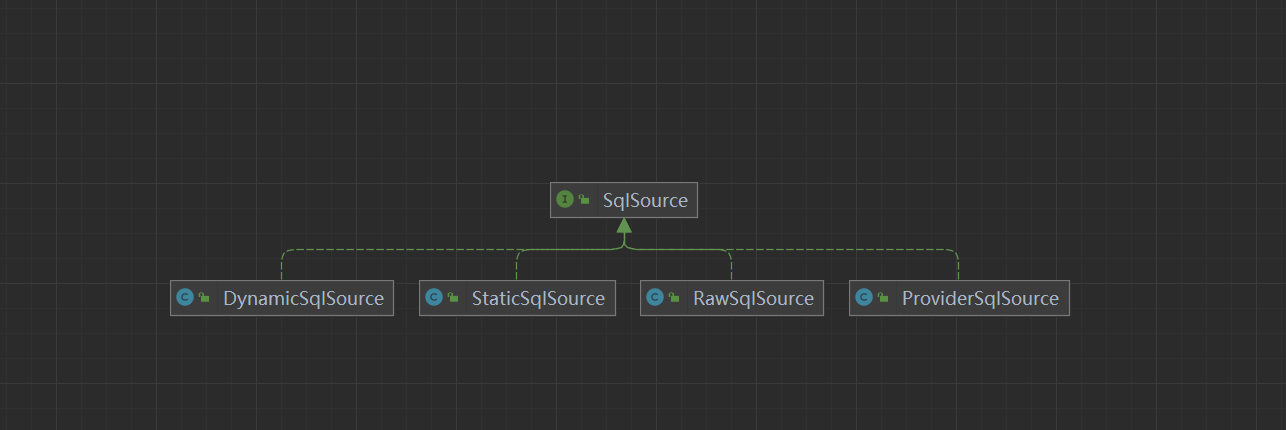
- DynamicSqlSource:针对动态 SQL 和 ${} 占位符的 SQL
- RawSqlSource:针对 #{}占位符的 SQL
- ProviderSqlSource:针对 @*Provider 注解 提供的 SQL
- StaticSqlSource:仅包含有 ?占位符的 SQL
- 下面我们来看看getBoundSql的方法,获取一个BoundSql对象
//SQL源码,对应于我们所写在配置文件中的SQL语句。包含占位符,无法直接执行。可以展开分析就是分行的sql语句text。
private SqlSource sqlSource;
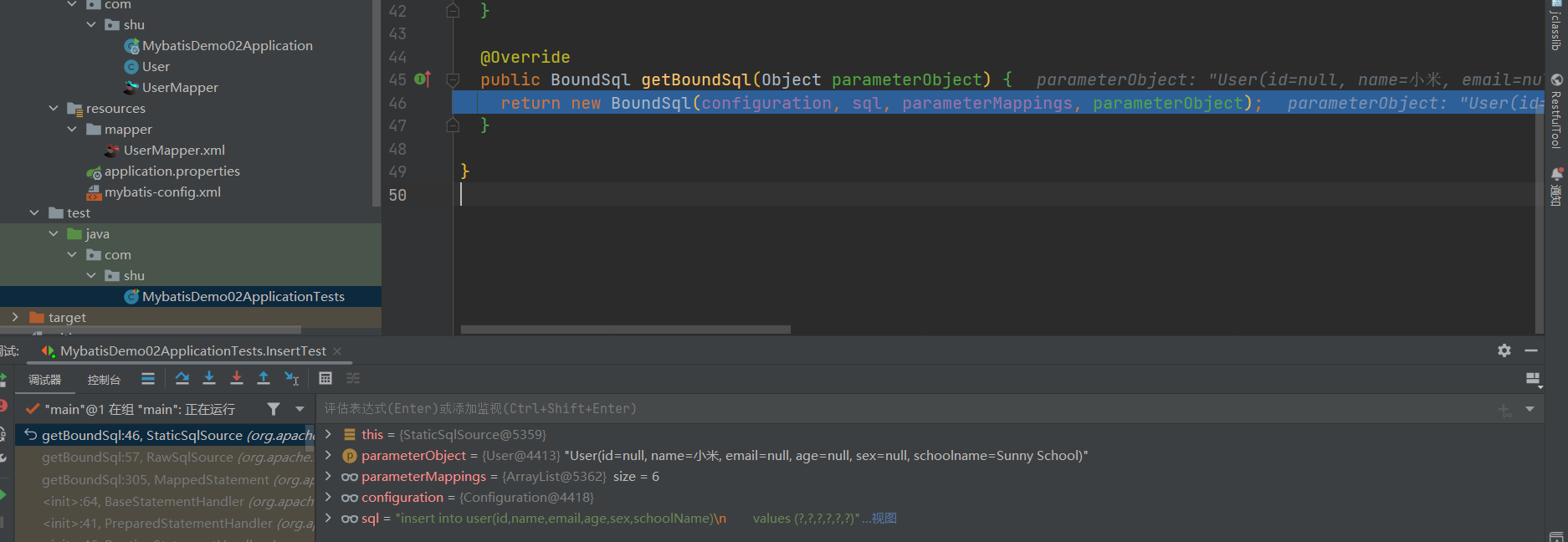
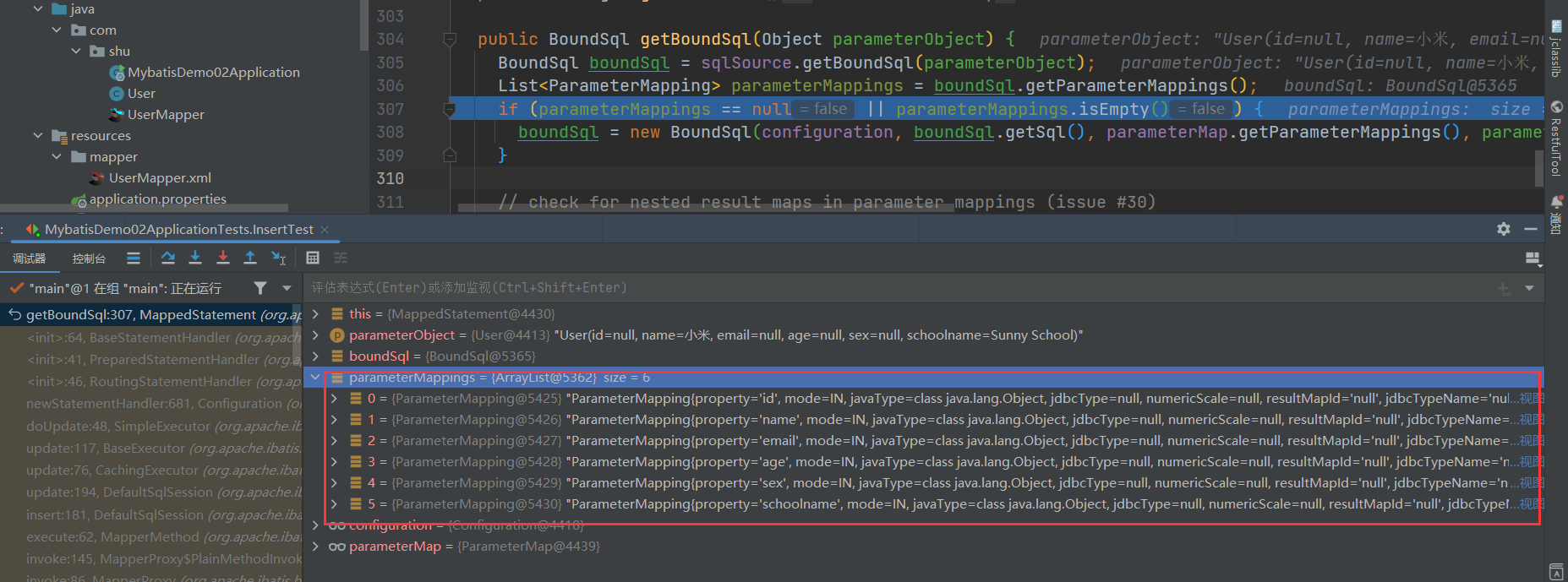
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 获取绑定的sql
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 获取参数隐射
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
// 判断是否为空或为null
if (parameterMappings == null || parameterMappings.isEmpty()) {
boundSql = new BoundSql(configuration, boundSql.getSql(), parameterMap.getParameterMappings(), parameterObject);
}
// check for nested result maps in parameter mappings (issue #30)
for (ParameterMapping pm : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {
String rmId = pm.getResultMapId();
if (rmId != null) {
ResultMap rm = configuration.getResultMap(rmId);
if (rm != null) {
hasNestedResultMaps |= rm.hasNestedResultMaps();
}
}
}
return boundSql;
}
/**
* 组建一个BoundSql对象
* @param parameterObject 参数对象
* @return 组件的BoundSql对象
*/
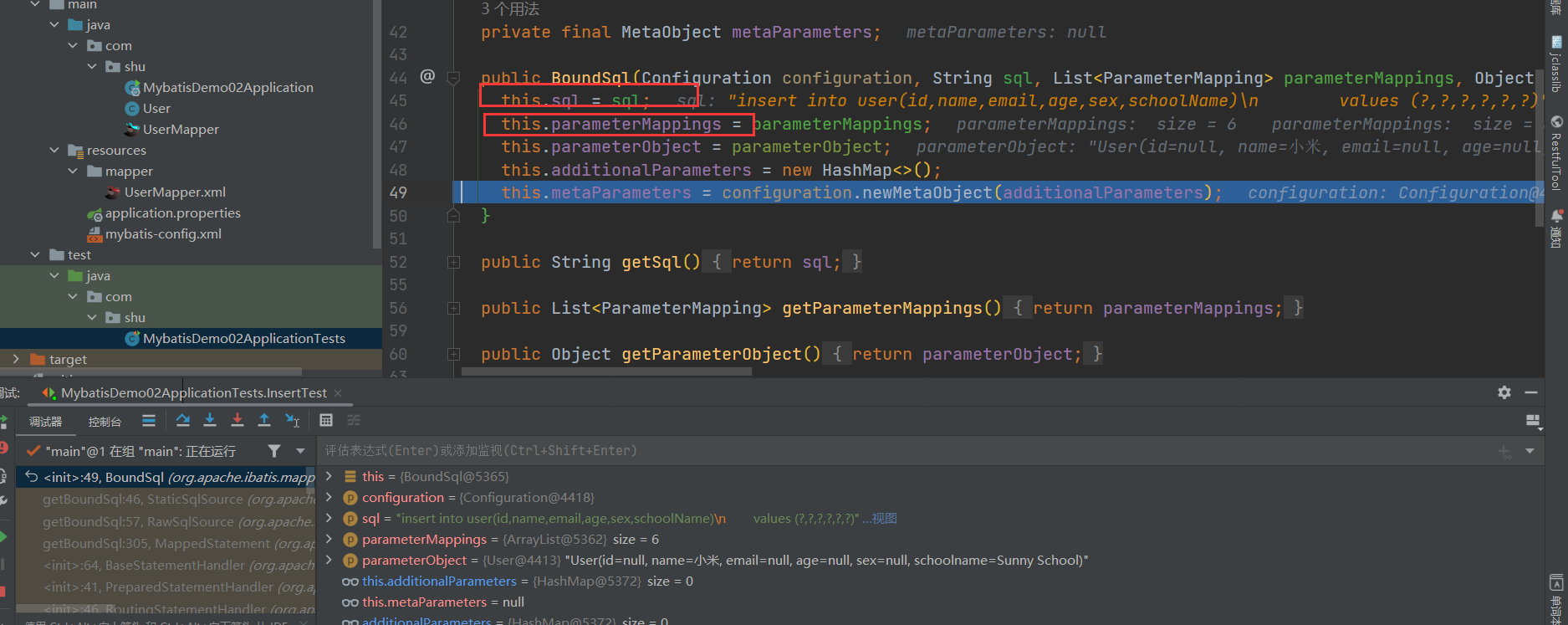
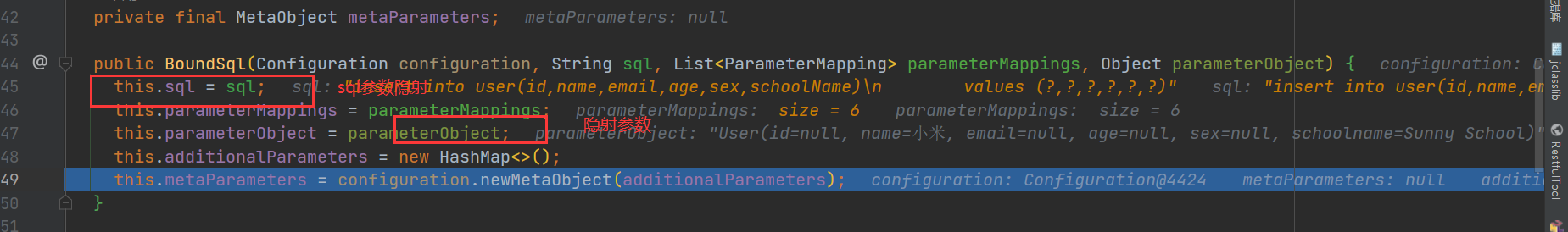
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
return new BoundSql(configuration, sql, parameterMappings, parameterObject);
}
// 参数映射列表
private final List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings;
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
1.6 执行器配置参数处理器ParameterHandler
Mybatis 的 ParameterHandler 是一个接口,用于将 SQL 语句中的参数设置到 PreparedStatement 中。Mybatis 内部会使用 ParameterHandler 来处理 SQL 语句中的参数,通常不需要用户直接使用。
/**
* 创建参数处理器
* @param mappedStatement SQL操作的信息
* @param parameterObject 参数对象
* @param boundSql SQL语句信息
* @return 参数处理器
*/
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
// 创建参数处理器
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
// 将参数处理器交给拦截器链进行替换,以便拦截器链中的拦截器能注入行为
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
// 返回最终的参数处理器
return parameterHandler;
}
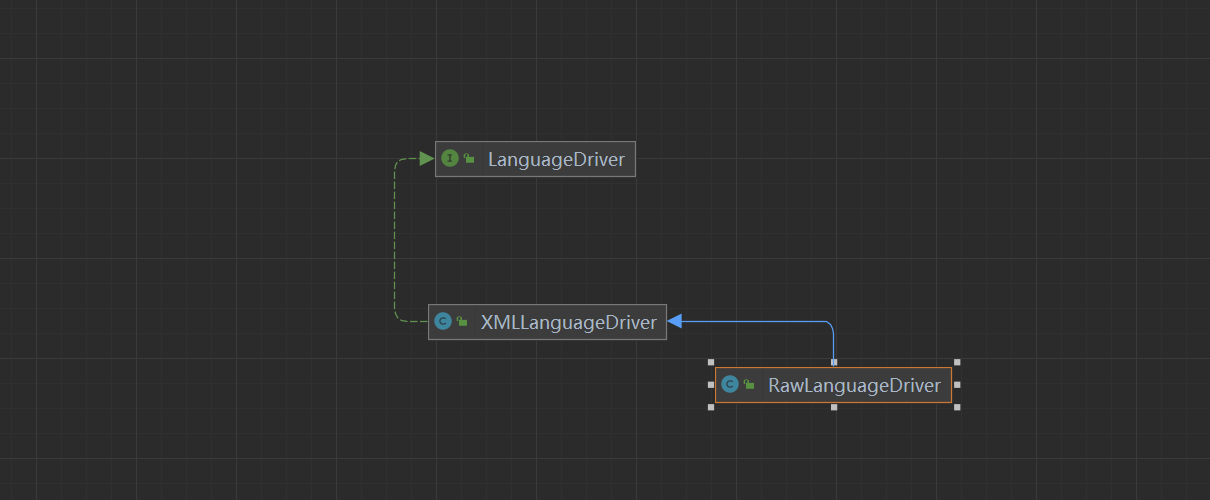
- 了解参数处理器我们首先需要看看LanguageDriver类
- Mybatis LanguageDriver 是 Mybatis 的一个功能,允许用户使用自定义的语言来编写 Mybatis 的映射语句。 Mybatis 默认支持一些常用的语言,如 SQL 和 Java,但是 LanguageDriver 功能允许用户使用自己喜欢的语言来编写映射语句,使得开发人员可以更加灵活地使用 Mybatis。
// 脚本语言解释器
// 在接口上注解的SQL语句,就是由它进行解析的
// @Select("select * from `user` where id = #{id}")
//User queryUserById(Integer id);
public interface LanguageDriver {
/**
* 创建参数处理器。参数处理器能将实参传递给JDBC statement。
* @param mappedStatement 完整的数据库操作节点
* @param parameterObject 参数对象
* @param boundSql 数据库操作语句转化的BoundSql对象
* @return 参数处理器
*/
ParameterHandler createParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql);
/**
* 创建SqlSource对象(基于映射文件的方式)。该方法在MyBatis启动阶段,读取映射接口或映射文件时被调用
* @param configuration 配置信息
* @param script 映射文件中的数据库操作节点
* @param parameterType 参数类型
* @return SqlSource对象
*/
SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType);
/**
* 创建SqlSource对象(基于注解的方式)。该方法在MyBatis启动阶段,读取映射接口或映射文件时被调用
* @param configuration 配置信息
* @param script 注解中的SQL字符串
* @param parameterType 参数类型
* @return SqlSource对象,具体来说是DynamicSqlSource和RawSqlSource中的一种
*/
SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String script, Class<?> parameterType);
}
- 返回一个默认的参数处理器,通过参数处理器为PreparedStatement设置参数
// 返回一个默认的参数处理器
@Override
public ParameterHandler createParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
return new DefaultParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
}
public class DefaultParameterHandler implements ParameterHandler {
// 类型处理器注册表
private final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry;
// MappedStatement对象(包含完整的增删改查节点信息)
private final MappedStatement mappedStatement;
// 参数对象
private final Object parameterObject;
// BoundSql对象(包含SQL语句、参数、实参信息)
private final BoundSql boundSql;
// 配置信息
private final Configuration configuration;
public DefaultParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
this.mappedStatement = mappedStatement;
this.configuration = mappedStatement.getConfiguration();
this.typeHandlerRegistry = mappedStatement.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry();
this.parameterObject = parameterObject;
this.boundSql = boundSql;
}
@Override
public Object getParameterObject() {
return parameterObject;
}
/**
* 为语句设置参数
* @param ps 语句
*/
@Override
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
// 取出参数列表
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
// ParameterMode.OUT是CallableStatement的输出参数,已经单独注册。故忽略
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
// 取出属性名称
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
// 从附加参数中读取属性值
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
// 参数对象是基本类型,则参数对象即为参数值
value = parameterObject;
} else {
// 参数对象是复杂类型,取出参数对象的该属性值
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
// 确定该参数的处理器
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
// 此方法最终根据参数类型,调用java.sql.PreparedStatement类中的参数赋值方法,对SQL语句中的参数赋值
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException | SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
}
后面的为执行器设置一个默认的结果处理器我就不说了
1.7 拿到StatementHandler具体的执行
- 获取数据库连接,执行sql语句,封装结果返回
// 返回一个StatementHandler对象
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
@Override
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.update(stmt);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
// 准备语句
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
// 获取连接
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// 从Connection中创建一个Statement
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// 为Statement绑定实参,这就要参考具体的实现类
handler.parameterize(stmt);
// 返回 Statement
return stmt;
}
/**
* 为语句设置参数
* @param ps 语句
*/
@Override
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
// 取出参数列表
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
// ParameterMode.OUT是CallableStatement的输出参数,已经单独注册。故忽略
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
// 取出属性名称
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
// 从附加参数中读取属性值
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
// 参数对象是基本类型,则参数对象即为参数值
value = parameterObject;
} else {
// 参数对象是复杂类型,取出参数对象的该属性值
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
// 确定该参数的处理器
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
// 此方法最终根据参数类型,调用java.sql.PreparedStatement类中的参数赋值方法,对SQL语句中的参数赋值
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException | SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
- 交个处理器执行handler.update(stmt),返回结果
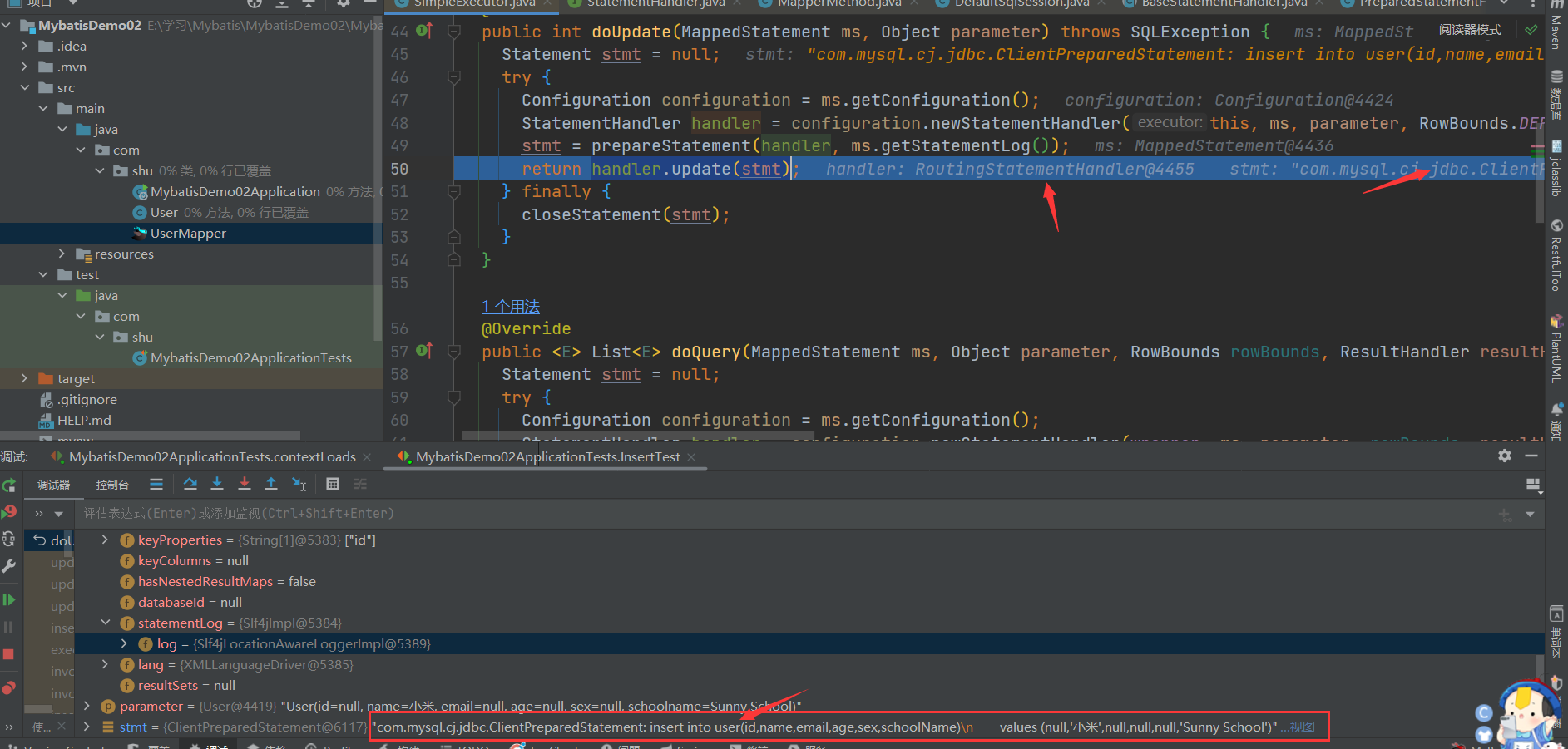
- 更新语句,
@Override
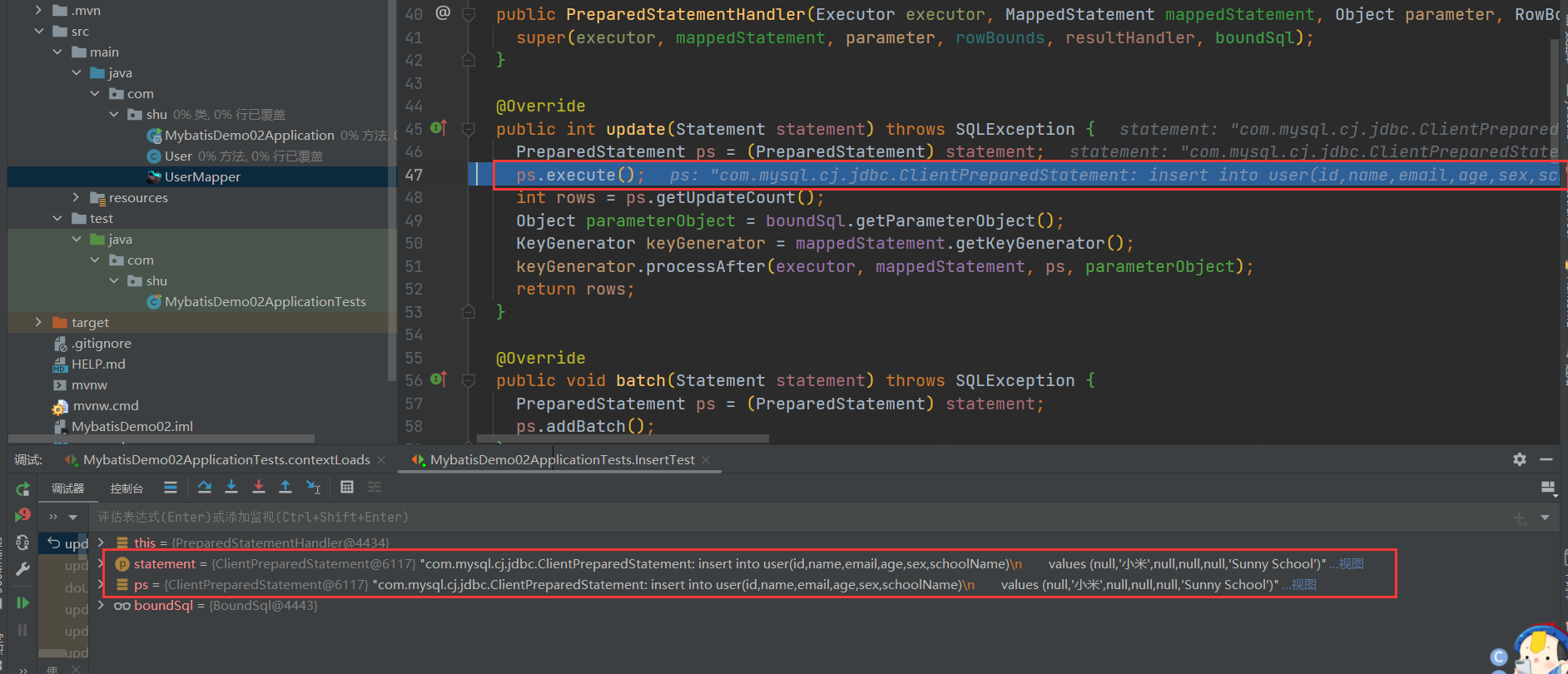
public int update(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
ps.execute();
int rows = ps.getUpdateCount();
Object parameterObject = boundSql.getParameterObject();
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator();
keyGenerator.processAfter(executor, mappedStatement, ps, parameterObject);
return rows;
}
PreparedStatement.execute() 是用于执行预编译的 SQL 语句的方法。它可以通过传递参数来执行带有占位符的预编译语句。
这个方法的返回值是一个布尔值,表示该语句是否返回结果集。如果返回 true,则表示该语句返回了结果集;如果返回 false,则表示该语句没有返回结果集。
例如:
PreparedStatement stmt = conn.prepareStatement("SELECT * FROM users WHERE name=?");
stmt.set String(1, "John");
boolean hasResultSet = stmt.execute();
在这个例子中,我们创建了一个预编译的语句,并且使用 setString 方法为第一个占位符设置了参数。然后,我们使用 execute 方法执行该语句,并将返回值保存在 hasResultSet 变量中。




![[ 数据结构 ] 最小生成树(MST)--------普里姆算法、克鲁斯卡尔算法](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/d4c1992fa2d996adcdb37cdcadc2b1d6.png)