目录
一. 概念
二. 队列的使用
三. 队列模拟实现
四. 循环队列
五. 面试题
一. 概念
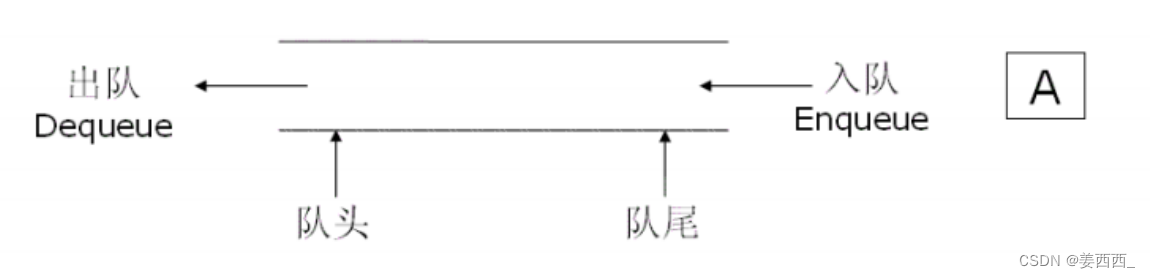

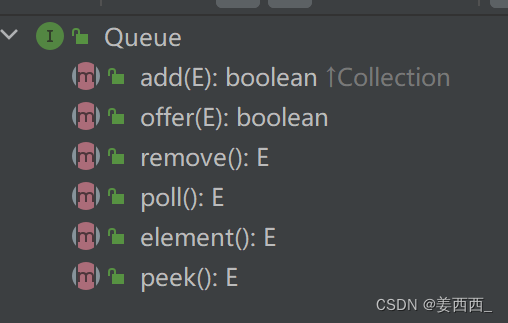
在Queue接口的方法里, 我们看到有add remove element 这些是继承于Collection接口的, 而offer poll peek是接口本身的,他们的使用效果基本一致
二. 队列的使用
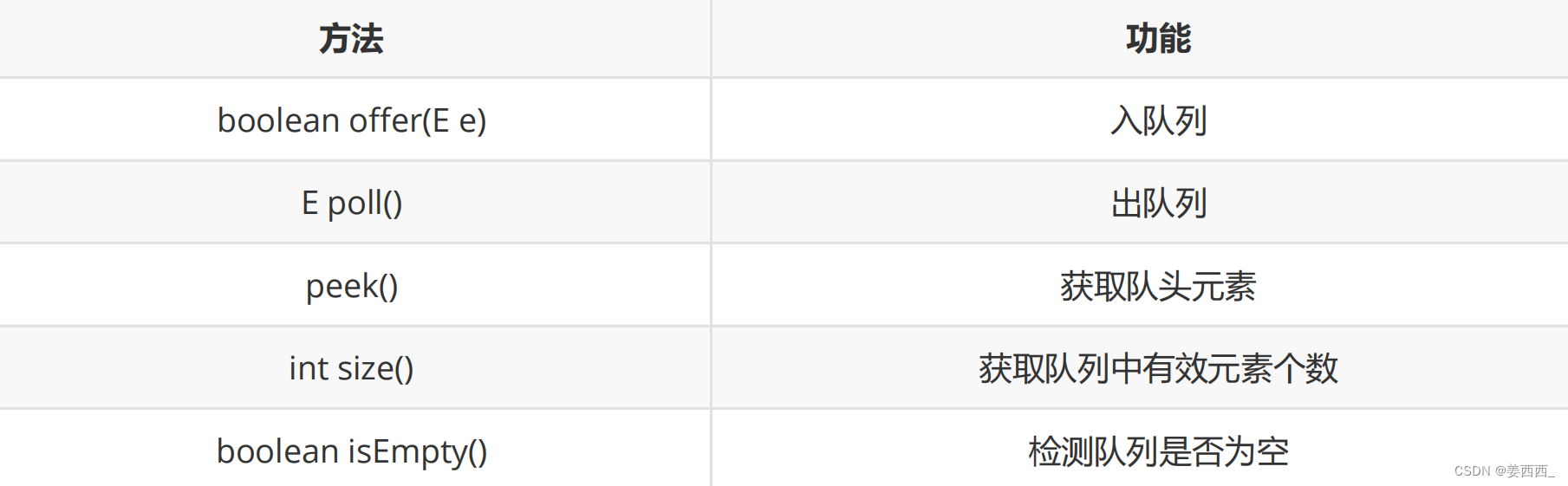
注意:Queue是个接口,在实例化时必须实例化LinkedList的对象,因为LinkedList实现了Queue接口。
public static void main ( String [] args ) {Queue < Integer > q = new LinkedList <> ();q . offer ( 1 );q . offer ( 2 );q . offer ( 3 );q . offer ( 4 );q . offer ( 5 ); // 从队尾入队列System . out . println ( q . size ());System . out . println ( q . peek ()); // 获取队头元素q . poll ();System . out . println ( q . poll ()); // 从队头出队列,并将删除的元素返回if ( q . isEmpty ()){System . out . println ( " 队列空 " );} else {System . out . println ( q . size ());}}
三. 队列模拟实现
public class MyQueue {
static class ListNode{
public int val;
public ListNode prev;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
public ListNode head;
public ListNode last;
//入队
public void offer(int val){
ListNode node = new ListNode(val);
if(head == null){
head = last = node;
}else{
last.next = node;
node.prev = last;
last = node;
}
}
//出队
public int poll(){
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
int val;
if(head.next == null){
val = head.val;
head = null;
last = null;
return val;
}
val = head.val;
head = head.next;
head.prev = null;
return val;
}
public boolean empty(){
return head == null;
}
public int peek(){
if(head ==null){
return -1;
}
return head.val;
}
}四. 循环队列
数组下标循环的小技巧

队尾指针向后:
rear = (rear + 偏移量) %array.length
队尾指针向前:
rear = (rear + array.length - 偏移量) %array.length
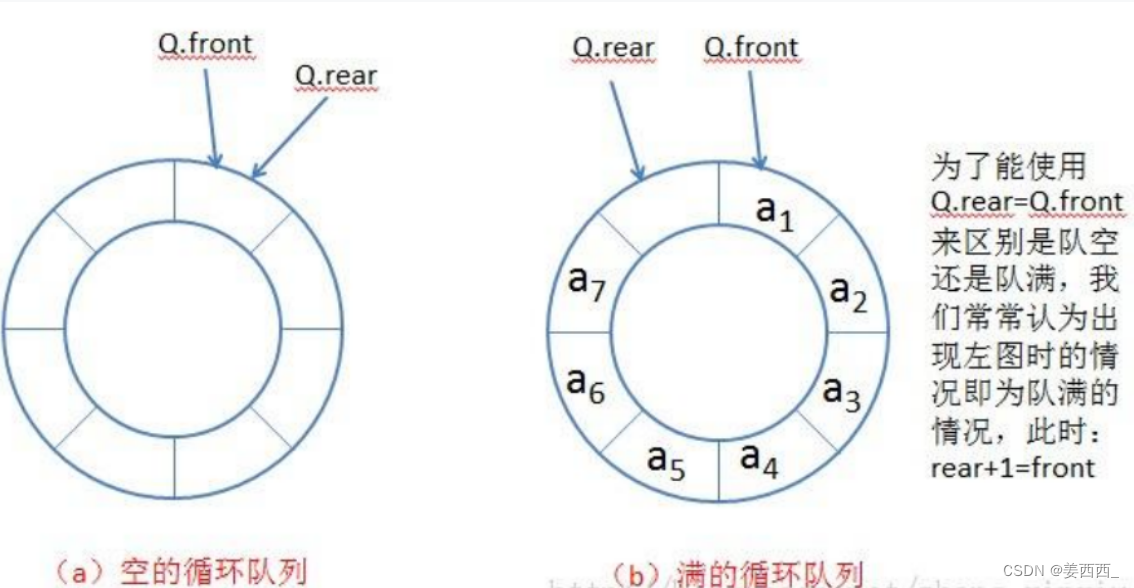
2. 保留一个位置, 浪费一个空间
设计一个循环队列 链接
class MyCircularQueue {
public int[] elem;
public int front;
public int rear;
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
elem = new int[k+1];
}
//入队
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
elem[rear] = value;
rear = (rear+1)%elem.length;
return true;
}
//删除队头元素
public boolean deQueue() {
if(isEmpty()){
return false;
}
front = (front + 1)%elem.length;
return true;
}
//得到队头元素
public int Front() {
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
return elem[front];
}
//得到队尾元素
public int Rear() {
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
int index = (rear + elem.length - 1)%elem.length;
return elem[index];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == rear;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear + 1)%elem.length == front;
}
}
五. 双端队列
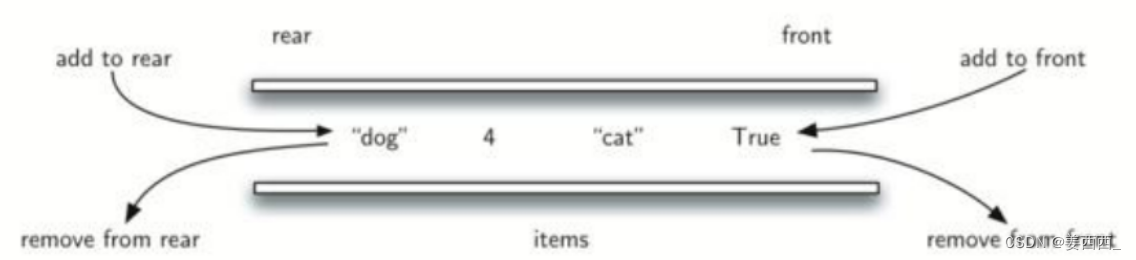
Deque是一个接口,使用时必须创建LinkedList的对象。
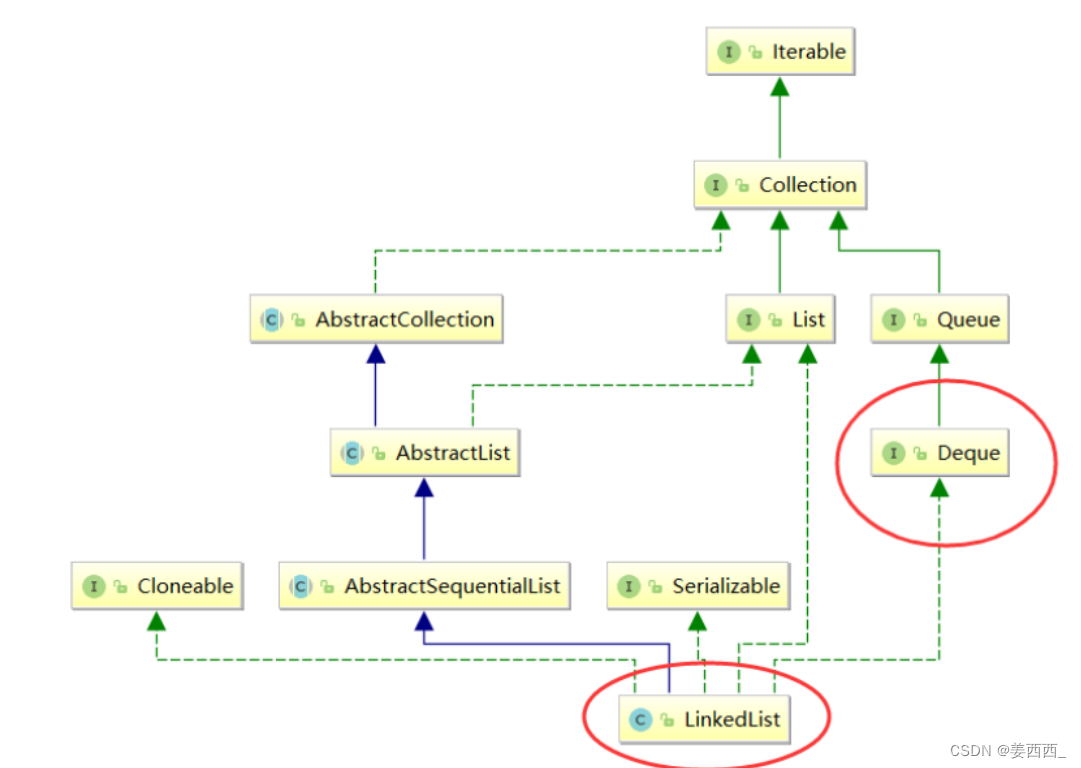
Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();// 双端队列的线性实现Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();// 双端队列的链式实现
五. 面试题
1. 用队列实现栈 链接
思路:一个队列是不能实现栈的, 需要用两个队列
1. 入栈, 当两个队列都为空时, 放在第一个队列里
2. 再次入栈时, 放在不为空的队列
3. 出栈时, 出不为空的队列, 出size-1个元素, 剩下的一个就是要出栈的元素
代码:
class MyStack {
private Queue<Integer> qu1;
private Queue<Integer> qu2;
public MyStack() {
qu1 = new LinkedList<>();
qu2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
if(empty()){
qu1.offer(x);
return;
}
if(!qu1.isEmpty()){
qu1.offer(x);
}else{
qu2.offer(x);
}
}
public int pop() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
if(!qu1.isEmpty()){
int size = qu1.size();
for(int i = 0;i < size-1;i++){
qu2.offer(qu1.poll());
}
return qu1.poll();
}else{
int size = qu2.size();
for(int i = 0;i < size-1;i++){
qu1.offer(qu2.poll());
}
return qu2.poll();
}
}
public int top() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
if(!qu1.isEmpty()){
int size = qu1.size();
for(int i = 0;i < size-1;i++){
qu2.offer(qu1.poll());
}
int tmp = qu1.peek();
qu2.offer(qu1.poll());
return tmp;
}else{
int size = qu2.size();
for(int i = 0;i < size-1;i++){
qu1.offer(qu2.poll());
}
int tmp = qu2.peek();
qu1.offer(qu2.poll());
return tmp;
}
}
public boolean empty() {
return qu1.isEmpty() && qu2.isEmpty();
}
}
2. 用栈实现队列 链接
思路:一个栈不能实现队列, 需要两个栈
1. 入队, 把数据放在第一个栈
2. 出栈, 出第二个栈的栈顶元素即可, 如果第二个栈为空, 将里面的所有元素放到第二个栈
3. 当两个栈都为空时, 说明模拟的队列为空
class MyQueue {
private Stack<Integer> s1;
private Stack<Integer> s2;
public MyQueue() {
s1 = new Stack<>();
s2 = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
s1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
if(s2.isEmpty()){
while(!s1.isEmpty()){
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
}
return s2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
if(s2.isEmpty()){
while(!s1.isEmpty()){
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
}
return s2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return s1.isEmpty() && s2.isEmpty();
}
}



![[vscode] 1. 在编辑器的标签页下显示文件目录(标签页显示面包屑) 2. 在标题栏上显示当前文件的完整路径](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/30566a1eb352438daac2757a7366bd4d.png)