文章目录
- 前言
- 一、FLM文件是什么?
- 二、FLM文件结构
- 1.FlashPrg.c
- 2.FlashPrg.c
- 三、解析FLM文件
- 1.解析flm文件
- 四、设计flash驱动抽象层
- 五、快速使用
前言
在进行Flash操作时,一般我们需要设计一套Flash抽象层,至少要包括flash的init,read、write、erase这些操作。但每更换一个单片机或者flash器件就要额外去编写flash驱动去适配init,read、write、erase。尽管有会者不难的属性加持,但适配所有的单片机或者flash器件,工作量也可想而知。
本文为大家提供一个适配几乎任意单片机型号的flash驱动,之所以说是几乎,是因为我们这次要借东风,而这个东风就是Keil的FLM文件。
项目开源地址:
一、FLM文件是什么?
熟悉Keil的朋友们都知道,当我们要下载编译好的镜像到Flash时,首先要做的一步就是选择合适的Flash下载算法,而这个算法本身就是一个FLM文件:

所谓Flash下载算法,是负责擦除,下载应用数据到flash的一个软件。而Keil往往会集成不少FLM文件以支持大多数的flash型号。
当然,这些算法也是根据不同型号的flash所编写的。只不过,前人们已经为我们种好了大树,我们可以直接在树下乘凉了。
二、FLM文件结构
Keil规定了FLM文件的构成,它是一成不变的,我们才可以放心的对文件本身进行解析,并为自己所用。
生成FLM文件的程序中,有两个非常重要的文件,分别是
- FlashPrg.c中包含编程算法。
- FlashDev.c中包含设备参数。
1.FlashPrg.c
FlashPrg.c文件包含强制性flash编程函数Init、UnInit、EraseSector和ProgramPage。可选地,根据设备特性,可以实现函数EraseChip、BlankCheck和Verify 。
| Function Name | Indication | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BlankCheck | optional | Check and compare patterns. |
| EraseChip | optional | Delete entire Flash memory content. |
| EraseSector | mandatory | Delete Flash memory content of a specific sector. |
| Init | mandatory | Initialize and prepare device for Flash programming. |
| ProgramPage | mandatory | Write the application into the Flash memory. |
| UnInit | mandatory | De-initialize the microcontroller after one of the Flash programming steps. |
| Verify | optional | Compare Flash memory content with the program code. |
其中有4个是必须要有的,我们来逐一说明:
- Init
函数Init为 Flash 编程初始化微控制器。每当尝试将程序下载到 Flash 时都会调用它。
int Init (unsigned long adr, unsigned long clk, unsigned long fnc);
参数adr指定设备的基址。
参数clk指定用于编程设备的时钟频率。
参数fnc是一个数字:
1 代表擦除。
2代表程序。
3代表验证。
Code Example:
int Init (unsigned long adr, unsigned long clk, unsigned long fnc) {
// Zero Wait State
FLASH->ACR = 0x00000000;
// Unlock Flash
FLASH->KEYR = FLASH_KEY1;
FLASH->KEYR = FLASH_KEY2;
// Test if IWDG is running (IWDG in HW mode)
if ((FLASH->OBR & 0x04) == 0x00) {
// Set IWDG time out to ~32.768 second
IWDG->KR = 0x5555; // Enable write access to IWDG_PR and IWDG_RLR
IWDG->PR = 0x06; // Set prescaler to 256
IWDG->RLR = 4095; // Set reload value to 4095
}
return (0);
}
- ProgramPage
函数ProgramPage用于将代码写入闪存。它被调用以将程序下载到 Flash。由于flash通常以块或页的形式组织,因此函数ProgramPage的参数不得跨越这些闪存页的对齐边界。页面大小在结构 FlashDevice 中指定,值为Program Page Size。
int ProgramPage ( unsigned long adr, unsigned long sz, unsigned char *buf);
参数adr指定要编程的页面的起始地址。它由主机编程系统与flash页面的起始地址对齐。
参数sz指定数据缓冲区中的数据大小。主机编程系统确保不跨越页面边界。
参数buf指向包含要编程的数据的数据缓冲区。
Code Example:
int ProgramPage (unsigned long adr, unsigned long sz, unsigned char *buf) {
sz = (sz + 1) & ~1; // Adjust size for Half Words
while (sz) {
FLASH->CR |= FLASH_PG; // Programming Enabled
M16(adr) = *((unsigned short *)buf); // Program Half Word
while (FLASH->SR & FLASH_BSY);
FLASH->CR &= ~FLASH_PG; // Programming Disabled
// Check for Errors
if (FLASH->SR & (FLASH_PGERR | FLASH_WRPRTERR)) {
FLASH->SR |= FLASH_PGERR | FLASH_WRPRTERR;
return (1); // Failed
}
// Go to next Half Word
adr += 2;
buf += 2;
sz -= 2;
}
return (0); // Done
}
- EraseSector
函数EraseSector删除从参数adr指定的地址开始的扇区内容。
int EraseSector (unsigned long adr);
参数adr扇区地址
Code Example:
int EraseSector (unsigned long adr) {
FLASH->CR |= FLASH_PER; // Page Erase Enabled
FLASH->AR = adr; // Page Address
FLASH->CR |= FLASH_STRT; // Start Erase
while (FLASH->SR & FLASH_BSY) {
IWDG->KR = 0xAAAA; // Reload IWDG
}
FLASH->CR &= ~FLASH_PER; // Page Erase Disabled
return (0); // Done
}
- UnInit
函数UnInit取消初始化微控制器,并在擦除、编程或验证步骤结束时调用。
int UnInit (unsigned long fnc);
Code Example
int UnInit (unsigned long fnc) {
// Lock Flash
FLASH->CR |= FLASH_LOCK;
return (0);
}
2.FlashPrg.c
文件FlashDev.c包含以下参数定义:
- Flash编程功能。
- FlashDevice结构:
struct FlashDevice const FlashDevice = {
FLASH_DRV_VERS, // 驱动版本,请勿修改!
"New Device 256kB Flash" , // 设备名称
ONCHIP, // 设备类型
0x00000000, // 设备起始地址
0x00040000, // 以字节为单位的设备大小 (256kB)
1024, // 编程页面大小
0, // 保留,必须为0
0xFF, // 已擦除内存的初始内容
100, // 程序页面超时 100 毫秒
3000, // 擦除扇区超时 3000 毫秒
// 指定扇区的大小和地址
0x002000, 0x000000, // 扇区大小 8kB(8 个扇区)
0x010000, 0x010000, // 扇区大小 64kB(2 个扇区)
0x002000, 0x030000, // 扇区大小 8kB(8 个扇区)
SECTOR_END
};
Device Name通常显示在工具中,用于识别 Flash 算法。确保此名称反映设备名称。
编程页面大小指定使用函数ProgramPage进行编程 的块大小。对于块大小较小的设备,最好指定物理块大小的倍数,因为这可以减少与目标的通信开销。快速编程的最佳块大小为 1024 字节,但系统本身并不限制此大小值。
三、解析FLM文件
1.解析flm文件
下面让我们解析一下现有的FLM文件,以STM32F4xx_1024.FLM为例:
将ARM:CMSIS Pack文件夹(通常在D:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Arm\Packs\Keil\STM32F4xx_DFP\2.15.0\CMSIS\Flash)中的内容复制到一个新文件夹中。
打开命令行工具,输入arm-none-eabi-readelf -a STM32F4xx_1024.FLM:
$ arm-none-eabi-readelf -a STM32F4xx_1024.FLM
ELF Header:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 01 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Class: ELF32
Data: 2's complement, little endian
Version: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
ABI Version: 0
Type: EXEC (Executable file)
Machine: ARM
Version: 0x1
Entry point address: 0x0
Start of program headers: 12172 (bytes into file)
Start of section headers: 12236 (bytes into file)
Flags: 0x5000000, Version5 EABI
Size of this header: 52 (bytes)
Size of program headers: 32 (bytes)
Number of program headers: 2
Size of section headers: 40 (bytes)
Number of section headers: 16
Section header string table index: 15
Section Headers:
[Nr] Name Type Addr Off Size ES Flg Lk Inf Al
[ 0] NULL 00000000 000000 000000 00 0 0 0
[ 1] PrgCode PROGBITS 00000000 000034 000144 00 AX 0 0 4
[ 2] PrgData PROGBITS 00000144 000178 000004 00 WA 0 0 4
[ 3] DevDscr PROGBITS 00000148 00017c 0010a0 00 A 0 0 4
[ 4] .debug_abbrev PROGBITS 00000000 00121c 0005a4 00 0 0 1
[ 5] .debug_frame PROGBITS 00000000 0017c0 000104 00 0 0 1
[ 6] .debug_info PROGBITS 00000000 0018c4 00064c 00 0 0 1
[ 7] .debug_line PROGBITS 00000000 001f10 000218 00 0 0 1
[ 8] .debug_loc PROGBITS 00000000 002128 0001b8 00 0 0 1
[ 9] .debug_macinfo PROGBITS 00000000 0022e0 000614 00 0 0 1
[10] .debug_pubnames PROGBITS 00000000 0028f4 000096 00 0 0 1
[11] .symtab SYMTAB 00000000 00298c 000110 10 12 9 4
[12] .strtab STRTAB 00000000 002a9c 000100 00 0 0 1
[13] .note NOTE 00000000 002b9c 00001c 00 0 0 4
[14] .comment PROGBITS 00000000 002bb8 000334 00 0 0 1
[15] .shstrtab STRTAB 00000000 002eec 0000a0 00 0 0 1
Key to Flags:
W (write), A (alloc), X (execute), M (merge), S (strings), I (info),
L (link order), O (extra OS processing required), G (group), T (TLS),
C (compressed), x (unknown), o (OS specific), E (exclude),
y (purecode), p (processor specific)
There are no section groups in this file.
Program Headers:
Type Offset VirtAddr PhysAddr FileSiz MemSiz Flg Align
LOAD 0x000034 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00148 0x00148 RWE 0x4
LOAD 0x00017c 0x00000148 0x00000148 0x010a0 0x010a0 R 0x4
Section to Segment mapping:
Segment Sections...
00 PrgCode PrgData
01 DevDscr
There is no dynamic section in this file.
There are no relocations in this file.
There are no unwind sections in this file.
Symbol table '.symtab' contains 17 entries:
Num: Value Size Type Bind Vis Ndx Name
0: 00000000 0 NOTYPE LOCAL DEFAULT UND
1: 00000000 0 NOTYPE LOCAL DEFAULT 1 $t
2: 00000122 0 NOTYPE LOCAL DEFAULT 1 $d
3: 00000144 0 NOTYPE LOCAL DEFAULT 2 $d.realdata
4: 00000148 0 NOTYPE LOCAL DEFAULT 3 $d.realdata
5: 00000000 0 FILE LOCAL DEFAULT ABS FlashPrg.c
6: 00000000 0 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 1 .text
7: 00000000 0 FILE LOCAL DEFAULT ABS FlashDev.c
8: 00000148 4256 SECTION LOCAL DEFAULT 3 .constdata
9: 00000000 0 NOTYPE GLOBAL HIDDEN ABS BuildAttributes$$THM_ISAv
10: 00000001 28 FUNC GLOBAL HIDDEN 1 GetSecNum
11: 0000001d 46 FUNC GLOBAL HIDDEN 1 Init
12: 0000004b 14 FUNC GLOBAL HIDDEN 1 UnInit
13: 00000059 44 FUNC GLOBAL HIDDEN 1 EraseChip
14: 00000085 76 FUNC GLOBAL HIDDEN 1 EraseSector
15: 000000d1 82 FUNC GLOBAL HIDDEN 1 ProgramPage
16: 00000148 4256 OBJECT GLOBAL HIDDEN 3 FlashDevice
No version information found in this file.
Displaying notes found at file offset 0x00002b9c with length 0x0000001c:
Owner Data size Description
ARM 0x0000000c Unknown note type: (0x40000000)
通过Symbol table信息我们可以找到Init、UnInit、EraseSector和ProgramPage函数所在的位置。
我们还需要根据Section Headers所描述的位置提取出Prgcode(代码),PrgData(数据),DevDscr(设备描述)的信息。
在命令行中输入arm-none-eabi-objdum -s -d STM32F4xx_1024.FLM:-s参数可以将所有段的内容一十六进制方式打印出来,-d参数可以将所有包含指令的段反汇编。
$ arm-none-eabi-objdump -s -d STM32F4xx_1024.FLM
STM32F4xx_1024.FLM: file format elf32-littlearm
Contents of section PrgCode:
0000 0003000e 202802d3 4009001d 70471028 .... (..@...pG.(
0010 02d30009 c01c7047 80087047 42484149 ......pG..pGBHAI
0020 41604249 41600021 0160c168 f0221143 A`BIA`.!.`.h.".C
0030 c1604069 800606d4 3e483d49 01600621 .`@i....>H=I.`.!
0040 41603d49 81600020 70473748 01694205 A`=I.`. pG7H.iB.
0050 11430161 00207047 10b53348 01690424 .C.a. pG..3H.i.$
0060 21430161 0169a203 11430161 3349314a !C.a.i...C.a3I1J
0070 00e01160 c368db03 fbd40169 a1430161 ...`.h.....i.C.a
0080 002010bd 30b5fff7 bbff2749 ca68f023 . ..0.....'I.h.#
0090 1a43ca60 02240c61 0a690007 400e0243 .C.`.$.a.i..@..C
00a0 0a610869 e2031043 08612448 214a00e0 .a.i...C.a$H!J..
00b0 1060cd68 ed03fbd4 0869a043 0861c868 .`.h.....i.C.a.h
00c0 0006000f 03d0c868 1843c860 012030bd .......h.C.`. 0.
00d0 70b5154d c91c8908 eb688900 f0263343 p..M.....h...&3C
00e0 eb600023 2b61164b 17e02c69 1c432c61 .`.#+a.K..,i.C,a
00f0 14680460 ec68e403 fcd42c69 64086400 .h.`.h....,id.d.
0100 2c61ec68 2406240f 04d0e868 3043e860 ,a.h$.$....h0C.`
0110 012070bd 001d121d 091f0029 e5d10020 . p........)...
0120 70bd0000 23016745 003c0240 ab89efcd p...#.gE.<.@....
0130 55550000 00300040 ff0f0000 aaaa0000 UU...0.@........
0140 01020000 ....
Contents of section PrgData:
0144 00000000 ....
Contents of section DevDscr:
0148 01015354 4d333246 34787820 466c6173 ..STM32F4xx Flas
0158 68000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 h...............
0168 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 ................
0178 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 ................
0188 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 ................
0198 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 ................
01a8 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 ................
01b8 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 ................
01c8 00000100 00000008 00001000 00040000 ................
01d8 00000000 ff000000 64000000 70170000 ........d...p...
01e8 00400000 00000000 00000100 00000100 .@..............
01f8 00000200 00000200 ffffffff ffffffff ................
我们所需要的正是以上信息,接下来的任务只需要写一个上位机,将以上文件提取出来即可,这个上位机我已经写好,工具:
允许以后生成STM32F4xx_1024.FLM.c文件,直接添加到我们的工程中即可,生成的代码如下:
#include "flash_blob.h"
#define OPS_OFFSET ((uint32_t)&flash_code)
#define DEV_OFFSET ((uint32_t)&flash_dev)
#define RAM_OFFSET ((uint32_t)&rw_data)
static const uint32_t flash_code[] =
{
0X0E000300,0XD3022820,0X1D000940,0X28104770,0X0900D302,0X47701CC0,0X47700880,0X49414842,
0X49426041,0X21036041,0X68C16001,0X431122F0,0X694060C1,0XD4060680,0X493D483E,0X21066001,
0X493D6041,0X20006081,0X48374770,0X05426901,0X61014311,0X47702000,0X4833B510,0X24046901,
0X61014321,0X03A26901,0X61014311,0X4A314933,0X6011E000,0X03DB68C3,0X6901D4FB,0X610143A1,
0XBD102000,0XF7FFB530,0X4927FFBB,0X23F068CA,0X60CA431A,0X610C2402,0X0700690A,0X43020E40,
0X6908610A,0X431003E2,0X48246108,0XE0004A21,0X68CD6010,0XD4FB03ED,0X43A06908,0X68C86108,
0X0F000600,0X68C8D003,0X60C84318,0XBD302001,0X4D15B570,0X08891CC9,0X008968EB,0X433326F0,
0X230060EB,0X4B16612B,0X692CE017,0X612C431C,0X60046814,0X03E468EC,0X692CD4FC,0X00640864,
0X68EC612C,0X0F240624,0X68E8D004,0X60E84330,0XBD702001,0X1D121D00,0X29001F09,0X2000D1E5,
0X0000BD70,0X45670123,0X40023C00,0XCDEF89AB,0X00005555,0X40003000,0X00000FFF,0X0000AAAA,
0X00000201,0X00000000,
};
static const uint32_t flash_dev[] =
{
0X54530101,0X4632334D,0X20787834,0X73616C46,0X00000068,0X00000000,0X00000000,0X00000000,
0X00000000,0X00000000,0X00000000,0X00000000,0X00000000,0X00000000,0X00000000,0X00000000,
0X00000000,0X00000000,0X00000000,0X00000000,0X00000000,0X00000000,0X00000000,0X00000000,
0X00000000,0X00000000,0X00000000,0X00000000,0X00000000,0X00000000,0X00000000,0X00000000,
0X00010000,0X08000000,0X00100000,0X00000400,0X00000000,0X000000FF,0X00000064,0X00001770,
0X00004000,0X00000000,0X00010000,0X00010000,0X00020000,0X00020000,0XFFFFFFFF,0XFFFFFFFF,
};
static uint32_t rw_data[] =
{
0X00000000,
};
static flash_blob_device_t flash_device =
{
(void*)(OPS_OFFSET + 0X001D), // Init
(void*)(OPS_OFFSET + 0X004B), // UnInit
(void*)(OPS_OFFSET + 0X0059), // EraseChip
(void*)(OPS_OFFSET + 0X0085), // EraseSector
(void*)(OPS_OFFSET + 0X00D1), // ProgramPage
(void*)(DEV_OFFSET),
(void*)(RAM_OFFSET),
};
static int flash_blob_device_register(void)
{
flash_dev_register(&flash_device);
return 0 ;
}
INIT_BOARD_EXPORT(flash_blob_device_register);
四、设计flash驱动抽象层
接下来,为了方便后续使用,需要设计一个flash驱动抽象层,代码如下:
flash_blob.h
#ifndef FLASH_BLOB_H
#define FLASH_BLOB_H
#include "rtthread.h"
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define VERS 1 // Interface Version 1.01
#define UNKNOWN 0 // Unknown
#define ONCHIP 1 // On-chip Flash Memory
#define EXT8BIT 2 // External Flash Device on 8-bit Bus
#define EXT16BIT 3 // External Flash Device on 16-bit Bus
#define EXT32BIT 4 // External Flash Device on 32-bit Bus
#define EXTSPI 5 // External Flash Device on SPI
#define SECTOR_NUM 16 // Max Number of Sector Items
struct FlashSectors {
unsigned long szSector; // Sector Size in Bytes
unsigned long AddrSector; // Address of Sector
};
typedef struct FlashDevice {
unsigned short Vers; // Version Number and Architecture
char DevName[128]; // Device Name and Description
unsigned short DevType; // Device Type: ONCHIP, EXT8BIT, EXT16BIT, ...
unsigned long DevAdr; // Default Device Start Address
unsigned long szDev; // Total Size of Device
unsigned long szPage; // Programming Page Size
unsigned long Res; // Reserved for future Extension
unsigned char valEmpty; // Content of Erased Memory
unsigned long toProg; // Time Out of Program Page Function
unsigned long toErase; // Time Out of Erase Sector Function
struct FlashSectors sectors[SECTOR_NUM];
}flash_dev_t;
typedef struct {
int (*Init)(uint32_t adr, uint32_t clk, uint32_t fnc);
int (*UnInit)(uint32_t fnc);
int (*EraseChip)(void);
int (*EraseSector)(uint32_t adr);
int (*ProgramPage)(uint32_t adr, uint32_t sz, uint8_t* buf);
}flash_ops_t;
typedef struct
{
flash_ops_t tFlashops;
flash_dev_t *ptFlashDev;
int *pPrgData;
rt_slist_t slist;
}flash_blob_t;
extern void flash_dev_register(flash_blob_t *ptFlashDevice);
extern bool target_flash_init(uint32_t flash_start, int32_t size);
extern bool target_flash_uninit(uint32_t flash_start);
extern int32_t target_flash_write(uint32_t addr, const uint8_t *buf, int32_t size);
extern int32_t target_flash_erase(uint32_t addr, int32_t size);
extern int32_t target_flash_read(uint32_t addr, const uint8_t *buf, int32_t size);
#endif
flash_blob.c
#include "flash_blob.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "string.h"
static bool s_bIsInit = false;
static rt_slist_t _slist_head = RT_SLIST_OBJECT_INIT(_slist_head);
register int *pPrgDataBase __asm("r9");
void flash_dev_register(flash_blob_t *ptFlashDevice)
{
rt_slist_init(&(ptFlashDevice->slist));
rt_slist_append(&_slist_head, &(ptFlashDevice->slist));
}
static flash_blob_t * flash_dev_find(uint32_t flash_start)
{
rt_slist_t *node;
rt_slist_for_each(node, &_slist_head) {
flash_blob_t *ptFlashDevice = rt_slist_entry(node, flash_blob_t, slist);
if(flash_start >= ptFlashDevice->ptFlashDev->DevAdr &&
flash_start < ptFlashDevice->ptFlashDev->DevAdr + ptFlashDevice->ptFlashDev->szDev) {
return ptFlashDevice;
}
}
return NULL;
}
bool target_flash_init(uint32_t flash_start, int32_t size)
{
if (flash_start % 4 != 0) {
LOG_E("flash addr must be 4-byte alignment");
return NULL;
}
flash_blob_t *ptFlashDevice = flash_dev_find(flash_start);
if(ptFlashDevice != NULL) {
pPrgDataBase = ptFlashDevice->pPrgData;
ptFlashDevice->tFlashops.Init(flash_start, 0, 0);
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool target_flash_uninit(uint32_t flash_start)
{
flash_blob_t *ptFlashDevice = flash_dev_find(flash_start);
if(ptFlashDevice != NULL) {
pPrgDataBase = ptFlashDevice->pPrgData;
ptFlashDevice->tFlashops.UnInit(flash_start);
return true;
}
return true;
}
int target_flash_write(uint32_t addr, const uint8_t *buf, int32_t size)
{
flash_blob_t *ptFlashDevice = flash_dev_find(addr);
if(ptFlashDevice != NULL) {
pPrgDataBase = ptFlashDevice->pPrgData;
while(size > 0) {
uint32_t write_size = size > ptFlashDevice->ptFlashDev->szPage ? ptFlashDevice->ptFlashDev->szPage : size;
if( 0 != ptFlashDevice->tFlashops.ProgramPage(addr, write_size, (uint8_t *)buf)) {
LOG_E("Programming Failed");
return -1;
}
addr += write_size;
buf += write_size;
size -= write_size;
}
return size;
}
return -1;
}
int32_t target_flash_read(uint32_t addr, const uint8_t *buf, int32_t size)
{
flash_blob_t *ptFlashDevice;
pPrgDataBase = ptFlashDevice->pPrgData;
return size;
}
int32_t target_flash_erase(uint32_t addr, int32_t size)
{
int32_t wSector, wRemainLen;
flash_blob_t *ptFlashDevice = flash_dev_find(addr);
if(ptFlashDevice != NULL) {
if (size > ptFlashDevice->ptFlashDev->szDev) {
LOG_E("erase outrange flash size! addr is (0x%p)\n", (void *)(addr + size));
return -1;
}
pPrgDataBase = ptFlashDevice->pPrgData;
wRemainLen = size;
while(wRemainLen > 0) {
if(0 != ptFlashDevice->tFlashops.EraseSector(addr)) {
LOG_E("erase Failed! addr is (0x%p)\n", (void *)addr);
return -1;
}
for(wSector = 0; wSector < SECTOR_NUM; wSector++) {
if(ptFlashDevice->ptFlashDev->sectors[wSector + 1].szSector == 0XFFFFFFFF )
break;
if(((addr - ptFlashDevice->ptFlashDev->DevAdr) < ptFlashDevice->ptFlashDev->sectors[wSector + 1].AddrSector) &&
((addr - ptFlashDevice->ptFlashDev->DevAdr) >= ptFlashDevice->ptFlashDev->sectors[wSector].AddrSector) )
break;
}
addr += ptFlashDevice->ptFlashDev->sectors[wSector].szSector;
wRemainLen -= ptFlashDevice->ptFlashDev->sectors[wSector].szSector;
}
return size;
}
return -1;
}
int32_t target_flash_verify (uint32_t addr, uint8_t *buf, int32_t size)
{
return size;
}
五、快速使用
本项目借用了rtthread的自动初始化机制和链表,所以最快的使用方式是直接作为rtthread的软件包使用,使用方法如下:
1.在rtthread软件包中找到flash_blob,然后添加进工程。
2. 通过tools文件下的工具,生成对应的xxx.FLM.c文件,将xxx.FLM.c添加进工程,如果有多个flash器件,可以连续添加。
注意:多个设备的话每个flash的FlashDevice 的设备起始地址不可重叠,flash抽象层根据地址,自动选择相应的驱动。
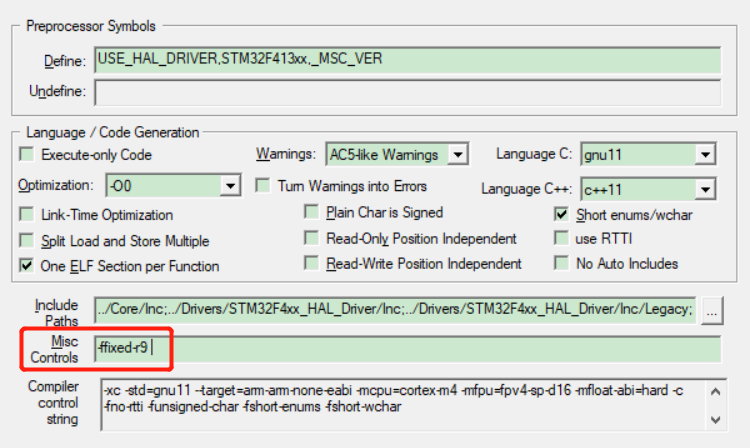
3.由于flash驱动需要占用“r9”寄存器,所以需要在编译选项中添加-ffixed-r9
以上步骤完成后,就可以快速使用了,例如将YMODEM接收到的数据,写到flash中,代码如下:
uint8_t *ymodem_call_back_receive(uint8_t *pchBuffer, uint16_t hwSize)
{
static char *s_pchFileName = NULL, *s_pchFileSize = NULL;
static uint32_t s_wFileSize = 0, s_wRemainLen = 0, s_wOffSet = 0;
static enum {
START = 0,
RECEIVE,
END,
} s_tState = {START};
switch(s_tState) {
case START:
s_wOffSet = 0;
s_pchFileName = (char *)&pchBuffer[0];
s_pchFileSize = (char *)&pchBuffer[strlen(s_pchFileName) + 1];
s_wFileSize = atol(s_pchFileSize);
LOG_D("Ymodem file_name:%s", s_pchFileName);
LOG_D("Ymodem file_size:%d", s_wFileSize);
if(target_flash_init(APP_PART_ADDR, s_wFileSize) == false) {
LOG_E("target flash uninit.");
return NULL;
}
if(target_flash_erase(APP_PART_ADDR, s_wFileSize) < 0) {
LOG_E("target flash erase error.");
return NULL;
}
s_tState = RECEIVE;
break;
case RECEIVE:
s_wRemainLen = s_wFileSize - s_wOffSet;
if(hwSize > s_wRemainLen) {
hwSize = s_wRemainLen;
s_tState = END;
}
if(target_flash_write(APP_PART_ADDR + s_wOffSet, pchBuffer, hwSize) < 0) {
LOG_E("target flash write data error.");
return NULL;
}
s_wOffSet += hwSize;
break;
case END:
target_flash_uninit(APP_PART_ADDR);
s_tState = START;
break;
}
return s_chBuffer;
}