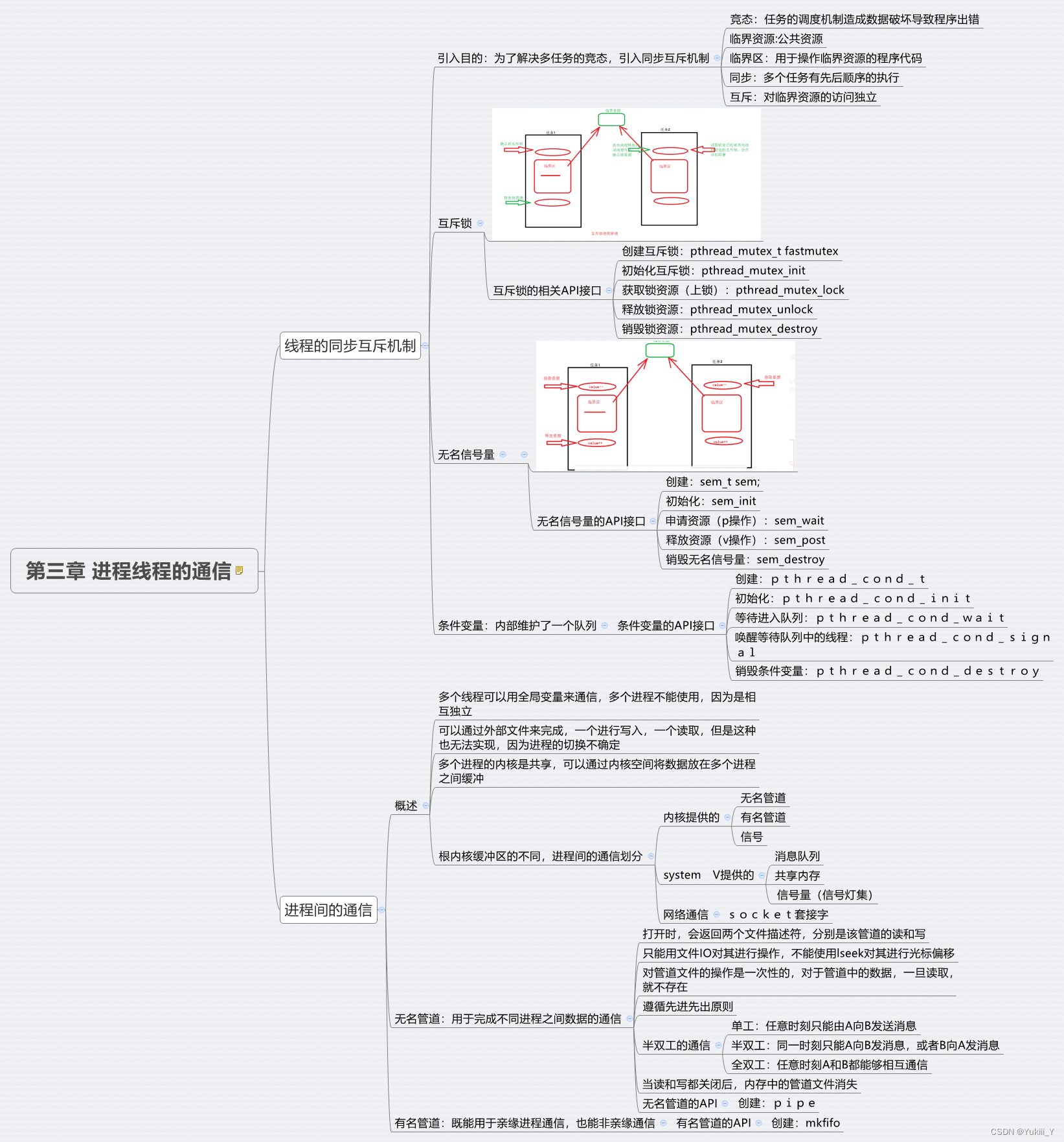
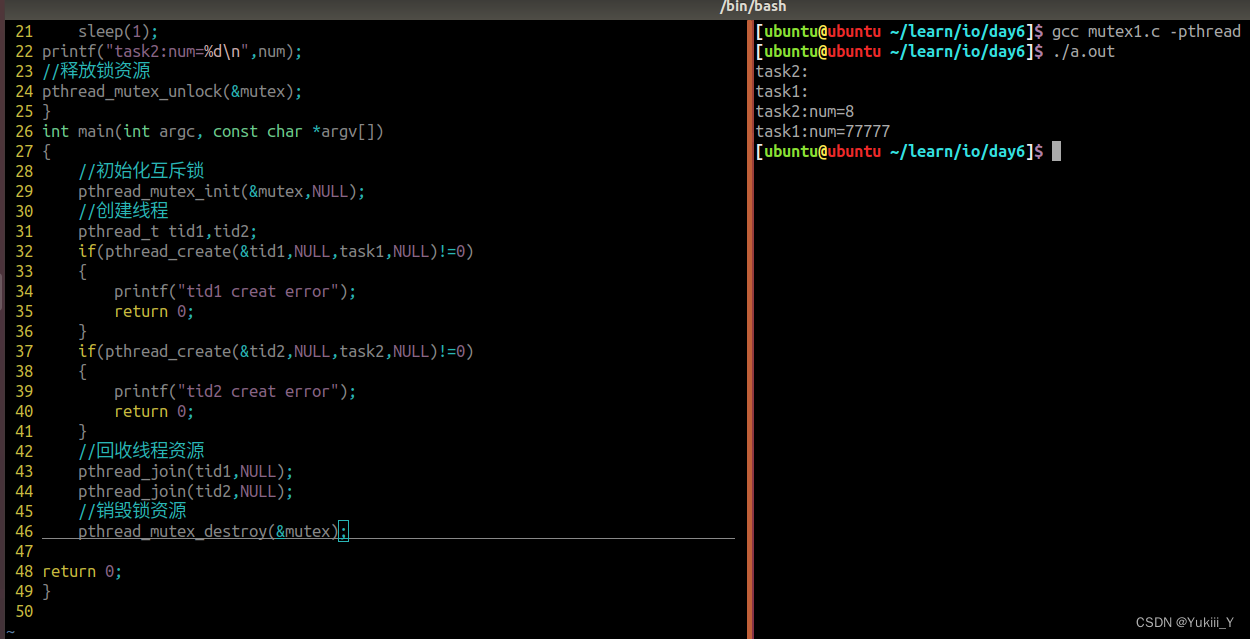
将互斥机制的代码实现
#include<myhead.h>
int num=7;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;//创建互斥锁变量
void *task1(void *arg)
{
printf("task1:\n");
//获取锁资源
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
num=77777;
sleep(2);
printf("task1:num=%d\n",num);
//释放锁资源
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
void *task2(void *arg)
{
printf("task2:\n");
//获取锁资源
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
num=num+1;
sleep(1);
printf("task2:num=%d\n",num);
//释放锁资源
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//初始化互斥锁
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);
//创建线程
pthread_t tid1,tid2;
if(pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,task1,NULL)!=0)
{
printf("tid1 creat error");
return 0;
}
if(pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0)
{
printf("tid2 creat error");
return 0;
}
//回收线程资源
pthread_join(tid1,NULL);
pthread_join(tid2,NULL);
//销毁锁资源
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}
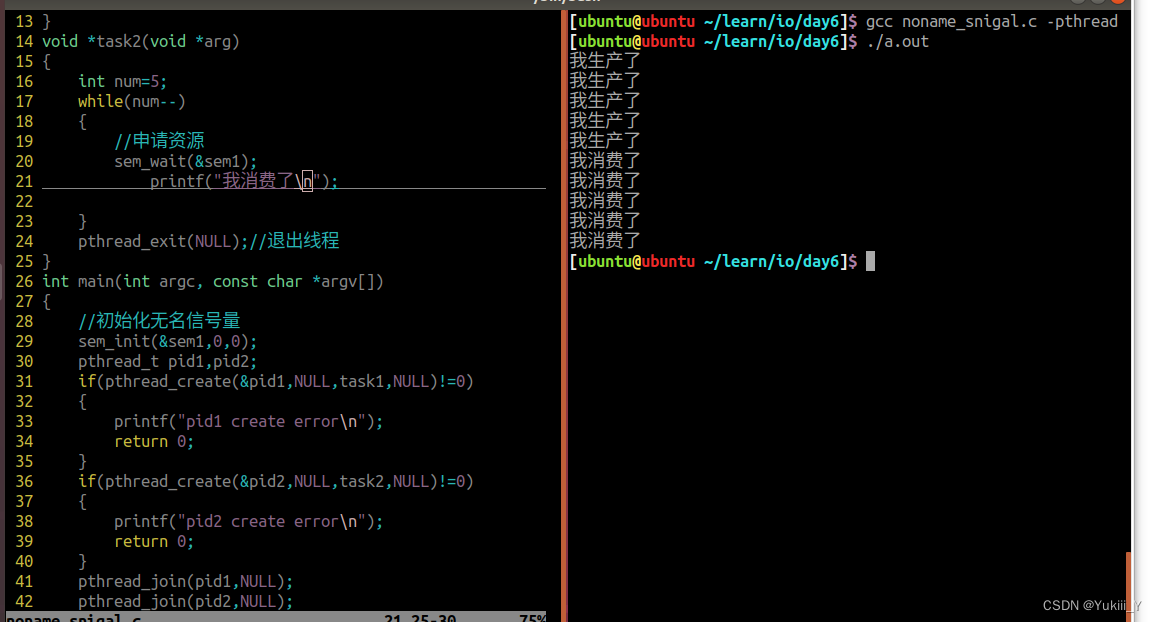
将无名信号量的代码实现重新敲一遍
#include<myhead.h>
sem_t sem1;//创建无名信号量1
void *task1(void *arg)
{
int num=5;
while(num--)
{
printf("我生产了\n");
sem_post(&sem1);//释放资源
}
pthread_exit(NULL);//退出线程
}
void *task2(void *arg)
{
int num=5;
while(num--)
{
//申请资源
sem_wait(&sem1);
printf("我消费了\n");
}
pthread_exit(NULL);//退出线程
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//初始化无名信号量
sem_init(&sem1,0,0);
pthread_t pid1,pid2;
if(pthread_create(&pid1,NULL,task1,NULL)!=0)
{
printf("pid1 create error\n");
return 0;
}
if(pthread_create(&pid2,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0)
{
printf("pid2 create error\n");
return 0;
}
pthread_join(pid1,NULL);
pthread_join(pid2,NULL);
sem_destroy(&sem1);
return 0;
}
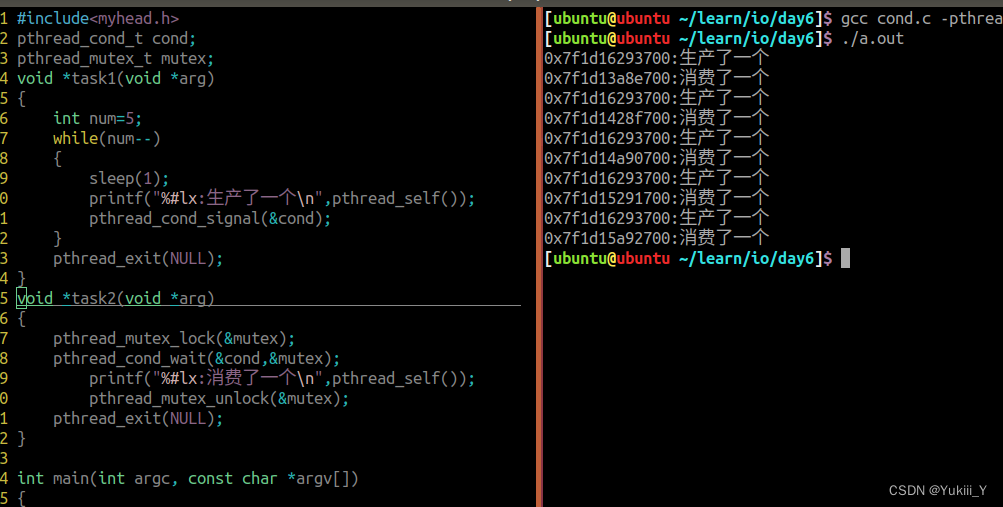
将条件变量的代码实现重新敲一遍
#include<myhead.h>
pthread_cond_t cond;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
void *task1(void *arg)
{
int num=5;
while(num--)
{
sleep(1);
printf("%#lx:生产了一个\n",pthread_self());
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *task2(void *arg)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex);
printf("%#lx:消费了一个\n",pthread_self());
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//初始化条件变量
pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL);
//初始化互斥锁
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);
//创建线程
pthread_t tid1,tid2,tid3,tid4,tid5,tid6;
if(pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,task1,NULL)!=0)
{
printf("tid1 create error\n");
return 0;
}
if(pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0)
{
printf("tid1 create error\n");
return 0;
}
if(pthread_create(&tid3,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0)
{
printf("tid1 create error\n");
return 0;
}
if(pthread_create(&tid4,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0)
{
printf("tid1 create error\n");
return 0;
}
if(pthread_create(&tid5,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0)
{
printf("tid1 create error\n");
return 0;
}
if(pthread_create(&tid6,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0)
{
printf("tid1 create error\n");
return 0;
}
pthread_join(tid1,NULL);
pthread_join(tid2,NULL);
pthread_join(tid3,NULL);
pthread_join(tid4,NULL);
pthread_join(tid5,NULL);
pthread_join(tid6,NULL);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}
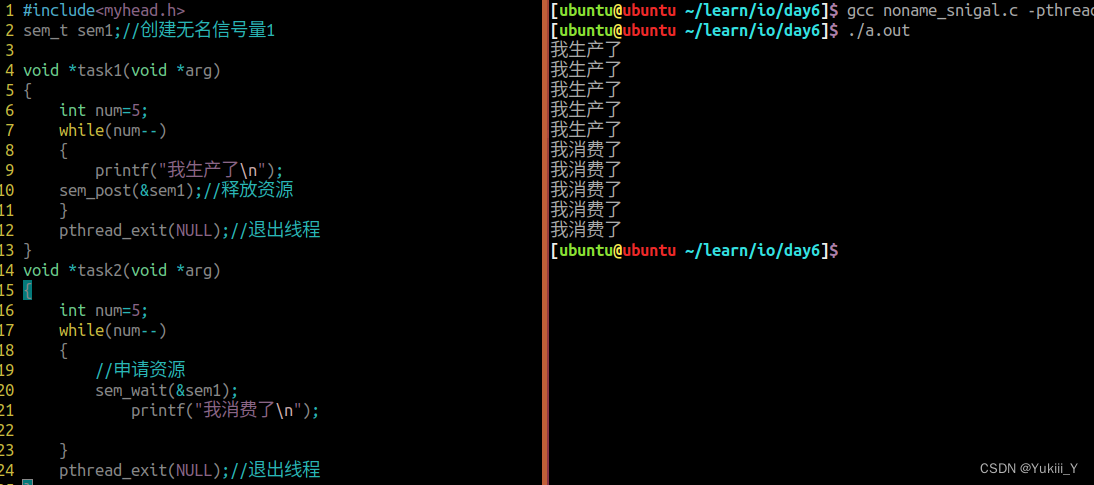
将无名管道的代码实现重新敲一遍
#include<myhead.h>
sem_t sem1;//创建无名信号量1
void *task1(void *arg)
{
int num=5;
while(num--)
{
printf("我生产了\n");
sem_post(&sem1);//释放资源
}
pthread_exit(NULL);//退出线程
}
void *task2(void *arg)
{
int num=5;
while(num--)
{
//申请资源
sem_wait(&sem1);
printf("我消费了\n");
}
pthread_exit(NULL);//退出线程
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//初始化无名信号量
sem_init(&sem1,0,0);
pthread_t pid1,pid2;
if(pthread_create(&pid1,NULL,task1,NULL)!=0)
{
printf("pid1 create error\n");
return 0;
}
if(pthread_create(&pid2,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0)
{
printf("pid2 create error\n");
return 0;
}
pthread_join(pid1,NULL);
pthread_join(pid2,NULL);
sem_destroy(&sem1);
return 0;
}
将有名管道的代码实现重新敲一遍
name_creat.c
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//创建管道
if(mkfifo("./myfifo",0664)==-1)
{
perror("mkfifo error");
return -1;
}
getchar();//阻塞
system("rm myfifo");
return 0;
}
write_namepipe.c
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//打开管道
int wfd=-1;
//只写打开文件
if((wfd=open("./myfifo",O_WRONLY))==-1)
{
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
//定义容器
char wbuf[128]="";
while(1)
{
printf("please input:\n");
fgets(wbuf,sizeof(wbuf),stdin);
wbuf[strlen(wbuf)-1]=0;
//将数据写入管道
write(wfd,wbuf,strlen(wbuf));
//判断是否退出
if(strcmp(wbuf,"quit")==0)
{
break;
}
close(wfd);
return 0;
}
return 0;
}
read_namepipe.c
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//打开管道文件
int rfd=-1;
//只读形式打开
if((rfd=open("./myfifo",O_RDONLY))==-1)
{
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
//定义容器
char rbuf[100]="";
while(1)
{
//清空
bzero(rbuf,sizeof(rbuf));
//读取管道中的数据
read(rfd,rbuf,sizeof(rbuf));
//输出结果
printf("receive data is:%s\n",rbuf);
//判断结果
if(strcmp(rbuf,"quit")==0)
{
break;
}
}
close(rfd);
return 0;
}