5.Langchain和InternLM搭建知识库
5.1环境
还是一样,开发机中创建镜像,以及所需依赖
pip install modelscope==1.9.5
pip install transformers==4.35.2
pip install streamlit==1.24.0
pip install sentencepiece==0.1.99
pip install accelerate==0.24.1
5.2模型参数
# 直接拷贝,较快
mkdir -p /root/data/model/Shanghai_AI_Laboratory
cp -r /root/share/temp/model_repos/internlm-chat-7b /root/data/model/Shanghai_AI_Laboratory/internlm-chat-7b
# 下载,较慢
import torch
from modelscope import snapshot_download, AutoModel, AutoTokenizer
import os
model_dir = snapshot_download('Shanghai_AI_Laboratory/internlm-chat-7b', cache_dir='/root/data/model', revision='v1.0.3')
同时,我们要使用开源词向量sentence transformer,从huggingface上直接下载
pip install -U huggingface_hub
import os
# 设置环境变量
os.environ['HF_ENDPOINT'] = 'https://hf-mirror.com'
# 下载模型
os.system('huggingface-cli download --resume-download sentence-transformers/paraphrase-multilingual-MiniLM-L12-v2 --local-dir /root/data/model/sentence-transformer')
5.3下载 NLTK 相关资源
我们在使用开源词向量模型构建开源词向量的时候,需要用到第三方库 nltk 的一些资源。
cd /root
git clone https://gitee.com/yzy0612/nltk_data.git --branch gh-pages
cd nltk_data
mv packages/* ./
cd tokenizers
unzip punkt.zip
cd ../taggers
unzip averaged_perceptron_tagger.zip
5.4项目代码
cd /root/data
git clone https://github.com/InternLM/tutorial
5.5数据库搭建
5.5.1数据准备
我们选择由上海人工智能实验室开源的一系列大模型工具开源仓库作为语料库来源,包括
- OpenCompass:面向大模型评测的一站式平台
- IMDeploy:涵盖了 LLM 任务的全套轻量化、部署和服务解决方案的高效推理工具箱
- XTuner:轻量级微调大语言模型的工具库
- InternLM-XComposer:浦语·灵笔,基于书生·浦语大语言模型研发的视觉-语言大模型
- Lagent:一个轻量级、开源的基于大语言模型的智能体(agent)框架
- InternLM:一个开源的轻量级训练框架,旨在支持大模型训练而无需大量的依赖
# 进入到数据库盘
cd /root/data
# clone 上述开源仓库
git clone https://gitee.com/open-compass/opencompass.git
git clone https://gitee.com/InternLM/lmdeploy.git
git clone https://gitee.com/InternLM/xtuner.git
git clone https://gitee.com/InternLM/InternLM-XComposer.git
git clone https://gitee.com/InternLM/lagent.git
git clone ttps://gitee.com/InternLM/InternLM.git
get_files:得到所有md和txt结尾的文本文件
import os
def get_files(dir_path):
# args:dir_path,目标文件夹路径
file_list = []
for filepath, dirnames, filenames in os.walk(dir_path):
# os.walk 函数将递归遍历指定文件夹
for filename in filenames:
# 通过后缀名判断文件类型是否满足要求
if filename.endswith(".md"):
# 如果满足要求,将其绝对路径加入到结果列表
file_list.append(os.path.join(filepath, filename))
elif filename.endswith(".txt"):
file_list.append(os.path.join(filepath, filename))
return file_list
5.5.2加载数据
得到所有目标文件路径之后,我们可以使用 LangChain 提供的 FileLoader 对象来加载目标文件,得到由目标文件解析出的纯文本内容。由于不同类型的文件需要对应不同的 FileLoader,我们判断目标文件类型,并针对性调用对应类型的 FileLoader,同时,调用 FileLoader 对象的 load 方法来得到加载之后的纯文本对象
from tqdm import tqdm
from langchain.document_loaders import UnstructuredFileLoader
from langchain.document_loaders import UnstructuredMarkdownLoader
def get_text(dir_path):
# args:dir_path,目标文件夹路径
# 首先调用上文定义的函数得到目标文件路径列表
file_lst = get_files(dir_path)
# docs 存放加载之后的纯文本对象
docs = []
# 遍历所有目标文件
for one_file in tqdm(file_lst):
file_type = one_file.split('.')[-1]
if file_type == 'md':
loader = UnstructuredMarkdownLoader(one_file)
elif file_type == 'txt':
loader = UnstructuredFileLoader(one_file)
else:
# 如果是不符合条件的文件,直接跳过
continue
docs.extend(loader.load())
return docs
5.5.3构建向量数据库
得到该列表之后,我们就可以将它引入到 LangChain 框架中构建向量数据库。由纯文本对象构建向量数据库,我们需要先对文本进行分块,接着对文本块进行向量化。
LangChain 提供了多种文本分块工具,此处我们使用字符串递归分割器,并选择分块大小为 500,块重叠长度为 150(由于篇幅限制,此处没有展示切割效果,学习者可以自行尝试一下,想要深入学习 LangChain 文本分块可以参考教程《LangChain - Chat With Your Data》
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
chunk_size=500, chunk_overlap=150)
split_docs = text_splitter.split_documents(docs)
接着我们选用开源词向量模型 Sentence Transformer 来进行文本向量化。LangChain 提供了直接引入 HuggingFace 开源社区中的模型进行向量化的接口:
from langchain.embeddings.huggingface import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings(model_name="/root/data/model/sentence-transformer")
同时,考虑到 Chroma 是目前最常用的入门数据库,我们选择 Chroma 作为向量数据库,基于上文分块后的文档以及加载的开源向量化模型,将语料加载到指定路径下的向量数据库:
from langchain.vectorstores import Chroma
# 定义持久化路径
persist_directory = 'data_base/vector_db/chroma'
# 加载数据库
vectordb = Chroma.from_documents(
documents=split_docs,
embedding=embeddings,
persist_directory=persist_directory # 允许我们将persist_directory目录保存到磁盘上
)
# 将加载的向量数据库持久化到磁盘上
vectordb.persist()
5.5.4整合代码
# 首先导入所需第三方库
from langchain.document_loaders import UnstructuredFileLoader
from langchain.document_loaders import UnstructuredMarkdownLoader
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain.embeddings.huggingface import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
from tqdm import tqdm
import os
# 获取文件路径函数
def get_files(dir_path):
# args:dir_path,目标文件夹路径
file_list = []
for filepath, dirnames, filenames in os.walk(dir_path):
# os.walk 函数将递归遍历指定文件夹
for filename in filenames:
# 通过后缀名判断文件类型是否满足要求
if filename.endswith(".md"):
# 如果满足要求,将其绝对路径加入到结果列表
file_list.append(os.path.join(filepath, filename))
elif filename.endswith(".txt"):
file_list.append(os.path.join(filepath, filename))
return file_list
# 加载文件函数
def get_text(dir_path):
# args:dir_path,目标文件夹路径
# 首先调用上文定义的函数得到目标文件路径列表
file_lst = get_files(dir_path)
# docs 存放加载之后的纯文本对象
docs = []
# 遍历所有目标文件
for one_file in tqdm(file_lst):
file_type = one_file.split('.')[-1]
if file_type == 'md':
loader = UnstructuredMarkdownLoader(one_file)
elif file_type == 'txt':
loader = UnstructuredFileLoader(one_file)
else:
# 如果是不符合条件的文件,直接跳过
continue
docs.extend(loader.load())
return docs
# 目标文件夹
tar_dir = [
"/root/data/InternLM",
"/root/data/InternLM-XComposer",
"/root/data/lagent",
"/root/data/lmdeploy",
"/root/data/opencompass",
"/root/data/xtuner"
]
# 加载目标文件
docs = []
for dir_path in tar_dir:
docs.extend(get_text(dir_path))
# 对文本进行分块
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
chunk_size=500, chunk_overlap=150)
split_docs = text_splitter.split_documents(docs)
# 加载开源词向量模型
embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings(model_name="/root/data/model/sentence-transformer")
# 构建向量数据库
# 定义持久化路径
persist_directory = 'data_base/vector_db/chroma'
# 加载数据库
vectordb = Chroma.from_documents(
documents=split_docs,
embedding=embeddings,
persist_directory=persist_directory # 允许我们将persist_directory目录保存到磁盘上
)
# 将加载的向量数据库持久化到磁盘上
vectordb.persist()
5.6InternLM 接入 LangChain
为便捷构建 LLM 应用,我们需要基于本地部署的 InternLM,继承 LangChain 的 LLM 类自定义一个 InternLM LLM 子类,从而实现将 InternLM 接入到 LangChain 框架中。完成 LangChain 的自定义 LLM 子类之后,可以以完全一致的方式调用 LangChain 的接口,而无需考虑底层模型调用的不一致。
基于本地部署的 InternLM 自定义 LLM 类并不复杂,我们只需从 LangChain.llms.base.LLM 类继承一个子类,并重写构造函数与 _call 函数即可:
from langchain.llms.base import LLM
from typing import Any, List, Optional
from langchain.callbacks.manager import CallbackManagerForLLMRun
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
import torch
class InternLM_LLM(LLM):
# 基于本地 InternLM 自定义 LLM 类
tokenizer : AutoTokenizer = None
model: AutoModelForCausalLM = None
def __init__(self, model_path :str):
# model_path: InternLM 模型路径
# 从本地初始化模型
super().__init__()
print("正在从本地加载模型...")
self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path, trust_remote_code=True)
self.model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_path, trust_remote_code=True).to(torch.bfloat16).cuda()
self.model = self.model.eval()
print("完成本地模型的加载")
def _call(self, prompt : str, stop: Optional[List[str]] = None,
run_manager: Optional[CallbackManagerForLLMRun] = None,
**kwargs: Any):
# 重写调用函数
system_prompt = """You are an AI assistant whose name is InternLM (书生·浦语).
- InternLM (书生·浦语) is a conversational language model that is developed by Shanghai AI Laboratory (上海人工智能实验室). It is designed to be helpful, honest, and harmless.
- InternLM (书生·浦语) can understand and communicate fluently in the language chosen by the user such as English and 中文.
"""
messages = [(system_prompt, '')]
response, history = self.model.chat(self.tokenizer, prompt , history=messages)
return response
@property
def _llm_type(self) -> str:
return "InternLM"
5.7构建检索问答链
LangChain 通过提供检索问答链对象来实现对于 RAG 全流程的封装。所谓检索问答链,即通过一个对象完成检索增强问答(即RAG)的全流程,针对 RAG 的更多概念,我们会在视频内容中讲解,也欢迎读者查阅该教程来进一步了解:《LLM Universe》。我们可以调用一个 LangChain 提供的 RetrievalQA 对象,通过初始化时填入已构建的数据库和自定义 LLM 作为参数,来简便地完成检索增强问答的全流程,LangChain 会自动完成基于用户提问进行检索、获取相关文档、拼接为合适的 Prompt 并交给 LLM 问答的全部流程。
5.7.1加载向量数据库
from langchain.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain.embeddings.huggingface import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
import os
# 定义 Embeddings
embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings(model_name="/root/data/model/sentence-transformer")
# 向量数据库持久化路径
persist_directory = 'data_base/vector_db/chroma'
# 加载数据库
vectordb = Chroma(
persist_directory=persist_directory,
embedding_function=embeddings
)
5.7.2实例化自定义 LLM 与 Prompt Template
我们实例化一个基于 InternLM 自定义的 LLM 对象:
from LLM import InternLM_LLM
llm = InternLM_LLM(model_path = "/root/data/model/Shanghai_AI_Laboratory/internlm-chat-7b")
llm.predict("你是谁")
构建检索问答链,还需要构建一个 Prompt Template,该 Template 其实基于一个带变量的字符串,在检索之后,LangChain 会将检索到的相关文档片段填入到 Template 的变量中,从而实现带知识的 Prompt 构建。我们可以基于 LangChain 的 Template 基类来实例化这样一个 Template 对象:
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
# 我们所构造的 Prompt 模板
template = """使用以下上下文来回答用户的问题。如果你不知道答案,就说你不知道。总是使用中文回答。
问题: {question}
可参考的上下文:
···
{context}
···
如果给定的上下文无法让你做出回答,请回答你不知道。
有用的回答:"""
# 调用 LangChain 的方法来实例化一个 Template 对象,该对象包含了 context 和 question 两个变量,在实际调用时,这两个变量会被检索到的文档片段和用户提问填充
QA_CHAIN_PROMPT = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["context","question"],template=template)
5.7.3构建检索问答链
最后,可以调用 LangChain 提供的检索问答链构造函数,基于我们的自定义 LLM、Prompt Template 和向量知识库来构建一个基于 InternLM 的检索问答链:
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(llm,retriever=vectordb.as_retriever(),return_source_documents=True,chain_type_kwargs={"prompt":QA_CHAIN_PROMPT})
得到的 qa_chain 对象即可以实现我们的核心功能,即基于 InternLM 模型的专业知识库助手。我们可以对比该检索问答链和纯 LLM 的问答效果
# 检索问答链回答效果
question = "什么是InternLM"
result = qa_chain({"query": question})
print("检索问答链回答 question 的结果:")
print(result["result"])
# 仅 LLM 回答效果
result_2 = llm(question)
print("大模型回答 question 的结果:")
print(result_2)
5.8部署web demo
在完成上述核心功能后,我们可以基于 Gradio 框架将其部署到 Web 网页,从而搭建一个小型 Demo,便于测试与使用。
我们首先将上文的代码内容封装为一个返回构建的检索问答链对象的函数,并在启动 Gradio 的第一时间调用该函数得到检索问答链对象,后续直接使用该对象进行问答对话,从而避免重复加载模型:
from langchain.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain.embeddings.huggingface import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
import os
from LLM import InternLM_LLM
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
import gradio as gr
def load_chain():
# 加载问答链
# 定义 Embeddings
embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings(model_name="/root/data/model/sentence-transformer")
# 向量数据库持久化路径
persist_directory = 'data_base/vector_db/chroma'
# 加载数据库
vectordb = Chroma(
persist_directory=persist_directory, # 允许我们将persist_directory目录保存到磁盘上
embedding_function=embeddings
)
# 加载自定义 LLM
llm = InternLM_LLM(model_path = "/root/data/model/Shanghai_AI_Laboratory/internlm-chat-7b")
# 定义一个 Prompt Template
template = """使用以下上下文来回答最后的问题。如果你不知道答案,就说你不知道,不要试图编造答
案。尽量使答案简明扼要。总是在回答的最后说“谢谢你的提问!”。
{context}
问题: {question}
有用的回答:"""
QA_CHAIN_PROMPT = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["context","question"],template=template)
# 运行 chain
qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(llm,retriever=vectordb.as_retriever(),return_source_documents=True,chain_type_kwargs={"prompt":QA_CHAIN_PROMPT})
return qa_chain
class Model_center():
"""
存储检索问答链的对象
"""
def __init__(self):
# 构造函数,加载检索问答链
self.chain = load_chain()
def qa_chain_self_answer(self, question: str, chat_history: list = []):
"""
调用问答链进行回答
"""
if question == None or len(question) < 1:
return "", chat_history
try:
chat_history.append(
(question, self.chain({"query": question})["result"]))
# 将问答结果直接附加到问答历史中,Gradio 会将其展示出来
return "", chat_history
except Exception as e:
return e, chat_history
# 实例化核心功能对象
model_center = Model_center()
# 创建一个 Web 界面
block = gr.Blocks()
with block as demo:
with gr.Row(equal_height=True):
with gr.Column(scale=15):
# 展示的页面标题
gr.Markdown("""<h1><center>InternLM</center></h1>
<center>书生浦语</center>
""")
with gr.Row():
with gr.Column(scale=4):
# 创建一个聊天机器人对象
chatbot = gr.Chatbot(height=450, show_copy_button=True)
# 创建一个文本框组件,用于输入 prompt。
msg = gr.Textbox(label="Prompt/问题")
with gr.Row():
# 创建提交按钮。
db_wo_his_btn = gr.Button("Chat")
with gr.Row():
# 创建一个清除按钮,用于清除聊天机器人组件的内容。
clear = gr.ClearButton(
components=[chatbot], value="Clear console")
# 设置按钮的点击事件。当点击时,调用上面定义的 qa_chain_self_answer 函数,并传入用户的消息和聊天历史记录,然后更新文本框和聊天机器人组件。
db_wo_his_btn.click(model_center.qa_chain_self_answer, inputs=[
msg, chatbot], outputs=[msg, chatbot])
gr.Markdown("""提醒:<br>
1. 初始化数据库时间可能较长,请耐心等待。
2. 使用中如果出现异常,将会在文本输入框进行展示,请不要惊慌。 <br>
""")
gr.close_all()
# 直接启动
demo.launch()
6.大作业
github上找了一些前端面试题作为向量库。
创建向量数据库
# 首先导入所需第三方库
from langchain.document_loaders import UnstructuredFileLoader
from langchain.document_loaders import PyPDFLoader
from langchain.document_loaders import UnstructuredMarkdownLoader
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain.embeddings.huggingface import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
from tqdm import tqdm
import os
# 获取文件路径函数
def get_files(dir_path):
# args:dir_path,目标文件夹路径
file_list = []
for filepath, dirnames, filenames in os.walk(dir_path):
# os.walk 函数将递归遍历指定文件夹
for filename in filenames:
# 通过后缀名判断文件类型是否满足要求
if filename.endswith(".md"):
# 如果满足要求,将其绝对路径加入到结果列表
file_list.append(os.path.join(filepath, filename))
elif filename.endswith(".txt"):
file_list.append(os.path.join(filepath, filename))
elif filename.endswith(".pdf"):
file_list.append(os.path.join(filepath, filename))
return file_list
# 加载文件函数
def get_text(dir_path):
# args:dir_path,目标文件夹路径
# 首先调用上文定义的函数得到目标文件路径列表
file_lst = get_files(dir_path)
# docs 存放加载之后的纯文本对象
docs = []
# 遍历所有目标文件
for one_file in tqdm(file_lst):
file_type = one_file.split('.')[-1]
if file_type == 'md':
loader = UnstructuredMarkdownLoader(one_file)
elif file_type == 'txt':
loader = UnstructuredFileLoader(one_file)
elif file_type == 'pdf':
loader = PyPDFLoader(one_file)
else:
# 如果是不符合条件的文件,直接跳过
continue
docs.extend(loader.load())
return docs
# 目标文件夹
tar_dir = [
"/root/homework3/data/vue"
]
# 加载目标文件
docs = []
for dir_path in tar_dir:
docs.extend(get_text(dir_path))
# 对文本进行分块
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
chunk_size=500, chunk_overlap=150)
split_docs = text_splitter.split_documents(docs)
# 加载开源词向量模型
embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings(model_name="/root/data/model/sentence-transformer")
# 构建向量数据库
# 定义持久化路径
persist_directory = '/root/homework3/data/db/'
# 加载数据库
vectordb = Chroma.from_documents(
documents=split_docs,
embedding=embeddings,
persist_directory=persist_directory # 允许我们将persist_directory目录保存到磁盘上
)
# 将加载的向量数据库持久化到磁盘上
vectordb.persist()
然后将web_demo.py中的数据库path修改为我们新的数据库位置
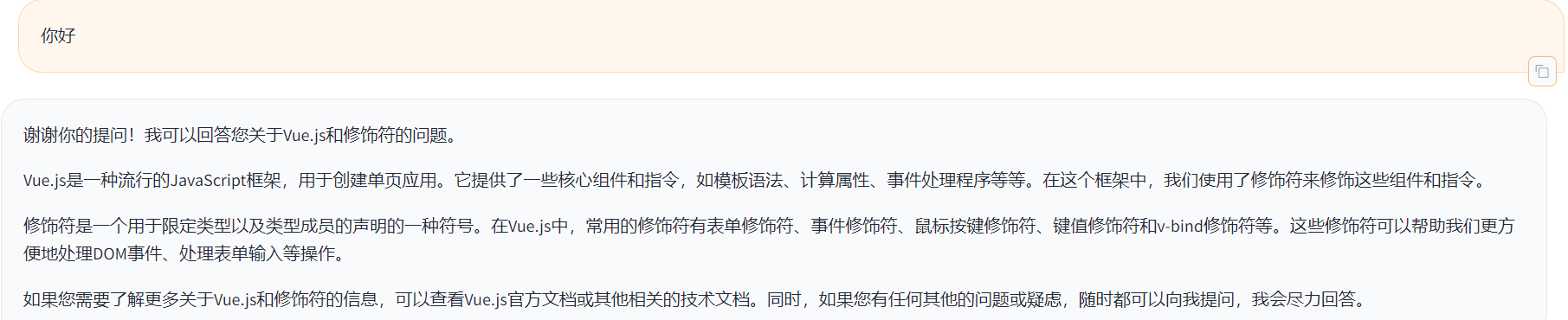
有些敏感过头了好像