Redisson获取/释放分布式锁原理以及watchDog机制相关源码分析
- 使用到的重点类继承结构
- RedissonLock
- ExpirationEntry
- 获取锁的代码逻辑
- tryLock()
- tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit)
- tryAcquire(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId)
- tryAcquireAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId)
- tryLockInnerAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command)
- scheduleExpirationRenewal(long threadId)
- renewExpiration()
- renewExpirationAsync(long threadId)
- subscribe(long threadId)
- 释放锁代码逻辑
- unlock()
- unlockAsync(long threadId)
- unlockInnerAsync(threadId)
- cancelExpirationRenewal(Long threadId)
- removeThreadId(long threadId)
本文详细的介绍了Redisson获取锁、释放锁流程中使用的到方法,并通过流程序号、注释的方式解读源码
使用到的重点类继承结构
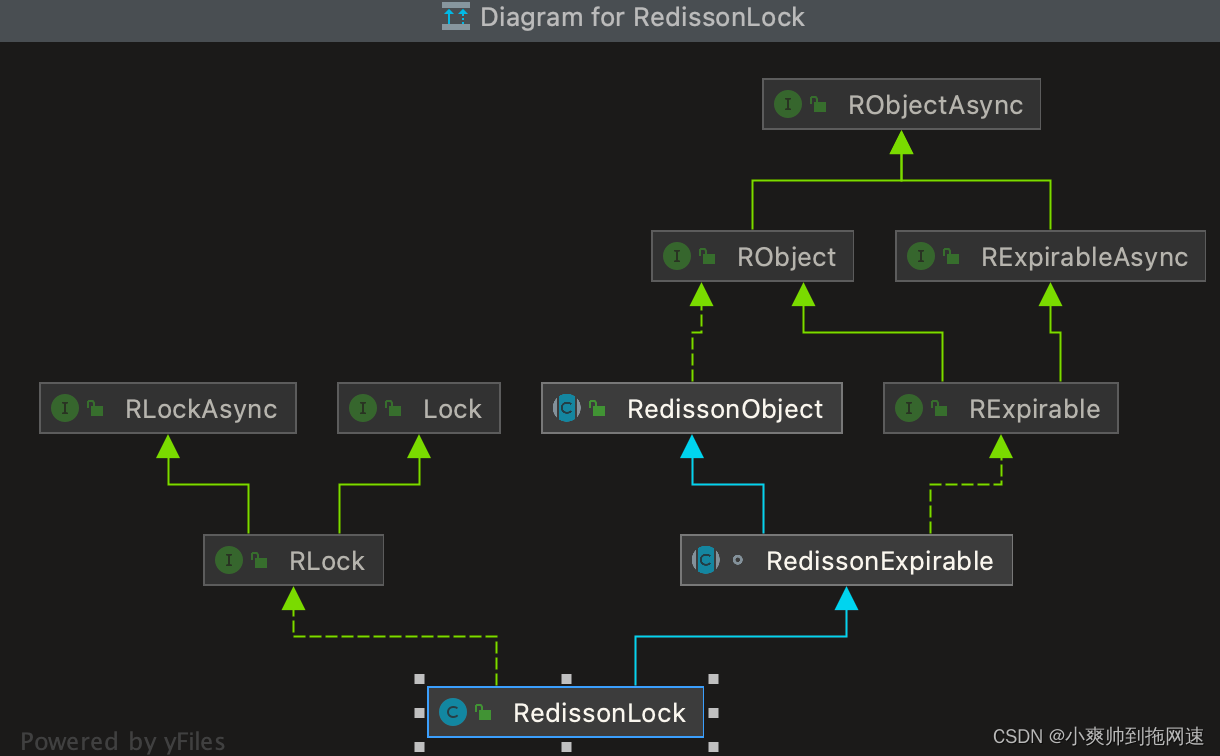
RedissonLock
RedissonLock 继承 RedissonExpirable 实现了RLock接口
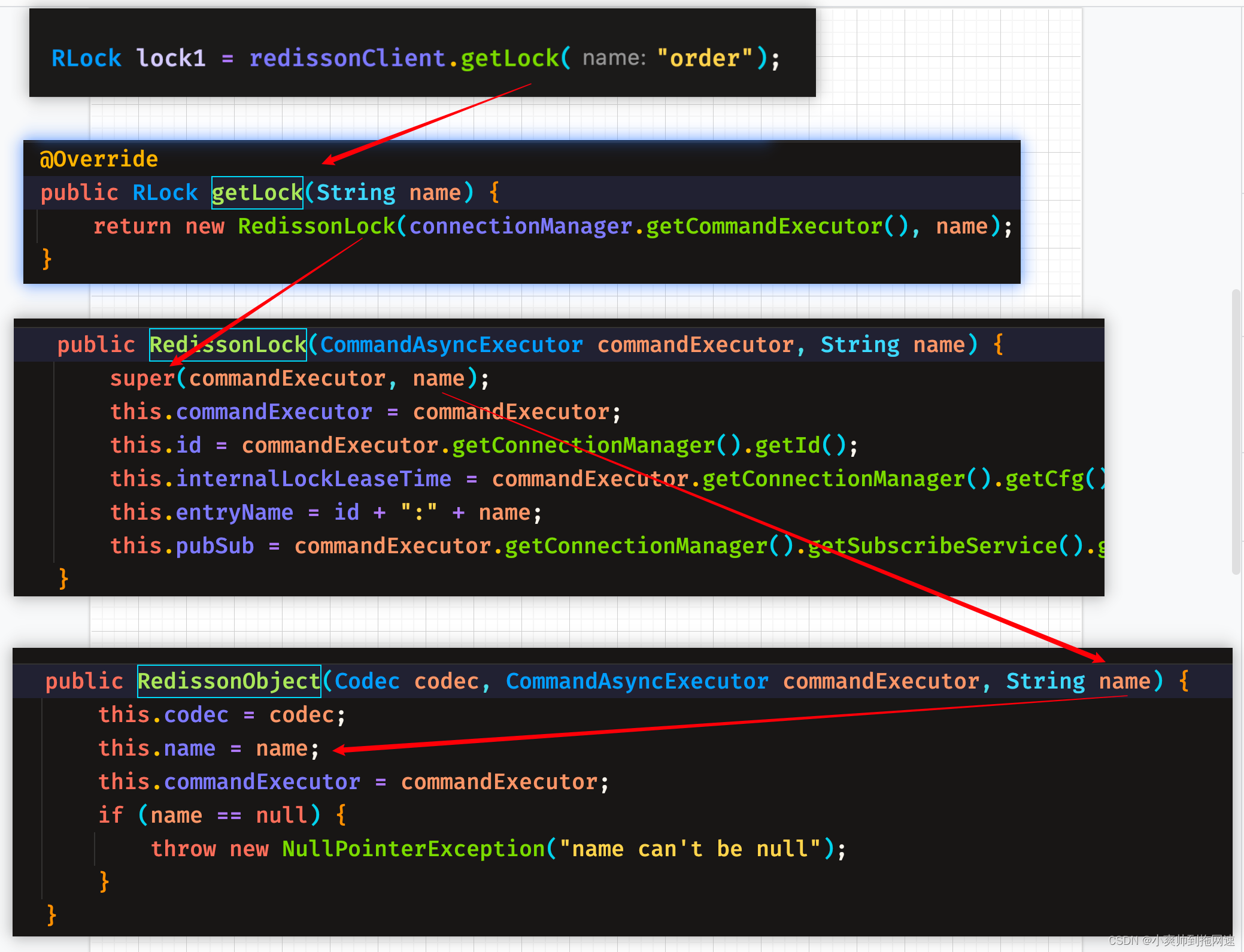
在使用RedisClient工具类调用getLock时通过实现类Redisson重写的getLock方法,创建RedissonLock
参数1:redis命令的执行者
参数2:使用redisson获取分布式锁的key
@Override
public RLock getLock(String name) {
return new RedissonLock(connectionManager.getCommandExecutor(), name);
}
public class RedissonLock extends RedissonExpirable implements RLock {
// 静态内部类,在watchDog机制执行锁续命时使用
public static class ExpirationEntry{}
// 静态内部类,在当前jvm进程中是唯一的,用于保存全局使用到watchDog锁续命机制的线程详情
private static final ConcurrentMap<String, ExpirationEntry> EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// 如果获取锁时没有设置锁过期释放时间leaseTime 默认为30s
protected long internalLockLeaseTime;
public RedissonLock(CommandAsyncExecutor commandExecutor, String name) {
// 初始化父类RedissonExpirable,进而间接初始化RedissonObject
super(commandExecutor, name);
this.commandExecutor = commandExecutor;
this.id = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getId();
// 执行watchDog逻辑使用到,默认为30s
this.internalLockLeaseTime = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout();
this.entryName = id + ":" + name;
// 使用redis的发布订阅模型
// 获取到锁线程:释放锁时发布所释放信号
// 获取锁时设置等待时间并且获取不到锁的线程:订阅其他线程释放锁时的信号
this.pubSub = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getSubscribeService().getLockPubSub();
}
}
ExpirationEntry
在没有获取释放锁时间即leaseTime为-1时,会使用ExpirationEntry用于保存当前获取锁线程以及执行锁续命的定时任务
// ExpirationEntry 是RedissonLock的静态内部类
// 使用到此类说明当前线程已经获取锁成功了
public static class ExpirationEntry {
private final Map<Long, Integer> threadIds = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// volatile 保证成员变量Timeout的修改其他线程立即可见
private volatile Timeout timeout;
public ExpirationEntry() {
super();
}
// 添加当前获取锁的线程id
public synchronized void addThreadId(long threadId) {
Integer counter = threadIds.get(threadId);
// 判断是否锁重入
if (counter == null) {
counter = 1;
} else {
// 当前为锁重入
counter++;
}
// 记录当前线程获取锁次数
threadIds.put(threadId, counter);
}
public synchronized boolean hasNoThreads() {
return threadIds.isEmpty();
}
public synchronized Long getFirstThreadId() {
if (threadIds.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
// threadIds最终只会保存一个值,因为每次线程都会创建一个新的entry,但是会在RedissonLock的全局静态内部变量EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP判断当前线程是否存在该entry,存在则锁重入,不存在在该线程第一次获取锁
return threadIds.keySet().iterator().next();
}
// 释放锁时执行,包含判断锁重入逻辑
public synchronized void removeThreadId(long threadId) {
Integer counter = threadIds.get(threadId);
if (counter == null) {
return;
}
counter--;
if (counter == 0) {
threadIds.remove(threadId);
} else {
threadIds.put(threadId, counter);
}
}
public void setTimeout(Timeout timeout) {
this.timeout = timeout;
}
public Timeout getTimeout() {
return timeout;
}
}
获取锁的代码逻辑
我们先来看下RedissonLock实现类tryLock()空参的方式实现
tryLock()
@Override
public boolean tryLock() {
return get(tryLockAsync());
}
@Override
public RFuture<Boolean> tryLockAsync() {
// 获取当前线程id
return tryLockAsync(Thread.currentThread().getId());
}
@Override
public RFuture<Boolean> tryLockAsync(long threadId) {
// 可以发现调用的是无参的tryLock()方法,则默认的waitTime、leaseTime 都是-1
return tryAcquireOnceAsync(-1, -1, null, threadId);
}
private RFuture<Boolean> tryAcquireOnceAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
// 如果设置了释放锁的时间,则不会走watchDog的超时续约逻辑
if (leaseTime != -1) {
return tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_NULL_BOOLEAN);
}
// 走锁的超时续命逻辑,后面会着重分析
RFuture<Boolean> ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(),
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_NULL_BOOLEAN);
ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
return;
}
// lock acquired
if (ttlRemaining) {
scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;
}
如果调用的是带参数的tryLock(long waitTime, TimeUnit unit) 最终调用的tryAcquireAsync()方法与tryLock()无参方法如出一辙,所以我们着重分析带参数的tryLock方法
// 入参: 等待获取锁的时间;时间单位
lock.tryLock(1L, TimeUnit.SECONDS); ------------- 1
@Override
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
// 第二个参数为锁过期时间,没有传默认为-1
return tryLock(waitTime, -1, unit); ------------- 2
}
tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit)
着重分析一下该方法的实现
@Override
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
// 将获取锁等待时间转换为毫秒
long time = unit.toMillis(waitTime);
// 获取当前时间
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 获取当前线程
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
// 走获取锁逻辑
Long ttl = tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId); ------------- 3 ---------- 16
// lock acquired
if (ttl == null) {
// 执行获取锁时,获取锁成功返回null,获取锁失败返回该所的剩余生存时间
return true;
}
// 这里我们默认获取锁失败,接着往下分析
// time为获取锁时的等待时间,减掉第一次获取锁消耗的时间
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current; ---------- 17
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
// 锁的等待时间小于等于0,则返回获取锁失败
return false;
}
// 重新获取当前时间
current = System.currentTimeMillis();
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribeFuture = subscribe(threadId); ---------- 18 ---------- 20
// 如果等待time毫秒的时间间隔内,其他线程释放锁并且发布释放锁信号
// 则subscribeFuture.await(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)返回true,否则返回false
if (!subscribeFuture.await(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
// 返回false,没有获取到其他线程的释放锁信号
if (!subscribeFuture.cancel(false)) {
subscribeFuture.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
// 取消订阅成功
unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);
}
});
}
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
try {
// 获取到其他线程释放锁信号
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
// 重新判断等待获取锁时间是否小于等于0
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
// 获取锁失败
return false;
}
while (true) {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 重新尝试获取锁
ttl = tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired
if (ttl == null) {
// ttl返回null,获取锁成功
return true;
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
// waiting for message
currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 采用信号量等待直接灵活判断剩余等待时间
if (ttl >= 0 && ttl < time) {
// 锁剩余过期时间大于0 并且 过期时间小于获取锁等待时间
// 这里使用信号量机制去等待(等待时间为锁剩余过期时间)
subscribeFuture.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
// 等待时间为剩余的获取锁的等待时间
subscribeFuture.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
// 到这说明信号量等待机制已经过了等待时间
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
// 如果time小于0,说明是ttl>time的信号量等待机制,表示在该线程的获取锁等待时间结束了,锁依旧不会过期,则直接返回失败,不会再尝试获取锁
return false;
}
} ---------- 21 // 重新进入while循环,直至获取锁成功,或者获取锁等待时间<0跳出循环
} finally {
// 取消订阅
unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);
}
// 代码迭代
// return get(tryLockAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit));
}
tryAcquire(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId)
private Long tryAcquire(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
// get的方法入参是RFuture,调用get方法会阻塞等待直到RFuture方法执行完毕
return get(tryAcquireAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId)); ------------- 4 ---------- 15
}
tryAcquireAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId)
getLockWatchdogTimeout默认为30s
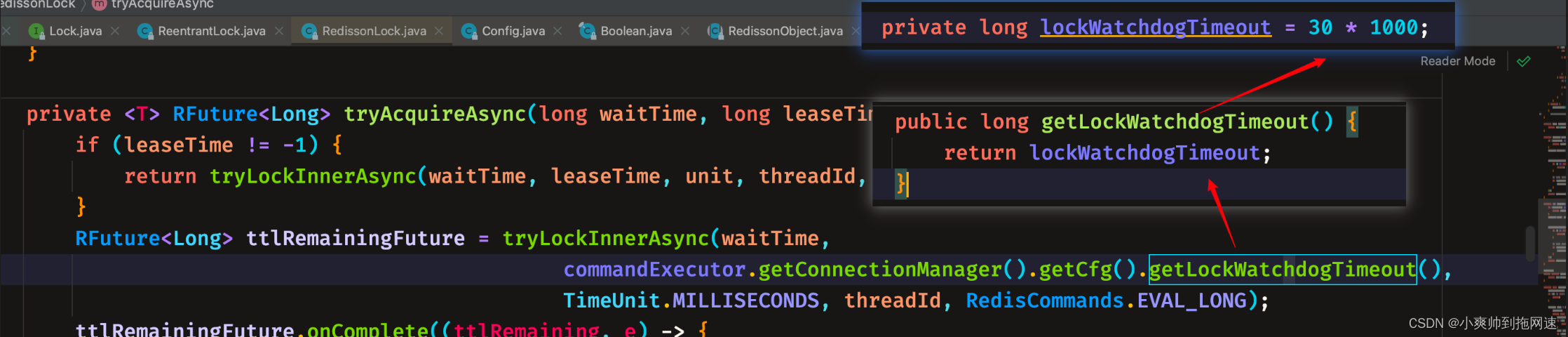
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
if (leaseTime != -1) {
// 如果没有传入锁过期时间,则不会走watchDog逻辑
return tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
}
// 没有传入锁过期时间,走watchDog逻辑
// 参数1:获取锁等待时间 参数2:30s 参数3:时间单位为毫秒 参数4:当前线程id 参数5:lua脚本返回值类型为Long
// 重点查看一下该方法实现
// 异步执行获取锁方法
RFuture<Long>ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync
(waitTime,commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(),
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG); ---------- 5
// 执行完异步方法后,ttlRemaining 为该方法的返回值,e为异步方法抛出的异常
ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> { ---------- 7
if (e != null) {
// 如果抛出异常,则直接返回不做任何处理
return;
}
// lock acquired
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
// 返回值为null代表加锁成功
// 加锁成功并且没有设置leaseTime为-1,调用时通过getLockWatchdogTimeout赋值为30s
// 入参为当前线程id
scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId); ---------- 8
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture; ---------- 14
}
tryLockInnerAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand command)
下面的lua脚本中,变量的声明如下:
KEYS[1] : getName()
ARGV[1]:internalLockLeaseTime
ARGV[2] :getLockName(threadId)
getName() 获取的name名就是通过Redisson客户端获取的锁的名字
getLockName(threadId)是通过UUID + 当前的线程id拼凑而成,这样做的目的首先是防止锁误删逻辑,其次是在分布式或者集群环境下,保证不会出现不同jvm进程下出现线程id相同的偶然现象
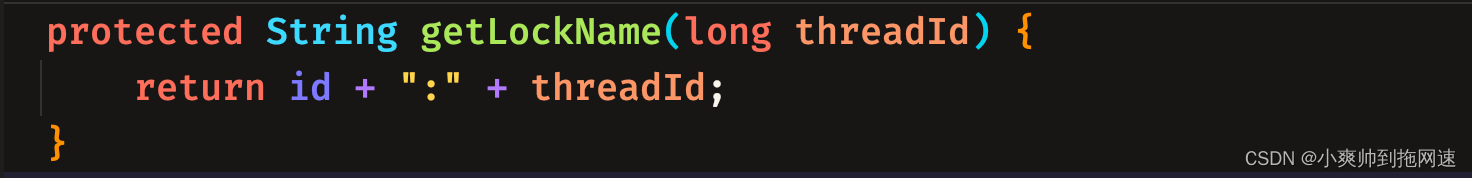
在分析lua脚本之前,我们要先明确一件事情,redisson是有可重入锁的实现,所以采用了类似synchronized、ReentrantLock ,通过维护一个整型变量来实现锁重入,而redisson则采用了hash的数据结构:<k1,<k2,v>>
- k1就是对应入参getName()
- k2对应入参getLockName(threadId)
- v对应的是锁的重入次数
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
// 锁释放时间 30s
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime); ---------- 6
// 执行lua脚本
return evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command, ---------- 7
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " + // 判断getLock()传入的key是否存在
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " + // 不存在说明当前没有线程加锁,那就直接加锁
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " + // 设置锁的过期时间 30s
"return nil; " + // 返回null代表获取锁成功
"end; " +
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " + // 锁存在,判断是不是当前线程的锁
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " + // 是当前线程的锁,说明是锁重入,v++
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " + // 重新设置锁的过期的时间为30s
"return nil; " + // 返回null代表锁重入成功,同样是获取锁成功
"end; " +
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);", // 获取锁失败,返回锁的过期时间
Collections.singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
注意,该方法的返回值是RFuture(是异步执行的方法),并且lua脚本的返回是Long类型的过期时间,这些都是在调用tryLockInnerAsync是传入RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG 定好的
scheduleExpirationRenewal(long threadId)
查看这个方法前我们先看一下ExpirationEntry类的结构
private void scheduleExpirationRenewal(long threadId) {
// 用于保存当前线程id、设置定时任务
ExpirationEntry entry = new ExpirationEntry(); ---------- 9
// RedissonLock静态内部类(全局唯一)
// EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP 是以锁名为key,ExpirationEntry为value的高并发map
// getEntryName() 为创建RedissonLock的构造方法时进行赋值,this.entryName = id + ":" + name;
// putIfAbsent 该方法最终调用putVal(key,value,true) 第
// 三个参数为true,代表如果key重复,则不会替换旧值,最终返回旧值
// 如果key没有重复则设置值,返回null
ExpirationEntry oldEntry = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.putIfAbsent(getEntryName(), entry);
if (oldEntry != null) {
// 重复,说明是锁重入
oldEntry.addThreadId(threadId);
} else {
// 没有重复
entry.addThreadId(threadId);
// 锁续命的真正逻辑在这里
// 注意,只有该线程第一次获取获取锁成功才会执行锁续命
renewExpiration(); ---------- 10
}
}
renewExpiration()
通过方法名字我们大致能够猜出,是执行重新设置锁的过期时间
private void renewExpiration() {
// 在RedissonLock取出全局保存的线程id
ExpirationEntry ee = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName());
if (ee == null) {
return;
}
// 创建定时任务
Timeout task = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
// 由于lambda访问的外部变量必须是不可变变量,并且EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP是高并发的map,可能存在被其他线程移除的风险,所以这里再取一遍
ExpirationEntry ent = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName()); ---------- 11
if (ent == null) {
return;
}
// 获取线程id
Long threadId = ent.getFirstThreadId();
if (threadId == null) {
return;
}
// 异步执行
RFuture<Boolean> future = renewExpirationAsync(threadId); ---------- 12
// 异步方法执行完成
future.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
log.error("Can't update lock " + getName() + " expiration", e);
return;
}
if (res) {
// reschedule itself
// 返回true则进行递归调用
// 乍一看这里会无限递归,是否会导致栈递归深度过大导致栈溢出,显然定时任务是10s一次是不会发生栈溢出的情况
// 锁续命什么时候结束,如果我们获取锁的时候没有设置锁的过期时间,leaseTime为0,则会保证我们业务还没有执行完之前,锁一定不会过期,只有主观认为业务执行完了去调用unLock()并且保存的整型变量自减后为0,才会真正停止锁续命逻辑的10s一次的定时任务
renewExpiration(); ---------- 15
}
});
}
// 该定时任务10s后执行
}, internalLockLeaseTime / 3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// renewExpirationAsync(threadId) 方法是异步执行的,当前线程会先将该定时任务存储在ExpirationEntry中
// 为后续取消任务做准备
ee.setTimeout(task); ---------- 13
}
renewExpirationAsync(long threadId)
这里是执行锁续命的lua脚本,先解释下lua脚本使用到的变量:
KEYS[1]:name为获取锁传入的key名 Collections.singletonList(getName())
ARGV[1]:锁的过期时间 internalLockLeaseTime 默认为30s
ARGV[2]:当前线程标识,由UUID+线程id组成
返回值类型:
RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN 为布尔值,lua脚本中返回1 代表true;返回0代表false
protected RFuture<Boolean> renewExpirationAsync(long threadId) {
return evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " + // 判断当前线程是否加锁成功,是否存在key
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " + // 存在,重新设置锁的过期时间为30s
"return 1; " + // 返回1 代表成功 ---------- 14
"end; " +
"return 0;", // 返回0 代表失败
Collections.singletonList(getName()),
internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
subscribe(long threadId)
获取不到锁则会去订阅其他线程释放锁的信号
采用的是redis的pubSub发布订阅模型
protected RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribe(long threadId) {
return pubSub.subscribe(getEntryName(), getChannelName()); ---------- 19
}
释放锁代码逻辑
释放锁的代码逻辑类似于ReentrantLock,他们都实现了Lock接口
unlock()
@Override
public void unlock() {
try {
// get() 执行的是异步线程
get(unlockAsync(Thread.currentThread().getId())); ---------- 1
} catch (RedisException e) {
if (e.getCause() instanceof IllegalMonitorStateException) {
throw (IllegalMonitorStateException) e.getCause();
} else {
throw e;
}
}
// 代码迭代
// Future<Void> future = unlockAsync();
// future.awaitUninterruptibly();
// if (future.isSuccess()) {
// return;
// }
// if (future.cause() instanceof IllegalMonitorStateException) {
// throw (IllegalMonitorStateException)future.cause();
// }
// throw commandExecutor.convertException(future);
}
unlockAsync(long threadId)
@Override
public RFuture<Void> unlockAsync(long threadId) {
RPromise<Void> result = new RedissonPromise<Void>();
RFuture<Boolean> future = unlockInnerAsync(threadId); ---------- 2 ---------- 4
// 执行完异步方法后执行
future.onComplete((opStatus, e) -> {
// 取消锁续命机制
cancelExpirationRenewal(threadId); ---------- 5
if (e != null) {
result.tryFailure(e);
return;
}
if (opStatus == null) {
IllegalMonitorStateException cause = new IllegalMonitorStateException("attempt to unlock lock, not locked by current thread by node id: " + id + " thread-id: " + threadId);
result.tryFailure(cause);
return;
}
result.trySuccess(null);
});
return result;
}
unlockInnerAsync(threadId)
同样解释一下lua脚本中使用到的变量:
KEYS[1]:获取锁的key,getName()
KEYS[2]:发布释放锁的信号量通道key,getChannelName(),"redisson_lock__channel:{ getName()} "
ARGV[1]:发布释放锁信号值value,LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE,静态常量0L
ARGV[2]:watchDog机制中锁续命默认的30s internalLockLeaseTime
ARGV[3]:线程标识,getLockName(threadId) “UUID:线程id”
方法返回值为布尔值 RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN
返回null :删除锁失败
返回0:锁重入
返回1:删除锁成功
protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId) {
return evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then " + // 判断锁释放存在
"return nil;" +
"end; " +
"local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); " + // 锁存在并且自减1
"if (counter > 0) then " + // 自减后如果整型变量大于0 ,说明是锁重入
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); " + // 锁重入则进行锁续命
"return 0; " +
"else " +
"redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); " + // 不是锁重入,删除锁
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " + // 发布锁释放的信号量,在获取锁失败的线程中进行订阅
"return 1; " + ---------- 3
"end; " +
"return nil;",
Arrays.asList(getName(), getChannelName()), LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE, internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
cancelExpirationRenewal(Long threadId)
取消锁续命机制
void cancelExpirationRenewal(Long threadId) {
// 从redisson全局静态变量map中获取当前线程表示代表的ExpirationEntry
ExpirationEntry task = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName()); ---------- 6
if (task == null) {
return;
}
if (threadId != null) {
// 移除
task.removeThreadId(threadId); ---------- 7 ---------- 9
}
if (threadId == null || task.hasNoThreads()) {
Timeout timeout = task.getTimeout();
if (timeout != null) {
// 如果有定时任务,则取消定时任务
timeout.cancel();
}
// 移除后,在renewExpiration()方法执行锁续命的逻辑中,就不会从 EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP命中,跳出锁续命递归逻辑
EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.remove(getEntryName());
}
}
removeThreadId(long threadId)
public synchronized void removeThreadId(long threadId) {
Integer counter = threadIds.get(threadId);
if (counter == null) {
return;
}
counter--;
if (counter == 0) {
// 没有发生锁重入
threadIds.remove(threadId); ---------- 8
} else {
// 锁重入现象
threadIds.put(threadId, counter);
}
}
至此,Redisson中获取锁、释放锁以及watchDog机制在源码中的详细作用都分析完了,有其他不同见解的小伙伴欢迎在评论区中指出




![[Leetcode] 二叉树的深度、平衡二叉树](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/6e0d7da902a479298f7981bfc78b8efc.png)