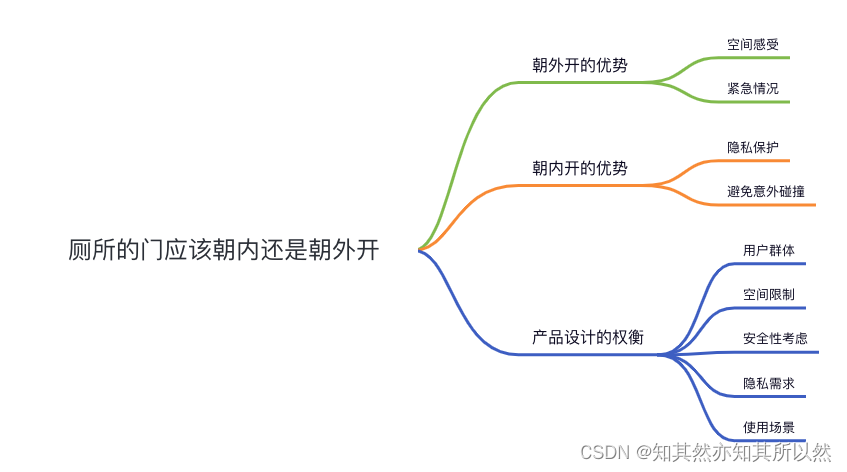
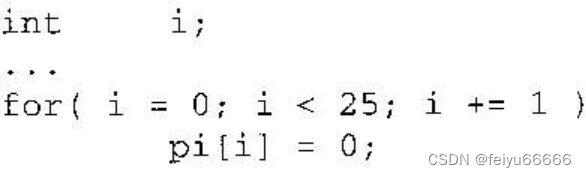1.程序下载网址:https://github.com/HongbiaoZ/autonomous_exploration_development_environment
2.相关参考资料:
https://blog.csdn.net/lizjiwei/article/details/124437157
Matlab用采样的离散点做前向模拟三次样条生成路径点-CSDN博客
CMU团队开源的局部路径导航算法 localPlanner 代码详解以及如何适用于现实移动机器人_cmu-exploration localplanner-CSDN博客
3.相关参数:

Path_id:取值范围0-343,即对应7*7*7
Group_id:取值范围0-7
Path.ply文件:对应某一个朝向(rotdir)下的所有路径点,7个group,每个group是(0-1)线段100等份插值旋转得来的,每个group又有第二段(1-2)和第三段(2-3)的线性插值。故一条路径(0-3距离长度)的路径点数量为(3/0.01+1=301),一共有7*7*7个可选择方向(路径),故Path.ply共包含301*7*7*7=103243个点
Pathlist.ply文件(endpath数组)(7*7*7):是某一个rotdir方向下的路径终点,用于将每个路径终点的得分加到对应rotdir方向下的group_id中,用于选择最佳的路径组n*rotdir+group_id
Startpath.ply文件:数据行数(101*7),存储7个路径组下的101个第一段路径点(101是因为其是在0-1线段内,以0.01进行插值,旋转得到的平滑路径点)
存储在rotdir方向下,在pathscale尺寸下的相对rotdir的路径点,在获取下一个运动路径时,需要读取statpath中相对于rotdir的路径点,并根据朝向交rotAng和路径归一化尺寸pathScale,得到相对于车体坐标系的路径坐标。
readCorrespondences.txt:存储gridVoxelID体素网格序号和path.ply中所有path_id路径点序号和group_id之间的关系
4.对应的角度和坐标转换
坐标系转换:

Map为地图坐标系,通过map_sever扫图确定的,扫完图后,坐标系固定不变
Base_link坐标系是机器人坐标系,其yaw角为相对map坐标系的角度,坐标转换公式如上所示
计算目标点和路径之间的夹角

在 确定路径时,只确定对应rotdir下的group_id的那个路径(7),而后面的path_id只是用来对score分数加到对应的group_id(0-7)下,起到选择group_id的作用。选路径的话是从36*7(rotdir*group_num)里面选择(第一段),其序号为rotdir*groupnum(7)+ group_id。其中rotdir*groupnum对应该方向(rotdir)路径组group的起始序号,group_id为在该起始序号下,加上对应的group值。-------------在计算时与Pathlist相关
5.体素网格化:

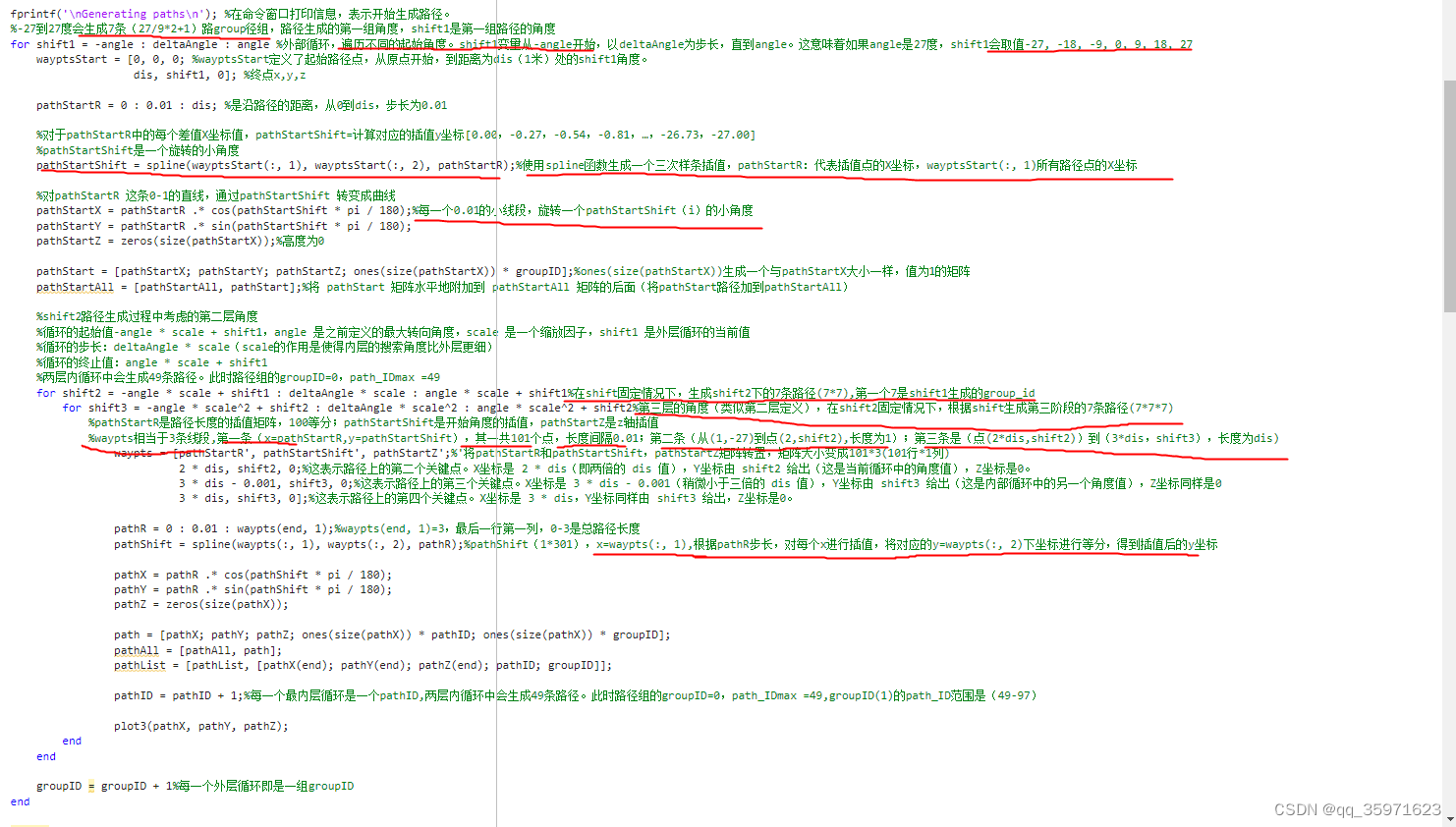
matlab生成的路径以及对应的体素网格
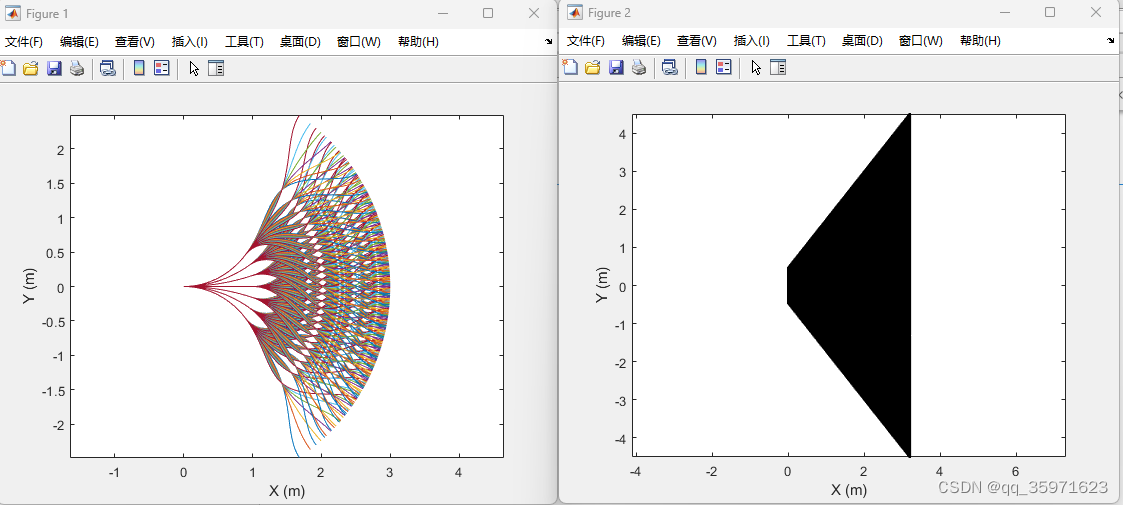
网格体范围为(0,searchRadius)(0,-searchRadius)(offsetX,offsetY)(offsetX,-offsetY)组成的梯形
MATLAB生成体素网格的核心代码

localplanner中对于体素网格的应用
6.核心代码:
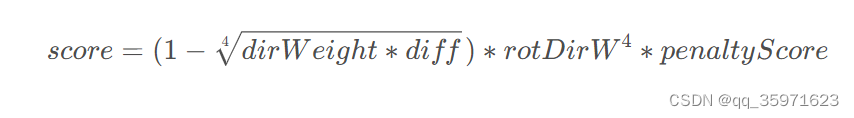
计算每条路径(path_id)的成本,并将其加到对应的(group_id),在后续路径选择中,选择累计score最高的路径

选择成本最高的朝向rotdir下的group_id,检索对应start_path文件下的id,找到对应的相对朝向角rotdir的路径,并通过rotAng将其转化到相对车体坐标系下,将对应路径发布到话题/free
7.全代码运行逻辑图
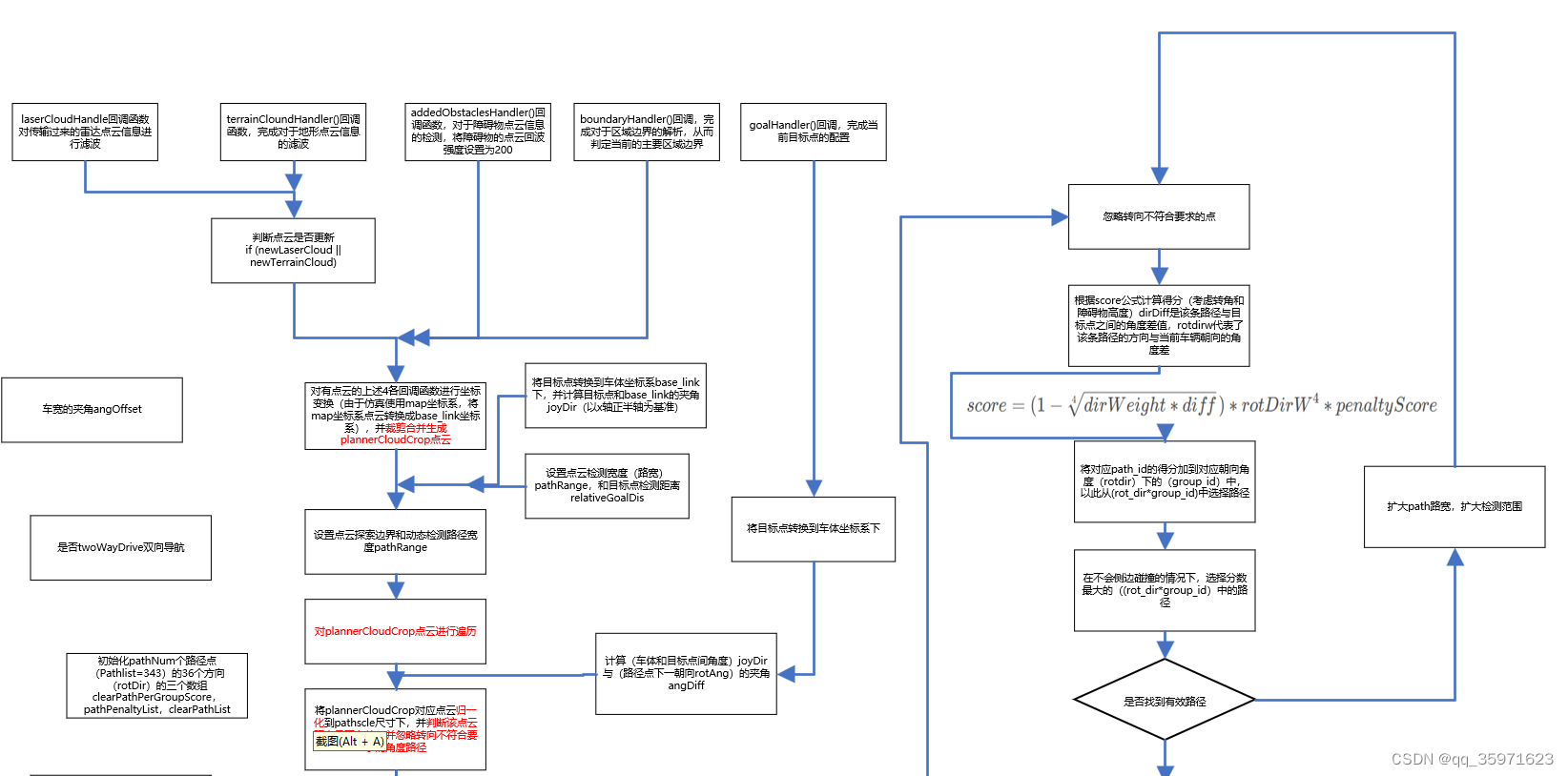
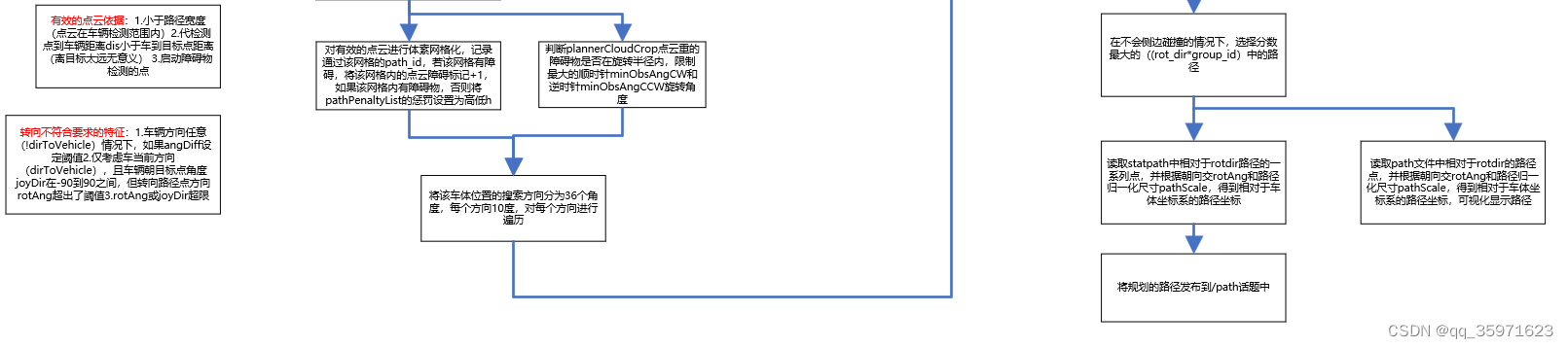
8.全代码注释:
#include <math.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <message_filters/subscriber.h>
#include <message_filters/synchronizer.h>
#include <message_filters/sync_policies/approximate_time.h>
#include <std_msgs/Bool.h>
#include <std_msgs/Float32.h>
#include <nav_msgs/Path.h>
#include <nav_msgs/Odometry.h>
#include <geometry_msgs/PointStamped.h>
#include <geometry_msgs/PolygonStamped.h>
#include <sensor_msgs/Imu.h>
#include <sensor_msgs/PointCloud2.h>
#include <sensor_msgs/Joy.h>
#include <tf/transform_datatypes.h>
#include <tf/transform_broadcaster.h>
#include <pcl_conversions/pcl_conversions.h>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h>
#include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree_flann.h>
//局部路径规划--碰撞避免
using namespace std;
const double PI = 3.1415926;
#define PLOTPATHSET 1
string pathFolder;
double vehicleLength = 0.6;
double vehicleWidth = 0.6;
double sensorOffsetX = 0;
double sensorOffsetY = 0;
bool twoWayDrive = true;
double laserVoxelSize = 0.05;
double terrainVoxelSize = 0.2;
bool useTerrainAnalysis = false;
bool checkObstacle = true;
bool checkRotObstacle = false;
double adjacentRange = 3.5;
double obstacleHeightThre = 0.2;
double groundHeightThre = 0.1;
double costHeightThre = 0.1;
double costScore = 0.02;
bool useCost = false;
const int laserCloudStackNum = 1;
int laserCloudCount = 0;
int pointPerPathThre = 2;
double minRelZ = -0.5;// 未使用地面分割时,裁剪点云时的最小高度
double maxRelZ = 0.25;
double maxSpeed = 1.0;
double dirWeight = 0.02;
double dirThre = 90.0;
bool dirToVehicle = false;//是否以车辆为主方向计算被遮挡的路径(限制车辆前进方向?)
double pathScale = 1.0;
double minPathScale = 0.75;
double pathScaleStep = 0.25;
bool pathScaleBySpeed = true;
double minPathRange = 1.0;
double pathRangeStep = 0.5;
bool pathRangeBySpeed = true;
bool pathCropByGoal = true;
bool autonomyMode = false;
double autonomySpeed = 1.0;
double joyToSpeedDelay = 2.0;
double joyToCheckObstacleDelay = 5.0;
double goalClearRange = 0.5;
double goalX = 0;
double goalY = 0;
float joySpeed = 0;
float joySpeedRaw = 0;
float joyDir = 0;
const int pathNum = 343;//7*7*7
const int groupNum = 7;//groupNum对应第一级分裂的组数
float gridVoxelSize = 0.02;//体素网格大小
//网格体范围为(0,searchRadius)(0,-searchRadius)(offsetX,offsetY)(offsetX,-offsetY)组成的梯形
float searchRadius = 0.45;//searchRadius 搜索半径,(一个体素网格点搜索附近相关路径点的半径)。略大于车的对角线半径(sqrt(0.6*0.6+0.6*0.6))
float gridVoxelOffsetX = 3.2;//体素网格x坐标上(车体坐标系)的偏移量,传感器检测范围??(离车最远x位置的体素网格距离)
float gridVoxelOffsetY = 4.5;//离车最远的X处体素网格对应的Y的坐标
const int gridVoxelNumX = 161;//数量 offsetX/voxelSize
const int gridVoxelNumY = 451;
const int gridVoxelNum = gridVoxelNumX * gridVoxelNumY;
//创建点云指针,用来存储和处理激光雷达和地形数据
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr laserCloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>());//这个点云用于存储原始的激光雷达数据
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr laserCloudCrop(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>());//用于存储处理过的激光雷达数据,例如,只保留一定范围内的点。
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr laserCloudDwz(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>());//用于存储降采样Downsized(例如,通过体素网格过滤)后的激光雷达数据。
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr terrainCloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>());//用于存储原始的地形数据点云
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr terrainCloudCrop(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>());//存储裁剪后的地形数据点云,可能同样只包含特定区域内的点。
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr terrainCloudDwz(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>());//降采样后的地形数据点云
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr laserCloudStack[laserCloudStackNum];//雷达点云数组,可能用于存储laserCloudStackNum个经过降采样后的激光雷达点云
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr plannerCloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>());//用于路径规划过程中,存储所有需要考虑的点。
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr plannerCloudCrop(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>());//路径规划过程中裁剪后的点云,只包含与路径规划相关的点。
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr boundaryCloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>());//表示导航边界的点云
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr addedObstacles(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>());//存储在规划过程中额外加入的障碍物
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr startPaths[groupNum];//第一次采样时的路径点(点最多的路径)
#if PLOTPATHSET == 1
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr paths[pathNum];//存储路径规划器可能计算出的多条路径的点云(根据startPaths组成一条最终的局部路径path)
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr freePaths(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>());//用于存储所有未被障碍物阻挡的路径(所有 clearPathList[i] < pointPerPathThre 的路径)
#endif
//路径相关数组
int pathList[pathNum] = {0};//用于存储与路径相关的索引或标记
float endDirPathList[pathNum] = {0};//计算该条路径末端点与当前位置的角度,并存储在数组中
int clearPathList[36 * pathNum] = {0};//clearPathList存储障碍物数量(36代表360度方向,相对于每一条路径分裂成了36条分布在各个方向的路径)
float pathPenaltyList[36 * pathNum] = {0};//一个浮点数组,用于记录给定方向上路径的惩罚得分,这可能与路径的障碍物或不平整度有关。
float clearPathPerGroupScore[36 * groupNum] = {0};//一个浮点数组,记录了每个组中路径的得分,用于路径选择。
std::vector<int> correspondences[gridVoxelNum];//存储可能与每个网格体素相对应的路径索引。
//状态标志:
bool newLaserCloud = false;//如果接收到新的激光雷达点云,则设置为true
bool newTerrainCloud = false;//如果接收到新的地形点云,则设置为true
//时间记录:
double odomTime = 0;//记录最近一次接收到的里程计数据的时间戳。
double joyTime = 0;//记录最近一次接收到的游戏手柄数据的时间戳。
//车辆状态:
float vehicleRoll = 0, vehiclePitch = 0, vehicleYaw = 0;//分别记录车辆的滚转、俯仰和偏航角。
float vehicleX = 0, vehicleY = 0, vehicleZ = 0;//记录车辆在三维空间中的位置。
//点云过滤器:
pcl::VoxelGrid<pcl::PointXYZI> laserDwzFilter, terrainDwzFilter;//用于降采样激光雷达和地形点云数据。通过这种方式,可以减少处理的数据量,同时保留足够的信息进行路径规划
//处理从机器人的运动传感器或定位系统接收到的里程计信息的回调函数
//基于传入的里程计消息更新机器人的方向和位置,并且考虑到了里程计传感器与机器人参考点之间的偏移。
//这些信息对于导航、路径规划以及与传感器数据协调移动等任务至关重要。
void odometryHandler(const nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr& odom)
{
odomTime = odom->header.stamp.toSec();//从里程计消息的头部提取时间戳,并将其转换为秒。时间戳对于与机器人环境中的其他事件同步传感器读数非常重要
double roll, pitch, yaw;
geometry_msgs::Quaternion geoQuat = odom->pose.pose.orientation;//从里程计消息中获取了机器人的方向,表示为四元数。四元数是避免万向锁问题并且在表示方向时比欧拉角更稳定的旋转编码方式
tf::Matrix3x3(tf::Quaternion(geoQuat.x, geoQuat.y, geoQuat.z, geoQuat.w)).getRPY(roll, pitch, yaw);//使用tf(变换)库的Quaternion类,将四元数转换为3x3旋转矩阵,然后调用getRPY方法将旋转矩阵转换为滚转(roll)、俯仰(pitch)和偏航(yaw)的欧拉角
vehicleRoll = roll;
vehiclePitch = pitch;
vehicleYaw = yaw;
//确保了即使传感器不在车辆的中心,位置测量也能反映车辆相对于全局坐标系的真实位置
vehicleX = odom->pose.pose.position.x - cos(yaw) * sensorOffsetX + sin(yaw) * sensorOffsetY;//1.获取车辆的当前位置odom->pose.pose.position.x 2.考虑传感器相对于车辆中心的偏移量sensorOffsetX,校正从传感器位置到车辆中心点位置
vehicleY = odom->pose.pose.position.y - sin(yaw) * sensorOffsetX - cos(yaw) * sensorOffsetY;
vehicleZ = odom->pose.pose.position.z;//Z位置直接从里程计消息中取得,没有进行偏移调整,因为对于地面机器人来说(假设地形平坦),垂直偏移通常不太关键
}
//回调函数:接收传感器原始数据,对其进行处理,然后将处理后的数据存储为PCL(点云库)的点云数据结构以便进一步使用
//函数的目的是从激光雷达传感器实时处理数据,裁剪出与车辆相邻的点云部分(保留距离车体dis < adjacentRange),并通过降采样减少数据量,从而使后续的处理更加高效。
//处理后的点云可以用于多种应用,包括障碍物检测、路径规划、地图构建等
void laserCloudHandler(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr& laserCloud2)
{
if (!useTerrainAnalysis) {//检查是否进行地形分析,如果不进行地形分析,则处理点云数据,否则跳过。
laserCloud->clear();//清空当前点云
pcl::fromROSMsg(*laserCloud2, *laserCloud);//将ROS的PointCloud2消息格式转换为PCL库可以处理的点云格式
//裁剪点云:
pcl::PointXYZI point;//初始化一个临时的pcl::PointXYZI点。
laserCloudCrop->clear();//清空裁剪后的点云laserCloudCrop。
int laserCloudSize = laserCloud->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudSize; i++) {//遍历转换后的点云中的每一个点
point = laserCloud->points[i];
float pointX = point.x;
float pointY = point.y;
float pointZ = point.z;
float dis = sqrt((pointX - vehicleX) * (pointX - vehicleX) + (pointY - vehicleY) * (pointY - vehicleY));//计算每个点到车辆当前位置(vehicleX, vehicleY)的距离
if (dis < adjacentRange) {//如果点在一个给定的邻近范围内(adjacentRange,设定的裁剪点云时的距离,车辆周围用于检测障碍物的区域大小),
point.x = pointX;
point.y = pointY;
point.z = pointZ;
laserCloudCrop->push_back(point);//则将其添加到裁剪后的点云laserCloudCrop中
}
}
//laserCloudCrop(裁减后点云)-》laserDwzFilter降采样-》laserCloudDwz
laserCloudDwz->clear();//清空降采样后的点云以准备存储新数据。
laserDwzFilter.setInputCloud(laserCloudCrop);//设置体素栅格滤波器的输入为裁剪后的点云
laserDwzFilter.filter(*laserCloudDwz);//应用体素栅格滤波器对点云进行降采样,以减少点的数量,提高处理速度,结果存储在laserCloudDwz中
newLaserCloud = true;//设置一个标志,表明现在有一个新的处理过的激光雷达点云可用
}
}
//处理地形相关(障碍)的点云数据而设计的ROS消息回调
//处理这些数据可能包括从原始点云中筛选出与车辆相邻的点(dis < adjacentRange),提取和保存与地形相关的信息,特别是那些可能影响机器人导航和路径规划的障碍物。
void terrainCloudHandler(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr& terrainCloud2)
{
if (useTerrainAnalysis) {//当useTerrainAnalysis标志被设置为true时,处理地形相关的点云数据
terrainCloud->clear();//清除存储在terrainCloud变量中的所有旧点云数据
pcl::fromROSMsg(*terrainCloud2, *terrainCloud);//将ROS的点云消息转换为PCL库可以处理的点云格式。
pcl::PointXYZI point;
terrainCloudCrop->clear();
int terrainCloudSize = terrainCloud->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < terrainCloudSize; i++) {
point = terrainCloud->points[i];
float pointX = point.x;
float pointY = point.y;
float pointZ = point.z;
float dis = sqrt((pointX - vehicleX) * (pointX - vehicleX) + (pointY - vehicleY) * (pointY - vehicleY));
//如果点位于车辆旁边的adjacentRange距离内,并且点的强度超过障碍物高度阈值obstacleHeightThre或者使用成本分析useCost
if (dis < adjacentRange && (point.intensity > obstacleHeightThre || useCost)) {//intensity代表点云距离地面的高度
point.x = pointX;
point.y = pointY;
point.z = pointZ;
terrainCloudCrop->push_back(point);//将该点添加到裁剪后的点云terrainCloudCrop中。
}
}
terrainCloudDwz->clear();
terrainDwzFilter.setInputCloud(terrainCloudCrop);
terrainDwzFilter.filter(*terrainCloudDwz);
newTerrainCloud = true;
}
}
//用于处理游戏手柄(joystick)输入的ROS消息回调。它解析从游戏手柄传入的数据,并据此更新车辆控制和导航状态
void joystickHandler(const sensor_msgs::Joy::ConstPtr& joy)
{
joyTime = ros::Time::now().toSec();//记录接收到游戏手柄输入的时刻
joySpeedRaw = sqrt(joy->axes[3] * joy->axes[3] + joy->axes[4] * joy->axes[4]);//根据游戏手柄的两个轴(通常是左摇杆的水平和垂直轴)的输入值计算原始速度
joySpeed = joySpeedRaw;
//将计算出的速度joySpeed限制在一定范围内(0到1之间)。如果摇杆的垂直轴值为0,则速度设置为0
if (joySpeed > 1.0) joySpeed = 1.0;
if (joy->axes[4] == 0) joySpeed = 0;
//如果速度大于0,则计算出一个方向角度joyDir。这是通过atan2函数根据摇杆的两个轴值计算得到的,表示摇杆的倾斜方向
if (joySpeed > 0) {
joyDir = atan2(joy->axes[3], joy->axes[4]) * 180 / PI;
if (joy->axes[4] < 0) joyDir *= -1;
}
//处理两向驱动
//如果twoWayDrive为false且摇杆的垂直轴值小于0(倒车),则速度设置为0。
//这意味着如果车辆不支持两向驱动(即不能倒车),则只在摇杆向前推时允许有速度
if (joy->axes[4] < 0 && !twoWayDrive) joySpeed = 0;
//设置自主模式:
//根据游戏手柄的另一个轴(可能是扳机按钮)的值设置autonomyMode。
//如果这个轴的值大于-0.1,则设置为手动模式;否则,设置为自主模式
if (joy->axes[2] > -0.1) {
autonomyMode = false;
} else {
autonomyMode = true;
}
//根据游戏手柄的另一个轴的值设置checkObstacle标志。
//如果这个轴的值大于-0.1,则启用障碍物检测;否则,禁用
if (joy->axes[5] > -0.1) {
checkObstacle = true;
} else {
checkObstacle = false;
}
}
//ROS消息回调,用于处理包含目标点位置的geometry_msgs::PointStamped消息
void goalHandler(const geometry_msgs::PointStamped::ConstPtr& goal)
{
goalX = goal->point.x;//从传入的消息中提取目标点的X坐标,并将其赋值给全局变量goalX
goalY = goal->point.y;
}
//ROS消息回调,用于处理类型为std_msgs::Float32的速度消息
//在自主模式下根据接收到手柄的速度消息调整机器人的速度
//通过考虑来自游戏手柄的输入和延迟,这个函数有助于平滑地在手动控制和自主控制之间过渡
void speedHandler(const std_msgs::Float32::ConstPtr& speed)
{
double speedTime = ros::Time::now().toSec();//获取当前时间的秒数,用于确定消息的接收时间
//检查自主模式和延迟条件
//调整速度条件:当前是自主模式(autonomyMode为true)+自上次接收到游戏手柄输入以来已经过去了一定的时间(speedTime - joyTime > joyToSpeedDelay),这避免了游戏手柄输入与自主速度指令之间的冲突+上次从游戏手柄接收到的原始速度为0
if (autonomyMode && speedTime - joyTime > joyToSpeedDelay && joySpeedRaw == 0) {
joySpeed = speed->data / maxSpeed;//将接收到的速度值(speed->data)除以预设的最大速度值(maxSpeed),从而将速度归一化到0到1的范围内
//限制速度范围:
if (joySpeed < 0) joySpeed = 0;
else if (joySpeed > 1.0) joySpeed = 1.0;
}
}
//ROS消息回调,用于处理包含边界信息的geometry_msgs::PolygonStamped消息
//将接收到的边界信息转换为点云形式,以便进一步使用
//通过在边界多边形的每两个顶点之间插入额外的点来创建一个密集的边界点云
void boundaryHandler(const geometry_msgs::PolygonStamped::ConstPtr& boundary)//接收一个指向(/navigation_boundary话题)相应消息类型(geometry_msgs::PolygonStamped)的指针(& boundary)作为参数
{
boundaryCloud->clear();//清空之前存储的边界点云数据,准备接收新的边界数据
pcl::PointXYZI point, point1, point2;//声明了三个pcl::PointXYZI类型的点变量(point, point1, point2)用于存储和处理边界点
int boundarySize = boundary->polygon.points.size();
if (boundarySize >= 1) {//如果边界包含至少一个点,则初始化point2为边界的第一个点。
point2.x = boundary->polygon.points[0].x;
point2.y = boundary->polygon.points[0].y;
point2.z = boundary->polygon.points[0].z;
}
for (int i = 0; i < boundarySize; i++) {
point1 = point2;//赋值,point1=前一个点的位置,point2=当前点位置
point2.x = boundary->polygon.points[i].x;
point2.y = boundary->polygon.points[i].y;
point2.z = boundary->polygon.points[i].z;
if (point1.z == point2.z) {//如果前一个点和当前点在同一平面
float disX = point1.x - point2.x;
float disY = point1.y - point2.y;
float dis = sqrt(disX * disX + disY * disY);//计算两点之间距离
int pointNum = int(dis / terrainVoxelSize) + 1;//根据这个距离和设定的体素大小(terrainVoxelSize),计算两点之间应该插入的点数(平滑路径)
for (int pointID = 0; pointID < pointNum; pointID++) {//以point1和point2为顶点计算插入点坐标
point.x = float(pointID) / float(pointNum) * point1.x + (1.0 - float(pointID) / float(pointNum)) * point2.x;
point.y = float(pointID) / float(pointNum) * point1.y + (1.0 - float(pointID) / float(pointNum)) * point2.y;
point.z = 0;
point.intensity = 100.0;//每个点的强度值设置为100.0(激光反射?100=障碍物?)
//在内部循环中,对于每个计算出的插入点,这个循环重复添加该点pointPerPathThre次到boundaryCloud点云中。
//这可能是为了在点云中加重这些特定的边界点,使得它们在后续的处理中更加突出或易于识别
for (int j = 0; j < pointPerPathThre; j++) {//当一条路径上存在两个障碍点,即 pointPerPathThre=2,该路径才会认为被遮挡
boundaryCloud->push_back(point);
}
}
}
}
}
//用于处理障碍物点云的ROS消息回调,将障碍物回波强度设置为200
void addedObstaclesHandler(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr& addedObstacles2)
{
addedObstacles->clear();//清空已有的附加障碍物点云:
pcl::fromROSMsg(*addedObstacles2, *addedObstacles);//将ROS消息格式的点云数据转换为PCL库可以处理的点云格式。
int addedObstaclesSize = addedObstacles->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < addedObstaclesSize; i++) {
addedObstacles->points[i].intensity = 200.0;//将所有附加障碍物的强度设置为200.0,可能是为了在后续的处理中将这些障碍物与其他类型的点云数据区分开来
}
}
//ROS消息回调,用于处理std_msgs::Bool类型的消息,这些消息指示是否应该检查障碍物
//根据接收到的消息,在自主模式下启用或禁用障碍物检查
//这种机制允许系统在自主导航时根据消息checkObs动态调整是否进行障碍物检测,以应对可能存在的障碍物,同时也避免了与手动控制输入冲突
void checkObstacleHandler(const std_msgs::Bool::ConstPtr& checkObs)
{
double checkObsTime = ros::Time::now().toSec();//代码获取当前时间的秒数,用于确定消息的接收时间
if (autonomyMode && checkObsTime - joyTime > joyToCheckObstacleDelay) {//当前是自主模式,自上次接收到游戏手柄输入以来已经过去了一定的时间(延迟是为了避免手动控制输入与自主模式下的障碍物检查指令之间的冲突)
checkObstacle = checkObs->data;//将接收到的障碍物检查状态(checkObs->data)赋值给checkObstacle。这个变量控制着是否应该检查障碍物
}
}
//用于读取PLY(Polygon File Format)文件头,PLY文件用于存储三维模型数据
//从PLY文件的头部提取点的数量
int readPlyHeader(FILE *filePtr)
{
char str[50];//用于存储从文件中读取的字符串
int val, pointNum;
string strCur, strLast;//声明两个字符串变量,用于存储当前读取的字符串和上一次读取的字符串。
while (strCur != "end_header") {//使用while循环读取文件,直到找到"end_header"字符串。PLY文件头以"end_header"结束
val = fscanf(filePtr, "%s", str);//读取文件中的字符串
if (val != 1) {//如果fscanf返回值不为1,表示读取失败
printf ("\nError reading input files, exit.\n\n");
exit(1);
}
strLast = strCur;//将当前字符串赋值作为上一个时刻字符串赋值
strCur = string(str);
if (strCur == "vertex" && strLast == "element") {//当找到字符串序列“element vertex”时,意味着接下来的数字表示点的数量。
val = fscanf(filePtr, "%d", &pointNum);//读取点的数量
if (val != 1) {
printf ("\nError reading input files, exit.\n\n");
exit(1);
}
}
}
return pointNum;
}
//从一个PLY文件中读取起始路径的点云数据,并根据组ID将这些点分配到不同的路径组中
//通过读取这些点,系统可以了解在特定场景或环境下预先设定的潜在路径(相对朝向角的路径)
void readStartPaths()
{
string fileName = pathFolder + "/startPaths.ply";
FILE *filePtr = fopen(fileName.c_str(), "r");//FILE表示文件流类型,只读模式打开一个名为fileName的文件,并将文件流指针赋值给filePtr
if (filePtr == NULL) {
printf ("\nCannot read input files, exit.\n\n");
exit(1);
}
int pointNum = readPlyHeader(filePtr);//调用readPlyHeader函数获得PLY文件点数
pcl::PointXYZ point;
int val1, val2, val3, val4, groupID;
//每一行的startPaths.ply文件代表一个pointNum,一行4列,代表X,Y,Z和groupID(组别)
for (int i = 0; i < pointNum; i++) {//对于每个点,读取其X、Y、Z坐标和所属的组ID(groupID)
val1 = fscanf(filePtr, "%f", &point.x);//&point.x: 这是一个指向浮点变量的指针,fscanf会从filePtr文件流指针将读取到的浮点数存储在这个变量中。在这种情况下,它指向point结构中的x成员
val2 = fscanf(filePtr, "%f", &point.y);
val3 = fscanf(filePtr, "%f", &point.z);
val4 = fscanf(filePtr, "%d", &groupID);
if (val1 != 1 || val2 != 1 || val3 != 1 || val4 != 1) {//如果任何一个值未能成功读取,函数打印错误信息并退出
printf ("\nError reading input files, exit.\n\n");
exit(1);
}
if (groupID >= 0 && groupID < groupNum) {
//startPaths是存储rotdir方向上group_id对应位置的点云数组(表示下一个机器人要走的路径).
startPaths[groupID]->push_back(point);//将对应的第groupID点的point输入到第groupID个pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr类型的全局变量startPaths树组
}
}
fclose(filePtr);
}
#if PLOTPATHSET == 1//如果为真,则编译该指令和对应的#endif之间的代
//从一个PLY文件中读取路径数据,并将这些数据存储到相应的数据结构中
void readPaths()
{
string fileName = pathFolder + "/paths.ply";
FILE *filePtr = fopen(fileName.c_str(), "r");
if (filePtr == NULL) {
printf ("\nCannot read input files, exit.\n\n");
exit(1);
}
int pointNum = readPlyHeader(filePtr);
pcl::PointXYZI point;
int pointSkipNum = 30;
int pointSkipCount = 0;
int val1, val2, val3, val4, val5, pathID;//看paths.ply文件结构,一行5个变量,代表X,Y,Z,pathID,group_id
for (int i = 0; i < pointNum; i++) {//按行取点
val1 = fscanf(filePtr, "%f", &point.x);
val2 = fscanf(filePtr, "%f", &point.y);
val3 = fscanf(filePtr, "%f", &point.z);
val4 = fscanf(filePtr, "%d", &pathID);//pathID
val5 = fscanf(filePtr, "%f", &point.intensity);//group_id,强度?
if (val1 != 1 || val2 != 1 || val3 != 1 || val4 != 1 || val5 != 1) {
printf ("\nError reading input files, exit.\n\n");
exit(1);
}
if (pathID >= 0 && pathID < pathNum) {
pointSkipCount++;
if (pointSkipCount > pointSkipNum) {//在点云中每隔一定数量(pointSkipNum=30)的点添加一个点
paths[pathID]->push_back(point);//pathID(0-343)
pointSkipCount = 0;
}
}
}
fclose(filePtr);
}
#endif
//对每条路径的终点位置和方向的记录(末梢路径)
void readPathList()
{
string fileName = pathFolder + "/pathList.ply";
FILE *filePtr = fopen(fileName.c_str(), "r");
if (filePtr == NULL) {
printf ("\nCannot read input files, exit.\n\n");
exit(1);
}
if (pathNum != readPlyHeader(filePtr)) {
printf ("\nIncorrect path number, exit.\n\n");
exit(1);
}
int val1, val2, val3, val4, val5, pathID, groupID;
float endX, endY, endZ;
for (int i = 0; i < pathNum; i++) {//pathList.ply文件中包含列的变量,x,y,z,pathID, groupID
val1 = fscanf(filePtr, "%f", &endX);//将第一列的数据存入&endX指针
val2 = fscanf(filePtr, "%f", &endY);
val3 = fscanf(filePtr, "%f", &endZ);
val4 = fscanf(filePtr, "%d", &pathID);//7*7*7
val5 = fscanf(filePtr, "%d", &groupID);
if (val1 != 1 || val2 != 1 || val3 != 1 || val4 != 1 || val5 != 1) {
printf ("\nError reading input files, exit.\n\n");
exit(1);
}
if (pathID >= 0 && pathID < pathNum && groupID >= 0 && groupID < groupNum) {//如果读取的路径ID和组ID在有效范围内
pathList[pathID] = groupID;//groupID==groupNum=7对应第一级分裂的组数,分裂路径的尾端(第二段=49)ID,将第二段ID和第一段ID关联起来
endDirPathList[pathID] = 2.0 * atan2(endY, endX) * 180 / PI;//计算该条路径末端点与当前位置(以rotdir为基准)的角度,并存储在数组中
}
}
fclose(filePtr);
}
//建立网格体素和路径之间的对应关系
//将correspondences点,按行号放入每一个树组中,一个树组(一行)对应一条路径?
//在基于点云的导航系统中,这些对应关系可能用于快速确定哪些路径与特定的空间区域相关联
void readCorrespondences()
{
string fileName = pathFolder + "/correspondences.txt";
FILE *filePtr = fopen(fileName.c_str(), "r");
if (filePtr == NULL) {
printf ("\nCannot read input files, exit.\n\n");
exit(1);
}
int val1, gridVoxelID, pathID;
for (int i = 0; i < gridVoxelNum; i++) {//遍历
val1 = fscanf(filePtr, "%d", &gridVoxelID);//将correspondences.txt第一列元素赋值给&gridVoxelID指针
if (val1 != 1) {
printf ("\nError reading input files, exit.\n\n");
exit(1);
}
while (1) {
val1 = fscanf(filePtr, "%d", &pathID);//将correspondences.txt未读完的元素赋值给&&pathID指针
if (val1 != 1) {
printf ("\nError reading input files, exit.\n\n");
exit(1);
}
if (pathID != -1) {//如果pathID != -1,即路径有效,将对应的gridVoxelID行数据依次读入pathID
if (gridVoxelID >= 0 && gridVoxelID < gridVoxelNum && pathID >= 0 && pathID < pathNum) {
correspondences[gridVoxelID].push_back(pathID);//gridVoxelID是文件的第一列数据,pathID是第2-n列数据(代表对应的终点路径序号)
}
} else {
break;
}
}
}
fclose(filePtr);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "localPlanner");// 初始化ROS系统,并命名节点为localPlanner。
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::NodeHandle nhPrivate = ros::NodeHandle("~");
//从参数服务器获取配置参数(从launch获取)
nhPrivate.getParam("pathFolder", pathFolder);//获取路径文件
nhPrivate.getParam("vehicleLength", vehicleLength); //车长
nhPrivate.getParam("vehicleWidth", vehicleWidth);//车宽
nhPrivate.getParam("sensorOffsetX", sensorOffsetX);//获取传感器相对质心的X、Y轴偏移量
nhPrivate.getParam("sensorOffsetY", sensorOffsetY);
nhPrivate.getParam("twoWayDrive", twoWayDrive);//双向驱动模式(在launch文件中默认为true)
nhPrivate.getParam("laserVoxelSize", laserVoxelSize);//激光点云数据处理时使用的体素网格大小,这个值决定了将点云空间划分为多大的立方体(体素),以进行下采样或密度过滤
nhPrivate.getParam("terrainVoxelSize", terrainVoxelSize);//获取地形点云的体素网格大小
nhPrivate.getParam("useTerrainAnalysis", useTerrainAnalysis);//检查是否使用地形分析:
nhPrivate.getParam("checkObstacle", checkObstacle);//是否应该执行障碍物检测(路径中的障碍物检测)
nhPrivate.getParam("checkRotObstacle", checkRotObstacle);//是否在考虑旋转时检测障碍物
nhPrivate.getParam("adjacentRange", adjacentRange);//裁剪点云时的距离,车辆周围用于检测障碍物的区域大小
nhPrivate.getParam("obstacleHeightThre", obstacleHeightThre);//阈值,定义何种高度的对象应被视为障碍物
nhPrivate.getParam("groundHeightThre", groundHeightThre);//用于区分地面和非地面点的阈值,在地形分析或地面分割算法中常见
nhPrivate.getParam("costHeightThre", costHeightThre);//计算路径惩罚得分的权重
nhPrivate.getParam("costScore", costScore);//最小惩罚得分
nhPrivate.getParam("useCost", useCost);//是否应该在路径规划或导航中考虑成本计算(false)
nhPrivate.getParam("pointPerPathThre", pointPerPathThre);//每条路径需要有几个被遮挡的点(每条路径上需要有多少个点被视为被遮挡或阻塞的阈值,大于pointPerPathThre被视为障碍?)
nhPrivate.getParam("minRelZ", minRelZ);//未使用地面分割时,裁剪点云时的最小高度,可以用于过滤掉过低的点,可能对于避免地面噪声很有用
nhPrivate.getParam("maxRelZ", maxRelZ);//未使用地面分割时,裁剪点云时的最大高度
nhPrivate.getParam("maxSpeed", maxSpeed);//最大速度
nhPrivate.getParam("dirWeight", dirWeight);//计算得分时转向角度的权重,用来评估转向的难度或代价,更高的权重意味着转向的影响在总体评估中占据更重要的地位
nhPrivate.getParam("dirThre", dirThre);//最大转向角
nhPrivate.getParam("dirToVehicle", dirToVehicle);//是否以车辆为主方向计算被遮挡的路径(false)。转向决策是否主要基于车辆的当前朝向,如果设置为false,路径规划可能不会主要考虑车辆的当前朝向,以目标点的方向计算附近方向的路径,不考虑车辆的转弯半径的约束,可以直接转向目标点前进。这可能使得车辆在选择路径时更加灵活
nhPrivate.getParam("pathScale", pathScale);//路径尺度(路径的大小或长度与某个参考值(如车辆尺寸或环境尺寸)的比例关系),在狭窄的空间中减小路径规模,或在开放的空间中增加路径规模以优化行进路线
nhPrivate.getParam("minPathScale", minPathScale);//最小路径尺度,这个参数确保路径不会因为缩放而变得太小
nhPrivate.getParam("pathScaleStep", pathScaleStep);//路径尺度的调整步长,对pathScale逐步细调路径的尺度
nhPrivate.getParam("pathScaleBySpeed", pathScaleBySpeed);//是否根据速度调整路径尺度(true)
nhPrivate.getParam("minPathRange", minPathRange);//路径规划时要考虑的最小有效范围或距离
nhPrivate.getParam("pathRangeStep", pathRangeStep);//路径范围的调整步长。用于定义当需要增加或减少路径的考虑范围时,每次调整的大小
nhPrivate.getParam("pathRangeBySpeed", pathRangeBySpeed);//是否根据速度调整路径的范围(true)
nhPrivate.getParam("pathCropByGoal", pathCropByGoal);//(true)只考虑目标点+goalClearRange范围内的点云。特别是当目标点附近的区域包含重要的导航信息时(如障碍物、通道等),使用pathCropByGoal可以提高路径规划的质量。
nhPrivate.getParam("autonomyMode", autonomyMode);//是否处于完全自主导航模式(true)
nhPrivate.getParam("autonomySpeed", autonomySpeed);//定义了在自主模式下机器人或车辆的默认或期望行驶速度。
nhPrivate.getParam("joyToSpeedDelay", joyToSpeedDelay);//从接收遥控器指令到机器人或车辆调整其速度的时间延迟
nhPrivate.getParam("joyToCheckObstacleDelay", joyToCheckObstacleDelay);//遥控器发出指令和系统开始检测障碍物之间的时间延迟(导航手动切换)。这有助于管理遥控器输入与自动障碍物检测系统之间的交互
nhPrivate.getParam("goalClearRange", goalClearRange);//当 pathCropByGoal = true 时,点云距离超过目标点+该值则不被处理
nhPrivate.getParam("goalX", goalX);//局部路径目标点x(0)
nhPrivate.getParam("goalY", goalY);//局部路径目标点y(0)
//设置订阅话题
ros::Subscriber subOdometry = nh.subscribe<nav_msgs::Odometry>//当接收到/state_estimation话题消息更新时启动odometryHandler回调函数 (消息格式:nav_msgs::Odometry消息内容:关于机器人或车辆的位置和方向(姿态)信息)
("/state_estimation", 5, odometryHandler);//odometryHandler是当接收到新的里程计消息时调用的回调函数,更新机器人姿态
ros::Subscriber subLaserCloud = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>
("/registered_scan", 5, laserCloudHandler);//laserCloudHandler是registered_scan话题回调函数,通过裁剪点云时的距离adjacentRange(车辆周围用于检测障碍物的区域大小),对点云进行裁减并进一步通过体素网格降采样
ros::Subscriber subTerrainCloud = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>//terrain_map话题由terrainAnalysis节点发布(.cpp)
("/terrain_map", 5, terrainCloudHandler);//terrainCloudHandler地形分析,裁减与障碍物相关点云,并进行降采用
ros::Subscriber subJoystick = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::Joy> ("/joy", 5, joystickHandler);//joystickHandler回调,解析从游戏手柄传入的数据,并据此更新车辆控制和导航状态
ros::Subscriber subGoal = nh.subscribe<geometry_msgs::PointStamped> ("/way_point", 5, goalHandler);//订阅way_point话题,更新局部目标点坐标
ros::Subscriber subSpeed = nh.subscribe<std_msgs::Float32> ("/speed", 5, speedHandler);//在自主模式下根据接收到手柄的速度消息调整机器人的速度
ros::Subscriber subBoundary = nh.subscribe<geometry_msgs::PolygonStamped> ("/navigation_boundary", 5, boundaryHandler);//通过在边界多边形的每两个顶点之间插入额外的点来创建一个密集的边界点云
ros::Subscriber subAddedObstacles = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2> ("/added_obstacles", 5, addedObstaclesHandler);//用于处理附加障碍物点云(动态障碍物,以强度区别)
ros::Subscriber subCheckObstacle = nh.subscribe<std_msgs::Bool> ("/check_obstacle", 5, checkObstacleHandler);//自主导航时根据消息checkObs动态调整是否进行障碍物检测
ros::Publisher pubPath = nh.advertise<nav_msgs::Path> ("/path", 5);//发布路径话题,话题数据对象是pubPath
nav_msgs::Path path;
#if PLOTPATHSET == 1
ros::Publisher pubFreePaths = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2> ("/free_paths", 2);//发布可视化路径
#endif
//ros::Publisher pubLaserCloud = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2> ("/stacked_scans", 2);
printf ("\nReading path files.\n");
if (autonomyMode) {
joySpeed = autonomySpeed / maxSpeed;
if (joySpeed < 0) joySpeed = 0;
else if (joySpeed > 1.0) joySpeed = 1.0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudStackNum; i++) {//laserCloudStackNum堆栈的大小
laserCloudStack[i].reset(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < groupNum; i++) {
startPaths[i].reset(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>());//reset随后使paths[i]指向一个新创建的pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>对象(清空数组原来数据?)
}
#if PLOTPATHSET == 1
for (int i = 0; i < pathNum; i++) {
paths[i].reset(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>());
}
#endif
for (int i = 0; i < gridVoxelNum; i++) {//表示网格体素的总数
correspondences[i].resize(0);//初始化了一个名为correspondences的数组,这个数组中的每个元素都是一个向量,用于存储网格体素与路径之间的对应关系
}
laserDwzFilter.setLeafSize(laserVoxelSize, laserVoxelSize, laserVoxelSize);//laserDwzFilter是pcl::VoxelGrid过滤器对象,它们用于对点云数据进行下采样,setLeafSize方法是用来设置体素网格的大小
terrainDwzFilter.setLeafSize(terrainVoxelSize, terrainVoxelSize, terrainVoxelSize);
//通过path文件夹中的相关文件,读取对应的路径点
readStartPaths();//通过.ply文件读取第一次采样的路径(路径开始点?)(离线路径)
#if PLOTPATHSET == 1
readPaths();//读取一系列预定义的路径或路径选项
#endif
readPathList();//每条路径最后一个点的路径(离线文件)
readCorrespondences();//路径点path_id和碰撞体素网格的索引关系
printf ("\nInitialization complete.\n\n");
//以下为输入数据处理
ros::Rate rate(100);
bool status = ros::ok();
while (status) {
ros::spinOnce();
if (newLaserCloud || newTerrainCloud) {//如果有新的激光或地形点云数据到达(经过点云的裁减,体素降采用)
if (newLaserCloud) {
newLaserCloud = false;//将标志位重置,表示当前批次的数据正在处理
laserCloudStack[laserCloudCount]->clear();//清空当前索引的点云堆栈,laserCloudCount当前堆栈序列索引
*laserCloudStack[laserCloudCount] = *laserCloudDwz;;//将降采样的激光点云 (laserCloudDwz) 存储到该位置。
//laserCloudStackNum表示点云堆栈的大小(堆栈一共可以存储laserCloudStackNum个点云)
laserCloudCount = (laserCloudCount + 1) % laserCloudStackNum;//%取余:当 laserCloudCount 达到 laserCloudStackNum(堆栈大小)时,它会自动回绕到 0,堆栈的开始处覆盖最早的数据。
plannerCloud->clear();// 清空规划用的点云
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudStackNum; i++) {//遍历堆栈的尺寸
*plannerCloud += *laserCloudStack[i];//将降采用后的点云添加到路径规划点云(plannerCloud)中
}
}
if (newTerrainCloud) {
newTerrainCloud = false;
plannerCloud->clear();
*plannerCloud = *terrainCloudDwz;//将滤波后的的地形点云(障碍)(terrainCloudDwz) 存储到其中
}
//对roll,pitch,yaw角处理,获得对应的sin和cos值
float sinVehicleRoll = sin(vehicleRoll);
float cosVehicleRoll = cos(vehicleRoll);
float sinVehiclePitch = sin(vehiclePitch);
float cosVehiclePitch = cos(vehiclePitch);
float sinVehicleYaw = sin(vehicleYaw);//车辆yaw角是相对map坐标系的角度
float cosVehicleYaw = cos(vehicleYaw);
//在仿真中,点云信息输出的坐标系是map全局坐标系。对于实际的车辆而言,点云数据进行标定之后就将点云坐标系直接转变为车辆坐标系,所以这部分内容需要删改
//所用到的局部路径目标点都是在base_link下的,所以对所有的map点云信息都旋转变换到base_link车体坐标系下
//在实际的获得激光雷达的数据中,不需要转换
pcl::PointXYZI point;
plannerCloudCrop->clear();
int plannerCloudSize = plannerCloud->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < plannerCloudSize; i++) {//plannerCloud是经过上述裁减和降采样后的所有点云
float pointX1 = plannerCloud->points[i].x - vehicleX;//以车辆的当前位置(vehicleX)为原点,重新构建其他点的相对坐标系位置
float pointY1 = plannerCloud->points[i].y - vehicleY;
float pointZ1 = plannerCloud->points[i].z - vehicleZ;
point.x = pointX1 * cosVehicleYaw + pointY1 * sinVehicleYaw;
point.y = -pointX1 * sinVehicleYaw + pointY1 * cosVehicleYaw;
point.z = pointZ1;
point.intensity = plannerCloud->points[i].intensity;//plannerCloudSize数据带intensity障碍物高度
float dis = sqrt(point.x * point.x + point.y * point.y);
if (dis < adjacentRange && ((point.z > minRelZ && point.z < maxRelZ) || useTerrainAnalysis)) {//点云裁减
plannerCloudCrop->push_back(point);//将在小于车体adjacentRange距离范围和障碍物和地面间的点存入导航路径点云plannerCloudCrop
}
}
//处理边界点云数据,目的是将边界点云从其原始坐标系转换到车辆的局部坐标系中,并对其进行筛选(同上)
int boundaryCloudSize = boundaryCloud->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < boundaryCloudSize; i++) {
point.x = ((boundaryCloud->points[i].x - vehicleX) * cosVehicleYaw
+ (boundaryCloud->points[i].y - vehicleY) * sinVehicleYaw);
point.y = (-(boundaryCloud->points[i].x - vehicleX) * sinVehicleYaw
+ (boundaryCloud->points[i].y - vehicleY) * cosVehicleYaw);
point.z = boundaryCloud->points[i].z;
point.intensity = boundaryCloud->points[i].intensity;
float dis = sqrt(point.x * point.x + point.y * point.y);
if (dis < adjacentRange) {
plannerCloudCrop->push_back(point);
}
}
//将 addedObstacles点云(动态障碍物)中的每个点转换到车辆的局部坐标系中,并且只保留那些在车辆周围一定范围(adjacentRange)内的点
int addedObstaclesSize = addedObstacles->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < addedObstaclesSize; i++) {
point.x = ((addedObstacles->points[i].x - vehicleX) * cosVehicleYaw
+ (addedObstacles->points[i].y - vehicleY) * sinVehicleYaw);
point.y = (-(addedObstacles->points[i].x - vehicleX) * sinVehicleYaw
+ (addedObstacles->points[i].y - vehicleY) * cosVehicleYaw);
point.z = addedObstacles->points[i].z;
point.intensity = addedObstacles->points[i].intensity;
float dis = sqrt(point.x * point.x + point.y * point.y);
if (dis < adjacentRange) {
plannerCloudCrop->push_back(point);
}
}
float pathRange = adjacentRange;// 设置了点云探索的边界值
if (pathRangeBySpeed) pathRange = adjacentRange * joySpeed;
if (pathRange < minPathRange) pathRange = minPathRange;
float relativeGoalDis = adjacentRange;// 将点云探索的边界值赋予相对的目标距离
//自动模式下,计算目标点(map)在base_link下的坐标,并计算和限制车辆到目标点的转角
if (autonomyMode) {
float relativeGoalX = ((goalX - vehicleX) * cosVehicleYaw + (goalY - vehicleY) * sinVehicleYaw);
float relativeGoalY = (-(goalX - vehicleX) * sinVehicleYaw + (goalY - vehicleY) * cosVehicleYaw);
relativeGoalDis = sqrt(relativeGoalX * relativeGoalX + relativeGoalY * relativeGoalY);//计算车辆当前位置到目标点的相对距离。
joyDir = atan2(relativeGoalY, relativeGoalX) * 180 / PI;//计算出车辆到目标点的角度(与x轴正方向的角度)
if (!twoWayDrive) {//如果非双向导航,限制向目标点转角最大为90度(始终保持向前或向后)
if (joyDir > 90.0) joyDir = 90.0;
else if (joyDir < -90.0) joyDir = -90.0;
}
}
bool pathFound = false;//用来指示是否找到了有效路径。它的初始值设置为 false,表示还没有找到路径
float defPathScale = pathScale;//设置路宽pathScale
if (pathScaleBySpeed) pathScale = defPathScale * joySpeed;//动态路宽(速度控制)
if (pathScale < minPathScale) pathScale = minPathScale;
//以下为通过点云信息确定路径上是否存在障碍物??
while (pathScale >= minPathScale && pathRange >= minPathRange) {//该点云是在车辆检测范围内的话
//初始化clearPathList,pathPenaltyList,clearPathPerGroupScore树组
for (int i = 0; i < 36 * pathNum; i++) {//pathNum路径点个数,对于每个点,考虑36个可能的转向方向(rotDir),每个方向对应10度的旋转
clearPathList[i] = 0;//存储每条路径上的障碍物数量
pathPenaltyList[i] = 0;//记录给定方向上路径的惩罚得分
}
for (int i = 0; i < 36 * groupNum; i++) {//groupNum路径组数
clearPathPerGroupScore[i] = 0;//clearPathPerGroupScore每个路径组的得分
}
float minObsAngCW = -180.0;
float minObsAngCCW = 180.0;//逆时针旋转角度赋初始值(最大的逆时针转向角度)
float diameter = sqrt(vehicleLength / 2.0 * vehicleLength / 2.0 + vehicleWidth / 2.0 * vehicleWidth / 2.0);//计算车辆对角线长度用于判断障碍物是否在车辆的转向路径内
float angOffset = atan2(vehicleWidth, vehicleLength) * 180.0 / PI;//angOffset 是车辆对角线与车辆前进方向之间的角度差,帮助计算出这个转弯动作是否会导致车辆的任何部分与障碍物碰撞
int plannerCloudCropSize = plannerCloudCrop->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < plannerCloudCropSize; i++) {
float x = plannerCloudCrop->points[i].x / pathScale;//归一化,尺度调整通常用于在不同级别的精度下处理点云数据,
float y = plannerCloudCrop->points[i].y / pathScale;
float h = plannerCloudCrop->points[i].intensity;//点云高度
float dis = sqrt(x * x + y * y);//点云到车的距离
//判断点云中的某个点是否应该被考虑在路径规划中,如果符合条件则继续处理
//判断条件:1.小于路径宽度(点云在车辆检测范围内)2.代检测点到车辆距离dis小于车到目标点距离(离目标太远无意义) 3.启动障碍物检测的点
if (dis < pathRange / pathScale && (dis <= (relativeGoalDis + goalClearRange) / pathScale || !pathCropByGoal) && checkObstacle) {
for (int rotDir = 0; rotDir < 36; rotDir++) {//36个方向
float rotAng = (10.0 * rotDir - 180.0) * PI / 180;//每个转向方向(当前位置转到路径点位置角度),计算其对应的旋转角度(rotAng),将度数转换为弧度
float angDiff = fabs(joyDir - (10.0 * rotDir - 180.0));//计算的是车辆朝目标点(joyDir)与每个可能转向方向之间的角度差
if (angDiff > 180.0) {//将角度差规范化到180度以内
angDiff = 360.0 - angDiff;
}
//决定了哪些转向方向应该被考虑
//在路径选择不考虑车辆的当前方向(!dirToVehicle)情况下,如果去的路径点角度和目标角度差超过了设定阈值(dirThre=90),则该方向被忽略
//如果路径选择考虑车辆的当前方向(dirToVehicle),且车辆朝目标点角度joyDir在-90到90之间,但转向路径点方向超出了阈值,则该方向被忽略。
//对于车辆转向路径方向超出正负90度的情况,忽略该方向
if ((angDiff > dirThre && !dirToVehicle) || (fabs(10.0 * rotDir - 180.0) > dirThre && fabs(joyDir) <= 90.0 && dirToVehicle) ||
((10.0 * rotDir > dirThre && 360.0 - 10.0 * rotDir > dirThre) && fabs(joyDir) > 90.0 && dirToVehicle)) {
continue;
}
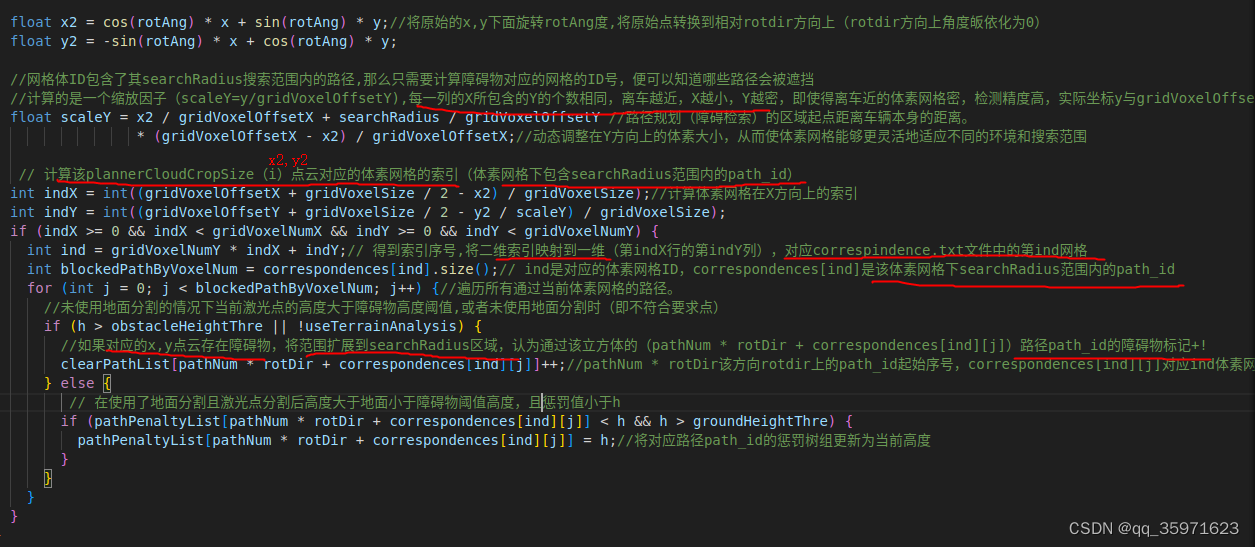
float x2 = cos(rotAng) * x + sin(rotAng) * y;//将原始的x,y下面旋转rotAng度,将原始点转换到相对rotdir方向上(rotdir方向上角度皈依化为0)
float y2 = -sin(rotAng) * x + cos(rotAng) * y;
//网格体ID包含了其searchRadius搜索范围内的路径,那么只需要计算障碍物对应的网格的ID号,便可以知道哪些路径会被遮挡
//计算的是一个缩放因子(scaleY=y/gridVoxelOffsetY),每一列的X所包含的Y的个数相同,离车越近,X越小,Y越密,即使得离车近的体素网格密,检测精度高,实际坐标y与gridVoxelOffsetY的相似三角形比例
float scaleY = x2 / gridVoxelOffsetX + searchRadius / gridVoxelOffsetY //路径规划(障碍检索)的区域起点距离车辆本身的距离。
* (gridVoxelOffsetX - x2) / gridVoxelOffsetX;//动态调整在Y方向上的体素大小,从而使体素网格能够更灵活地适应不同的环境和搜索范围
// 计算该plannerCloudCropSize(i)点云对应的体素网格的索引(体素网格下包含searchRadius范围内的path_id)
int indX = int((gridVoxelOffsetX + gridVoxelSize / 2 - x2) / gridVoxelSize);//计算体素网格在X方向上的索引
int indY = int((gridVoxelOffsetY + gridVoxelSize / 2 - y2 / scaleY) / gridVoxelSize);
if (indX >= 0 && indX < gridVoxelNumX && indY >= 0 && indY < gridVoxelNumY) {
int ind = gridVoxelNumY * indX + indY;// 得到索引序号,将二维索引映射到一维(第indX行的第indY列),对应correspindence.txt文件中的第ind网格
int blockedPathByVoxelNum = correspondences[ind].size();// ind是对应的体素网格ID,correspondences[ind]是该体素网格下searchRadius范围内的path_id
for (int j = 0; j < blockedPathByVoxelNum; j++) {//遍历所有通过当前体素网格的路径。
//未使用地面分割的情况下当前激光点的高度大于障碍物高度阈值,或者未使用地面分割时(即不符合要求点)
if (h > obstacleHeightThre || !useTerrainAnalysis) {
//如果对应的x,y点云存在障碍物,将范围扩展到searchRadius区域,认为通过该立方体的(pathNum * rotDir + correspondences[ind][j])路径path_id的障碍物标记+!
clearPathList[pathNum * rotDir + correspondences[ind][j]]++;//pathNum * rotDir该方向rotdir上的path_id起始序号,correspondences[ind][j]对应ind体素网格下第j个位置俄path_id索引
} else {
// 在使用了地面分割且激光点分割后高度大于地面小于障碍物阈值高度,且惩罚值小于h
if (pathPenaltyList[pathNum * rotDir + correspondences[ind][j]] < h && h > groundHeightThre) {
pathPenaltyList[pathNum * rotDir + correspondences[ind][j]] = h;//将对应路径path_id的惩罚树组更新为当前高度
}
}
}
}
}
}
//障碍物不在前面而是在侧面,转向的过程中可能会碰撞
//判断是否存在这种点云,: 判断点云到车辆的距离是否小于车辆转弯直径 ,但点云不在车体内部, 并且h超过了障碍物阈值(障碍物)(if的前三个条件)
if (dis < diameter / pathScale && (fabs(x) > vehicleLength / pathScale / 2.0 || fabs(y) > vehicleWidth / pathScale / 2.0) &&
(h > obstacleHeightThre || !useTerrainAnalysis) && checkRotObstacle) {
float angObs = atan2(y, x) * 180.0 / PI;// 点云的方向
if (angObs > 0) {// 左边
if (minObsAngCCW > angObs - angOffset) minObsAngCCW = angObs - angOffset;//记录的逆时针方向上的最近障碍物角度(点云角度-车辆角度偏移量)
if (minObsAngCW < angObs + angOffset - 180.0) minObsAngCW = angObs + angOffset - 180.0;
} else {// 右边
if (minObsAngCW < angObs + angOffset) minObsAngCW = angObs + angOffset;
if (minObsAngCCW > 180.0 + angObs - angOffset) minObsAngCCW = 180.0 + angObs - angOffset;
}
}
}
//防止转弯碰撞
if (minObsAngCW > 0) minObsAngCW = 0;//顺时针方向上最近障碍物的角度范围大于0,说明车辆在右侧有障碍物,为了避免碰撞,将最近障碍物的角度范围设为0
if (minObsAngCCW < 0) minObsAngCCW = 0;
//路径得分计算??
for (int i = 0; i < 36 * pathNum; i++) {//遍历36个方向(rotDir)中的每一条路径
int rotDir = int(i / pathNum);//第几个方向
float angDiff = fabs(joyDir - (10.0 * rotDir - 180.0));///计算的是车辆朝目标点(joyDir)与每个可能转向方向(10.0 * rotDir - 180,)之间的角度差
if (angDiff > 180.0) {
angDiff = 360.0 - angDiff;//归一化到0-180
}
//决定了哪些转向方向应该被忽略
//在路径选择不考虑车辆的当前方向(!dirToVehicle)情况下,如果去的路径点角度和目标角度差超过了设定阈值(dirThre=90),则该方向被忽略
//如果路径选择考虑车辆的当前方向(dirToVehicle),且车辆朝目标点角度joyDir在-90到90之间,但转向路径点方向超出了阈值(车体朝向不能改变),则该方向被忽略。
//对于车辆转向路径方向超出正负90度的情况,忽略该方向
if ((angDiff > dirThre && !dirToVehicle) || (fabs(10.0 * rotDir - 180.0) > dirThre && fabs(joyDir) <= 90.0 && dirToVehicle) ||
((10.0 * rotDir > dirThre && 360.0 - 10.0 * rotDir > dirThre) && fabs(joyDir) > 90.0 && dirToVehicle)) {
continue;
}
//检查路径上的障碍物数量低于阈值时,计算路径得分的具体过程
if (clearPathList[i] < pointPerPathThre) {//路径的障碍物数量是否低于阈值 pointPerPathThre
float penaltyScore = 1.0 - pathPenaltyList[i] / costHeightThre;//计算惩罚的分,penaltyScore越接近1越好(惩罚小)
if (penaltyScore < costScore) penaltyScore = costScore;//如果惩罚分数低于设定的最小分数 costScore,则将其设为最小分数
//dirDiff该条路径与目标点之间的角度差值,(因为endDirPathList[i % pathNum]0-343包含在某一朝向rotdir内,要再减去(10.0 * rotDir - 180.0))
float dirDiff = fabs(joyDir - endDirPathList[i % pathNum] - (10.0 * rotDir - 180.0));
if (dirDiff > 360.0) {
dirDiff -= 360.0;
}
if (dirDiff > 180.0) {
dirDiff = 360.0 - dirDiff;
}
float rotDirW;//9是y轴负方向,27是y轴正方向,rotDirW代表了该条路径的方向与当前车辆朝向的角度差
if (rotDir < 18) rotDirW = fabs(fabs(rotDir - 9) + 1);
else rotDirW = fabs(fabs(rotDir - 27) + 1);
//该目标函数考虑机器人的转角和障碍物高度
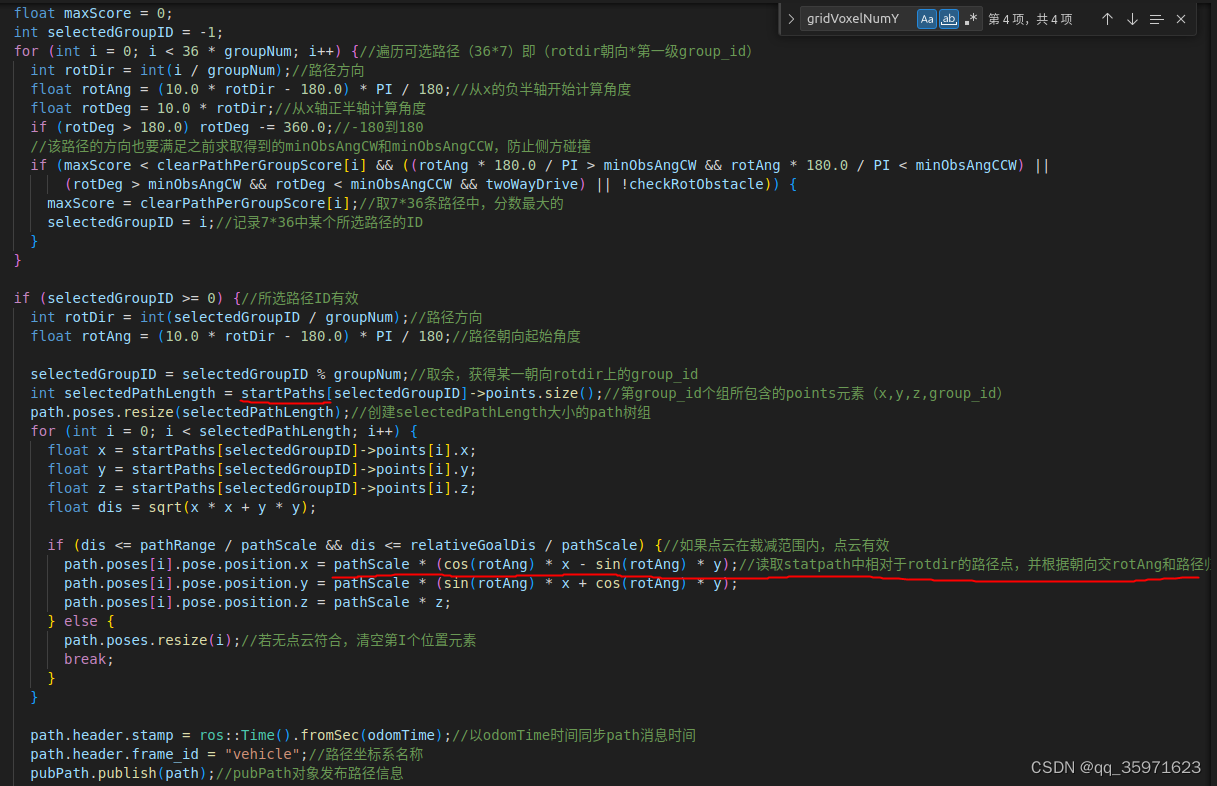
float score = (1 - sqrt(sqrt(dirWeight * dirDiff))) * rotDirW * rotDirW * rotDirW * rotDirW * penaltyScore;
if (score > 0) {
//将所有path_id下的分数加到对应path_id下的groupid中,用于选择对应rotdir的groupid(确定第一级路径)
//定位到特定路径组groupid,groupNum * rotDir是该方向上的groupid起始序号,pathList[i % pathNum]]0-343该条路径对应的groupid(0-7)中的一个
clearPathPerGroupScore[groupNum * rotDir + pathList[i % pathNum]] += score;//i % pathNum=(取余0-343)对应path_id序号,pathList获得对应path_id的第一级groupid
}
}
}
float maxScore = 0;
int selectedGroupID = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < 36 * groupNum; i++) {//遍历可选路径(36*7)即(rotdir朝向*第一级group_id)
int rotDir = int(i / groupNum);//路径方向
float rotAng = (10.0 * rotDir - 180.0) * PI / 180;//从x的负半轴开始计算角度
float rotDeg = 10.0 * rotDir;//从x轴正半轴计算角度
if (rotDeg > 180.0) rotDeg -= 360.0;//-180到180
//该路径的方向也要满足之前求取得到的minObsAngCW和minObsAngCCW,防止侧方碰撞
if (maxScore < clearPathPerGroupScore[i] && ((rotAng * 180.0 / PI > minObsAngCW && rotAng * 180.0 / PI < minObsAngCCW) ||
(rotDeg > minObsAngCW && rotDeg < minObsAngCCW && twoWayDrive) || !checkRotObstacle)) {
maxScore = clearPathPerGroupScore[i];//取7*36条路径中,分数最大的
selectedGroupID = i;//记录7*36中某个所选路径的ID
}
}
if (selectedGroupID >= 0) {//所选路径ID有效
int rotDir = int(selectedGroupID / groupNum);//路径方向
float rotAng = (10.0 * rotDir - 180.0) * PI / 180;//路径朝向起始角度
selectedGroupID = selectedGroupID % groupNum;//取余,获得某一朝向rotdir上的group_id
int selectedPathLength = startPaths[selectedGroupID]->points.size();//第group_id个组所包含的points元素(x,y,z,group_id)
path.poses.resize(selectedPathLength);//创建selectedPathLength大小的path树组
for (int i = 0; i < selectedPathLength; i++) {
float x = startPaths[selectedGroupID]->points[i].x;
float y = startPaths[selectedGroupID]->points[i].y;
float z = startPaths[selectedGroupID]->points[i].z;
float dis = sqrt(x * x + y * y);
if (dis <= pathRange / pathScale && dis <= relativeGoalDis / pathScale) {//如果点云在裁减范围内,点云有效
path.poses[i].pose.position.x = pathScale * (cos(rotAng) * x - sin(rotAng) * y);//读取statpath中相对于rotdir的路径点,并根据朝向交rotAng和路径归一化尺寸pathScale,得到相对于车体坐标系的路径坐标
path.poses[i].pose.position.y = pathScale * (sin(rotAng) * x + cos(rotAng) * y);
path.poses[i].pose.position.z = pathScale * z;
} else {
path.poses.resize(i);//若无点云符合,清空第I个位置元素
break;
}
}
path.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(odomTime);//以odomTime时间同步path消息时间
path.header.frame_id = "vehicle";//路径坐标系名称
pubPath.publish(path);//pubPath对象发布路径信息
//用于生成无碰撞路径freePaths
#if PLOTPATHSET == 1
freePaths->clear();
for (int i = 0; i < 36 * pathNum; i++) {//遍历可选路径(36*7)即(rotdir朝向*第一级group_id)
int rotDir = int(i / pathNum);
float rotAng = (10.0 * rotDir - 180.0) * PI / 180;
float rotDeg = 10.0 * rotDir;
if (rotDeg > 180.0) rotDeg -= 360.0;
float angDiff = fabs(joyDir - (10.0 * rotDir - 180.0));//目标方向(joyDir)与路径方向(10.0 * rotDir - 180.0)之间的绝对角度差,
if (angDiff > 180.0) {
angDiff = 360.0 - angDiff;
}
//忽略不符合条件的路径
//在路径选择不考虑车辆的当前方向(!dirToVehicle)情况下,如果去的路径点角度和目标角度差超过了设定阈值(dirThre=90),则该方向被忽略
//如果路径选择考虑车辆的当前方向(dirToVehicle),且车辆朝目标点角度joyDir在-90到90之间,但转向路径点方向超出了阈值(车体朝向不能改变),则该方向被忽略。
//对于车辆转向路径方向超出正负90度的情况,忽略该方向
if ((angDiff > dirThre && !dirToVehicle) || (fabs(10.0 * rotDir - 180.0) > dirThre && fabs(joyDir) <= 90.0 && dirToVehicle) ||
((10.0 * rotDir > dirThre && 360.0 - 10.0 * rotDir > dirThre) && fabs(joyDir) > 90.0 && dirToVehicle) ||
//minObsAngCW瞬时针允许非碰撞旋转的角度
!((rotAng * 180.0 / PI > minObsAngCW && rotAng * 180.0 / PI < minObsAngCCW) ||
(rotDeg > minObsAngCW && rotDeg < minObsAngCCW && twoWayDrive) || !checkRotObstacle)) {
continue;
}
if (clearPathList[i] < pointPerPathThre) {//clearPathList路径障碍物个树,路径点障碍物个树小于阈值2
int freePathLength = paths[i % pathNum]->points.size();//某rotdir方向,paths[i % pathNum]]该条路径对应的7个groupid中的一个
for (int j = 0; j < freePathLength; j++) {
point = paths[i % pathNum]->points[j];
float x = point.x;
float y = point.y;
float z = point.z;
float dis = sqrt(x * x + y * y);
if (dis <= pathRange / pathScale && (dis <= (relativeGoalDis + goalClearRange) / pathScale || !pathCropByGoal)) {
point.x = pathScale * (cos(rotAng) * x - sin(rotAng) * y);//将path文件中相对于rotdir下的路径转换为车体坐标系下
point.y = pathScale * (sin(rotAng) * x + cos(rotAng) * y);
point.z = pathScale * z;
point.intensity = 1.0;
freePaths->push_back(point);//可视化路径树组
}
}
}
}
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 freePaths2;
pcl::toROSMsg(*freePaths, freePaths2);// 将来自点云库(Point Cloud Library,PCL)格式的点云转换为ROS(机器人操作系统)消息格式
freePaths2.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(odomTime);
freePaths2.header.frame_id = "vehicle";
pubFreePaths.publish(freePaths2);//发布无碰撞路线消息
#endif
}
if (selectedGroupID < 0) {//如果未找到有效路径
if (pathScale >= minPathScale + pathScaleStep) {//扩大路径搜索范围
pathScale -= pathScaleStep;
pathRange = adjacentRange * pathScale / defPathScale;
} else {
pathRange -= pathRangeStep;
}
} else {
pathFound = true;
break;
}
}
pathScale = defPathScale;
if (!pathFound) {//在结束所有遍历后如果未找到路径
path.poses.resize(1);
path.poses[0].pose.position.x = 0;
path.poses[0].pose.position.y = 0;
path.poses[0].pose.position.z = 0;
path.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(odomTime);
path.header.frame_id = "vehicle";
pubPath.publish(path);
#if PLOTPATHSET == 1
freePaths->clear();
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 freePaths2;
pcl::toROSMsg(*freePaths, freePaths2);
freePaths2.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(odomTime);
freePaths2.header.frame_id = "vehicle";
pubFreePaths.publish(freePaths2);
#endif
}
/*sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 plannerCloud2;
pcl::toROSMsg(*plannerCloudCrop, plannerCloud2);
plannerCloud2.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(odomTime);
plannerCloud2.header.frame_id = "vehicle";
pubLaserCloud.publish(plannerCloud2);*/
}
status = ros::ok();
rate.sleep();
}
return 0;
}