知识回顾
- Tomcat 是 Servlet 容器,会解析 Java Web 应用下的 WEB-INF/web.xml 文件,得到相关的 Servlet 组件。
原理解析
Spring MVC 实际是定义了一个 DispatcherSevlet 来统一管理当前 Web 应用下的 Path 路径。在 DispatchSevlet 中持有了一个 Spring 容器 WebApplicationContext 。
具体流程为:DispatchSevlet#init -> 创建 Spring 容器 -> 发布事件 ApplicationRefreshEvent -> initStrategies(initHanderMppings、initHandlerAdapters、initExceptionHandlerResolvers)

interceptor 的 preHandle 的对三个参数 handler 是 Object 类型 ,而不是 HandlerMethod 类型
HandlerMapping
Interface to be implemented by objects that define a mapping between requests and handler objects.
This class can be implemented by application developers, although this is not necessary, as {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping} and {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping} are included in the framework. The former is the default if no HandlerMapping bean is registered in the application context.
HandlerMapping implementations can support mapped interceptors but do not have to. A handler will always be wrapped in a {@link HandlerExecutionChain} instance,optionally accompanied by some {@link HandlerInterceptor} instances. The DispatcherServlet will first call each HandlerInterceptor’s {@code preHandle} method in the given order, finally invoking the handler itself if all {@code preHandle} methods have returned {@code true}.
SpringMVC 九大组件之 HandlerMapping 深入分析
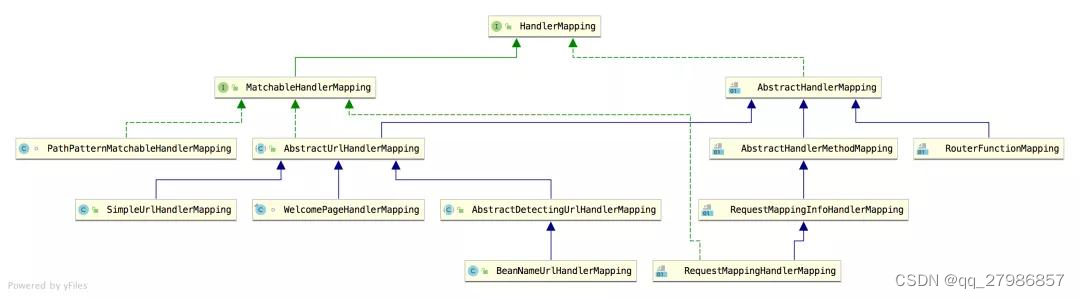
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 体系下的都是根据方法名进行匹配的,而 AbstractUrlHandlerMapping 体系下的都是根据 URL 路径进行匹配的。在 AbstractUrlHandlerMapping 体系下,一个 Handler 一般就是一个类,但是在 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 体系下,一个 Handler 就是一个 Mehtod,这也是我们目前使用 SpringMVC 时最常见的用法,即直接用 @RequestMapping 去标记一个方法,该方法就是一个 Handler。
HandlerAdapter
MVC framework SPI, allowing parameterization of the core MVC workflow.
Interface that must be implemented for each handler type to handle a request. This interface is used to allow the DispatcherServlet to be indefinitely extensible. The DispatcherServlet accesses all installed handlers through this interface, meaning that it does not contain code specific to any handler type.
Note that a handler can be of type Object. This is to enable handlers from other frameworks to be integrated with this framework without custom coding, as well as to allow for annotation-driven handler objects that do not obey any specific Java interface.
This interface is not intended for application developers. It is available to handlers who want to develop their own web workflow.
实现类
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
注入
SpringBoot 是通过 WebMvcAutoConfiguration.EnableWebMvcConfiguration#requestMappingHandlerAdapter 向 Spring 容器中注入了 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter。
SpringMVC 则通过 @EnableWebMvc 向 Spring 中注入该组件。
@Import(DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration.class)
public @interface EnableWebMvc {
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
}
public class WebMvcConfigurationSupport implements ApplicationContextAware, ServletContextAware {
@Bean
public RequestMappingHandlerAdapter requestMappingHandlerAdapter(
@Qualifier("mvcContentNegotiationManager") ContentNegotiationManager contentNegotiationManager,
@Qualifier("mvcConversionService") FormattingConversionService conversionService,
@Qualifier("mvcValidator") Validator validator) {
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter adapter = createRequestMappingHandlerAdapter();
adapter.setContentNegotiationManager(contentNegotiationManager);
adapter.setMessageConverters(getMessageConverters());
adapter.setWebBindingInitializer(getConfigurableWebBindingInitializer(conversionService, validator));
adapter.setCustomArgumentResolvers(getArgumentResolvers());
adapter.setCustomReturnValueHandlers(getReturnValueHandlers());
if (jackson2Present) {
adapter.setRequestBodyAdvice(Collections.singletonList(new JsonViewRequestBodyAdvice()));
adapter.setResponseBodyAdvice(Collections.singletonList(new JsonViewResponseBodyAdvice()));
}
AsyncSupportConfigurer configurer = getAsyncSupportConfigurer();
if (configurer.getTaskExecutor() != null) {
adapter.setTaskExecutor(configurer.getTaskExecutor());
}
if (configurer.getTimeout() != null) {
adapter.setAsyncRequestTimeout(configurer.getTimeout());
}
adapter.setCallableInterceptors(configurer.getCallableInterceptors());
adapter.setDeferredResultInterceptors(configurer.getDeferredResultInterceptors());
return adapter;
}
}
SpringMVC 通过 DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration#addArgumentResolvers 方法将 HandlerMethodArgumentResolver 添加到各个 WebMvcConfigurer(该组件会通过 setter 注入的方式注入到 DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration 中) 下。
@Configuration
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
private final WebMvcConfigurerComposite configurers = new WebMvcConfigurerComposite();
@Autowired(required = false)
public void setConfigurers(List<WebMvcConfigurer> configurers) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers);
}
}
// 省略其它代码...
}
Spring 中的 XxxRegistry、XxxRegistration 只是一种帮助传递数据的辅助类,比如下面的 InterceptorRegistry 就是为了将从各个 WebMvcConfigurer 中收集的 Interceptor,放入到 AbstractHandlerMapping#interceptors。
// From WebMvcConfigurationSupport.java
protected final Object[] getInterceptors(
FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService,
ResourceUrlProvider mvcResourceUrlProvider) {
if (this.interceptors == null) {
// 新建一个 Registry 对象
InterceptorRegistry registry = new InterceptorRegistry();
// 遍历所有 WebMvcConfigurer,将 interceptor 添加到 registry 中
addInterceptors(registry);
registry.addInterceptor(new ConversionServiceExposingInterceptor(mvcConversionService));
registry.addInterceptor(new ResourceUrlProviderExposingInterceptor(mvcResourceUrlProvider));
// 从 registry 中取出所有 interceptor 后,就可以被 JVM 回收了。
this.interceptors = registry.getInterceptors();
}
return this.interceptors.toArray();
}
/**
Helps with configuring a list of mapped interceptors.
Since: 3.1
*/
public class InterceptorRegistry {
// 封装了一个 interceptor 的容器
private final List<InterceptorRegistration> registrations = new ArrayList<>();
public InterceptorRegistration addInterceptor(HandlerInterceptor interceptor) {
InterceptorRegistration registration = new InterceptorRegistration(interceptor);
this.registrations.add(registration);
return registration;
}
protected List<Object> getInterceptors() {
return this.registrations.stream()
.sorted(INTERCEPTOR_ORDER_COMPARATOR)
.map(InterceptorRegistration::getInterceptor)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
// 省略其它...
}
public class InterceptorRegistration {
private final HandlerInterceptor interceptor;
@Nullable
private List<String> includePatterns;
@Nullable
private List<String> excludePatterns;
public InterceptorRegistration addPathPatterns(String... patterns) {
return addPathPatterns(Arrays.asList(patterns));
}
public InterceptorRegistration addPathPatterns(List<String> patterns) {
this.includePatterns = (this.includePatterns != null ?
this.includePatterns : new ArrayList<>(patterns.size()));
this.includePatterns.addAll(patterns);
return this;
}
// 将程序员自定义的 Interceptor 封装成 MappedInterceptor(新增一层,为 Interceptor 提供了根据「请求路径」按需拦截的能力)
protected Object getInterceptor() {
if (this.includePatterns == null && this.excludePatterns == null) {
return this.interceptor;
}
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = new MappedInterceptor(
StringUtils.toStringArray(this.includePatterns),
StringUtils.toStringArray(this.excludePatterns),
this.interceptor);
if (this.pathMatcher != null) {
mappedInterceptor.setPathMatcher(this.pathMatcher);
}
return mappedInterceptor;
}
}
RequestMappingHandlerMapping 实现了 HandlerMapping 接口,会在 DispatcherServlet 初始化过程中注入到 handlerMappings 字段中。
// From DispatcherServlet.java
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering
// a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found.
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No HandlerMappings declared for servlet '" + getServletName() +
"': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties");
}
}
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
if (mapping.usesPathPatterns()) {
this.parseRequestPath = true;
break;
}
}
}
最后这些 AbstractHandlerMapping#interceptors 将在 doDispatch 的时候,通过调用 org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#getHandler 被封装成 HandlerExecutionChain,这样 DispatcherServlet 就只需关注 HandlerExecutionChain(Handler execution chain, consisting of handler object and any handler interceptors),即模板流程方法都将被分发给 HandlerExecutionChain的方法。
作用
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 实现了 InitializingBean 接口,所以在完成 Bean 对象创建后,Spring 会自动回调其 afterPropertiesSet 方法,可以看出 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 主要完成了以下组件的注入:HandlerMethodArgumentResolver、HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler
// From RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.java
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
// Do this first, it may add ResponseBody advice beans
initControllerAdviceCache();
if (this.argumentResolvers == null) {
// 这里规定了自定义的 HandlerMethodArgumentResolver 比 Spring 内置的优先级要低
List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers = getDefaultArgumentResolvers();
this.argumentResolvers = new HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite().addResolvers(resolvers);
}
if (this.initBinderArgumentResolvers == null) {
List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers = getDefaultInitBinderArgumentResolvers();
this.initBinderArgumentResolvers = new HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite().addResolvers(resolvers);
}
if (this.returnValueHandlers == null) {
List<HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler> handlers = getDefaultReturnValueHandlers();
this.returnValueHandlers = new HandlerMethodReturnValueHandlerComposite().addHandlers(handlers);
}
}
WebMvcConfigurer
Defines callback methods to customize the Java-based configuration for Spring MVC enabled via @EnableWebMvc.
@EnableWebMvc-annotated configuration classes may implement this interface to be called back and given a chance to customize the default configuration.
InterceptorRegistry
HandlerMethodArgumentResolver
HandlerExceptionResolver
ServletInputStream
解决HttpServletRequest的输入流只能读取一次的问题
表单数据还好说,调用request的getParameterMap就能全部取出来。而json数据就有些麻烦了,因为json数据放在body中,我们需要通过request的输入流去读取。但问题在于request的输入流只能读取一次不能重复读取,所以我们在过滤器或拦截器里读取了request的输入流之后,请求走到controller层时就会报错。
InputStream默认不实现reset的相关方法,而ServletInputStream也没有重写reset的相关方法,这样就无法重复读取流,这就是我们从request对象中获取的输入流就只能读取一次的原因。
public class MultiReadHttpServletRequestWrapper extends HttpServletRequestWrapper {
private ByteArrayOutputStream cachedBytes;
public MultiReadHttpServletRequestWrapper(HttpServletRequest request) {
super(request);
}
@Override
public ServletInputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
if (cachedBytes == null) {
cacheInputStream();
}
return new CachedServletInputStream();
}
@Override
public BufferedReader getReader() throws IOException {
return new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(getInputStream()));
}
private void cacheInputStream() throws IOException {
cachedBytes = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
IOUtils.copy(super.getInputStream(), cachedBytes);
}
/**
* Created by xiangsky on 2018/3/28.
*/
protected class CachedServletInputStream extends ServletInputStream {
private ByteArrayInputStream inputStream;
public CachedServletInputStream() {
inputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(cachedBytes.toByteArray());
}
@Override
public boolean isFinished() {
return inputStream.available() <= 0;
}
@Override
public boolean isReady() {
return true;
}
@Override
public void setReadListener(ReadListener readListener) {
// 目前不需要实现
}
@Override
public int read() throws IOException {
return inputStream.read();
}
@Override
public int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException {
return inputStream.read(b, off, len);
}
}
}
@Controller 与 @RestController 联系与不同
@Controller 用在前后端未分离场景,用于返回渲染好的页面到客户端,@RestController (= @Controller + @ResponseBody)用于返回 JSON 数据(对于 Java 来说就是一个 Map 数据结构)给前端
SpringMVC中RequestBody注解的List参数传递方式
Controller方法参数:@RequestBody List ids,对应前端传参:[1, 2],前端传参 {“ids”: [1, 2]} 会报错。
Controller方法参数:@RequestBody UserIdentities ids,对应前端传参:{“ids”: [1, 2]} ,
所以 KS 定义了 @JsonParam,这样当在 Controller方法参数:@RequestBody List ids 时,前端可传参 {“ids”: [1, 2]} ,而不报错。
文章索引
- Spring系列之父子容器详解
- 父子容器特点: 1)父容器和子容器是相互隔离的,他们内部可以存在名称相同的bean;2)子容器可以访问父容器中的bean,而父容器不能访问子容器中的bean;3)调用子容器的getBean方法获取bean的时候,会沿着当前容器开始向上面的容器进行查找,直到找到对应的bean为止。
- BeanFactory接口,是spring容器的顶层接口,这个接口中的方法是支持容器嵌套结构查找的,比如我们常用的getBean方法,就是这个接口中定义的,调用getBean方法的时候,会从沿着当前容器向上查找,直到找到满足条件的bean为止。而ListableBeanFactory这个接口中的方法是不支持容器嵌套结构查找的。
- 通常我们使用springmvc的时候,采用3层结构,controller层,service层,dao层;父容器中会包含dao层和service层,而子容器中包含的只有controller层;这2个容器组成了父子容器的关系,controller层通常会注入service层的bean。采用父子容器可以避免有些人在service层去注入controller层的bean,导致整个依赖层次是比较混乱的。
Q1: 父子容器形成过程?how、when
A1:阿里一面:Spring和SpringMvc父子容器你能说清楚吗
注意:SpringBoot 开启的 Web 应用,默认只有一个 Spring 容器。
Q2:Controller 是何时解析注入的?
A2:抽象类 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 实现了 InitializingBean 接口,即在向 Spring 容器注入 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 实现类的 Bean 对象时,会在 afterPropertiesSet 方法中完成对 path 与 HandlerMethod 的映射关系构建。
// From AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.java
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
// 当 class 文件上标有 @Controller 或 @RequestMapping 时,获取该 Bean 的所有待 @RequestMapping 的方法,并将其注册到 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#mappingRegistry 中
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
// From RequestMappingHandlerMapping.java
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class));
}
附:
- AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 实现类是何时放入到 Spring 容器中的?WebMvcConfigurationSupport#requestMappingHandlerMapping 方法标注了 @Bean
- 获取 HandlerMehtod 的方法:AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#getHandlerInternal