至今我都清楚记得自己负责的系统请求云上关联系统时所报的异常信息。为了解决这个异常,我坚持让这个关联系统的负责人查看,并且毫不顾忌他的嘲讽和鄙视,甚至无视他烦躁的情绪。不过我还是高估了自己的脸皮,最终在其恶狠狠地抛下“你自己的问题为啥不自己看!”这句话后悻悻离开。当时,这个“超时”问题就铭刻在了我的脑海里。
回到座位,我就狠地翻起了代码,最终发现我们系统调用他们系统地请求会被包装到HystrixCommand子类对象中,然后通过调用该对象上地execute()方法来完成。但是我依旧没有弄明白超时是怎么实现的。直到今天,我才有了一个大概的思路。为了将自己的思路描述出来,先让我们看一些工作中经常用到的工具类吧。
1. CountDownLatch
首先要介绍的就是CountDownLatch。它是java并发包(java.util.concurrent)中提供的一个同步工具类,其允许一个或多个线程等待其他线程完成一组操作后再执行。它再多线程编程中主要用于实现线程间的协调和同步。接下来让我们看一下其源码:
public class CountDownLatch {
/**
* Synchronization control For CountDownLatch.
* Uses AQS state to represent count.
*/
private static final class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4982264981922014374L;
Sync(int count) {
setState(count);
}
int getCount() {
return getState();
}
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
return (getState() == 0) ? 1 : -1;
}
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
// Decrement count; signal when transition to zero
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
if (c == 0)
return false;
int nextc = c - 1;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
return nextc == 0;
}
}
}
private final Sync sync;
/**
* Constructs a {@code CountDownLatch} initialized with the given count.
*
* @param count the number of times {@link #countDown} must be invoked
* before threads can pass through {@link #await}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code count} is negative
*/
public CountDownLatch(int count) {
if (count < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("count < 0");
this.sync = new Sync(count);
}
/**
* Causes the current thread to wait until the latch has counted down to
* zero, unless the thread is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted}.
*
* <p>If the current count is zero then this method returns immediately.
*
* <p>If the current count is greater than zero then the current
* thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling purposes and lies
* dormant until one of two things happen:
* <ul>
* <li>The count reaches zero due to invocations of the
* {@link #countDown} method; or
* <li>Some other thread {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupts}
* the current thread.
* </ul>
*
* <p>If the current thread:
* <ul>
* <li>has its interrupted status set on entry to this method; or
* <li>is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted} while waiting,
* </ul>
* then {@link InterruptedException} is thrown and the current thread's
* interrupted status is cleared.
*
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread is interrupted
* while waiting
*/
public void await() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
}
/**
* Causes the current thread to wait until the latch has counted down to
* zero, unless the thread is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted},
* or the specified waiting time elapses.
*
* <p>If the current count is zero then this method returns immediately
* with the value {@code true}.
*
* <p>If the current count is greater than zero then the current
* thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling purposes and lies
* dormant until one of three things happen:
* <ul>
* <li>The count reaches zero due to invocations of the
* {@link #countDown} method; or
* <li>Some other thread {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupts}
* the current thread; or
* <li>The specified waiting time elapses.
* </ul>
*
* <p>If the count reaches zero then the method returns with the
* value {@code true}.
*
* <p>If the current thread:
* <ul>
* <li>has its interrupted status set on entry to this method; or
* <li>is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted} while waiting,
* </ul>
* then {@link InterruptedException} is thrown and the current thread's
* interrupted status is cleared.
*
* <p>If the specified waiting time elapses then the value {@code false}
* is returned. If the time is less than or equal to zero, the method
* will not wait at all.
*
* @param timeout the maximum time to wait
* @param unit the time unit of the {@code timeout} argument
* @return {@code true} if the count reached zero and {@code false}
* if the waiting time elapsed before the count reached zero
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread is interrupted
* while waiting
*/
public boolean await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryAcquireSharedNanos(1, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
/**
* Decrements the count of the latch, releasing all waiting threads if
* the count reaches zero.
*
* <p>If the current count is greater than zero then it is decremented.
* If the new count is zero then all waiting threads are re-enabled for
* thread scheduling purposes.
*
* <p>If the current count equals zero then nothing happens.
*/
public void countDown() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
/**
* Returns the current count.
*
* <p>This method is typically used for debugging and testing purposes.
*
* @return the current count
*/
public long getCount() {
return sync.getCount();
}
/**
* Returns a string identifying this latch, as well as its state.
* The state, in brackets, includes the String {@code "Count ="}
* followed by the current count.
*
* @return a string identifying this latch, as well as its state
*/
public String toString() {
return super.toString() + "[Count = " + sync.getCount() + "]";
}
}
从源码可以看出,CountDownLatch内部维护了一个计数器(counter),该计数器在构造时初始化为一个特定的值。其中有两个比较常用的方法:1.countDown()方法,当一个线程完成了自己的工作后调用此方法,会将计数器减1;2.await()方法,其会在主线程或者其他等待线程中调用,如果当前计数器不为0,则会阻塞等待,直到计数器递减至0为止。此外还有一个与await()方法作用类似的方法——await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit),该方法可以实现超时等待。在这个方法中,我们会传入一个等待的超时时间(timeout)和时间单位(TimeUnit)。如果在指定的时间内计数器到达0或者当前线程被中断,则该方法会返回true。如果计数器没有到达0并且等待时间超过了指定的超时时间,那么该方法将会返回false。下面让我们看一个例子:
public class SpringTransactionApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 当前线程等待 10 秒钟
if (!countDownLatch.await(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
System.out.println("超时");
return;
} else {
System.out.println("正常");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}.start();
// 主线程休眠 8 秒钟
try {
Thread.sleep(1000 * 8);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
// 主线程调用 CountDownLatch 上的 countDown() 方法
countDownLatch.countDown();
// 这里会有两种情况,如果主线程 - main 的等待时间超过了当前线程 - t1 的等待时间,那么当前线程 - t1 会输出“超时“
// 如果主线程 - main 的等待时间小于当前线程 - t1 的等待时间,则当前线程 - t1 会输出“正常”
}
}
通过执行这个例子,我们不难发现,在主线程等待8秒的时间里,没有任何线程调用CountDownLatch上的countDown()方法,所以线程t1在等待3秒后await(timeout, TimeUnit)方法直接返回了false,所以可以看到控制台输出了超时,如下图所示:

下面让我们一起梳理一下这个类的应用场景吧:
- 启动屏障:主线程等待多个子线程完成初始化或任务后才能继续执行。例如,在一个服务启动时,主线程需要等待所有组件和服务加载完毕。主线程创建一个CountDownLatch,并设置计数器为组件数量,每个组件加载完成后调用countDown()方法,当计数器归零时,主线程通过await()方法解除阻塞。
- 一次性活动:所有参与者准备好后开始执行一次性的活动,如比赛开始。想象一个学生跑步比赛的例子,所有参赛者(线程)准备就绪后,裁判(主线程)等待所有选手(通过CountDownLatch)表示准备完毕,然后鸣枪开始比赛。
- 批处理任务同步:在分布式系统中,可能需要等待多个独立的异步任务完成后再进行下一步操作。比如,你可能有一个工作线程池处理大量任务,主线程使用CountDownLatch来等待所有这些任务结束。
- 性能测试:在压力测试或性能基准测试中,可以用来确保所有并发线程都已开始执行任务后才开始测量时间,最后再等待所有线程完成以计算总耗时。
- 阶段控制:多阶段任务中,某个阶段需要等待前一阶段的所有工作全部完成。例如,在构建过程中,等待所有编译任务结束后再统一进行部署。
- 资源初始化:当某些共享资源必须在多个线程能够访问之前先完成初始化时,可以通过CountDownLatch来实现同步。
总的来看,CountDownLatch通常用于解决一个或多个线程必须等待一组其他线程完成各自的工作之后才能继续执行的问题。(仔细审视我们的超时案例,其编程模式与CountDownLatch通常要解决的问题一致)
2.Executor及其子类
Executor是java并发编程框架中的一个核心接口,位于java.util.concurrent包中。它定义了一种统一的方式来执行异步任务,即实现了Executor的对象能够接收Runnable对象作为任务,并负责安排这些任务在某一时刻执行。下面是Executor接口的源码:
public interface Executor {
/**
* Executes the given command at some time in the future. The command
* may execute in a new thread, in a pooled thread, or in the calling
* thread, at the discretion of the {@code Executor} implementation.
*
* @param command the runnable task
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if this task cannot be
* accepted for execution
* @throws NullPointerException if command is null
*/
void execute(Runnable command);
}
从上述源码可以看出,execute()方法会接收一个Runnable类型的任务参数。该任务将在Executor管理的线程中异步执行。通过这个接口,我们可以将关注点从如何创建和管理线程转移到如何定义和提交执行的任务上,从而简化了多线程编程模型,提高了程序的可读性和可维护性。另外,java提供了Executors工具类,它是一个静态工厂类,提供了多种预配置的线程池实现,比如固定大小的线程池、单线程执行器、可缓存线程池等等,这些都是ExecutorService接口(该接口继承了Executor接口)的实现,进一步增强了对线程池功能的支持,包括任务调度、线程生命周期管理以及任务结果的获取等。下面让我们来研究一下java并发包提供的一个扩展自Executor 接口的重要接口——ExecutorService,它提供了更多管理和控制线程池的方法。ExecutorService 提供了启动、执行和关闭线程池的能力,以及对异步任务的更丰富的控制,比如可以取消正在执行的任务,查询线程池状态,提交具有返回值的任务等。该接口中的主要方法包括:
- submit(Callable<T> task): 提交一个有返回值的任务,返回一个 Future 对象,通过该对象可以获取任务执行结果或者取消任务。
- submit(Runnable task, T result): 提交一个无返回值的任务,并提供一个结果,返回一个 Future 对象。
- execute(Runnable command): 执行一个 Runnable 类型的任务,与 Executor 接口中的方法一致。
- shutdown(): 关闭 ExecutorService,不再接收新任务,但会将已提交的任务执行完毕。
- shutdownNow(): 尝试停止所有正在执行的任务并返回尚未开始的任务列表。
- awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit): 等待所有任务都已完成,或者超过指定时间后终止等待。
- invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks): 执行给定的任务集合,当所有任务完成或超时后返回包含每个任务结果的 Future 列表。
- invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks): 执行给定的任务集合,返回第一个成功完成的任务的结果。
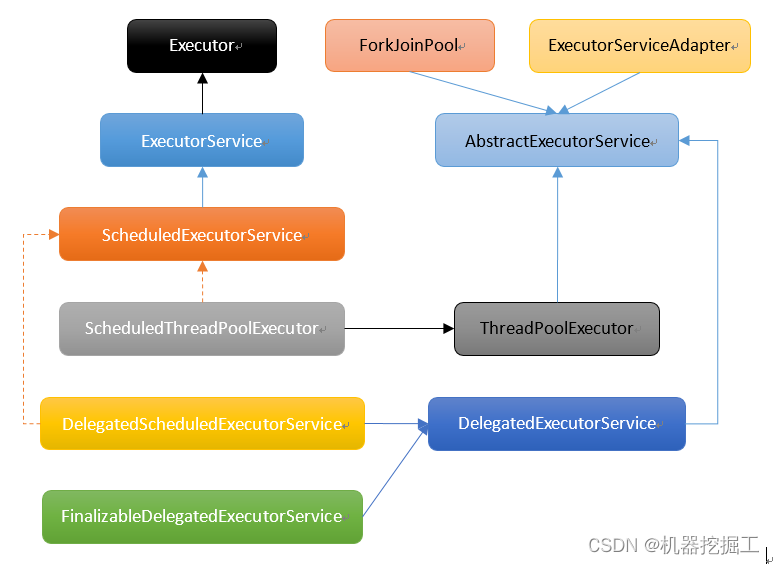
通过 ExecutorService,我们可以更加方便地管理和控制并发任务,有效地利用系统资源,提高程序的性能和响应速度等。下面让我们一起来看一下这个接口的继承体系:
首先跟大家说声抱歉,今天无法完成本篇文章的主旨了,明天我会继续就文章主旨进行梳理。