目录
一. 前言
二. JDK 代理的示例
2.1. 不需要 Maven 依赖
2.2. 定义实体
2.3. 被代理的类和接口
2.4. JDK 代理类
2.5. 使用代理
三. JDK 代理的流程
3.1. ProxyGenerator 生成代码
3.2. 从生成的 Proxy 代码看执行流程
四. Spring AOP 中 JDK代理的实现
4.1. Spring AOP JDK 代理的创建
4.2. Spring AOP JDK 代理的执行
一. 前言
JDK 动态代理是由 JDK 提供的工具类 Proxy 实现的,动态代理类是在运行时生成指定接口的代理类,每个代理实例(实现需要代理的接口)都有一个关联的调用处理程序对象,此对象实现了InvocationHandler,最终的业务逻辑是在 InvocationHandler 实现类的 invoke 方法上。
二. JDK 代理的示例
2.1. 不需要 Maven 依赖
JDK 动态代理不需要任何依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>com.lm.it</groupId>
<artifactId>lm-spring-demo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>05-lm-spring-demo-aop-proxy-jdk</artifactId>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<!--based on jdk proxy -->
<dependencies>
</dependencies>
</project>2.2. 定义实体
package com.lm.it.springframework.entity;
/**
* User
*/
public class User {
/**
* user's name.
*/
private String name;
/**
* user's age.
*/
private int age;
/**
* init.
*
* @param name name
* @param age age
*/
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}2.3. 被代理的类和接口
接口如下:
package tech.pdai.springframework.service;
import com.lm.it.springframework.entity.User;
import java.util.List;
/**
* UserService
*/
public interface IUserService {
/**
* find user list.
*
* @return user list
*/
List<User> findUserList();
/**
* add user
*/
void addUser();
}实现类如下:
package com.lm.it.springframework.service.impl;
import com.lm.it.springframework.entity.User;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
/**
* UserService
*/
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService {
/**
* find user list.
*
* @return user list
*/
@Override
public List<User> findUserList() {
return Collections.singletonList(new User("流华追梦", 18));
}
/**
* add user
*/
@Override
public void addUser() {
// do something
}
}2.4. JDK 代理类
代理类如下:
package com.lm.it.springframework.proxy;
import com.lm.it.springframework.service.IUserService;
import com.lm.it.springframework.service.impl.UserServiceImpl;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* This class is for proxy demo.
*/
public class UserLogProxy {
/**
* proxy target
*/
private IUserService target;
/**
* init.
*
* @param target target
*/
public UserLogProxy(UserServiceImpl target) {
super();
this.target = target;
}
/**
* get proxy.
*
* @return proxy target
*/
public IUserService getLoggingProxy() {
IUserService proxy;
ClassLoader loader = target.getClass().getClassLoader();
Class[] interfaces = new Class[]{IUserService.class};
InvocationHandler h = new InvocationHandler() {
/**
* proxy: 代理对象。 一般不使用该对象 method: 正在被调用的方法 args: 调用方法传入的参数
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
// log - before method
System.out.println("[before] execute method: " + methodName);
// call method
Object result = null;
try {
// 前置通知
result = method.invoke(target, args);
// 返回通知, 可以访问到方法的返回值
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 异常通知, 可以访问到方法出现的异常
}
// 后置通知. 因为方法可以能会出异常, 所以访问不到方法的返回值
// log - after method
System.out.println("[after] execute method: " + methodName + ", return value: " + result);
return result;
}
};
/**
* loader: 代理对象使用的类加载器.
* interfaces: 指定代理对象的类型. 即代理代理对象中可以有哪些方法.
* h: 当具体调用代理对象的方法时, 应该如何进行响应, 实际上就是调用 InvocationHandler 的 invoke 方法
*/
proxy = (IUserService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, interfaces, h);
return proxy;
}
}2.5. 使用代理
启动类中指定代理目标并执行。
package com.lm.it.springframework;
import com.lm.it.springframework.proxy.UserLogProxy;
import com.lm.it.springframework.service.IUserService;
import com.lm.it.springframework.service.impl.UserServiceImpl;
/**
* Jdk proxy demo.
*/
public class App {
/**
* main interface.
*
* @param args args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// proxy
IUserService userService = new UserLogProxy(new UserServiceImpl()).getLoggingProxy();
// call methods
userService.findUserList();
userService.addUser();
}
}启动上述类 main() 函数,运行结果如下:
[before] execute method: findUserList
[after] execute method: findUserList, return value: [User{name='pdai', age=18}]
[before] execute method: addUser
[after] execute method: addUser, return value: null三. JDK 代理的流程
JDK 动态代理自动生成的 class 是由 sun.misc.ProxyGenerator 来生成的。
3.1. ProxyGenerator 生成代码
我们看下 sun.misc.ProxyGenerator 生成代码的逻辑:
public class ProxyGenerator {
...
private static final boolean saveGeneratedFiles = (Boolean)AccessController.doPrivileged(new GetBooleanAction("sun.misc.ProxyGenerator.saveGeneratedFiles"));
...
/**
* Generate a proxy class given a name and a list of proxy interfaces.
*
* @param name the class name of the proxy class
* @param interfaces proxy interfaces
* @param accessFlags access flags of the proxy class
*/
public static byte[] generateProxyClass(final String name,
Class<?>[] interfaces,
int accessFlags)
{
ProxyGenerator gen = new ProxyGenerator(name, interfaces, accessFlags);
final byte[] classFile = gen.generateClassFile();
...
}
}generateClassFile() 方法如下:
/**
* Generate a class file for the proxy class. This method drives the
* class file generation process.
*/
private byte[] generateClassFile() {
/* 第一步:将所有方法包装成ProxyMethod对象 */
// 将Object类中hashCode、equals、toString方法包装成ProxyMethod对象
addProxyMethod(hashCodeMethod, Object.class);
addProxyMethod(equalsMethod, Object.class);
addProxyMethod(toStringMethod, Object.class);
// 将代理类接口方法包装成ProxyMethod对象
for (Class<?> intf : interfaces) {
for (Method m : intf.getMethods()) {
addProxyMethod(m, intf);
}
}
// 校验返回类型
for (List<ProxyMethod> sigmethods : proxyMethods.values()) {
checkReturnTypes(sigmethods);
}
/* 第二步:为代理类组装字段,构造函数,方法,static初始化块等 */
try {
// 添加构造函数,参数是InvocationHandler
methods.add(generateConstructor());
// 代理方法
for (List<ProxyMethod> sigmethods : proxyMethods.values()) {
for (ProxyMethod pm : sigmethods) {
// 字段
fields.add(new FieldInfo(pm.methodFieldName,
"Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;",
ACC_PRIVATE | ACC_STATIC));
// 上述ProxyMethod中的方法
methods.add(pm.generateMethod());
}
}
// static初始化块
methods.add(generateStaticInitializer());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new InternalError("unexpected I/O Exception", e);
}
if (methods.size() > 65535) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("method limit exceeded");
}
if (fields.size() > 65535) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("field limit exceeded");
}
/* 第三步:写入class文件 */
/*
* Make sure that constant pool indexes are reserved for the
* following items before starting to write the final class file.
*/
cp.getClass(dotToSlash(className));
cp.getClass(superclassName);
for (Class<?> intf: interfaces) {
cp.getClass(dotToSlash(intf.getName()));
}
/*
* Disallow new constant pool additions beyond this point, since
* we are about to write the final constant pool table.
*/
cp.setReadOnly();
ByteArrayOutputStream bout = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dout = new DataOutputStream(bout);
try {
/*
* Write all the items of the "ClassFile" structure.
* See JVMS section 4.1.
*/
// u4 magic;
dout.writeInt(0xCAFEBABE);
// u2 minor_version;
dout.writeShort(CLASSFILE_MINOR_VERSION);
// u2 major_version;
dout.writeShort(CLASSFILE_MAJOR_VERSION);
cp.write(dout); // (write constant pool)
// u2 access_flags;
dout.writeShort(accessFlags);
// u2 this_class;
dout.writeShort(cp.getClass(dotToSlash(className)));
// u2 super_class;
dout.writeShort(cp.getClass(superclassName));
// u2 interfaces_count;
dout.writeShort(interfaces.length);
// u2 interfaces[interfaces_count];
for (Class<?> intf : interfaces) {
dout.writeShort(cp.getClass(
dotToSlash(intf.getName())));
}
// u2 fields_count;
dout.writeShort(fields.size());
// field_info fields[fields_count];
for (FieldInfo f : fields) {
f.write(dout);
}
// u2 methods_count;
dout.writeShort(methods.size());
// method_info methods[methods_count];
for (MethodInfo m : methods) {
m.write(dout);
}
// u2 attributes_count;
dout.writeShort(0); // (no ClassFile attributes for proxy classes)
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new InternalError("unexpected I/O Exception", e);
}
return bout.toByteArray();
}一共三个步骤(把大象装进冰箱分几步?):
- 第一步(把冰箱门打开):准备工作,将所有方法包装成 ProxyMethod 对象,包括 Object 类中 hashCode、equals、toString 方法,以及被代理的接口中的方法;
- 第二步(把大象装进去):为代理类组装字段、构造函数、方法、static 初始化块等;
- 第三步(把冰箱门带上):写入 class 文件。
3.2. 从生成的 Proxy 代码看执行流程
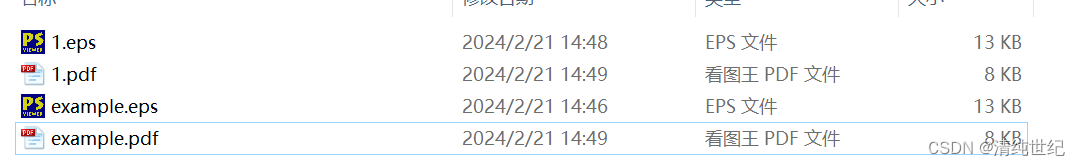
从上述 sun.misc.ProxyGenerator 类中可以看到,这个类里面有一个配置参数sun.misc.ProxyGenerator.saveGeneratedFiles,可以通过这个参数将生成的 Proxy 类保存在本地,比如设置为 true 执行后,生成的文件如下:

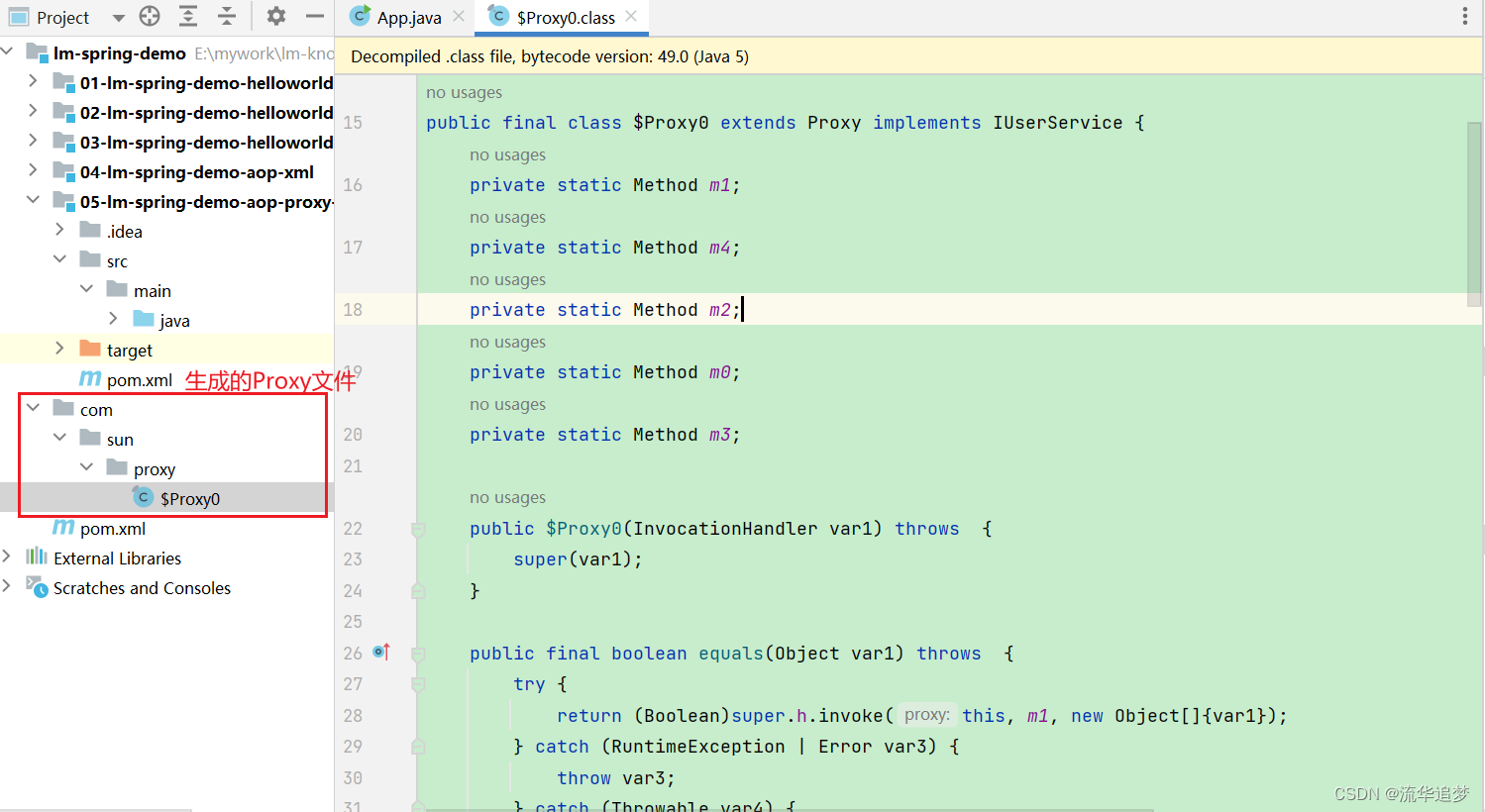
我们看下生成后的代码:
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package com.sun.proxy;
import com.lm.it.springframework.service.IUserService;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException;
import java.util.List;
// 所有类和方法都是final类型的
public final class $Proxy0 extends Proxy implements IUserService {
private static Method m1;
private static Method m4;
private static Method m2;
private static Method m0;
private static Method m3;
// 构造函数注入 InvocationHandler
public $Proxy0(InvocationHandler var1) throws {
super(var1);
}
public final boolean equals(Object var1) throws {
try {
return (Boolean)super.h.invoke(this, m1, new Object[]{var1});
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var3) {
throw var3;
} catch (Throwable var4) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var4);
}
}
public final List findUserList() throws {
try {
return (List)super.h.invoke(this, m4, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
public final String toString() throws {
try {
return (String)super.h.invoke(this, m2, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
public final int hashCode() throws {
try {
return (Integer)super.h.invoke(this, m0, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
public final void addUser() throws {
try {
super.h.invoke(this, m3, (Object[])null);
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {
throw var2;
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);
}
}
static {
try {
// 初始化 methods, 2个IUserService接口中的方法,3个Object中的接口
m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("equals", Class.forName("java.lang.Object"));
m4 = Class.forName("com.lm.it.springframework.service.IUserService").getMethod("findUserList");
m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("toString");
m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("hashCode");
m3 = Class.forName("com.lm.it.springframework.service.IUserService").getMethod("addUser");
} catch (NoSuchMethodException var2) {
throw new NoSuchMethodError(var2.getMessage());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var3) {
throw new NoClassDefFoundError(var3.getMessage());
}
}
}上述代码是比较容易理解的,主要流程是:
- ProxyGenerator 创建 Proxy 的具体类 $Proxy0;
- 由 static 初始化块初始化接口方法:2个 IUserService 接口中的方法,3个 Object 中的接口方法;
- 由构造函数注入 InvocationHandler;
- 执行的时候,通过 ProxyGenerator 创建的 Proxy,调用 InvocationHandler 的 invoke 方法,执行我们自定义的 invoke 方法。
四. Spring AOP 中 JDK代理的实现
Spring AOP 扮演的是 JDK 代理的创建和调用两个角色,我们通过这两个方向来看下 Spring AOP 的代码(JdkDynamicAopProxy 类)。
4.1. Spring AOP JDK 代理的创建
代理的创建比较简单,调用 getProxy() 方法,然后直接调用 JDK 中 Proxy.newProxyInstance() 方法将 ClassLoader 和被代理的接口方法传入即可。
@Override
public Object getProxy() {
return getProxy(ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
@Override
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, this.proxiedInterfaces, this);
}4.2. Spring AOP JDK 代理的执行
执行的方法如下:
/**
* Implementation of {@code InvocationHandler.invoke}.
* <p>Callers will see exactly the exception thrown by the target,
* unless a hook method throws an exception.
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
Object target = null;
try {
// 执行的是equal方法
if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself.
return equals(args[0]);
}
// 执行的是hashcode方法
else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself.
return hashCode();
}
// 如果是包装类,则dispatch to proxy config
else if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) {
// There is only getDecoratedClass() declared -> dispatch to proxy config.
return AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised);
}
// 用反射方式来执行切点
else if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&
method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {
// Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config...
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);
}
Object retVal;
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target,
// in case it comes from a pool.
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
// 获取拦截链
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
// Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct
// reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation.
if (chain.isEmpty()) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does
// nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying.
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
MethodInvocation invocation =
new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
// Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.
retVal = invocation.proceed();
}
// Massage return value if necessary.
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
if (retVal != null && retVal == target &&
returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) &&
!RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method
// is type-compatible. Note that we can't help if the target sets
// a reference to itself in another returned object.
retVal = proxy;
}
else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) {
throw new AopInvocationException(
"Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method);
}
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
// Must have come from TargetSource.
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
![[开源协议] 什么是MIT协议及其使用场景](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/766da73dfdf84a84b40b01493b318981.png)