文章目录
- 使用场景
- 代码示例
- 编译
- 运行示例程序
- 参考文章
使用场景
c++ 是面向对象的编程语言,比较方便实现某些第三方库,比如翻译其他面向对象语言的代码,比 c 语言要方便的多。而 c 语言跟 c++ 很亲和,可以用 c++ 来实现,编译成静态库,提供给 c 程序使用。 至于用静态库而不是动态库,是因为静态库会打包到 c 程序中,不需要依赖运行场景中是否有该库的存在,方便部署。当然,如果第三方库的代码量太大,直接打包导致程序体积膨胀剧烈的话可以考虑动态库。
代码示例
-
目录结构

-
代码预览
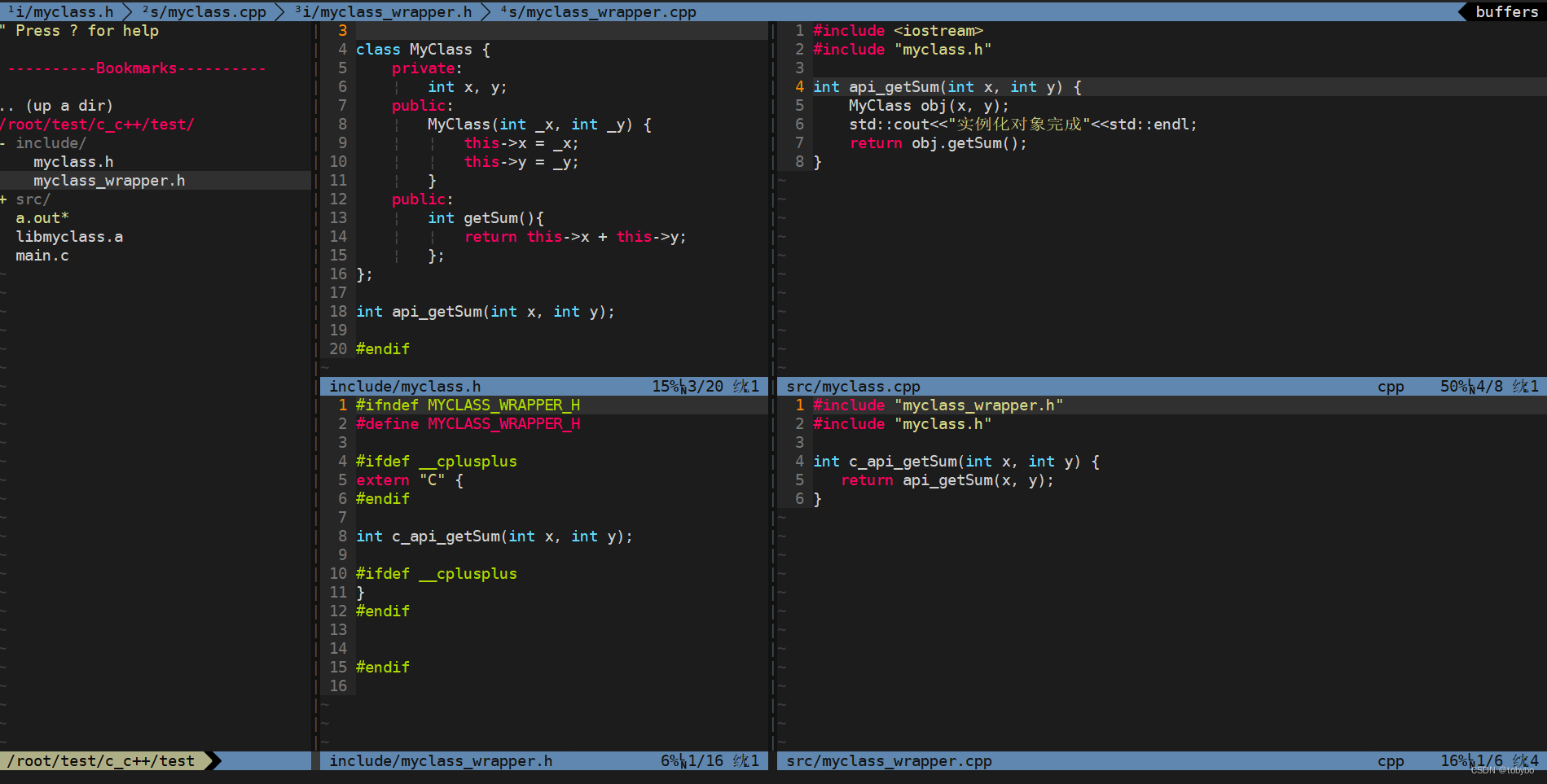
-
c++ 类库代码: myclass.h, myclass.cpp。在这些文件中实现第三方库的所有功能。
// myclass.h #ifndef MYCLASS_H #define MYCLASS_H class MyClass { private: int x, y; public: MyClass(int _x, int _y) { this->x = _x; this->y = _y; } public: int getSum(){ return this->x + this->y; }; }; int api_getSum(int x, int y); #endif// myclass.cpp #include <iostream> #include "myclass.h" int api_getSum(int x, int y) { MyClass obj(x, y); std::cout<<"实例化对象完成"<<std::endl; return obj.getSum(); } -
封装类库 api 为 c api 的 wrapper 文件:myclass_wrapper.h, myclass_wrapper.cpp。该文件只用于封装第三方库提供的 api 为c语言函数风格,不需要实现第三方库的具体功能,不使用第三方库的 c++ 类型,比如 class myclass。wrapper 中的函数需要用 extern “C” {} 包裹声明语句。
// myclass_wrapper.h #ifndef MYCLASS_WRAPPER_H #define MYCLASS_WRAPPER_H #ifdef __cplusplus extern "C" { #endif int c_api_getSum(int x, int y); #ifdef __cplusplus } #endif #endif// myclass_wrapper.cpp #include "myclass_wrapper.h" #include "myclass.h" int c_api_getSum(int x, int y) { return api_getSum(x, y); } -
c 程序示例代码:main.c
// main.c #include "stdio.h" #include "myclass_wrapper.h" int main(int argc, char **argv) { int sum = c_api_getSum(999, 2); printf("%d + %d = %d\n", 999, 2, sum); return 0; }
编译
#生成类库中间文件 myclass_wrapper.o myclass.o
g++ -std=c++11 -c src/myclass_wrapper.cpp src/myclass.cpp -Iinclude
#打包中间文件为静态库 libmyclass.a
ar -r libmyclass.a myclass_wrapper.o myclass.o
#编译 c 示例程序, -lstdc++ 是链接 c++ 标准库,为了在用到类似 <iostream> 的 c++ 库时能编译通过。
gcc -std=c99 main.c -o main -L./ -I./include -lmyclass -lstdc++
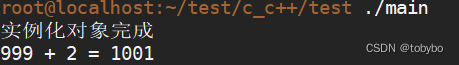
运行示例程序
./main
参考文章
- C调用C++库和C++调用C库的方法