使用sklearn.dataset 的make_regression创建用于线性回归的数据集
def create_dataset():
x, y, coef = make_regression(n_samples=100, noise=10, coef=True, bias=14.5, n_features=1, random_state=0)
return torch.tensor(x), torch.tensor(y), coef加载数据集,并拆分batchs训练集
def load_dataset(x, y, batch_size):
data_len = len(y)
batch_num = data_len // batch_size
for idx in range(batch_num):
start = idx * batch_num
end = idx * batch_num + batch_num
train_x = x[start : end]
train_y = y[start : end]
yield train_x, train_y定义初始权重和定义计算函数
w = torch.tensor(0.1, requires_grad=True, dtype=torch.float64)
b = torch.tensor(0, requires_grad=True, dtype=torch.float64)
def linear_regression(x):
return x * w + b损失函数使用平方差
def linear_loss(y_pred, y_true):
return (y_pred - y_true) ** 2优化参数使用梯度下降方法
def sgd(linear_rate, batch_size):
w.data = w.data - linear_rate * w.grad / batch_size
b.data = b.data - linear_rate * b.grad / batch_size训练代码
def train():
# 加载数据
x, y, coef = create_dataset()
data_len = len(y)
# 定义参数
batch_size = 10
epochs = 100
linear_rate = 0.01
# 记录损失值
epochs_loss = []
# 迭代
for eid in range(epochs):
total_loss = 0.0
for train_x, train_y in load_dataset(x, y, batch_size):
# 输入模型
y_pred = linear_regression(train_x)
# 计算损失
loss_num = linear_loss(y_pred, train_y.reshape(-1,1)).sum()
# 梯度清理
if w.grad is not None:
w.grad.zero_()
if b.grad is not None:
b.grad.zero_()
# 反向传播
loss_num.backward()
# 更新权重
sgd(linear_rate, batch_size)
# 统计损失数值
total_loss = total_loss + loss_num.item()
# 记录本次迭代的平均损失
b_loss = total_loss / data_len
epochs_loss.append(b_loss)
print("epoch={},b_loss={}".format(eid, b_loss))
# 显示预测线核真实线的拟合关系
print(w, b)
print(coef, 14.5)
plt.scatter(x, y)
test_x = torch.linspace(x.min(), x.max(), 1000)
y1 = torch.tensor([v * w + b for v in test_x])
y2 = torch.tensor([v * coef + 14.5 for v in test_x])
plt.plot(test_x, y1, label='train')
plt.plot(test_x, y2, label='true')
plt.grid()
plt.show()
# 显示损失值变化曲线
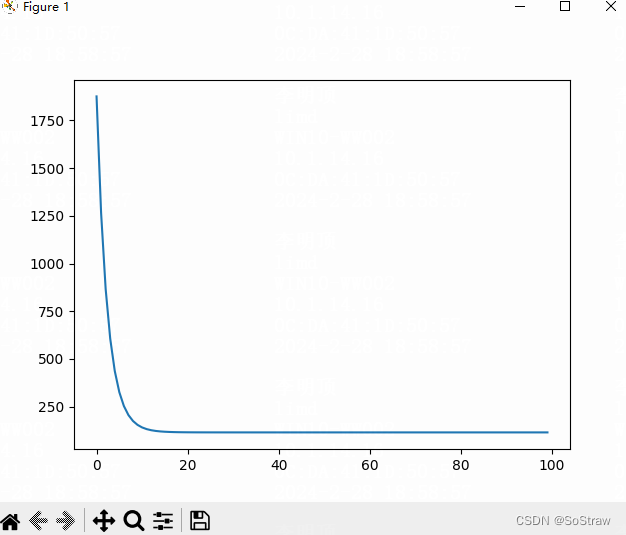
plt.plot(range(epochs), epochs_loss)
plt.show()
拟合显示还不错
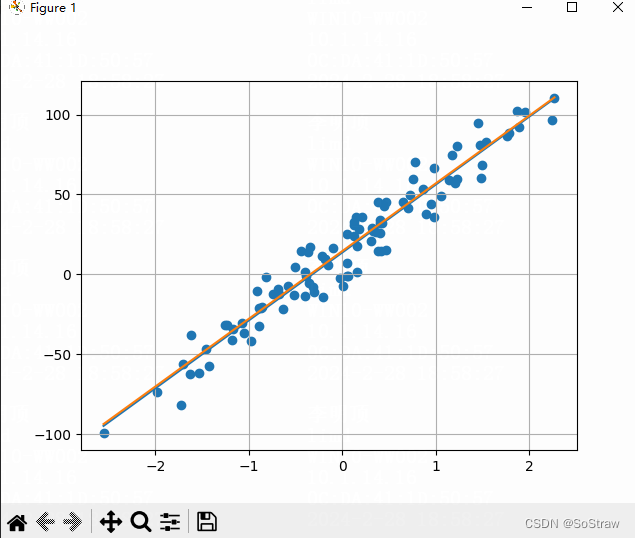
损失值在低5次迭代后基本就很小了