SpringBoot概述
Spring Boot是Spring提供的一个子项目,用于快速构建Spring应用程序
传统方式构建Spring应用程序
导入依赖繁琐

项目配置繁琐

为了简化如此繁琐的配置流程,SpringBoot这一子项目提供了如下特性
SpringBoot特性
起步依赖
本质上就是一个Maven坐标,整合了完成一个功能所需要的所有坐标
自动配置
遵循约定大于配置的原则,再boot程序启动后,一些Bean对象会自动注入到IOC容器,不需要手动声明,简化开发
其他特性
内嵌的Tomcat、Jetty(无需部署WAR文件)
外部化配置
不需要XML配置(properties/yml)
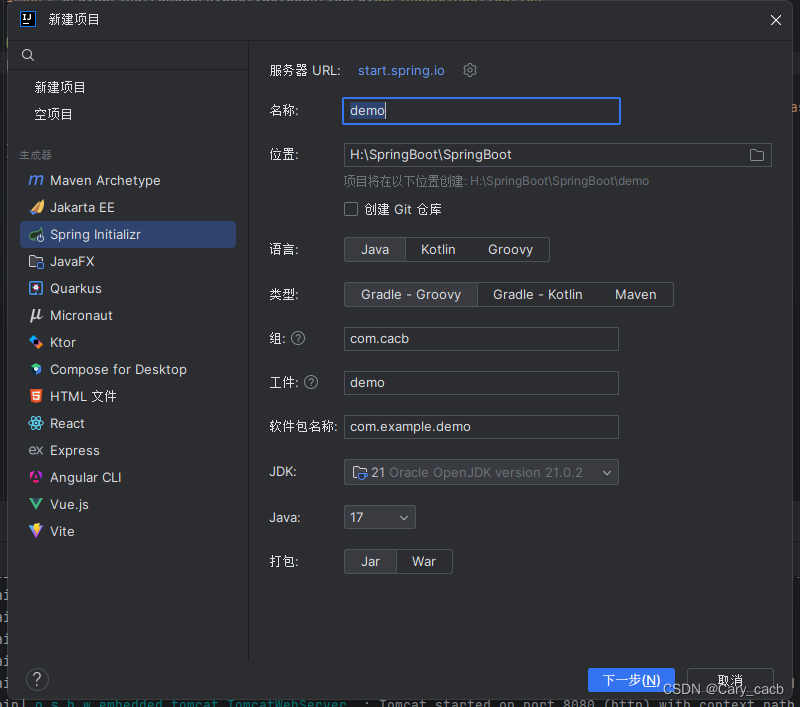
IDEA创建SpringBoot工程步骤
第一步、创建Maven工程
第二步、导入spring-boot-stater-web起步依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>第三步、编写Controller
以我用于测试的hellocontroller为例
@RestController
public class helloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
System.out.println("hello");
return "hello";
}
}
第四步、提供启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootQsDemo1Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootQsDemo1Application.class, args);
}
}
手动创建SpringBoot工程
第一步、创建Maven工程

第二步、引入依赖
继承parent工程
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.2.2</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>引入相应起步依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>第三步、提供启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootQsDemo1Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootQsDemo1Application.class, args);
}
}
SpringBoot 配置文件
properties配置文件
application.properties
以配置端口和访问路径为例
server.port=8080
server.servlet.context-path=/start
yaml配置文件
application.yml / application.yaml
同上例
server:
servlet:
context-path: /start2
port: 8282在实际开发中,更常用的是yaml配置文件
yaml层级表示更加明显
yml配置信息书写与获取
书写
第一种、三方技术配置信息
第二种、自定义配置信息
例如,如果我们在类中要调用email.username,email.code,email.host这三个值
在配置文件中就应该进行如下书写
application.properties
email.user=Cary_cacb
email.code=dawdawdadawd
email.host=smtp.qq.comapplication.yml / application.yaml
email:
user: Cary_cacb
code: awdawdawd
host: smtp.qq.com yml书写注意事项:
值前边必须有空格,作为分隔符
使用空格作为缩进表示层级关系,相同的层级左对齐
获取
以上面配置的三个键为例
在实体类中进行如下书写
@Value("${email.user}")
private String user;
@Value("${email.code}")
private String code;
@Value("${email.host}")
private String host;还可以使用@ConfigurationProperties()注解来完成
沿用上例
在实体类中进行如下书写
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "email")
@Component
public class EmailController {
private String user;
private String code;
private String host;
}注意事项:该注解中的perfix必须与配置未见中的前缀名一致
类内部的成员变量名与配置文件中的键名也要保持一致
SpringBoot 整合Mybatis
第一步、导入mybatis和mysql相关坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.3</version>
</dependency>第二步、配置application.yml配置文件
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/cary_cacb
username: root
password: psw第三步、书写相关文件,实现调用
以之前用过的tbl_book表为例
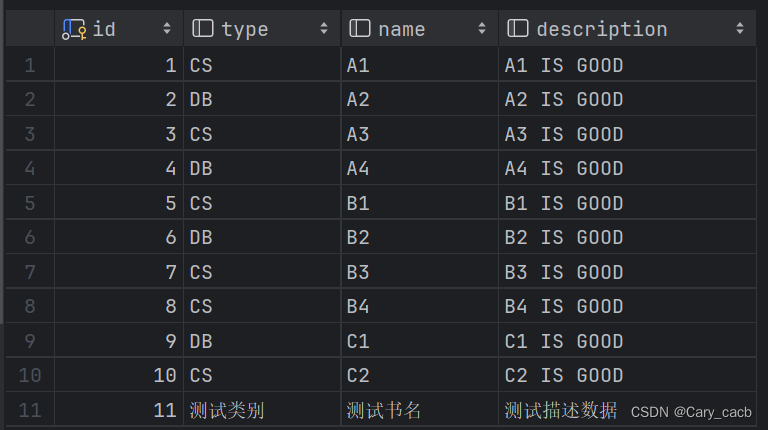
1、给出Book实体类
package com.cacb.springboot_mybatis.pojo;
public class Book {
private Integer id ;
private String type;
private String name;
private String description;
public Book(Integer id, String type, String name, String description) {
this.id = id;
this.type = type;
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"id=" + id +
", type='" + type + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", description='" + description + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
2、BookMapper
@Mapper
public interface BookMapper {
@Select("select * from tbl_book where id = #{id}")
public Book getByID(Integer id);
}
3、service层
public interface BookService {
public Book getByID(Integer id);
}
4、serviceimpl
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
@Autowired
private BookMapper bookMapper;
@Override
public Book getByID(Integer id) {
return bookMapper.getByID(id);
}
}5、controller
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
@RequestMapping("getByID")
public Book getByID(Integer id){
return bookService.getByID(id);
}
}使用测试软件测试结果如下:
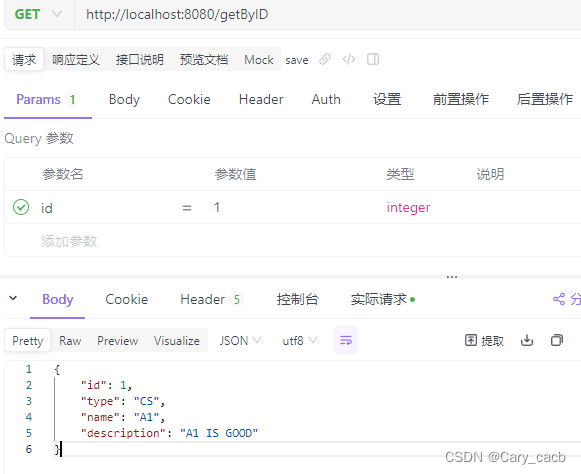



![[力扣 Hot100]Day20 旋转图像](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/c286c3e66fb64dd9be08f15b7f2f59a5.png)