目录
- 1. 栈与队列练习题
- 1.1 栈的括号匹配问题
- 1.2 用队列来实现栈
- 1.3 用栈来实现队列
- 1.4 扩展:循环队列
1. 栈与队列练习题
1.1 栈的括号匹配问题
- 题目信息:
- 题目链接:
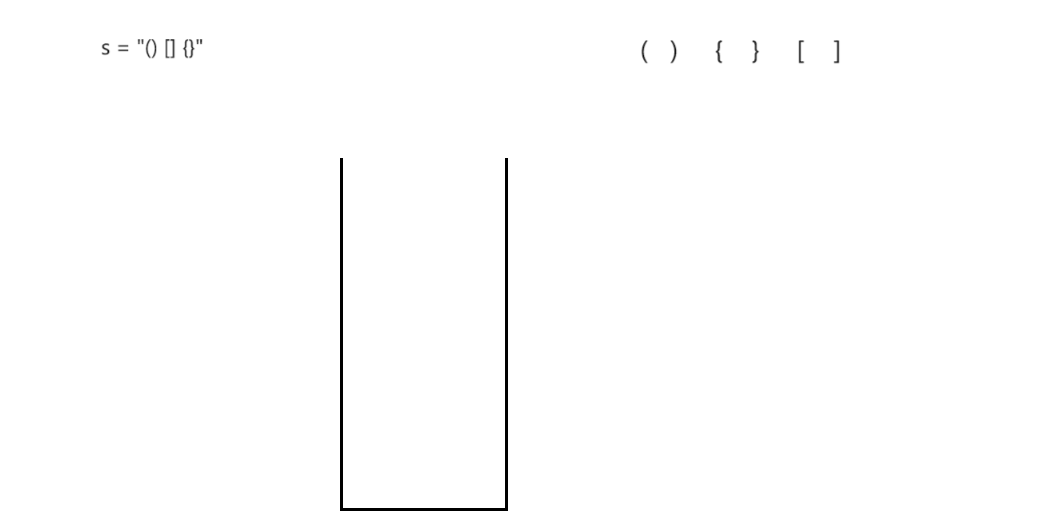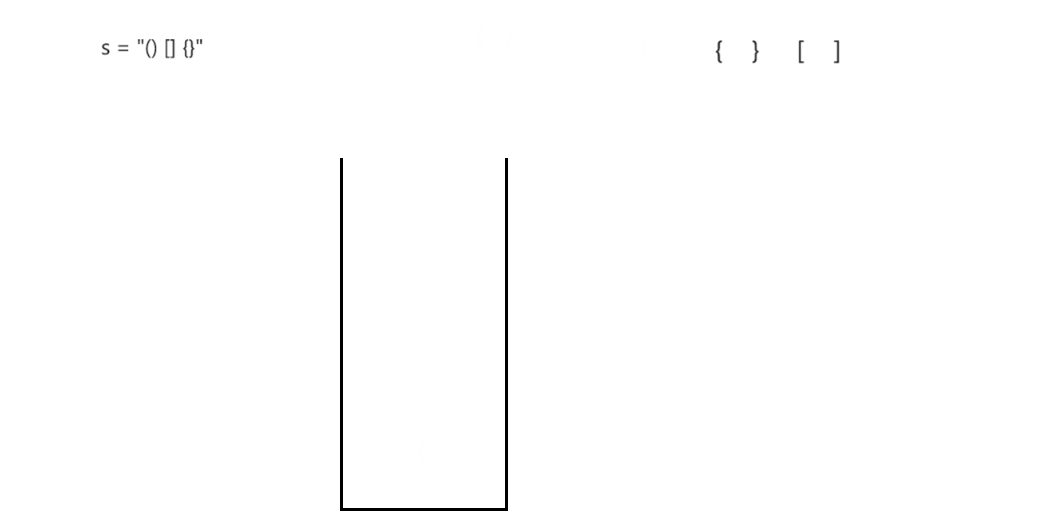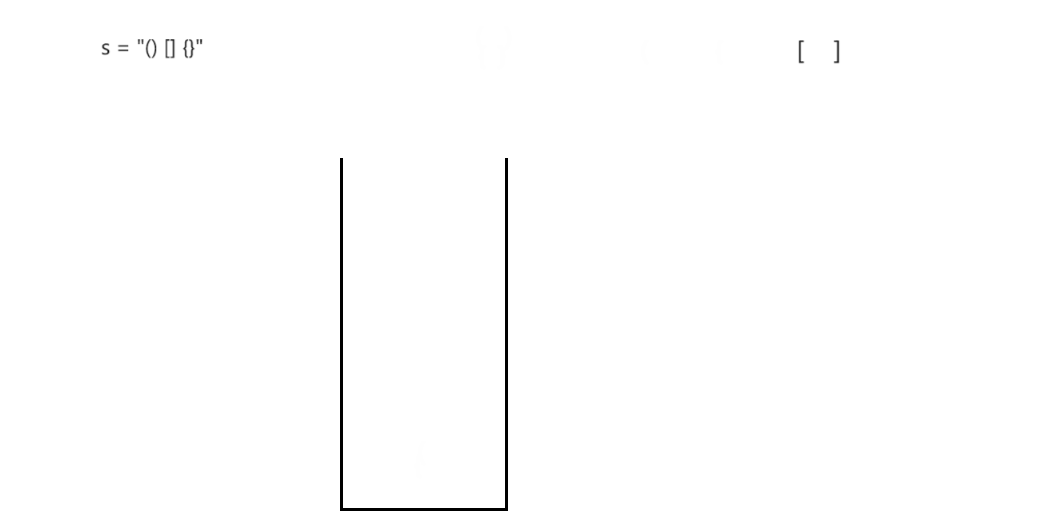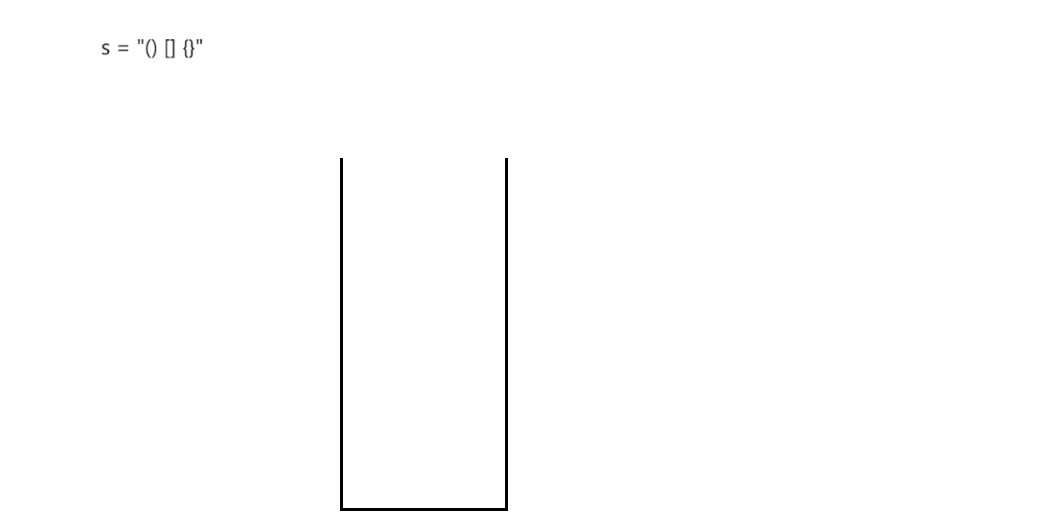
括号匹配问题
思路: 利用栈的后进先出特性来实现括号的匹配
- 当遇到 ‘(’,‘{’,‘[’,这三种括号时进行压栈
- 当遇到’)‘,’}‘,’]',这三种括号时将括号中的元素进行出栈匹配
过程演示:
typedef char STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* _a;
int _top; // 栈顶
int _capacity; // 容量
}Stack;
void CheckCapacity(Stack* ps)
{
if (ps->_capacity == ps->_top)
{
int newcapacity = ps->_capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->_capacity;
STDataType* data = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->_a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (data == NULL)
{
perror("realloc failed");
exit(-1);
}
ps->_a = data;
ps->_capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
void StackInit(Stack* ps)
{
ps->_capacity = 0;
ps->_top = 0;
ps->_a = NULL;
CheckCapacity(ps);
}
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data)
{
assert(ps);
CheckCapacity(ps);
ps->_a[ps->_top] = data;
ps->_top++;
}
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_top == 0;
}
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
ps->_top--;
}
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->_a[ps->_top - 1];
}
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_top;
}
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->_a);
ps->_capacity = ps->_top = 0;
}
bool isValid(char* s)
{
Stack st1;
StackInit(&st1);
int i = 0;
for(i = 0; s[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
if(s[i] == '(' || s[i] == '[' || s[i] == '{')
{
StackPush(&st1, s[i]);
}
else if(s[i] == ')' || s[i] == ']' || s[i] == '}')
{
if(StackEmpty(&st1))
{
return false;
}
char tmp = StackTop(&st1);
if(s[i] == ')' && tmp == '(')
{
StackPop(&st1);
}
else if(s[i] == ']' && tmp == '[')
{
StackPop(&st1);
}
else if(s[i] == '}' && tmp == '{')
{
StackPop(&st1);
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
if(StackEmpty(&st1))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
1.2 用队列来实现栈
- 题目信息:
- 题目链接:
用两个队列实现栈
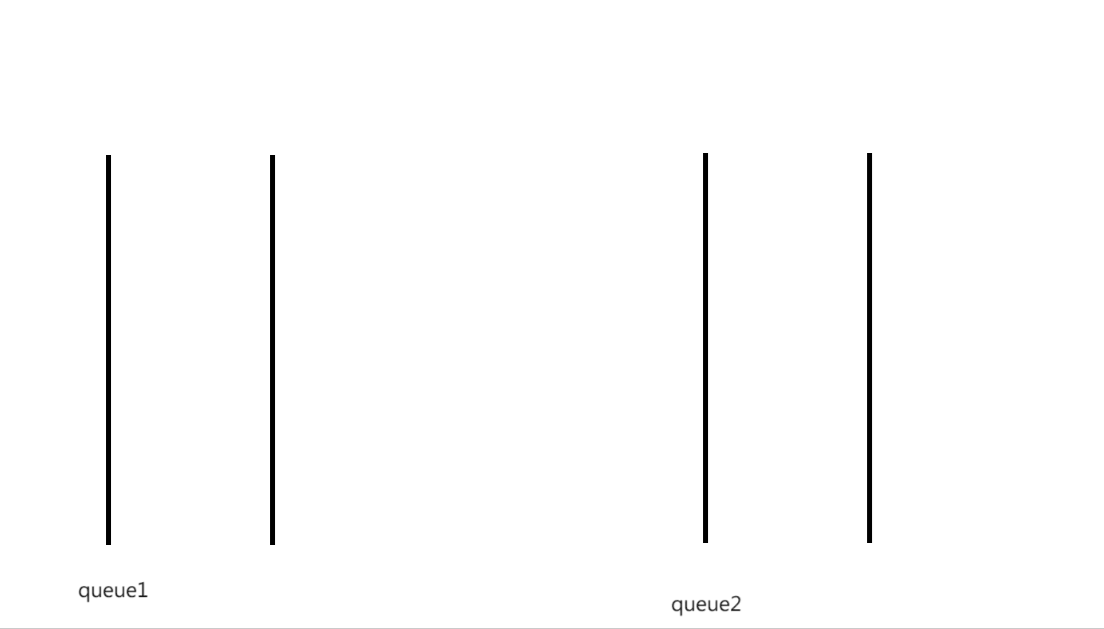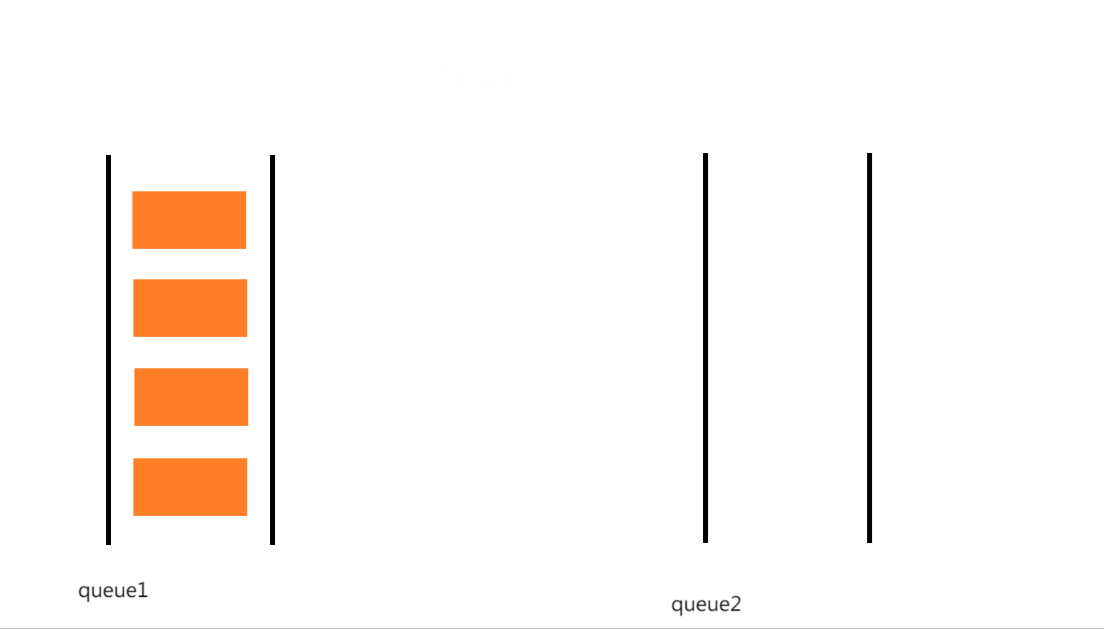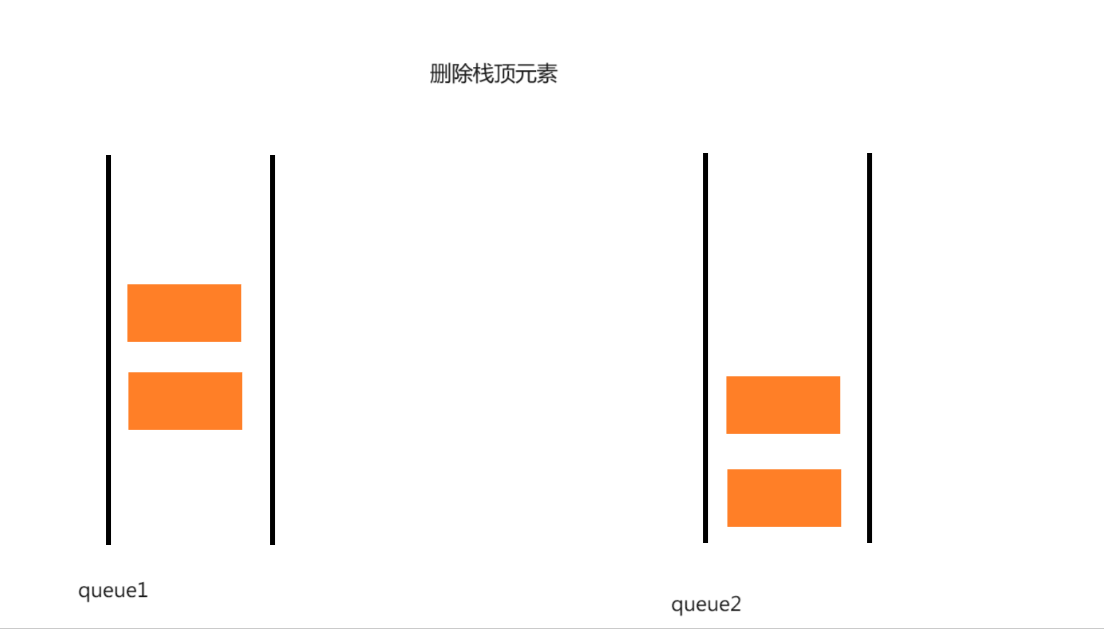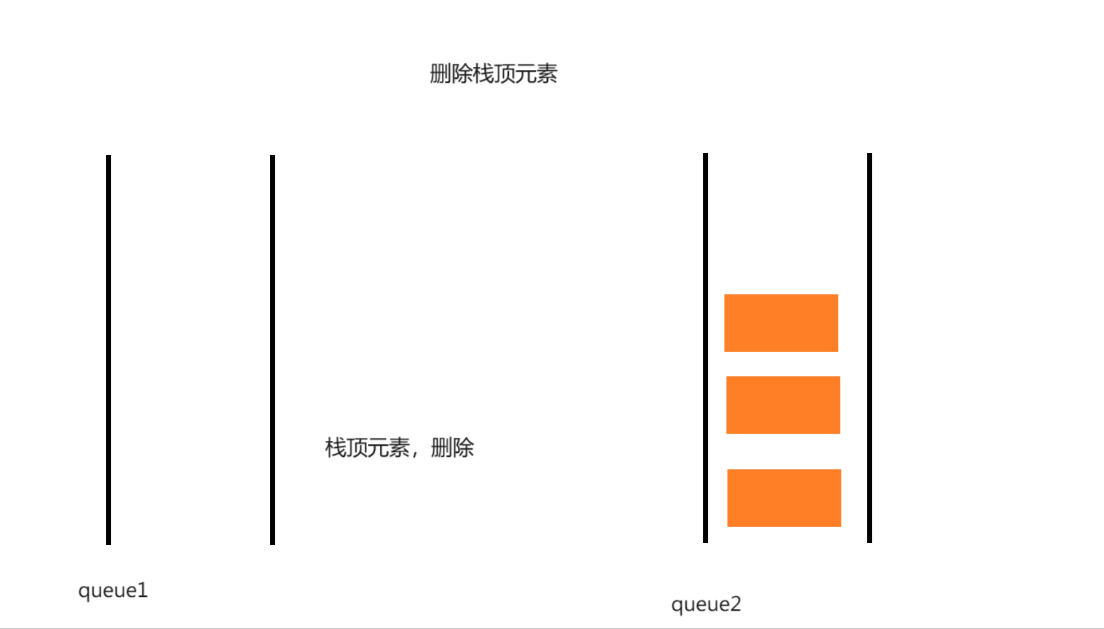
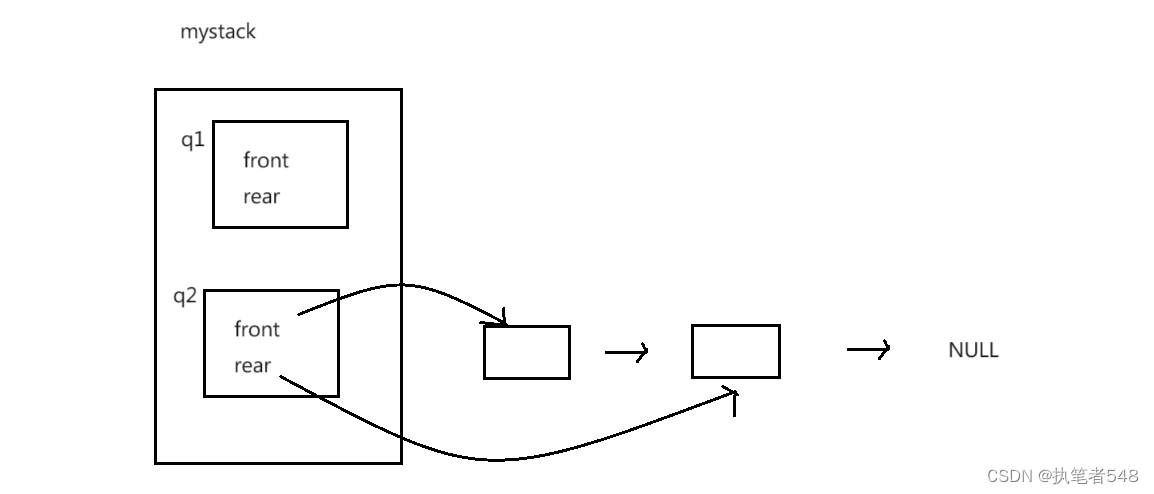
myStack结构:
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QListNode
{
struct QListNode* _pNext;
QDataType _data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* _front;
QNode* _rear;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
q->_front = q->_rear = NULL;
}
QNode* BuyNewNode2(QDataType data)
{
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc failed");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->_data = data;
newnode->_pNext = NULL;
return newnode;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType data)
{
assert(q);
QNode* newnode = BuyNewNode2(data);
if (q->_front == NULL)
{
q->_front = q->_rear = newnode;
}
else
{
q->_rear->_pNext = newnode;
q->_rear = q->_rear->_pNext;
}
}
int QueueEmpty(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
return q->_front == NULL;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
QNode* cur = q->_front->_pNext;
free(q->_front);
q->_front = cur;
if (q->_front == NULL)
{
q->_rear = NULL;
}
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->_front->_data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->_rear->_data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
int count = 0;
QNode* cur = q->_front;
while (cur)
{
cur = cur->_pNext;
count++;
}
return count;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
while (q->_front)
{
QueuePop(q);
}
}
typedef struct MyStack
{
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate()
{
MyStack* obj = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
QueueInit(&obj->q1);
QueueInit(&obj->q2);
return obj;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x)
{
assert(obj);
Queue* no_empty = &obj->q1;
if (QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
no_empty = &obj->q2;
}
QueuePush(no_empty, x);
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj)
{
assert(obj);
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj)
{
assert(obj);
assert(!myStackEmpty(obj));
Queue* no_empty = &obj->q1;
if (QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
no_empty = &obj->q2;
}
return QueueBack(no_empty);
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj)
{
Queue* no_empty = &obj->q1;
Queue* empty = &obj->q2;
if (QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
no_empty = &obj->q2;
empty = &obj->q1;
}
while (QueueSize(no_empty) > 1)
{
QueuePush(empty, QueueFront(no_empty));
QueuePop(no_empty);
}
int val = QueueFront(no_empty);
QueuePop(no_empty);
return val;
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj)
{
assert(obj);
Queue* no_empty = &obj->q1;
if (QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
no_empty = &obj->q2;
}
QueueDestroy(no_empty);
free(obj);
}
1.3 用栈来实现队列
- 题目信息:
- 题目链接:
用栈实现队列
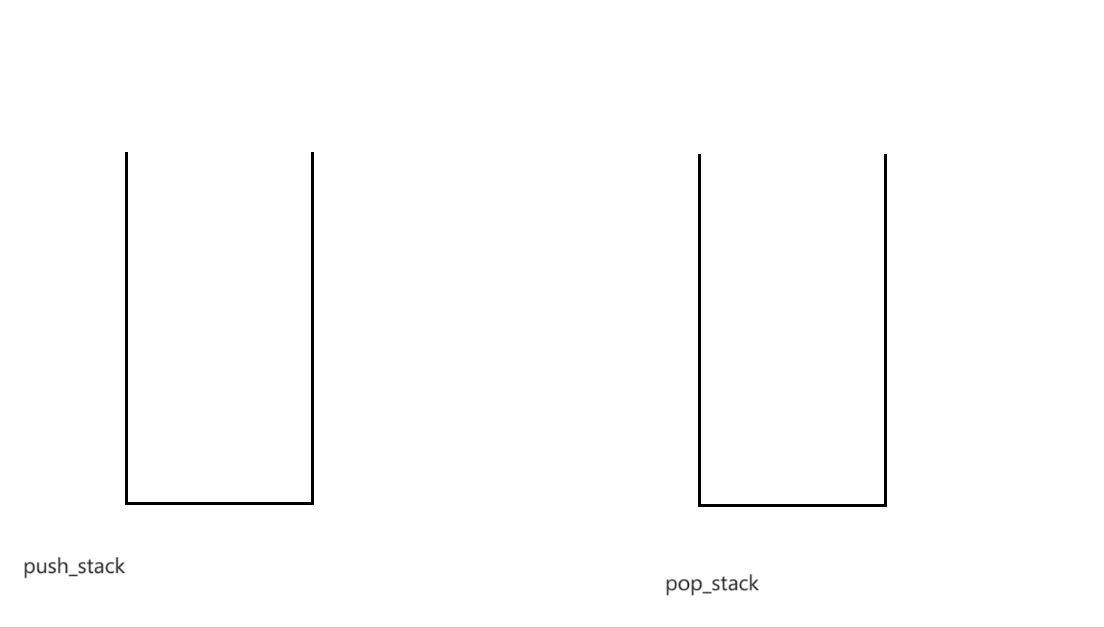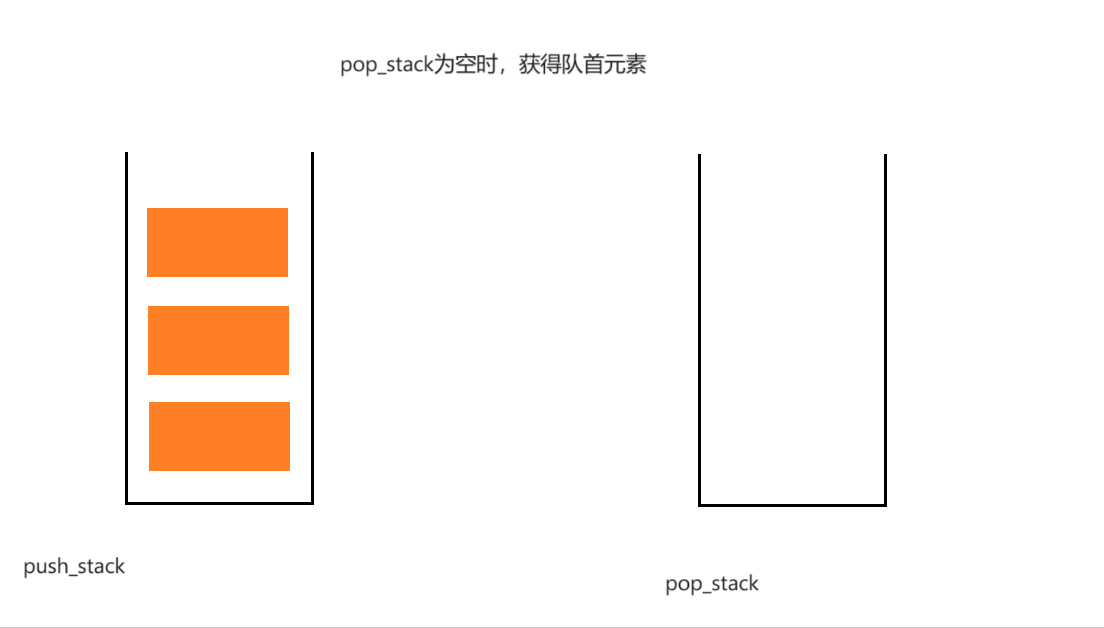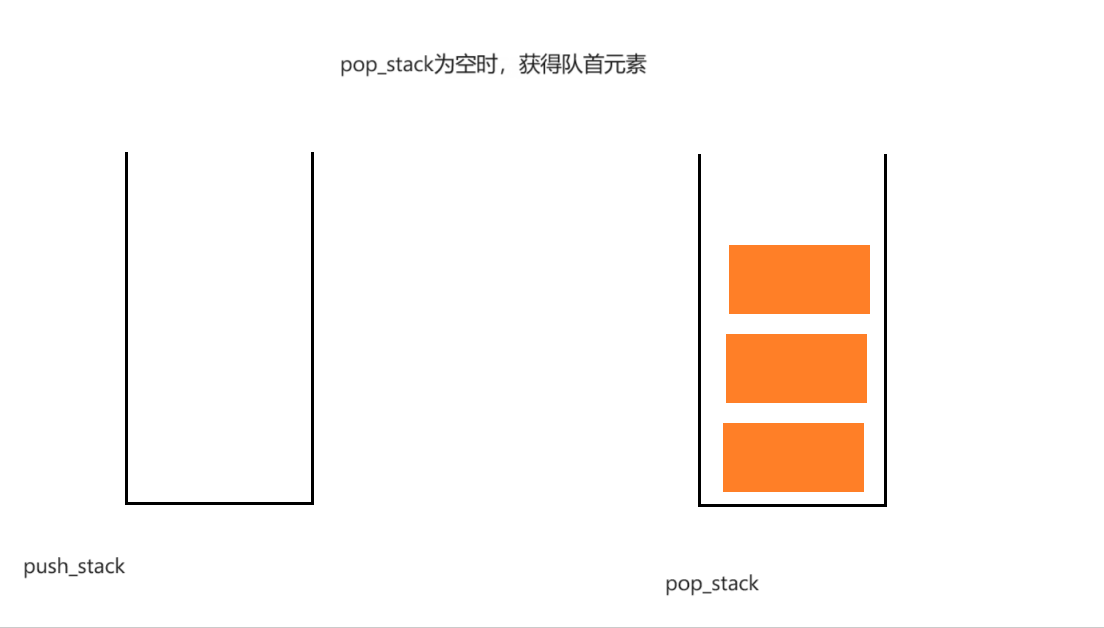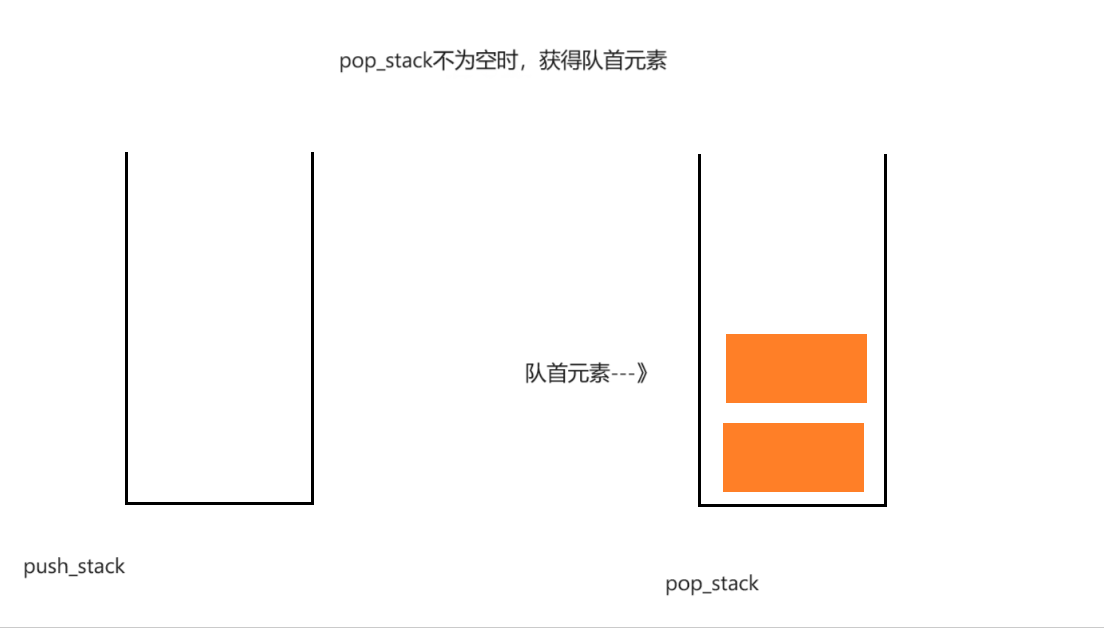
过程演示:
typedef char STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* _a;
int _top; // 栈顶
int _capacity; // 容量
}Stack;
void CheckCapacity(Stack* ps)
{
if (ps->_capacity == ps->_top)
{
int newcapacity = ps->_capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->_capacity;
STDataType* data = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->_a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (data == NULL)
{
perror("realloc failed");
exit(-1);
}
ps->_a = data;
ps->_capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
void StackInit(Stack* ps)
{
ps->_capacity = 0;
ps->_top = 0;
ps->_a = NULL;
CheckCapacity(ps);
}
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data)
{
assert(ps);
CheckCapacity(ps);
ps->_a[ps->_top] = data;
ps->_top++;
}
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_top == 0;
}
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
ps->_top--;
}
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->_a[ps->_top - 1];
}
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_top;
}
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->_a);
ps->_capacity = ps->_top = 0;
}
typedef struct
{
Stack push_stack;
Stack pop_stack;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate()
{
MyQueue* obj = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
StackInit(&obj->push_stack);
StackInit(&obj->pop_stack);
return obj;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x)
{
assert(obj);
StackPush(&obj->push_stack, x);
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj)
{
assert(obj);
return StackEmpty(&obj->push_stack) && StackEmpty(&obj->pop_stack);
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj)
{
assert(obj);
assert(!myQueueEmpty(obj));
if(StackEmpty(&obj->pop_stack))
{
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->push_stack))
{
StackPush(&obj->pop_stack, StackTop(&obj->push_stack));
StackPop(&obj->push_stack);
}
}
return StackTop(&obj->pop_stack);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj)
{
assert(obj);
assert(!myQueueEmpty(obj));
int data = myQueuePeek(obj);
StackPop(&obj->pop_stack);
return data;
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj)
{
assert(obj);
StackDestroy(&obj->push_stack);
StackDestroy(&obj->pop_stack);
free(obj);
}
1.4 扩展:循环队列
- 题目信息:
- 题目链接:
循环链表
过程演示:

typedef struct
{
int* data;
int c_front;
int c_rear;
int capacity_k;
} MyCircularQueue;
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k)
{
MyCircularQueue* obj = (MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
//k + 1为构建循环链表所需的空间大小
obj->data = (int*)malloc((k + 1) * sizeof(int));
//注:k为能够存储的元素个数,即链表存储数据的容量
obj->capacity_k = k;
obj->c_front = obj->c_rear = 0;
return obj;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
assert(obj);
int k = obj->capacity_k;
return obj->c_front % (k + 1) == (obj->c_rear + 1) % (k + 1);
}
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value)
{
assert(obj);
int k = obj->capacity_k;
if (!myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
{
int rear = obj->c_rear % (k + 1);
obj->data[rear] = value;
obj->c_rear++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
assert(obj);
int k = obj->capacity_k;
return obj->c_front % (k + 1) == obj->c_rear % (k + 1);
}
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
assert(obj);
if (!myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
obj->c_front++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
assert(obj);
int k = obj->capacity_k;
if (!myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
int front = obj->c_front % (k + 1);
return obj->data[front];
}
return -1;
}
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
assert(obj);
int k = obj->capacity_k;
if (!myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
int pre_rear = (obj->c_rear - 1) % (k + 1);
return obj->data[pre_rear];
}
return -1;
}
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
assert(obj);
free(obj->data);
free(obj);
}