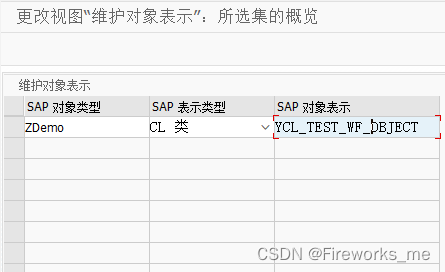
mksh运行分析
Shell
shell,壳子,即操作系统的壳子。这层壳子套在操作系统上,为用户提供与操作系统的交互手段。
操作系统的交互方式一般有,图形化交互(GUI)和命令行交付(CLI,command-line interface)。
- 套在操作系统上的壳子
Android系统中使用了一款叫mksh的shell程序,用于交互式的命令解释器。
- init.rc中定义了名为"console"的service,service对应的可执行程序是sh这个二进制,这个二进制程序由 exteranl/mksh/Android.bp定义。
service console /system/bin/sh
class core
console
disabled
user shell
group shell log readproc
seclabel u:r:shell:s0
setenv HOSTNAME console
mksh
mksh是一款开源的命令解释器(shell),aosp中的源码路径是external/mksh,编译后会在/system/bin下生成 "sh"可执行程序,init.rc中配置了开机启动这个二进制程序。当"sh"启动后,终端工具上就会出现我们常知的命令解释器,可以输入shell命令进行操作。
- 如果在rc中注释掉/system/bin/console,就无法通过命令行形式操作系统。
接下来以mksh接受终端输入命令(如:ls)的角度分析mksh的源码。
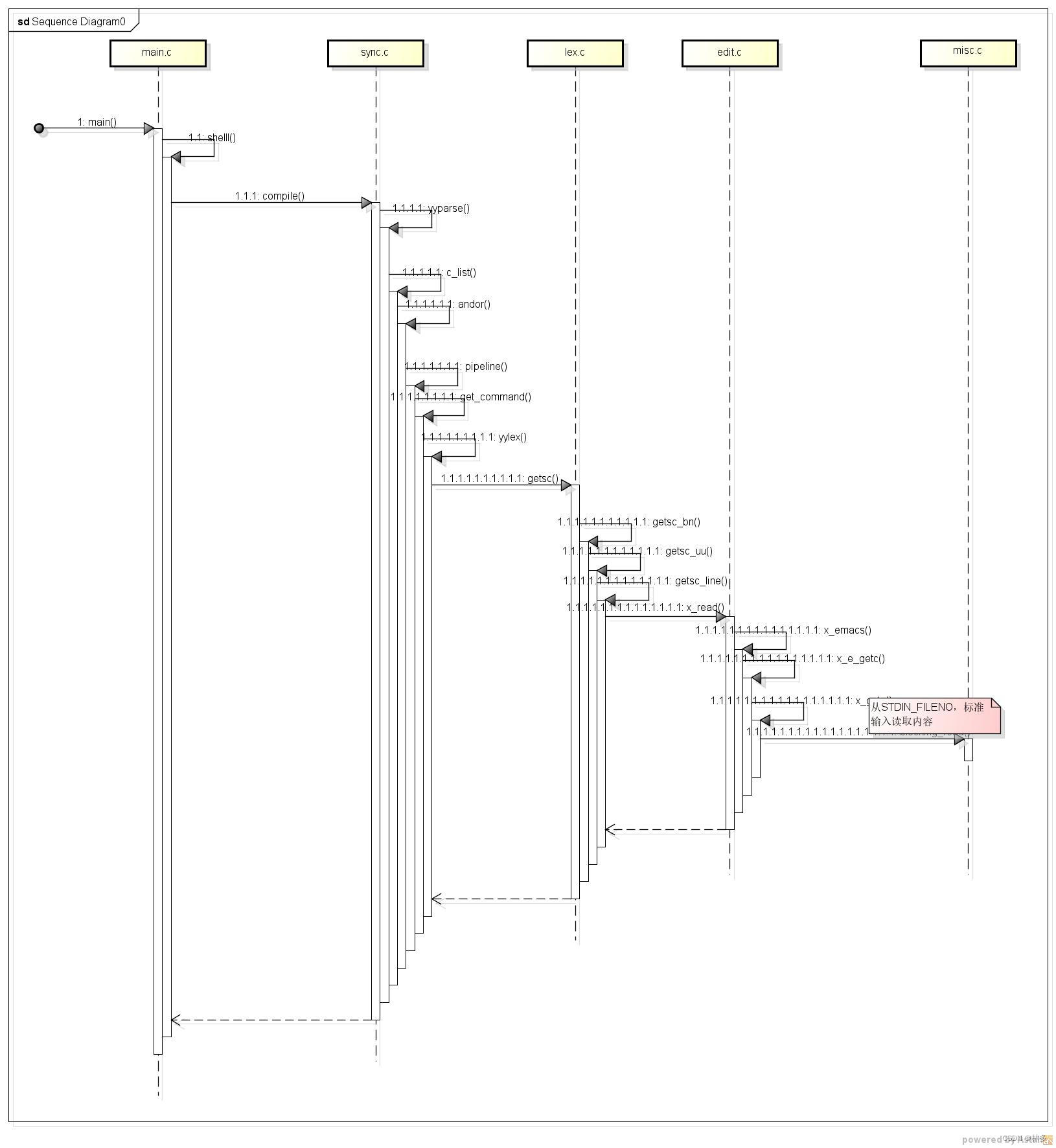
- 启动入口:main.c, main入口中调用函数main_init初始化mksh的运行环境,如果初始化没有问题,默认走shell函数。
int
main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int rv;
Source *s;
struct block *l;
if ((rv = main_init(argc, argv, &s, &l)) == 0) {
if (as_builtin) {
rv = c_builtin(l->argv);
} else {
shell(s, 0);
/* NOTREACHED */
}
}
return (rv);
}
- main.c: shell函数,根据函数的注释可以了解到,mksh通过这个函数解释从外部设备输入的命令,并且返回结果。这个函数中,通过while(1)循环监听command,当有command输入时,调用complime函数解析commnand.
/*
* run the commands from the input source, returning status.
*/
int
shell(Source * volatile s, volatile int level)
{
// 省略
while (/* CONSTCOND */ 1) {
if (trap)
runtraps(0);
if (s->next == NULL) {
if (Flag(FVERBOSE))
s->flags |= SF_ECHO;
else
s->flags &= ~SF_ECHO;
}
if (interactive) {
j_notify();
set_prompt(PS1, s);
}
t = compile(s, sfirst, true);
// 省略
}
}
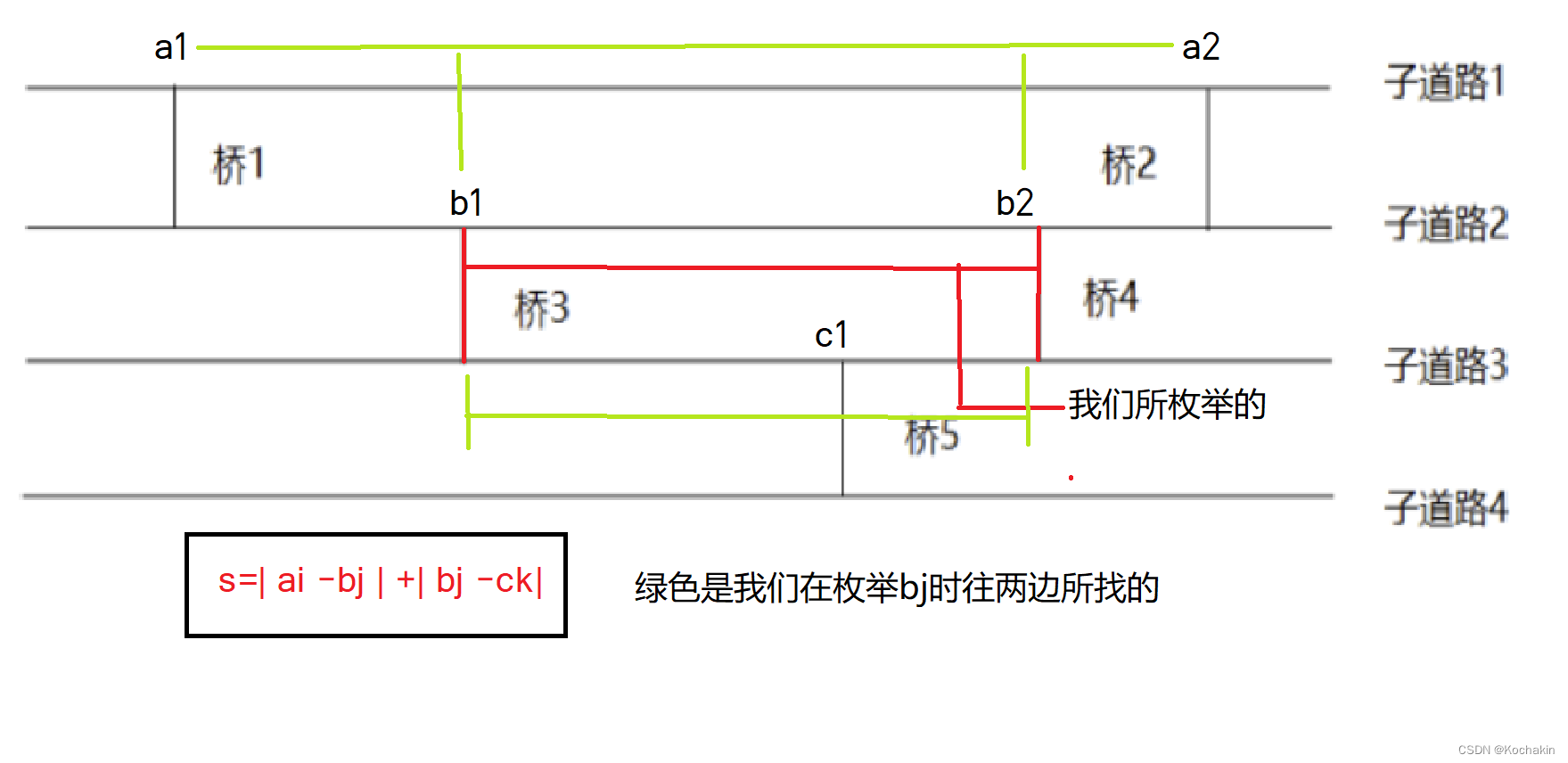
- sync.c: compile->yyparse->c_list->andor->pipeline->get_command->tpeek->yylex,上述为函数调用关系。
struct op *
compile(Source *s, bool skiputf8bom, bool doalias)
{
nesting.start_token = 0;
nesting.start_line = 0;
herep = heres;
source = s;
if (skiputf8bom)
yyskiputf8bom();
yyparse(doalias);
return (outtree);
}
static void
yyparse(bool doalias)
{
int c;
ACCEPT;
outtree = c_list(doalias ? ALIAS : 0, source->type == SSTRING);
c = tpeek(0);
if (c == 0 && !outtree)
outtree = newtp(TEOF);
else if (!cinttype(c, C_LF | C_NUL))
syntaxerr(NULL);
}
static struct op *
c_list(int sALIAS, bool multi)
{
struct op *t = NULL, *p, *tl = NULL;
int c;
bool have_sep;
while (/* CONSTCOND */ 1) {
p = andor(sALIAS);
// 省略
}
}
static struct op *
andor(int sALIAS)
{
struct op *t, *p;
int c;
t = pipeline(0, sALIAS);
if (t != NULL) {
while ((c = token(0)) == LOGAND || c == LOGOR) {
if ((p = pipeline(CONTIN, sALIAS)) == NULL)
syntaxerr(NULL);
t = block(c == LOGAND? TAND: TOR, t, p);
}
REJECT;
}
return (t);
}
static struct op *
pipeline(int cf, int sALIAS)
{
struct op *t, *p, *tl = NULL;
t = get_command(cf, sALIAS);
if (t != NULL) {
while (token(0) == '|') {
if ((p = get_command(CONTIN, sALIAS)) == NULL)
syntaxerr(NULL);
if (tl == NULL)
t = tl = block(TPIPE, t, p);
else
tl = tl->right = block(TPIPE, tl->right, p);
}
REJECT;
}
return (t);
}
static struct op *
get_command(int cf, int sALIAS)
{
// 省略
switch (tpeek(cf)) {
// 省略
}
#define tpeek(cf) ((reject) ? (symbol) : (REJECT, symbol = yylex(cf)))
- lex.c: yylex->getsc_bn->getsc__->getsc_line->xread。
#define o_getsc() (*source->str != '\0' && *source->str != '\\' && \
!backslash_skip ? *source->str++ : getsc_bn())
#define getsc() getsc_r((unsigned int)(unsigned char)o_getsc())
/* optimised getsc_uu() */
#define o_getsc_u() ((*source->str != '\0') ? *source->str++ : getsc_uu())
int
yylex(int cf)
{
// 省略
if (cf & ONEWORD)
// 省略
else if (cf & LETEXPR) {
// 省略
} else {
/* normal lexing */
state = (cf & HEREDELIM) ? SHEREDELIM : SBASE;
do {
c = getsc();
} while (ctype(c, C_BLANK));
if (c == '#') {
ignore_backslash_newline++;
do {
c = getsc();
} while (!ctype(c, C_NUL | C_LF));
ignore_backslash_newline--;
}
ungetsc(c);
}
// 省略
}
static int
getsc_bn(void)
{
int c, c2;
if (ignore_backslash_newline)
return (o_getsc_u());
if (backslash_skip == 1) {
backslash_skip = 2;
return (o_getsc_u());
}
backslash_skip = 0;
while (/* CONSTCOND */ 1) {
// 调用的是 getsc_uu
c = o_getsc_u();
if (c == '\\') {
if ((c2 = o_getsc_u()) == '\n')
/* ignore the \newline; get the next char... */
continue;
ungetsc_i(c2);
backslash_skip = 1;
}
return (c);
}
}
static int
getsc_uu(void)
{
Source *s = source;
int c;
while ((c = ord(*s->str++)) == 0) {
/* return 0 for EOF by default */
s->str = NULL;
switch (s->type) {
case SEOF:
s->str = null;
return (0);
case SSTDIN:
case SFILE:
getsc_line(s);
break;
// 省略
}
}
static void
getsc_line(Source *s)
{
// 省略
#ifndef MKSH_NO_CMDLINE_EDITING
if (have_tty && (
#if !MKSH_S_NOVI
Flag(FVI) ||
#endif
Flag(FEMACS) || Flag(FGMACS))) {
int nread;
nread = x_read(xp);
}
}
- edit.c : x_read ->x_emacs->x_e_getc->x_getc。x_getc这个函数使用了STDIN_FILENO,STDIN_FILENO表示标准输入设置,即从标准输入设备循环读取输入的命令,当遇到回车将解释输入的命令。
/*
* read an edited command line
*/
int
x_read(char *buf)
{
int i;
x_mode(true);
modified = 1;
if (Flag(FEMACS) || Flag(FGMACS))
i = x_emacs(buf);
#if !MKSH_S_NOVI
else if (Flag(FVI))
i = x_vi(buf);
#endif
else
/* internal error */
i = -1;
editmode = 0;
x_mode(false);
return (i);
}
static int
x_emacs(char *buf)
{
// 省略
while (/* CONSTCOND */ 1) {
x_flush();
if ((c = x_e_getc()) < 0)
return (0);
}
// 省略
}
static int
x_e_getc(void)
{
int c;
if (unget_char >= 0) {
c = unget_char;
unget_char = -1;
return (c);
}
#ifndef MKSH_SMALL
if (macroptr) {
if ((c = (unsigned char)*macroptr++))
return (c);
macroptr = NULL;
}
#endif
return (x_getc());
}
static int
x_getc(void)
{
#ifdef __OS2__
return (_read_kbd(0, 1, 0));
#else
char c;
ssize_t n;
while ((n = blocking_read(STDIN_FILENO, &c, 1)) < 0 && errno == EINTR)
if (trap) {
x_mode(false);
runtraps(0);
#ifdef SIGWINCH
if (got_winch) {
change_winsz();
if (x_cols != xx_cols && editmode == 1) {
/* redraw line in Emacs mode */
xx_cols = x_cols;
x_init_prompt(false);
x_adjust();
}
}
#endif
x_mode(true);
}
return ((n == 1) ? (int)(unsigned char)c : -1);
#endif
}
- misc.c: blocking_read的定义如下。
ssize_t
blocking_read(int fd, char *buf, size_t nbytes)
{
ssize_t ret;
bool tried_reset = false;
while ((ret = read(fd, buf, nbytes)) < 0) {
if (!tried_reset && errno == EAGAIN) {
if (reset_nonblock(fd) > 0) {
tried_reset = true;
continue;
}
errno = EAGAIN;
}
break;
}
return (ret);
}
- 函数调用时序图:




![LeetCode[264]丑数II](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/065f689857564f2cafcd7b6dbbe7a3a9.png)