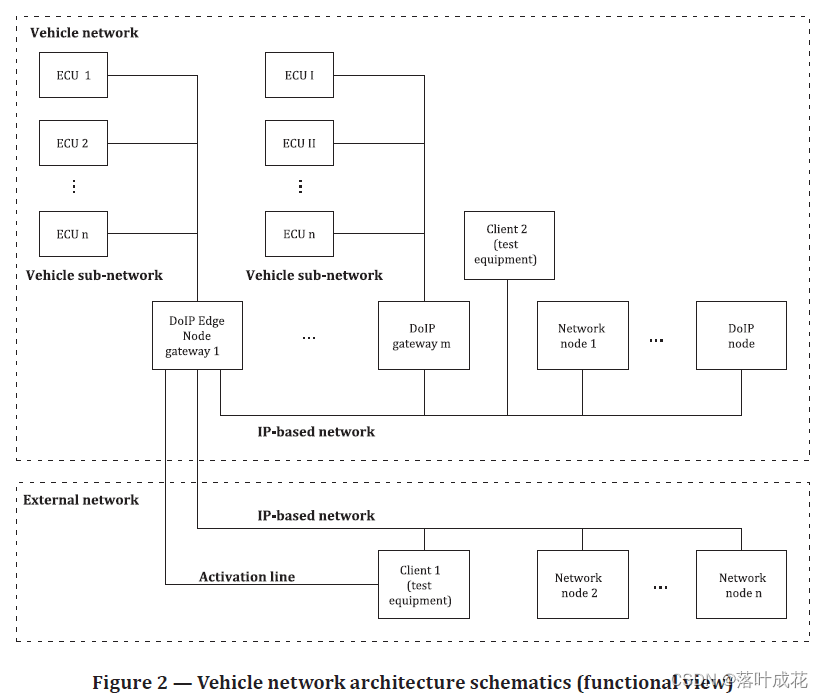
专属领域论文订阅
VX 关注{晓理紫},每日更新论文,如感兴趣,请转发给有需要的同学,谢谢支持
如果你感觉对你有所帮助,请关注我,每日准时为你推送最新论文。
为了答谢各位网友的支持,从今日起免费为300名读者提供订阅主题论文服务,只需VX关注公号并回复{邮箱+论文主题}(如:123456@xx.com + chatgpt@large language model @LLM),主题必须是同一个领域,最多三个关键词。解释权归博主所有
分类:
- 大语言模型LLM
- 视觉模型VLM
- 扩散模型
- 视觉语言导航VLN
- 强化学习 RL
- 模仿学习 IL
- 机器人
- 开放词汇,检测分割
[晓理紫]每日论文分享(有中文摘要,源码或项目地址)
== @ RL ==
标题: Curriculum-Based Reinforcement Learning for Quadrupedal Jumping: A Reference-free Design
作者: Vassil Atanassov, Jiatao Ding, Jens Kober
PubTime: 2024-01-29
Downlink: http://arxiv.org/abs/2401.16337v1
Project: https://youtu.be/nRaMCrwU5X8|
中文摘要: 深度强化学习(DRL)已经成为掌握爆发性和多功能四足跳跃技能的一种有前途的解决方案。然而,当前基于DRL的框架通常依赖于定义明确的参考轨迹,这些轨迹是通过捕捉动物运动或从现有控制器转移经验来获得的。这项工作探索了在不模仿参考轨迹的情况下学习动态跳跃的可能性。为此,我们将课程设计纳入DRL,以逐步完成具有挑战性的任务。从垂直原地跳跃开始,我们将学习到的策略推广到向前和对角跳跃,最后,学习跳过障碍。以期望的着陆位置、方向和障碍尺寸为条件,所提出的方法有助于大范围的跳跃运动,包括全向跳跃和健壮跳跃,减轻了预先提取参考的努力。特别是,在没有参考运动约束的情况下,实现了90厘米的向前跳跃,超过了现有文献中报道的类似机器人的先前记录。此外,即使在训练阶段没有遇到,也可以在柔软的草地上连续跳跃。展示我们结果的补充视频可以在https://youtu.be/nRaMCrwU5X8。
摘要: Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has emerged as a promising solution to mastering explosive and versatile quadrupedal jumping skills. However, current DRL-based frameworks usually rely on well-defined reference trajectories, which are obtained by capturing animal motions or transferring experience from existing controllers. This work explores the possibility of learning dynamic jumping without imitating a reference trajectory. To this end, we incorporate a curriculum design into DRL so as to accomplish challenging tasks progressively. Starting from a vertical in-place jump, we then generalize the learned policy to forward and diagonal jumps and, finally, learn to jump across obstacles. Conditioned on the desired landing location, orientation, and obstacle dimensions, the proposed approach contributes to a wide range of jumping motions, including omnidirectional jumping and robust jumping, alleviating the effort to extract references in advance. Particularly, without constraints from the reference motion, a 90cm forward jump is achieved, exceeding previous records for similar robots reported in the existing literature. Additionally, continuous jumping on the soft grassy floor is accomplished, even when it is not encountered in the training stage. A supplementary video showing our results can be found at https://youtu.be/nRaMCrwU5X8 .
标题: SPRINT: Scalable Policy Pre-Training via Language Instruction Relabeling
作者: Jesse Zhang, Karl Pertsch, Jiahui Zhang
PubTime: 2024-01-29
Downlink: http://arxiv.org/abs/2306.11886v3
Project: https://clvrai.com/sprint|
中文摘要: 利用丰富的技能集对机器人策略进行预训练,可以大大加快下游任务的学习速度。之前的研究通过自然语言指令来定义预训练任务,但这样做需要对成千上万条指令进行繁琐的人工标注。因此,我们提出了 SPRINT,这是一种可扩展的离线策略预训练方法,可大幅减少预训练各种技能所需的人力。我们的方法利用两个核心理念来自动扩展预训练任务的基础集:通过大型语言模型进行指令重标注,以及通过离线强化学习进行跨轨迹技能链。因此,SPRINT 预训练为机器人配备了更丰富的技能库。家庭模拟器和真实机器人厨房操作任务的实验结果表明,与以前的预训练方法相比,SPRINT能更快地学习新的长期任务。网站:https://clvrai.com/sprint。
摘要: Pre-training robot policies with a rich set of skills can substantially accelerate the learning of downstream tasks. Prior works have defined pre-training tasks via natural language instructions, but doing so requires tedious human annotation of hundreds of thousands of instructions. Thus, we propose SPRINT, a scalable offline policy pre-training approach which substantially reduces the human effort needed for pre-training a diverse set of skills. Our method uses two core ideas to automatically expand a base set of pre-training tasks: instruction relabeling via large language models and cross-trajectory skill chaining through offline reinforcement learning. As a result, SPRINT pre-training equips robots with a much richer repertoire of skills. Experimental results in a household simulator and on a real robot kitchen manipulation task show that SPRINT leads to substantially faster learning of new long-horizon tasks than previous pre-training approaches. Website at https://clvrai.com/sprint.
标题: SERL: A Software Suite for Sample-Efficient Robotic Reinforcement Learning
作者: Jianlan Luo, Zheyuan Hu, Charles Xu
PubTime: 2024-01-29
Downlink: http://arxiv.org/abs/2401.16013v1
Project: https://serl-robot.github.io/|
中文摘要: 近年来,机器人强化学习(RL)领域取得了重大进展,实现了处理复杂图像观察、在现实世界中训练以及整合辅助数据(如演示和先前经验)的方法。然而,尽管有这些进步,机器人RL仍然很难使用。从业者公认,这些算法的特定实现细节对于性能来说通常与算法的选择一样重要(如果不是更重要的话)。我们认为,机器人RL的广泛采用以及机器人RL方法的进一步发展的一个重大挑战是这种方法的相对不可及性。为了应对这一挑战,我们开发了一个精心实现的库,其中包含一个样本高效的非策略深度RL方法,以及计算奖励和重置环境的方法,一个广泛采用的机器人的高质量控制器,以及许多具有挑战性的示例任务。我们提供这个库作为社区的资源,描述它的设计选择,并展示实验结果。也许令人惊讶的是,我们发现我们的实施可以实现非常有效的学习,平均在每个策略25到50分钟的训练中获得PCB板组装、电缆布线和对象重新定位的策略,比文献中报告的类似任务的最先进结果有所改善。这些策略实现了完美或接近完美的成功率,即使在扰动下也具有极强的鲁棒性,并表现出紧急恢复和修正行为。我们希望这些有希望的结果和我们高质量的开源实现将为机器人社区提供一个工具,以促进机器人RL的进一步发展。我们的代码、文档和视频可以在https://serl-robot.github.io/
摘要: In recent years, significant progress has been made in the field of robotic reinforcement learning (RL), enabling methods that handle complex image observations, train in the real world, and incorporate auxiliary data, such as demonstrations and prior experience. However, despite these advances, robotic RL remains hard to use. It is acknowledged among practitioners that the particular implementation details of these algorithms are often just as important (if not more so) for performance as the choice of algorithm. We posit that a significant challenge to widespread adoption of robotic RL, as well as further development of robotic RL methods, is the comparative inaccessibility of such methods. To address this challenge, we developed a carefully implemented library containing a sample efficient off-policy deep RL method, together with methods for computing rewards and resetting the environment, a high-quality controller for a widely-adopted robot, and a number of challenging example tasks. We provide this library as a resource for the community, describe its design choices, and present experimental results. Perhaps surprisingly, we find that our implementation can achieve very efficient learning, acquiring policies for PCB board assembly, cable routing, and object relocation between 25 to 50 minutes of training per policy on average, improving over state-of-the-art results reported for similar tasks in the literature. These policies achieve perfect or near-perfect success rates, extreme robustness even under perturbations, and exhibit emergent recovery and correction behaviors. We hope that these promising results and our high-quality open-source implementation will provide a tool for the robotics community to facilitate further developments in robotic RL. Our code, documentation, and videos can be found at https://serl-robot.github.io/
标题: Context-aware Communication for Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning
作者: Xinran Li, Jun Zhang
PubTime: 2024-01-29
Downlink: http://arxiv.org/abs/2312.15600v2
GitHub: https://github.com/LXXXXR/CACOM|
中文摘要: 多智能体强化学习(MARL)中有效的通信协议对于促进合作和提高团队绩效至关重要。为了利用通信,许多先前的工作已经提出将本地信息压缩成单个消息,并将其广播给所有可到达的代理。然而,这种简单的消息传递机制可能无法向单个代理提供足够的、关键的和相关的信息,尤其是在带宽严重受限的情况下。这促使我们为MARL开发上下文感知通信方案,旨在向不同的代理传递个性化的消息。我们的通信协议名为CACOM,由两个阶段组成。在第一阶段,代理以广播的方式交换粗略的表示,为第二阶段提供上下文。接下来,代理在第二阶段利用注意力机制来选择性地为接收者生成个性化的消息。此外,我们采用学习步长量化(LSQ)技术进行消息量化,以减少通信开销。为了评估CACOM的有效性,我们将其与演员——评论家和基于价值的MARL算法相结合。协作基准任务的实证结果表明,在通信受限的情况下,CACOM提供了明显的性能增益。该代码可在https://github.com/LXXXXR/CACOM。
摘要: Effective communication protocols in multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) are critical to fostering cooperation and enhancing team perfo