文章目录
- 目标
- 设计
- 项目结构
- 四、实现
- 1、定义Advice拦截器链
- 2、定义Advisor访问者
- 3、方法前置拦截器——MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
- 4、代理工厂——ProxyFactory
- 5、融入Bean生命周期的自动代理创建者——InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 、DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
- 6、融入到Bean的生命周期
- 二、测试
- 1、准备
- 2、自定义拦截方法
- 3、spring.xml 配置 AOP
- 4、单元测试
- 总结
目标
AOP和spring的整合,最终能通过在 Spring xml配置的方式完成切面的操作
设计
怎么凭借 BeanPostProcessor 把动态代理融入到 Bean 的生命周期中,
如何组装各项切点、拦截、前置的功能和适配对应的代理器。
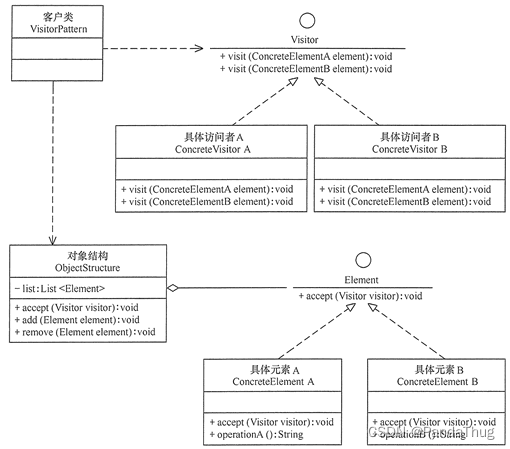
整体设计结构如下图:

为了可以让对象创建过程中,能把xml中配置的代理对象也就是切面的一些类对象实例化,就需要用到 BeanPostProcessor 提供的方法,因为这个类的中的方法可以分别作用与 Bean 对象执行初始化前后修改 Bean 的对象的扩展信息。
但这里需要集合于 BeanPostProcessor 实现新的接口和实现类,这样才能定向获取对应的类信息。
但因为创建的是代理对象不是之前流程里的普通对象,所以我们需要前置于其他对象的创建,所以在实际开发的过程中,需要在 **AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean 优先完成 Bean 对象的判断,**是否需要代理,有则直接返回代理对象。在Spring的源码中会有 createBean 和 doCreateBean 的方法拆分
项目结构

整个类关系图中可以看到,在以 BeanPostProcessor 接口实现继承的 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 接口后,做了一个自动代理创建的类 DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator,这个类的就是用于处理整个 AOP 代理融入到 Bean 生命周期中的核心类。
DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 会依赖于拦截器、代理工厂和Pointcut与Advisor的包装服务, AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor,由它提供切面、拦截方法和表达式。
Spring 的 AOP 把 Advice 细化了 BeforeAdvice、AfterAdvice、AfterReturningAdvice、ThrowsAdvice,目前我们做的测试案例中只用到了 BeforeAdvice,这部分可以对照 Spring 的源码进行补充测试。
四、实现
1、定义Advice拦截器链
/**
* @desc Advice前置拦截器链
*/
public interface BeforeAdvice extends Advice {
}
/**
* @desc Advice方法前置拦截器链
*/
public interface MethodBeforeAdvice extends BeforeAdvice {
void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable;
}
在 Spring 框架中,Advice 都是通过方法拦截器 MethodInterceptor 实现的。环绕 Advice 类似一个拦截器的链路,Before Advice、After advice等,不过暂时我们需要那么多就只定义了一个 MethodBeforeAdvice 的接口定义
2、定义Advisor访问者
public interface Advisor {
Advice getAdvice();
}
/**
* @desc 切入点访问者
*/
public interface PointcutAdvisor extends Advisor {
Pointcut getPointcut();
}
PointcutAdvisor 承担了 Pointcut 和 Advice 的组合,Pointcut 用于获取 JoinPoint,而 Advice 决定于 JoinPoint 执行什么操作。
/**
* @desc 表达式切入点访问者
*/
public class AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor implements PointcutAdvisor {
// 切面
private AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut;
// 具体的拦截方法
private Advice advice;
// 表达式
private String expression;
public void setExpression(String expression) {
this.expression = expression;
}
@Override
public Advice getAdvice() {
return advice;
}
@Override
public Pointcut getPointcut() {
if (pointcut == null) {
pointcut = new AspectJExpressionPointcut(expression);
}
return pointcut;
}
public void setAdvice(Advice advice) {
this.advice = advice;
}
}
AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor 实现了 PointcutAdvisor 接口,把切面 pointcut、拦截方法 advice 和具体的拦截表达式包装在一起。这样就可以在 xml 的配置中定义一个 pointcutAdvisor 切面拦截器了。
3、方法前置拦截器——MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
/**
* @desc 方法前置访问拦截器
*/
public class MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
private MethodBeforeAdvice advice;
public MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(MethodBeforeAdvice advice) {
this.advice = advice;
}
public MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor() {
}
public MethodBeforeAdvice getAdvice() {
return advice;
}
public void setAdvice(MethodBeforeAdvice advice) {
advice = advice;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
this.advice.before(methodInvocation.getMethod(),methodInvocation.getArguments(),methodInvocation.getThis());
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}
}
MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor 实现了 MethodInterceptor 接口,在 invoke 方法中调用 advice 中的 before 方法,传入对应的参数信息。
而这个 advice.before 则是用于自己实现 MethodBeforeAdvice 接口后做的相应处理。
其实可以看到具体的 MethodInterceptor 实现类,其实和我们之前做的测试是一样的,只不过现在交给了 Spring 来处理
4、代理工厂——ProxyFactory
/**
* @desc 代理工厂
*/
public class ProxyFactory {
private AdvisedSupport advisedSupport;
public ProxyFactory(AdvisedSupport advisedSupport) {
this.advisedSupport = advisedSupport;
}
public Object getProxy(){
return createAopProxy().getProxy();
}
private AopProxy createAopProxy(){
if (advisedSupport.isProxyTargetClass()) {
return new Cglib2AopProxy(advisedSupport);
}
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(advisedSupport);
}
}
其实这个代理工厂主要解决的是关于 JDK 和 Cglib 两种代理的选择问题,有了代理工厂就可以按照不同的创建需求进行控制。
5、融入Bean生命周期的自动代理创建者——InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 、DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
定义bean实例化前接口,凭借BeanPostProcessor实现aop,继承spring的关键
public interface InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* 在 Bean 对象执行初始化方法之前,执行此方法
*
* @param beanClass
* @param beanName
* @return
* @throws BeansException
*/
Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException;
}
/**
* @desc 融入Bean生命周期的自动代理创建者
*/
public class DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor, BeanFactoryAware {
private DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
this.beanFactory = (DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory;
}
/**
* @desc: 在 Bean 对象执行初始化方法之前,执行此方法(这个类最核心的方法)
**/
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(isInfrastructureClass(beanClass)){
return null;
}
Collection<AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor> advisors = beanFactory.getBeansOfType(AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor.class).values();
for (AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor advisor : advisors) {
ClassFilter classFilter = advisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter();
if(!classFilter.matches(beanClass)){
continue;
}
// 切面包装类初始化
AdvisedSupport advisedSupport = new AdvisedSupport();
TargetSource targetSource = null;
try {
// 实例化beanClass
targetSource = new TargetSource(beanClass.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 设置代理模式
advisedSupport.setProxyTargetClass(false);
// 被代理的对象
advisedSupport.setTargetSource(targetSource);
// 方法拦截器
advisedSupport.setMethodInterceptor((MethodInterceptor) advisor.getAdvice());
// 方法匹配器
advisedSupport.setMethodMatcher(advisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher());
return new ProxyFactory(advisedSupport).getProxy();
}
return null;
}
/**
* @desc: 是否为基础设施类,底层C实现
**/
private boolean isInfrastructureClass(Class<?> beanClass) {
return Advice.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) || Pointcut.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) || Advisor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass);
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
这个 DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 类的主要核心实现在于 postProcessBeforeInstantiation 方法中,从通过 beanFactory.getBeansOfType 获取 AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor 开始。
获取了 advisors 以后就可以遍历相应的 AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor 填充对应的属性信息,包括:目标对象、拦截方法、匹配器,之后返回代理对象即可。
那么现在调用方获取到的这个 Bean 对象就是一个已经被切面注入的对象了,当调用方法的时候,则会被按需拦截,处理用户需要的信息。
6、融入到Bean的生命周期
public abstract class AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory extends AbstractBeanFactory implements AutowireCapableBeanFactory {
private InstantiationStrategy instantiationStrategy = new CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy();
/**
* 创建bean
*/
@Override
protected Object createBean(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition, Object[] args) throws BeansException {
Object bean = null;
try {
// 判断是否返回代理bean对象(新增代码)
bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName,beanDefinition);
if(bean != null){
return bean;
}
bean = createBeanInstance(beanName,beanDefinition,args);
// 属性填充
applyPropertyvalues(beanName,bean,beanDefinition);
// 执行 Bean 的初始化方法和 BeanPostProcessor 的前置和后置处理方法
bean = initializeBean(beanName, bean, beanDefinition);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BeansException("Instantiation of bean failed", e);
}
// 注册实现了 DisposableBean 接口的 Bean 对象
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, beanDefinition);
// 判断 SCOPE_SINGLETON,SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
if(beanDefinition.isSingleton()){
registerSingleton(beanName,bean);
}
return bean;
}
// 在实例化前应用Bean后处理器 ——新增方法,与 “applyBeanPostProcessorBeforeInitialization” 是两个方法
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
// 在 Bean 对象执行初始化方法之前,执行此方法
if (processor instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
Object result = ((InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) processor).postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
}
return null;
}
// 新增方法,解析实例化前处理
protected Object resolveBeforeInstantiation(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
// 实例化前处理
Object bean = applyBeanPostProcessorBeforeInstantiation(beanDefinition.getBeanClass(), beanName);
if (bean != null) {
// 如果是代理对象,则直接进行初始化后处理
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean,beanName);
}
return bean;
}
// 省略与本章节无关代码
}
因为创建的是代理对象,不是之前流程里的普通对象,所以我们需要前置于其他对象的创建,即需要在 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean 优先完成 Bean 对象的判断,是否需要代理,有则直接返回代理对象,且执行出初始化后的逻辑。
二、测试
1、准备
public class UserService implements IUserService {
public String queryUserInfo() {
try {
Thread.sleep(new Random(1).nextInt(100));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "ljc,100001,上海";
}
public String register(String userName) {
try {
Thread.sleep(new Random(1).nextInt(100));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "注册用户:" + userName + " success!";
}
}
后面我们的测试过程,会给这个两个方法添加我们的拦截处理
2、自定义拦截方法
public class UserServiceBeforeAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
@Override
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("拦截方法:" + method.getName());
}
}
与上一章节的拦截方法相比,我们不再是实现 MethodInterceptor 接口,而是实现 MethodBeforeAdvice 环绕拦截。
在这个方法中我们可以获取到方法的一些信息,如果还开发了它的 MethodAfterAdvice 则可以两个接口一起实现
3、spring.xml 配置 AOP
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans>
<bean id="userService" class="springframework.test.bean.UserService"/>
<bean class="cn.ljc.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator"/>
<bean id="beforeAdvice" class="springframework.test.bean.UserServiceBeforeAdvice"/>
<bean id="methodInterceptor" class="cn.ljc.springframework.aop.framework.adapter.MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor">
<property name="advice" ref="beforeAdvice"/>
</bean>
<bean id="pointcutAdvisor" class="cn.ljc.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor">
<property name="expression" value="execution(* springframework.test.bean.IUserService.*(..))"/>
<property name="advice" ref="methodInterceptor"/>
</bean>
</beans>
这回再使用 AOP 就可以像 Spring 中一样,通过在 xml 中配置即可。因为我们已经把 AOP 的功能融合到 Bean 的生命周期里去了,你的新增拦截方法都会被自动处理。
4、单元测试
@Test
public void test_aop() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring.xml");
IUserService userService = applicationContext.getBean("userService", IUserService.class);
System.out.println("测试结果:" + userService.queryUserInfo());
}
在单元测试中你只需要按照正常获取和使用 Bean 对象即可,不过这个时候如果被切面拦截了,那么其实你获取到的就是对应的代理对象里面的处理操作了。
测试结果
拦截方法:queryUserInfo
测试结果:ljc,100001,上海
通过测试结果可以看到,我们已经让拦截方法生效了,也不需要自己手动处理切面、拦截方法等内容。
总结
到此,实现了aop切面和spring的整合,只需要配置xml,就可以了,不需要手动处理
实现的关键点则是依赖于beanPostProcessor,实例化前进行代理的处理