1、ioctl函数是用户程序来控制设备的函数
int ioctl(int fd, unsigned long request, ...);
函数功能:设备控制
参数:
@fd:文件描述符
@request:请求码
@...:可变参数 需要传递地址
返回值:成功返回0,失败返回-1,并且置位错误码
2、内核层与ioctl对应的接口函数:
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
3、代码实现:ioctl传递字符数组与结构体
1>对数组和结构体命令码进行封装:
#ifndef __LED_H__
#define __LED_H__
typedef struct{
int width;
int high;
}image_t;
#define UACCESS_BUF _IOW('a',1,char[128])
#define UACCESS_STRUCT _IOWR('b',0,image_t)
#endif
2>在long mydev_ioctl (struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)接口函数内,使用copy_from_user接收用户空间拷贝过来的信息,并进行打印,再使用copy_to_user函数将修改后的结构体信息拷贝到用户空间
#include<linux/init.h>
#include<linux/module.h>
#include<linux/fs.h>
#include<linux/uaccess.h>
#include<linux/io.h>
#include"./led.h"
#include<linux/device.h>
#define GNAME "mydev"
int major;
char kbuf[128]={0};
struct class *cls=NULL;
struct device *dev=NULL;
int mydev_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
//printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__);
return 0;
}
long mydev_ioctl(struct file *file,unsigned int cmd,unsigned long arg)
{
int ret;
image_t image;
switch(cmd)
{
case UACCESS_BUF:
ret = copy_from_user(kbuf,(void*)arg,sizeof(char)*128);
if(ret)
{
printk("copy from user char error\n");
return -EIO;
}
printk("kbuf=%s\n",kbuf);
break;
case UACCESS_STRUCT:
ret = copy_from_user(&image,(void*)arg,sizeof(image_t));
if(ret)
{
printk("copy from user image_t error\n");
return -EIO;
}
printk("image_t.width=%d image_t.high=%d\n",image.width,image.high);
image.width+=10;
image.high+=10;
ret = copy_to_user((void*)arg,&image,sizeof(image_t));
if(ret)
{
printk("copy to user image_t error\n");
return -EIO;
}
break;
}
return 0;
}
int mydev_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
//printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__);
return 0;
}
struct file_operations fops={
.open=mydev_open,
.unlocked_ioctl=mydev_ioctl,
.release=mydev_close,
};
static int __init mydev_init(void)
{
major=register_chrdev(0,GNAME,&fops);
if(major<0)
{
printk("register file\n");
return major;
}
printk("major=%d\n",major);
cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE,GNAME);
if(IS_ERR(cls))
{
return PTR_ERR(cls);
}
dev = device_create(cls,NULL,MKDEV(major,0),NULL,GNAME);
if(IS_ERR(dev))
{
return PTR_ERR(dev);
}
return 0;
}
static void __exit mydev_exit(void)
{
device_destroy(cls,MKDEV(major,0));
class_destroy(cls);
unregister_chrdev(major,GNAME);
}
module_init(mydev_init);
module_exit(mydev_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");3>编写用户程序,通过ioctl函数传递信息给内核空间,从而达到想要的操作结果,并进行打印
#include <stdio.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<sys/ioctl.h>
#include"led.h"
char buf[128] = "问灵十三年";
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int fd = -1;
int i=0;
int witch;
image_t image={20,1024};
fd = open("/dev/mydev",O_RDWR);
if(-1 == fd)
{
perror("open is error");
exit(1);
}
ioctl(fd,UACCESS_BUF,buf);
ioctl(fd,UACCESS_STRUCT,&image);
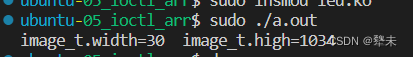
printf("image_t.width=%d image_t.high=%d\n",image.width,image.high);
close(fd);
return 0;
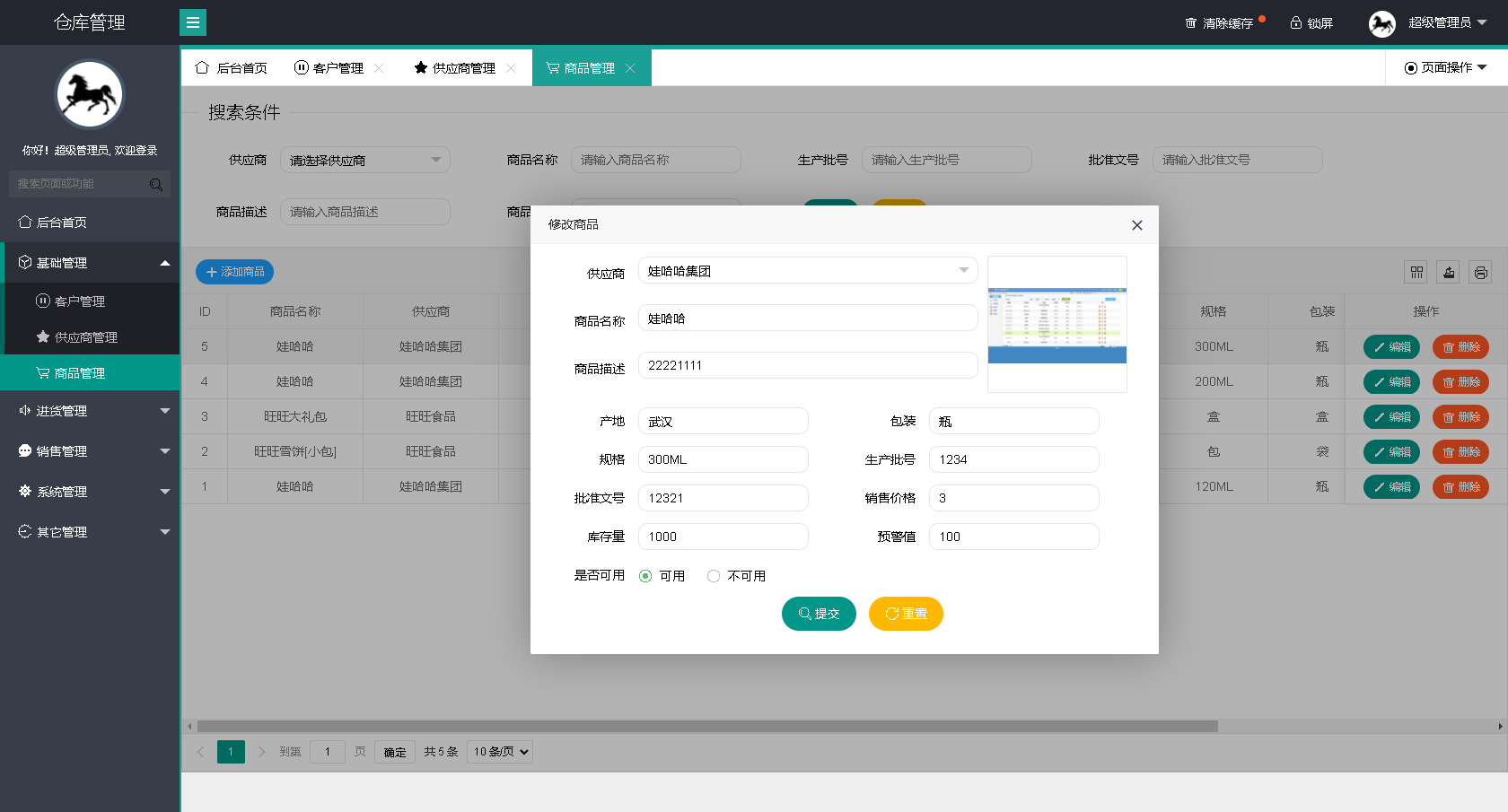
}4>通过dmesg查看内核层的打印信息,结果如下所示,应用层传递的数组信息以及结构体信息成功传递到内核层
![]()
5>执行应用层程序,终端打印结构体信息+10后的信息