文章目录
- 前言
- 相关Spring的定义接口
- 整体代码
- StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh")
- prepareRefresh()
- obtainFreshBeanFactory()
- registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory)
- SpringAOP原码流程
- @EnableAspectJAutoProxy
- AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的创建时机
- AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的执行时机
- 被代理方法的执行流程
前言
Spring 由17个方法构成,本文一以GenericApplicationContext为例
相关Spring的定义接口
- ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar
可以向容器注册自定义的RootBeanDefinition - BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
- BeanFactoryPostProcessor
在BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor方法执行后执行 - BeanPostProcessor
- InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
- SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
整体代码
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
this.prepareRefresh();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();
this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
this.initMessageSource();
this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
this.onRefresh();
this.registerListeners();
this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
this.finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException var10) {
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var10);
}
this.destroyBeans();
this.cancelRefresh(var10);
throw var10;
} finally {
this.resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start(“spring.context.refresh”)
this.applicationStartup初始化 :
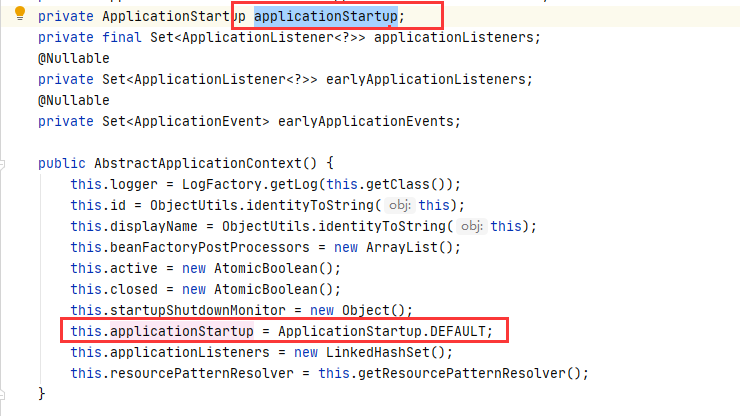
ApplicationStartup.DEFAULT :
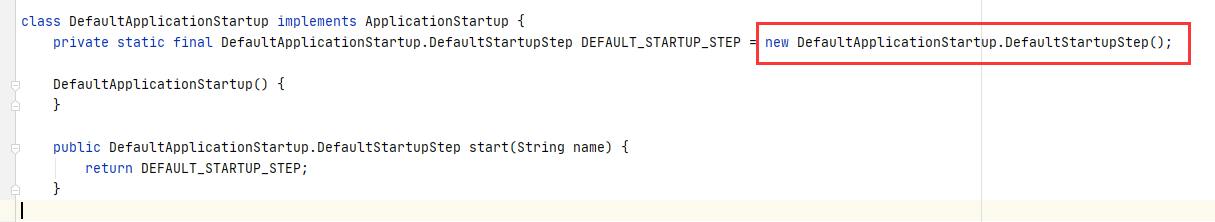
ApplicationStartup DEFAULT = new DefaultApplicationStartup();
prepareRefresh()
protected void prepareRefresh() {
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.closed.set(false);//设置关闭状态为真
this.active.set(true);//设置存活状态为真
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Refreshing " + this);
} else {
this.logger.debug("Refreshing " + this.getDisplayName());
}
}
this.initPropertySources(); //自身空实现,留给子类重写
this.getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) {
this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet(this.applicationListeners);//创建早期容器监听者
} else {
this.applicationListeners.clear();
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);//创建容器监听者
}
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet();//创建早期事件存放容器
}
this.getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties() 整体解析:
获取环境变量及系统变量
this.getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties() 中 getEnvironment() :
- getEnvironment()
public ConfigurableEnvironment getEnvironment() {
if (this.environment == null) {
this.environment = this.createEnvironment();
}
return this.environment;
}
- createEnvironment() :
return new StandardEnvironment();
public class StandardEnvironment extends AbstractEnvironment {
public static final String SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemEnvironment";
public static final String SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemProperties";
public StandardEnvironment() { //空构造调用父类构造,由父类调用customizePropertySources方法
}
protected StandardEnvironment(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
super(propertySources);
}
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(new PropertiesPropertySource("systemProperties", this.getSystemProperties()));//获取系统的参数变量
propertySources.addLast(new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource("systemEnvironment", this.getSystemEnvironment()));//获取系统环境变量
}
}
- AbstractEnvironment 构造器 :
public AbstractEnvironment() {
this(new MutablePropertySources()); //调用下面构造方法
}
protected AbstractEnvironment(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
this.logger = LogFactory.getLog(this.getClass());
this.activeProfiles = new LinkedHashSet();
this.defaultProfiles = new LinkedHashSet(this.getReservedDefaultProfiles());
this.propertySources = propertySources; //将propertySources赋值给本地propertySources变量
this.propertyResolver = this.createPropertyResolver(propertySources);
this.customizePropertySources(propertySources); //调用子类StandardEnvironment的customizePropertySources
}
总之是new 一个 StandardEnvironment 类然后调用其的customizePropertySources方法返回该 StandardEnvironment 类
this.getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties() 中的validateRequiredProperties():
调用的是之前返回的 StandardEnvironment的父类AbstractEnvironment propertyResolver属性的validateRequiredProperties的方法 :
propertyResolver.validateRequiredProperties();
propertyResolver属性是在上面创建StandardEnvironment时候调用其父类AbstractEnvironment(MutablePropertySources propertySources)构造中创建赋值的 :
this.propertyResolver = this.createPropertyResolver(propertySources);
而 createPropertyResolver(propertySources)则只是调用一个new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(propertySources);
validateRequiredProperties()方法最终调用的是PropertySourcesPropertyResolver的validateRequiredProperties方法
而PropertySourcesPropertyResolver 的validateRequiredProperties方法本身没有实现是继承父类的 AbstractPropertyResolver实现
最终this.getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties()实现方法是AbstractPropertyResolver.validateRequiredProperties():
public void validateRequiredProperties() {
MissingRequiredPropertiesException ex = new MissingRequiredPropertiesException();
Iterator var2 = this.requiredProperties.iterator();
while(var2.hasNext()) {
String key = (String)var2.next();
if (this.getProperty(key) == null) {
ex.addMissingRequiredProperty(key);
}
}
if (!ex.getMissingRequiredProperties().isEmpty()) {
throw ex;
}
}
从requiredProperties中遍历值并且判断是否在系统或环境变量存在该值
requiredProperties:
AbstractPropertyResolver的一个属性
private final Set<String> requiredProperties = new LinkedHashSet();
总结作用 :
Spring容器初始化的时候,会从集合requiredProperties中取出所有key,然后获取这些key的环境变量(包括系统环境变量和进程环境变量),如果有一个key对应的环境变量为空,就会抛出异常,导致spring容器初始化失败;
实战中使用 :
看了AbstractPropertyResolver类的validateRequiredProperties方法源码后,可以确定该方法能强制要求一些环境变量必须存在,否则停止spring启动,我们只要把我们认为必要的环境变量的key存入集合requiredProperties中即可,达到此目标需要解决下面两个问题:
- 如何将环境变量的key存入集合requiredProperties?
调用AbstractPropertyResolver类的setRequiredProperties方法,注意该方法是向集合requiredProperties中添加数据,并不会将已有数据清除; - 在什么时候执行AbstractPropertyResolver类的setRequiredProperties方法设置key?
创建一个AbstractApplicationContext的子类,重写initPropertySources方法,在此方法中执行AbstractPropertyResolver类的setRequiredProperties;
创建一个自定义ApplicationContext 并重写initPropertySources方法:
public void main() {
CustomApplicationContext customApplicationContext = new CustomApplicationContext();
customApplicationContext.refresh();
}
public class CustomApplicationContext extends GenericApplicationContext {
@Override
protected void initPropertySources() {
super.initPropertySources();
//把"MYSQL_HOST"作为启动的时候必须验证的环境变量
getEnvironment().setRequiredProperties("MYSQL_HOST");
}
}
上面写过initPropertySources实在 prepareRefresh() 时候调用 :
obtainFreshBeanFactory()
获取BeanFactory并刷新
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
this.refreshBeanFactory();
return this.getBeanFactory();
}
- refreshBeanFactory()内容 :
if (!this.refreshed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("GenericApplicationContext does not support multiple refresh attempts: just call 'refresh' once");
} else {
this.beanFactory.setSerializationId(this.getId());
}
- getBeanFactory()
返回 GenericApplicationContext 中的 DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory 属性
beanFactory 在 GenericApplicationContext 创建的时候创建的 :
public GenericApplicationContext() {
this.customClassLoader = false;
this.refreshed = new AtomicBoolean();
this.beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory)
SpringAOP原码流程
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
首先需了解@EnableAspectJAutoProxy:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar.class)
public @interface EnableAspectJAutoProxy {
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
}
它通过@Import(AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar.class)导入了一个AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar组件:
class AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
public void registerBeanDefinitions(
AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);
AnnotationAttributes enableAJAutoProxy \=
attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, EnableAspectJAutoProxy.class);
if (enableAJAutoProxy.getBoolean("proxyTargetClass")) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);
}
}
}
它实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口,这个接口可以向IOC容器中注册bean。 由此可以推测aop利用AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar自定义给容器中注册bean;BeanDefinetion
进入registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary方法,发现它给容器中注册了一个名为org.springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator,实例为AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的类。
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的创建时机
查看AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的继承关系图
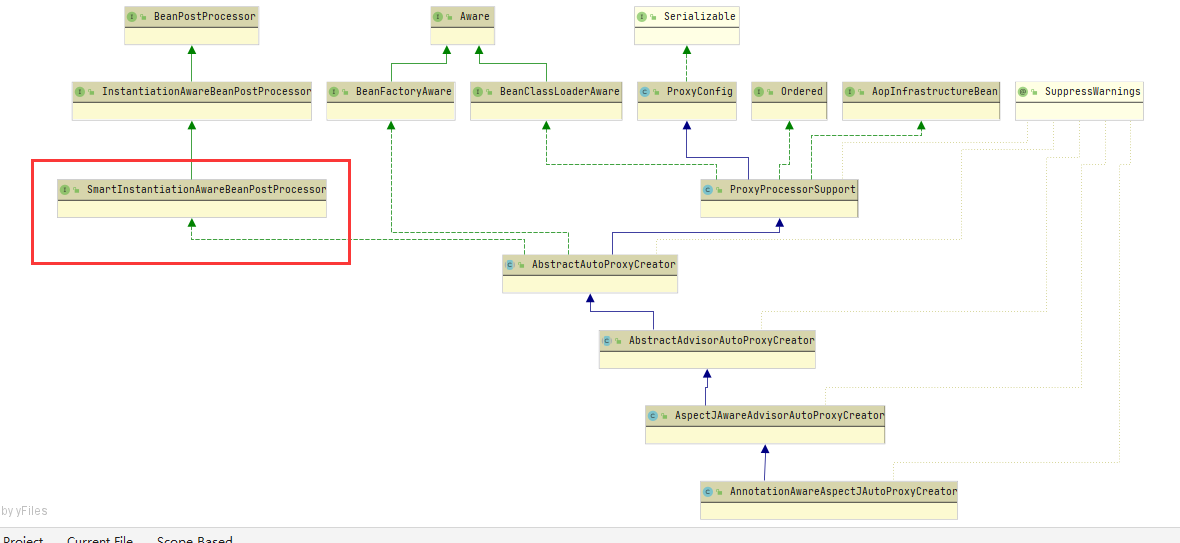
在此需要关注两点内容:
- 关注后置处理器SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor(在bean初始化完成前后做事情)
- 关注自动装配BeanFactory。
注意 :SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor是BeanPostProcessor的一个子接口
因此AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的创建时机:
1)、传入配置类,创建ioc容器
2)、注册配置类,调用refresh()刷新容器;
3)、registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);注册bean的后置处理器来方便拦截bean的创建;
1)、先获取ioc容器已经定义了的需要创建对象的所有BeanPostProcessor
2)、给容器中加别的BeanPostProcessor
3)、优先注册实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanPostProcessor;
4)、再给容器中注册实现了Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor;
5)、注册没实现优先级接口的BeanPostProcessor;
6)、注册BeanPostProcessor,实际上就是创建BeanPostProcessor对象,保存在容器中;
创建internalAutoProxyCreator的BeanPostProcessor【AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator】
1)、创建Bean的实例
2)、populateBean;给bean的各种属性赋值
3)、initializeBean:初始化bean;
1)、invokeAwareMethods():处理Aware接口的方法回调
2)、applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization():应用后置处理器的postProcessBeforeInitialization()
3)、invokeInitMethods();执行自定义的初始化方法
4)、applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization();执行后置处理器的postProcessAfterInitialization();
4)、BeanPostProcessor(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator)创建成功;--》aspectJAdvisorsBuilder
7)、把BeanPostProcessor注册到BeanFactory中;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(postProcessor);
在上面步骤
获取ioc容器已经定义了的需要创建对象的所有BeanPostProcessor中,因为AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator实现了SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口,而SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor是BeanPostProcessor的子接口,并且@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注册了AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的BeanDefinetion进容器,所以此步骤能获取到AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的BeanDefinetion
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的执行时机
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator是一个后置处理器,可以猜测它在其他bean的初始化前后进行了特殊处理。我在它父类的postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法进行了断点调试,其方法调用栈如下:
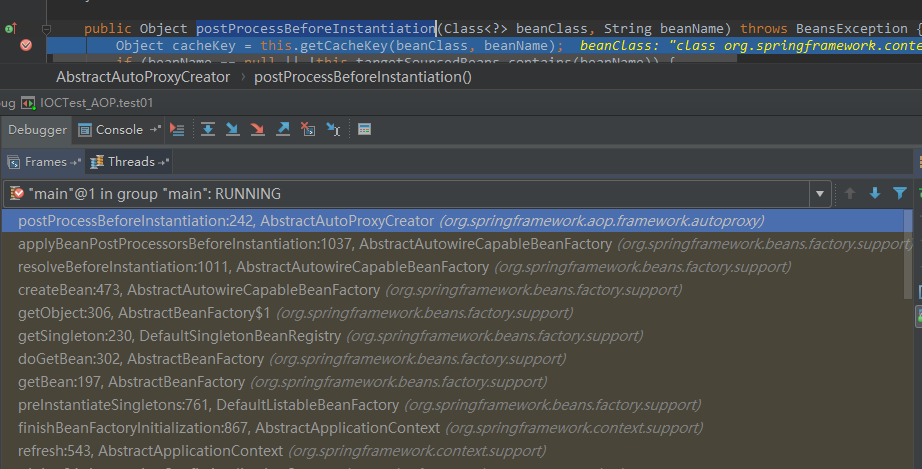
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);完成BeanFactory初始化工作;创建剩下的单实例bean
1)、遍历获取容器中所有的Bean,依次创建对象getBean(beanName);
getBean->doGetBean()->getSingleton()->createBean()
2)、createBean()创建bean
【AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator在所有bean创建之前会有一个拦截,InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,
会调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation()】
1)、先从缓存中获取当前bean,如果能获取到,说明bean是之前被创建过的,直接使用,否则再创建;
只要创建好的Bean都会被缓存起来
2)、createBean();创建bean;
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 会在任何bean创建之前先尝试返回bean的实例
【BeanPostProcessor是在Bean对象创建完成初始化前后调用的】
【InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor是在创建Bean实例之前先尝试用后置处理器返回对象的】
1)、resolveBeanClass()加载bean的class文件
2)、resolveBeforeInstantiation();解析BeforeInstantiation
希望后置处理器在此能返回一个代理对象;如果能返回代理对象就使用,如果不能就继续创建
1)、后置处理器先尝试返回对象;
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation
如果返回对象就再继续执行BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization,返回bean
3)、doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);真正的去创建一个bean实例
1)、createBeanInstance();实例化bean
populateBean();属性注入
initializeBean();初始化,执行各种生命周期方法和创建代理等
在步骤resolveBeforeInstantiation(),一般自定义的bean在此都不会获取到实例,此步骤有印象即可。
再深入解析initializeBean()方法 :
initializeBean()
如果bean实现了相关的接口,就调用执行相关接口
1)、invokeAwareMethods;执行BeanNameAware BeanClassLoaderAware BeanFactoryAware接口
2)、applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization;执行BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization
3)、invokeInitMethods; 执行初始化方法
4)、applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization;BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization;创建代理
这里重点关注AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类,其postProcessAfterInitialization方法在其父类AbstractAutoProxyCreator实现。
直接进入AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessAfterInitialization,代理创建入口就在此:
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
// earlyProxyReferences是一个ConcurrentHashMap,里面存放的是已经生成的代理
// 里面存放的是已经生成的代理(三级缓存可能会提前生成代理),如果有不会重复生成。
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
进入wrapIfNecessary,这里是创建代理的关键方法:
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
// advicedBeans表示已经判断过的bean,false表示此Bean不需要进行AOP,直接返回
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
// 当前正在创建的Bean不用进行AOP,比如切面Bean
/*
如果是基础设施类(Pointcut、Advice、Advisor 等接口的实现类),或是应该跳过的类,
则不应该生成代理,此时直接返回 bean,也就是代理不能给自己再加代理 就是不套娃
AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#shouldSkip
*/
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
// 查询当前bean匹配的Advice,找切面的过程(判断当前实例化的bean是否有切面,如果有则将切面返回)返回类型为 Advisor
// postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法也会调用 ;AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator实现
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
// 如果有切面,则生成bean的代理
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
// advisedBeans记录了某个Bean已经进行过AOP了
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// 创建代理,把被代理对象bean的实例封装到SingletonTargetSource中,生成当前实例化bean的代理对象
// 传入的bean是被代理实例,SingletonTargetSource持有了被代理实例的引用(一级缓存单例池中存的就是代理对象)
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
// 将代理对象返回
return proxy;
}
// 没有代理的情况,就是false
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
第一次进入shouldSkip方法会查询Spring容器内的所有@Aspecj相关的类,并将其相关方法注册成Advisor,并缓存起来,以便下次直接获取。
总结 :
通过@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注入AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator,其实现了BeanFactoryAware和SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口,间接实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor;
在Spring容器刷新时候调用registerBeanPostProcessors方法注册进容器;
在Spring创建完成Bean,执行生命周期后置处理器BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization时候,会调进入AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator执行代理创建逻辑,并返回需要的代理。
继续深入研究wrapIfNecessary
首先判断当前类是否需要代理,或者已经被代理过,返回原类。
重点关注getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean方法,实现在AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类:
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) {
// 找到候选的切面,就是寻找带有@Aspect注解的过程,把带有@Aspect的类封装成Advisor返回
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
return advisors.toArray();
}
findEligibleAdvisors方法寻找当前类匹配的Advisor,进入findEligibleAdvisors方法 :
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
// 找到候选的切面,就是寻找带有@Aspect注解的过程,把带有@Aspect的类封装成Advisor返回
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors(); //如果是通过@Aspect注解开启切面,子类AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator方法
// 判断候选的切面是否作用在当前beanClass上面,就是一个匹配的过程
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
// 针对有@Aspect注解的类添加一个默认的切面--->DefaultPointcutAdvisor,解决参数传递问题
// 进入AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类的extendAdvisors()方法
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); // AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
// 对有@Order、@Priority注解的类进行排序
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
进入AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator#findCandidateAdvisors:
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
// Add all the Spring advisors found according to superclass rules.
// 先找到所有Advisor类型的Bean,调用父类resolveBeforeInstantiation方法进入的话实现类是AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#findCandidateAdvisors
List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();
// Build Advisors for all AspectJ aspects in the bean factory.
// 再从所有@Aspect中解析得到Advisor对象
if (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null) {
// 创建候选的切面,对有@Aspect注解的类进行处理(包装Advice和Pointcut,还有切面的排序)****
advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());// 核心方法-构建Advisor
}
return advisors;
}
注意寻找的方法是this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors(),此方法就是从Spring容器中查询所有被@Aspect标注的方法,并转换成Advisor:
//GSCM 2024/1/23 解析容器中@Aspect注解标注的类构建成Advisor对象
public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() {
List<String> aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
synchronized (this) {
aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
aspectNames = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取Spring容器中所有实例的beanName
String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!isEligibleBean(beanName)) {
continue;
}
// We must be careful not to instantiate beans eagerly as in this case they
// would be cached by the Spring container but would not have been weaved.
// 首先拿到实例的类型
Class<?> beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName, false);
if (beanType == null) {
continue;
}
// 判断类上是否有@Aspect注解
if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) {
aspectNames.add(beanName);
// 获取切面的注解信息
AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);
if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) {
// 创建获取@Aspect注解类的实例工厂,MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory负责获取有@Aspect注解的实例
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
// 创建切面Advisor对象
List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);// 创建切面Advisor对象
// 放到缓存中
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);
}
else {
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
}
advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);
}
else {
// Per target or per this.
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName +
"' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton");
}
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
}
this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames;
return advisors;
}
}
}
if (aspectNames.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String aspectName : aspectNames) {
List<Advisor> cachedAdvisors = this.advisorsCache.get(aspectName);// 解析过一次后就从缓存中取
if (cachedAdvisors != null) {
advisors.addAll(cachedAdvisors);
}
else {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = this.aspectFactoryCache.get(aspectName);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
return advisors;
}
在此行List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);代码中,最终将@Aspect注解的类解析成为Advisor,返回的Advisor类型同一都为InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl。
进入this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory)方法:
public List<Advisor> getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory) {
// 从工厂中获取有@Aspect注解的类的反射对象Class
Class<?> aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();//GXXX 2023/11/21
// 从工厂中获取有@Aspect注解的类的名称
String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName();
validate(aspectClass);
// We need to wrap the MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory with a decorator
// so that it will only instantiate once.
// 创建工厂的装饰类,获取实例(只会获取一次)
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory =
new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory);
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
// 这里循环没有@Pointcut注解的方法,扫描有@Before、@Around、@After注解的方法,并进行排序,getAdvisorMethods()->
for (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass)) { // 进入本类的getAdvisorMethods()方法
// AspectJPrecedenceComparator.getAspectDeclarationOrder(Advisor).
// 获取Advisor*****(只要是有@Before、@After等注解的方法,它们分别和带有@Pointcut注解的方法组合,生成各自Advisor类)
// 封装Advisor,返回的实现类为InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, 0, aspectName);// 再进入本类的getAdvisor(),根据方法生成Advisor
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
// If it's a per target aspect, emit the dummy instantiating aspect.
if (!advisors.isEmpty() && lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) {
Advisor instantiationAdvisor = new SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor(lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory);
advisors.add(0, instantiationAdvisor);
}
// Find introduction fields.
for (Field field : aspectClass.getDeclaredFields()) {
Advisor advisor = getDeclareParentsAdvisor(field);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
return advisors;
}
这里遍历当前class的每个方法,为每个通知方法创建Advisor实例。
进入getAdvisor方法 :
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory,
int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) {
validate(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
// 获取AspectJExpressionPointcut对象,从注解中获取表达式
// candidateAdviceMethod就是有@Before、@After注解的方法
AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = getPointcut(
candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
if (expressionPointcut == null) {
return null;
}
// 创建真正的Advisor切面类,里面有pointcut和advice***进入InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl的构造方法
// expressionPointcut是pointcut,candidateAdviceMethod是advice
return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod,
this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);// 创建真正的切面类
}
在此针对每个目标方法创建对应的Advisor实例,具体创建逻辑在InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl的构造方法中:
this.instantiatedAdvice = instantiateAdvice(this.declaredPointcut);//GSCM 2024/2/28 创建当前方法对应advice实例的具体方法
此方法继续调用this.aspectJAdvisorFactory.getAdvice(),直接看aspectJAdvisorFactory.getAdvice():
public Advice getAdvice(Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {
// 获取有@Aspect注解的类,就是当前被@Aspect标注的class
Class<?> candidateAspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
validate(candidateAspectClass);
// 找到class上面的相关切面注解,并且包装成AspectJAnnotation对象
AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
.........
AbstractAspectJAdvice springAdvice;
// 根据方法上切面不同注解,创建相对应的的advice实例
switch (aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType()) {
case AtPointcut:
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Processing pointcut '" + candidateAdviceMethod.getName() + "'");
}
return null;
case AtAround:
// 环绕通知,实现了MethodInterceptor接口
springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtBefore:
// 前置通知,实现了MethodBeforeAdvice接口,没有实现MethodInterceptor接口
springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfter:
// 后置通知,实现了MethodInterceptor接口
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfterReturning:
// 结果通知,实现了AfterReturningAdvice接口,没有实现MethodInterceptor接口
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning())) {
springAdvice.setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning());
}
break;
case AtAfterThrowing:
// 异常通知,实现了MethodInterceptor接口
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing())) {
springAdvice.setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing());
}
break;
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"Unsupported advice type on method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
// Now to configure the advice...
springAdvice.setAspectName(aspectName);
springAdvice.setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrder);
String[] argNames = this.parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (argNames != null) {
springAdvice.setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames);
}
springAdvice.calculateArgumentBindings();
return springAdvice;
}
这里就是创建了目标方法对应具体的advice并赋值给InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl的instantiatedAdvice属性
被代理方法的执行流程
被Spring的Cglib代理的所有方法都会进入CglibAopProxy.DynamicAdvisedInterceptor#intercept方法;
//GSCM 2024/1/24 被cglib代理的对象调用首先进入此方法
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
Object target = null;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.getTargetSource();
try {
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool...
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
// ※获取调用执行链※
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
Object retVal;
// Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is,
// no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target.
if (chain.isEmpty() && CglibMethodInvocation.isMethodProxyCompatible(method)) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly.
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know
// it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot
// swapping or fancy proxying.
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = invokeMethod(target, method, argsToUse, methodProxy);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
// 执行代理方法调用链条
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
}
retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
DynamicAdvisedInterceptor有一个重要的属性private final AdvisedSupport advised,在创建代理的时候被赋值,里面包含被代理的原生类引用及执行链;
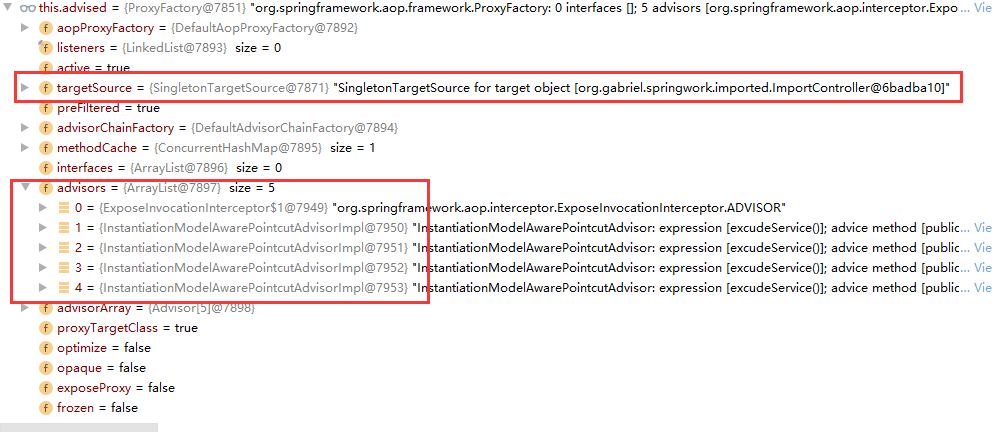
转换前
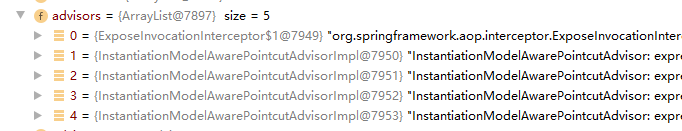
转换后
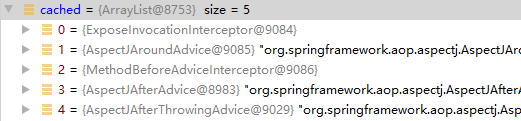
CglibMethodInvocation
ExposeInvocationInterceptor
AspectJAroundAdvice#invoke->调用切面层aspectJAdviceMethod.invoke
MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor#invoke
AspectJAfterAdvice#invoke
AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice#invoke
AspectJAroundAdvice
MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
AfterReturningAdviceAdapter
ThrowsAdviceAdapter
AspectJAfterAdvice
AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice -> MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
advisor、advice、adviced各自的含义
-
advisor 通知器包含advice和pointcut
-
advice 具体的某一个消息通知
-
adviced 用来配置代理(proxyFactory)
执行流程整理 :
postProcessAfterInitialization创建代理,第一次进来会遍历Spring容器内所有的带有@Aspect注解的类,遍历其类中的每个带有@Before、@Around、@After的方法,并将切点对象解析出来与当前方法的Method对象,封装成一个InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl实例,在InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl中构造函数中会根据Method的信息创建一个Advice对象并引用。遍历完成将这些类缓存起来,并且生成一个bean名称对应Advice的缓存,下次直接从缓存中。拿到Advice后默认添加一个ExposeInvocationInterceptor在最前面。再创建一个代理工厂ProxyFactory区创建代理,代理工厂选择Cglib还是Jdk去创建代理类,代理类保存着目标类的引用及Advisor调用链。
Cglib代理进入DynamicAdvisedInterceptor#intercept,再根据Advisor获取调用链进行包装(如果需要的话),包装成MethodInterceptor。创建一个ReflectiveMethodInvocation类调用proceed,里面保存着一个调用次数currentInterceptorIndex,按照顺序一个个调用Advisor调用链,并且将当前类作为参数一直传递下去,每次调用一个Advisor会将currentInterceptorIndex减一,直到与Advisor调用链数量一致,说明调用链已经执行完了。
再调用真实的目标对象方法,调用完成依次弹出栈。
调用栈示例,org.gabriel.springwork.boot是自定义包 :
at org.gabriel.springwork.imported.ImportController.isSuccess(ImportController.java:16)
at org.gabriel.springwork.imported.ImportController$$FastClassBySpringCGLIB$$7fcf3b6d.invoke(<generated>:-1)
at org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy.invoke(MethodProxy.java:218)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy$CglibMethodInvocation.invokeJoinpoint(CglibAopProxy.java:771)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed(ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java:163)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy$CglibMethodInvocation.proceed(CglibAopProxy.java:749)
at org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice.invoke(AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice.java:62)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed(ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java:186)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy$CglibMethodInvocation.proceed(CglibAopProxy.java:749)
at org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJAfterAdvice.invoke(AspectJAfterAdvice.java:47)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed(ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java:186)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy$CglibMethodInvocation.proceed(CglibAopProxy.java:749)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.adapter.MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor.invoke(MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor.java:56)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed(ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java:186)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy$CglibMethodInvocation.proceed(CglibAopProxy.java:749)
at org.springframework.aop.aspectj.MethodInvocationProceedingJoinPoint.proceed(MethodInvocationProceedingJoinPoint.java:88)
at org.gabriel.springwork.boot.config.DictAspect2.doAround(DictAspect2.java:35)
at jdk.internal.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:-1)
at jdk.internal.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62)
at jdk.internal.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:566)
at org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AbstractAspectJAdvice.invokeAdviceMethodWithGivenArgs(AbstractAspectJAdvice.java:644)
at org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AbstractAspectJAdvice.invokeAdviceMethod(AbstractAspectJAdvice.java:633)
at org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJAroundAdvice.invoke(AspectJAroundAdvice.java:70)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed(ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java:186)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy$CglibMethodInvocation.proceed(CglibAopProxy.java:749)
at org.springframework.aop.interceptor.ExposeInvocationInterceptor.invoke(ExposeInvocationInterceptor.java:95)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed(ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java:186)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy$CglibMethodInvocation.proceed(CglibAopProxy.java:749)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy$DynamicAdvisedInterceptor.intercept(CglibAopProxy.java:691)
at org.gabriel.springwork.imported.ImportController$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$20b0886d.isSuccess(<generated>:-1)
at org.gabriel.springwork.boot.GabrielSpringBoot.lambda$main$0(GabrielSpringBoot.java:31)
at org.gabriel.springwork.boot.GabrielSpringBoot$$Lambda$606.1849602253.accept(Unknown Source:-1)
at java.util.LinkedHashMap.forEach(LinkedHashMap.java:684)
at org.gabriel.springwork.boot.GabrielSpringBoot.main(GabrielSpringBoot.java:30)
Advisor相关实现类解析
AOP原文