一、PyMySQL的基本使用
使用pymysql 直接连接mysql
PyMySQL安装
pip3 install pymysql import pymysql
# 连接数据库,创建连接对象connection
# 连接对象作用是:连接数据库、发送数据库信息、处理回滚操作(查询中断时,数据库回到最初状态)、创建新的光标对象
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', # host属性
port=3308, # 端口号
user='root', # 用户名
password='123456', # 此处填登录数据库的密码
db='bt' , # 数据库名
charset=“utf8”
)
# 得到一个可以执行SQL语句的光标对象
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 执行完毕返回的结果集默认以元组显示
sql = """ """
# 执行SQL语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 关闭光标对象
cursor.close()
# 关闭数据库连接
conn.close()二、增删改查操作
2.2 添加多条数据
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# @Author: 喵酱
# @time: 2022 - 06 -18
# @File: test2.py
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', # host属性
port=3308, # 端口号
user='root', # 用户名
password='123456', # 此处填登录数据库的密码
db='bt' # 数据库名
)
# 获取一个光标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 定义要执行的sql语句
sql = 'insert into student(name,age) values(%s,%s);'
data = [
('july', 14),
('june', 25),
('marin', 36)
]
# 拼接并执行sql语句
cursor.executemany(sql, data)
# 涉及写操作要注意提交
conn.commit()
# 关闭连接
cursor.close()
conn.close()2.3 插入单条数据
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# @Author: 喵酱
# @time: 2022 - 06 -18
# @File: test3.py
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', # host属性
port=3308, # 端口号
user='root', # 用户名
password='123456', # 此处填登录数据库的密码
db='bt' # 数据库名
)
cursor = conn.cursor() # 获取一个光标
sql = 'insert into student (name,age) values (%s,%s);'
name = 'wuli'
age = 10
cursor.execute(sql, [name, age])
conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close()2.4 获取最新插入数据 (最后一条)
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# @Author: 喵酱
# @time: 2022 - 06 -18
# @File: test4.py
import pymysql
# 建立连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', # host属性
port=3308, # 端口号
user='root', # 用户名
password='123456', # 此处填登录数据库的密码
db='bt' # 数据库名
)
# 获取一个光标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 定义将要执行的SQL语句
sql = 'insert into student (name,age) values (%s,%s);'
name = 'wuli'
age = 10
cursor.execute(sql, [name, age])
conn.commit()
# 关闭连接
# 获取最新的那一条数据的ID
last_id = cursor.lastrowid
print("最后一条数据的ID是:", last_id)
cursor.close()
conn.close()2.5 删除操作
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# @Author: 喵酱
# @time: 2022 - 06 -18
# @File: test5.py
import pymysql
# 建立连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', # host属性
port=3308, # 端口号
user='root', # 用户名
password='123456', # 此处填登录数据库的密码
db='bt' # 数据库名
)
# 获取一个光标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 定义将要执行的SQL语句
sql = "delete from student where name=%s;"
name = "wuli"
# 拼接并执行SQL语句
cursor.execute(sql, [name])
# 涉及写操作注意要提交
conn.commit()
# 关闭连接
cursor.close()
conn.close()2.5 更改数据
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# @Author: 喵酱
# @time: 2022 - 06 -18
# @File: test6.py
import pymysql
# 建立连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', # host属性
port=3308, # 端口号
user='root', # 用户名
password='123456', # 此处填登录数据库的密码
db='bt' # 数据库名
)
# 获取一个光标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 定义将要执行的SQL语句
sql = "update student set age=%s where name=%s;"
# 拼接并执行SQL语句
cursor.execute(sql, [28,"ni"])
# 涉及写操作注意要提交
conn.commit()
# 关闭连接
cursor.close()
conn.close()三、查询数据
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# @Author: 喵酱
# @time: 2022 - 06 -18
# @File: test7.py
import pymysql
# 建立连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', # host属性
port=3308, # 端口号
user='root', # 用户名
password='123456', # 此处填登录数据库的密码
db='bt', # 数据库名
charset='utf8'
)
# 获取一个光标
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # 返回字典数据类型
# 定义将要执行的sql语句
sql = 'select name,age from student'
# 拼接并执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 取到查询结果
ret1 = cursor.fetchone() # 取一条
ret2 = cursor.fetchmany(3) # 取三条
ret3 = cursor.fetchone() # 取一条
cursor.close()
conn.close()
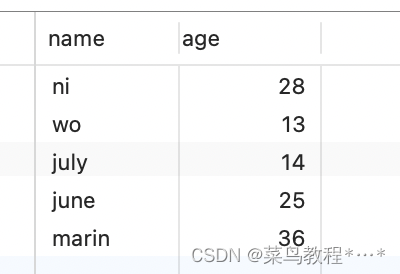
print(ret1)
print(ret2)
print(ret3)打印结果:
{'name': 'ni', 'age': 28}
[{'name': 'wo', 'age': 13}, {'name': 'july', 'age': 14}, {'name': 'june', 'age': 25}]
{'name': 'marin', 'age': 36}注意:
ret1 = cursor.fetchone() # 取一条
ret2 = cursor.fetchmany(3) # 取三条
ret3 = cursor.fetchone() # 取一条
这里的取一条,不是第一条,是依次往下取数据的,ret1 ,是第1条数据,ret2 ,是 2、3、4 数据。
ret3 是第5条数据。
四、数据回滚
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# @Author: 喵酱
# @time: 2022 - 06 -18
# @File: test8.py
import pymysql
# 建立连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', # host属性
port=3308, # 端口号
user='root', # 用户名
password='123456', # 此处填登录数据库的密码
db='bt', # 数据库名
charset='utf8'
)
# 获取一个光标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 定义将要执行的SQL语句
sql1 = "insert into student (name, age) values (%s, %s);"
sql2 = "insert into hobby (id, hobby) values (%s,%s);"
name = "july1"
age = 14
id = "我是错误的id" # id = "3"
hobby = "打游戏"
try:
# 拼接并执行SQL语句
cursor.execute(sql1, [name, age])
print(sql1)
cursor.execute(sql2, [id, hobby]) # 报错的SQL语句
# 涉及写操作注意要提交
conn.commit()
except Exception as e:
print(str(e))
# 有异常就回滚
conn.rollback()
# 关闭连接
cursor.close()
conn.close()发生异常后,2条数据,都没有写入库里。
六、python通过连接池连接数据库
6.1初始化 __init__
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.size = kwargs.get('size', 10)
self.kwargs = kwargs
self.conn_queue = queue.Queue(maxsize=self.size)
for i in range(self.size):
self.conn_queue.put(self._create_new_conn())size:连接池支持的连接数,这里定义为10
conn_queue:定义了一个队列,队列存放的是数据库的连接
for循环:建立好十个与数据库的连接,把这些连接放到队列中