一、什么是状态机
状态机,又称有限状态自动机,是表示有限个状态以及在这些状态之间的转移和动作等行为的计算模型。状态机的概念其实可以应用的各种领域,包括电子工程、语言学、哲学、生物学、数学和逻辑学等,例如日常生活中的电梯、风扇、门闸机等,都会涉及到多种状态,随着动作的执行会进行状态的转移,而在软件编程领域,采用状态机的思路同样可以简化我们的设计流程,会使代码的可读性和可维护性得到增加。
目前用的比较多的开源状态机如:Spring StateMachine、Squirrel StateMachine以及阿里开源一款轻量的Cola-StateMachine,本文主要介绍Spring的状态机的使用。
二、Spring状态机的核心概念
- transition:转换是原状态和目标状态之间的关系,用于将状态机从一种状态转移到另一种状态
- source:节点的当前状态
- target:节点的目标状态
- event:触发节点从当前状态到目标状态的动作,如从State A 到 State B
- guard:也叫“门卫”,当事件请求触发时,可以定义校验规则,用于校验是否可以执行后续action
- action:用于实现当前节点对应的业务逻辑(事件发生之后系统做出的反应)
- withChoice:当执行一个动作,可能导致多种结果时,可以选择使用choice+guard来跳转
- withInternal:我们支持三种不同类型的转换,external,internal和local。转换时通过信号触发的,该信号是发送到状态机的事件或计时器
三、Spring状态机使用示例
Spring StateMachine 是 Spring 官方提供的状态机实现。其核心组件如下:
- StateMachine:状态机实例,可以触发事件、执行状态转换,并获取当前状态等信息;
- StateMachineStateConfigurer:用于配置状态,定义状态机中的各种状态,并指定每个状态的行为和属性;
- StateMachineTransitionConfigurer:用于配置状态之间的转换关系,定义转换的触发事件、源状态、目标状态,以及转换的条件和动作;
- StateMachineConfigurationConfigurer:状态机系统配置,用于配置状态机的全局属性和行为,包括状态机的执行模式、并发策略、监听器等;
- StateMachineListenerAdapter:事件监听器,用于简化状态机事件监听器(StateMachineEventListener)的实现
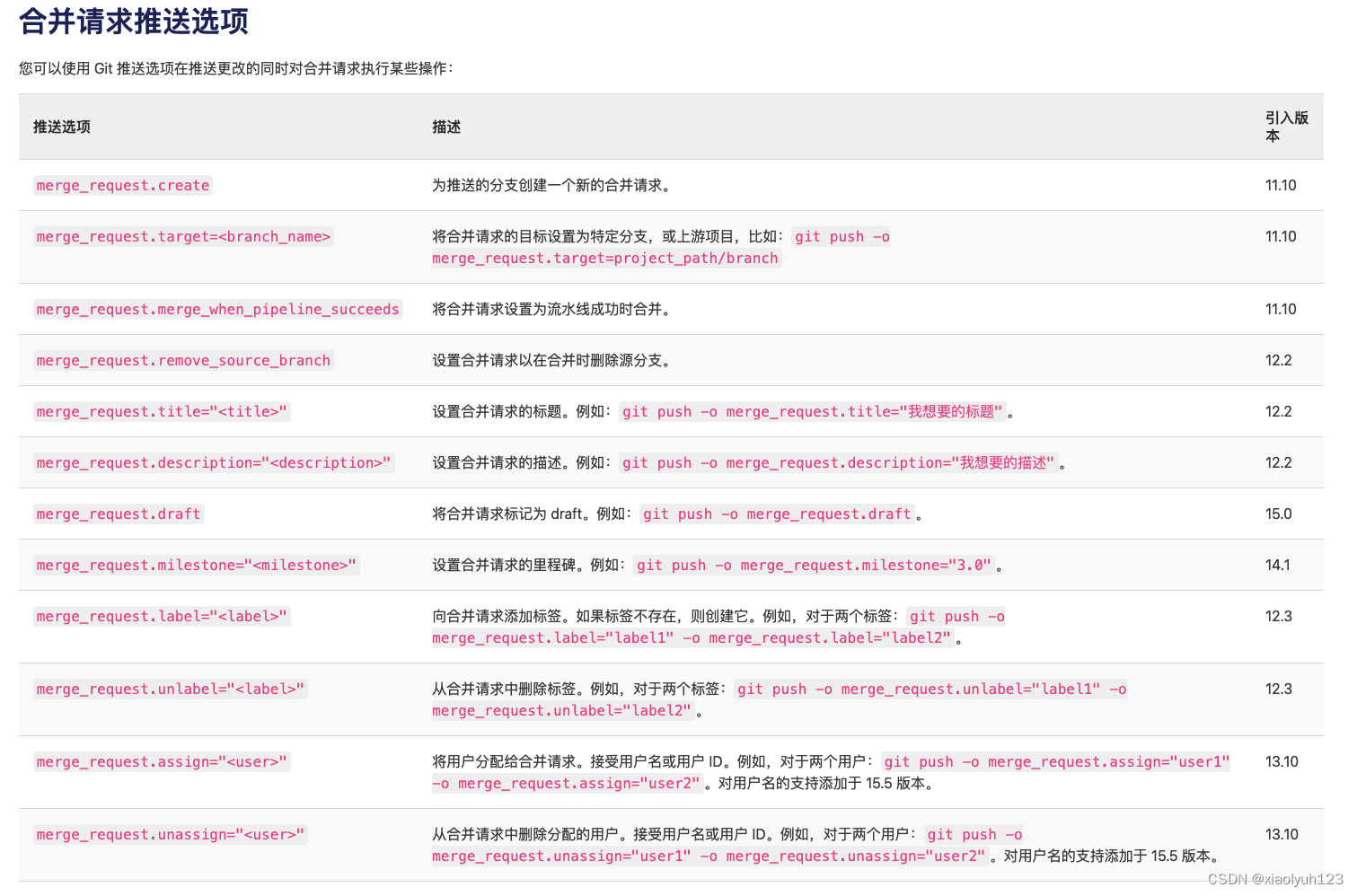
这里还是以抽奖奖励状态转换为例,奖励的状态转换图如下:

- 环境准备:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.statemachine</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-statemachine-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.5.0</version>
</dependency>
- 定义奖励状态以及事件的枚举类
public enum AwardState {
INACTIVE,
ACTIVE,
PAUSE,
FINISH
}
public enum AwardEvent {
AUTO_ACTIVATE,
AUTO_FINISH,
FINISH,
PAUSE,
RESUME
}
- 状态机配置类:
@Configuration
@EnableStateMachine
public class AwardStateMachineConfig extends EnumStateMachineConfigurerAdapter<AwardState, AwardEvent> {
@Autowired
private AwardStateMachineListener awardStateMachineListener;
@Override
public void configure(StateMachineStateConfigurer<AwardState, AwardEvent> states) throws Exception {
states
.withStates()
.initial(AwardState.INACTIVE)
.states(EnumSet.allOf(AwardState.class));
}
@Override
public void configure(StateMachineTransitionConfigurer<AwardState, AwardEvent> transitions) throws Exception {
transitions
.withExternal()
.source(AwardState.INACTIVE)
.target(AwardState.ACTIVE)
.event(AwardEvent.AUTO_ACTIVATE)
.and()
.withExternal()
.source(AwardState.INACTIVE)
.target(AwardState.FINISH)
.event(AwardEvent.AUTO_FINISH)
.and()
.withExternal()
.source(AwardState.ACTIVE)
.target(AwardState.FINISH)
.event(AwardEvent.FINISH)
.and()
.withExternal()
.source(AwardState.ACTIVE)
.target(AwardState.PAUSE)
.event(AwardEvent.PAUSE)
.and()
.withExternal()
.source(AwardState.PAUSE)
.target(AwardState.ACTIVE)
.event(AwardEvent.RESUME)
.and()
.withExternal()
.source(AwardState.PAUSE)
.target(AwardState.FINISH)
.event(AwardEvent.FINISH);
}
@Override
public void configure(StateMachineConfigurationConfigurer<AwardState, AwardEvent> config) throws Exception {
config.withConfiguration().autoStartup(true).listener(awardStateMachineListener);
}
}
- 状态机监听器:
@Component
public class AwardStateMachineListener extends StateMachineListenerAdapter<AwardState, AwardEvent> {
@Override
public void transition(Transition<AwardState, AwardEvent> transition) {
System.out.println("状态转移 from " + transition.getSource().getId() + " to " + transition.getTarget().getId());
}
/*@Override
public void stateChanged(State<AwardState, AwardEvent> from, State<AwardState, AwardEvent> to) {
System.out.println("状态改变 from " + from.getId() + " to " + to.getId());
}*/
}
- 奖励服务类
@Service
public class AwardStateMachineService {
@Resource
private StateMachine<AwardState, AwardEvent> stateMachine;
public void autoActivate() {
stateMachine.sendEvent(AwardEvent.AUTO_ACTIVATE);
}
public void autoFinish() {
stateMachine.sendEvent(AwardEvent.AUTO_FINISH);
}
public void finish() {
stateMachine.sendEvent(AwardEvent.FINISH);
}
public void pause() {
stateMachine.sendEvent(AwardEvent.PAUSE);
}
public void resume() {
stateMachine.sendEvent(AwardEvent.RESUME);
}
}
- 测试:
@SpringBootTest
class AwardStatemachineApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private AwardStateMachineService awardStateMachineService;
@Autowired
private StateMachine<AwardState, AwardEvent> stateMachine;
@Test
void awardStageTest() {
// 发送事件自动激活抽奖
awardStateMachineService.autoActivate();
// 检查状态是否变为ACTIVE
assert (stateMachine.getState().getId() == AwardState.ACTIVE);
// 发送事件暂停抽奖
awardStateMachineService.pause();
// 检查状态是否变为PAUSE
assert (stateMachine.getState().getId() == AwardState.PAUSE);
// 发送事件恢复抽奖
awardStateMachineService.resume();
// 检查状态是否变为ACTIVE
assert (stateMachine.getState().getId() == AwardState.ACTIVE);
// 发送事件结束抽奖
awardStateMachineService.finish();
// 检查状态是否变为FINISH
assert (stateMachine.getState().getId() == AwardState.FINISH);
}
}
测试执行结果:

可以看到 Spring 状态机很好的控制了奖励状态之间的流转。
总结:本文主要介绍了Spring状态机的一些基本概念,以及状态流转的使用方式,Spring状态机一些高级的用法,如状态的持久化、状态的并行(parallel,fork,join)、子状态机等,会在后面文章更新。
参考:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-statemachine/docs/2.0.2.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#glossary